Abstract
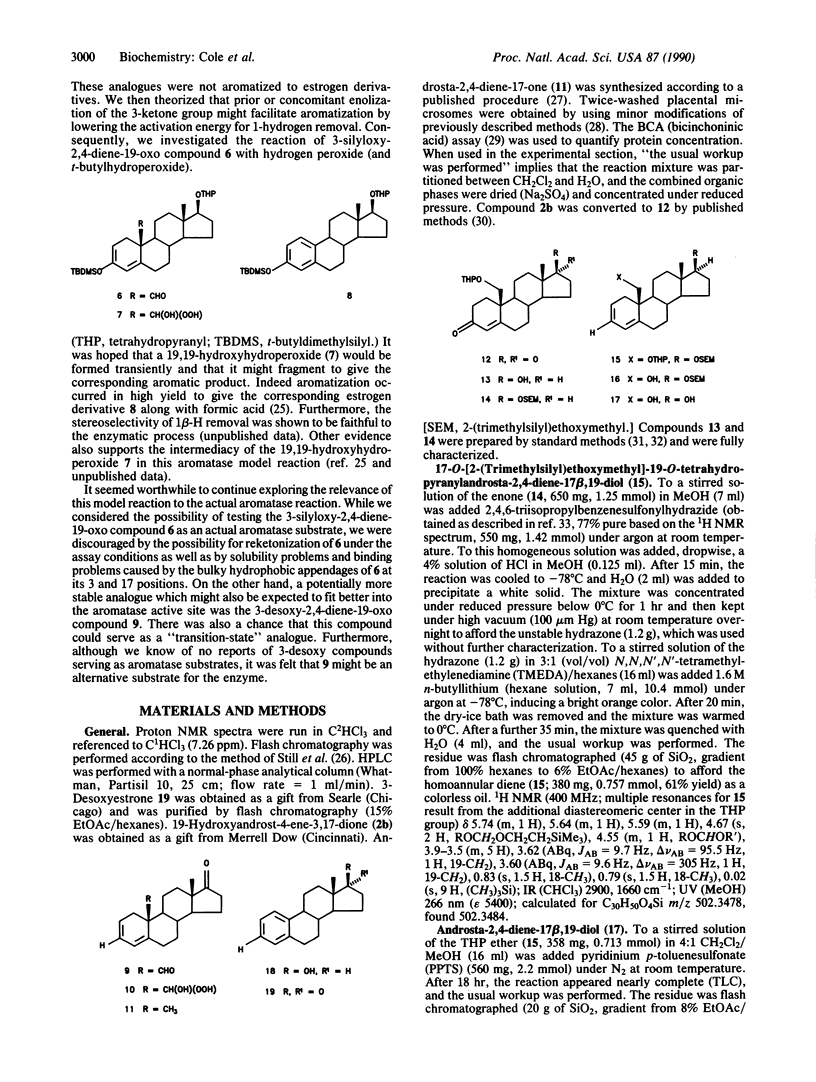
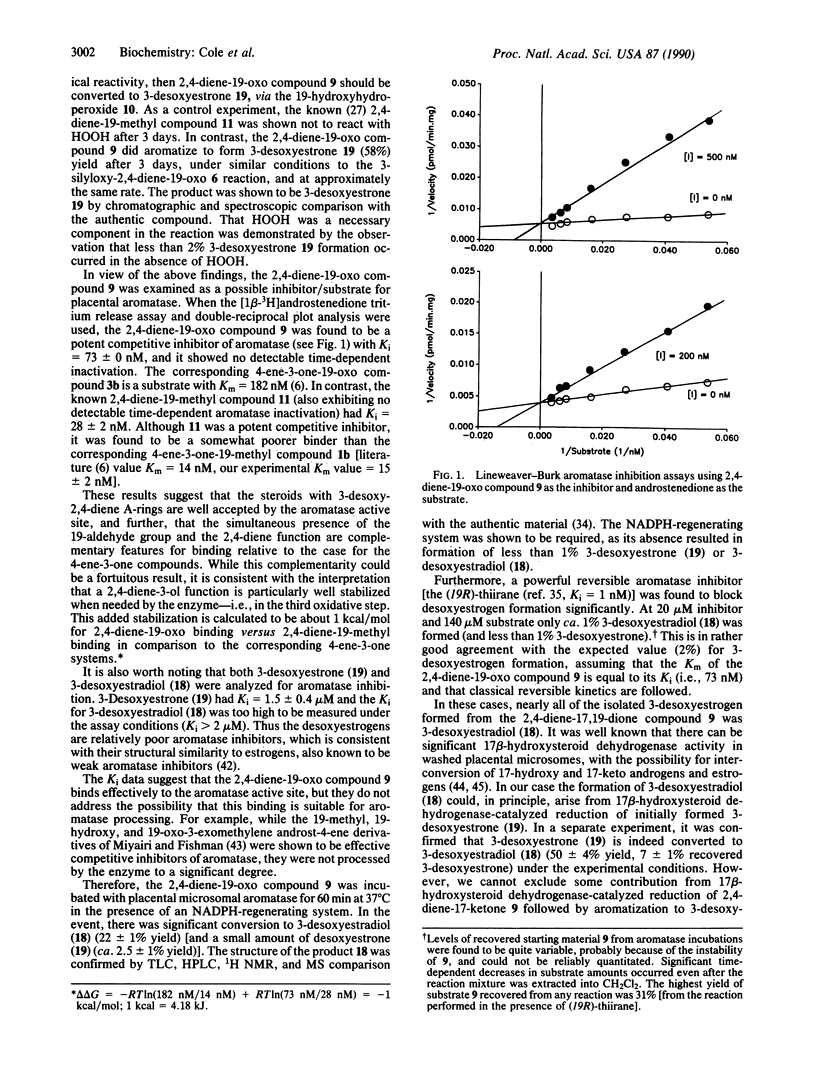
Human placental aromatase is a cytochrome P-450 enzyme system which converts androgens to estrogens by three successive oxidative reactions. The first two steps have been shown to be hydroxylations at the androgen 19-carbon, but the third step remains unknown. A leading theory for the third step involves ferric peroxide attack on the 19-oxo group to produce a 19,19-hydroxyferric peroxide intermediate and subsequent collapse to estrogen. We had previously developed a nonenzymatic peroxide model reaction which was based on the above-mentioned theory, and we demonstrated the importance of 3-ketone enolization in facilitating aromatization. This study discusses the synthesis and nonenzymatic and enzymatic study of a 3-desoxy-2,4-diene-19-oxo androgen analogue. This compound was found to be a potent nonenzymatic model substrate and competitive inhibitor of aromatase (Ki = 73 nM). Furthermore, in an unprecedented event, this compound served as a substrate for aromatase, with conversion to the corresponding 3-desoxyestrogen.
Full text
PDF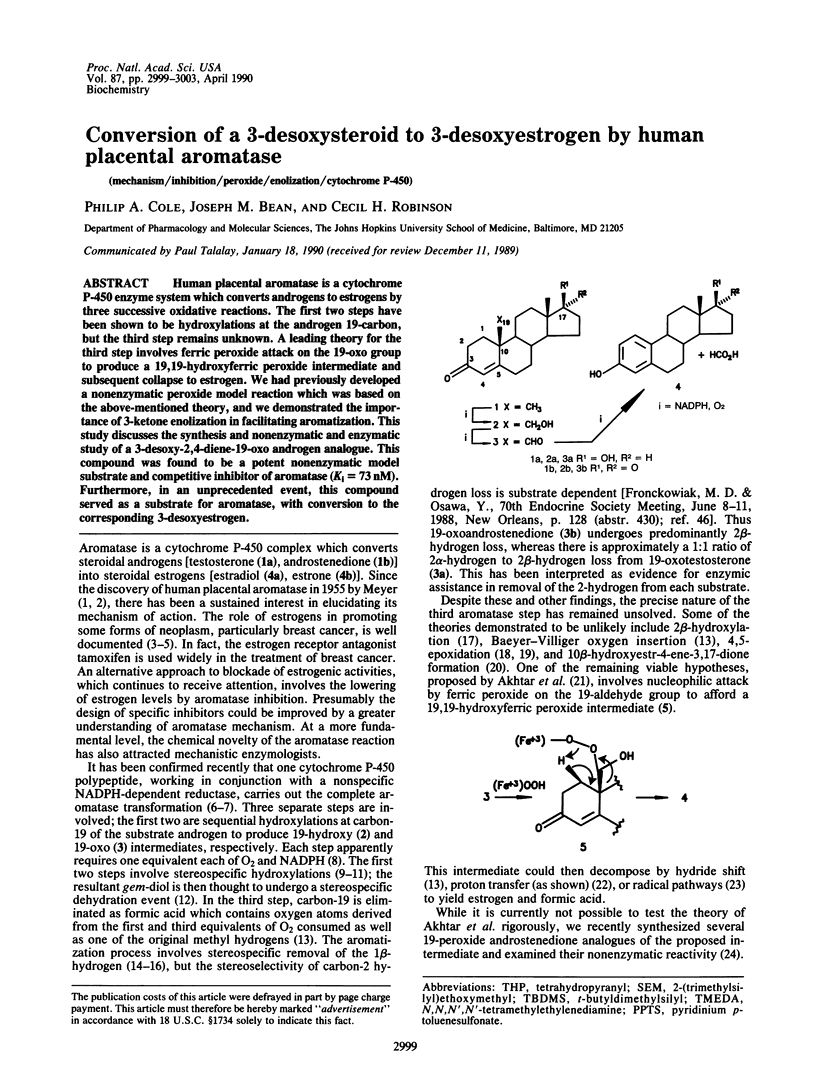


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhtar M., Calder M. R., Corina D. L., Wright J. N. Mechanistic studies on C-19 demethylation in oestrogen biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1982 Mar 1;201(3):569–580. doi: 10.1042/bj2010569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beusen D. D., Carrell H. L., Covey D. F. Metabolism of 19-methyl-substituted steroids by human placental aromatase. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7833–7841. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomquist C. H., Lindemann N. J., Hakanson E. Y. Steroid modulation of 17 beta-hydroxysteroid oxidoreductase activities in human placental villi in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Oct;65(4):647–652. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-4-647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandes S. J., Katzenellenbogen J. A. Fluorinated androgens and progestins: molecular probes for androgen and progesterone receptors with potential use in positron emission tomography. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;32(3):391–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braselton W. E., Jr, Engel L. L., Orr J. C. The flux of intermediates and products in aromatizaton of C19 steroids by human placental microsomes. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Oct 1;48(1):35–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie A. M. Aromatase inhibition and its pharmacologic implications. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Sep 15;34(18):3213–3219. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90337-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie H. J., Kripalani K. J., Possanza G. Studies on the mechanism of estrogen biosynthesis. VI. The stereochemistry of hydrogen elimination at C-2 during aromatization. J Am Chem Soc. 1969 Feb 26;91(5):1241–1242. doi: 10.1021/ja01033a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers W. E., Shih M. J., Furth P. S., Robinson C. H. Stereoselective inhibition of human placental aromatase. Steroids. 1987 Jul-Sep;50(1-3):121–134. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(83)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin C. J., Graham-Lorence S., McPhaul M., Mason J. I., Mendelson C. R., Simpson E. R. Isolation of a full-length cDNA insert encoding human aromatase system cytochrome P-450 and its expression in nonsteroidogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8948–8952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey D. F., Hood W. F., Beusen D. D., Carrell H. L. Hydroperoxides as inactivators of aromatase: 10 beta-hydroperoxy-4-estrene-3,17-dione, crystal structure and inactivation characteristics. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 6;23(23):5398–5406. doi: 10.1021/bi00318a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman J., Guzik H., Dixon D. Sterochemistry of estrogen biosynthesis. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4304–4309. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldkamp A. H., Hoehn W. M., Mikulec R. A., Nutting E. F., Cook D. L. The preparation and pharmacology of some 3-desoxyestratrienes. Lipid-shifting and estrogenic effects. J Med Chem. 1965 Jul;8(4):409–414. doi: 10.1021/jm00328a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellis J. T., Jr, Vickery L. E. Purification and characterization of human placental aromatase cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4413–4420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER A. S. 19-Hydroxylation of delta 4-Androstene-3,17-dione and dehydroepiandrosterone by bovine adrenals. Experientia. 1955 Mar 15;11(3):99–102. doi: 10.1007/BF02161690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER A. S. Conversion of 19-hydroxy-delta 4-androstene-3,17-dione to estrone by endocrine tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Jul;17(3):441–442. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90395-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcotte P. A., Robinson C. H. Synthesis and evaluation of 10 beta-substituted 4-estrene-3, 17-diones as inhibitors of human placental microsomal aromatase. Steroids. 1982 Mar;39(3):325–344. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(82)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyairi S., Fishman J. 3-Methylene-substituted androgens as novel aromatization inhibitors. Evidence of a requirement for C-3 oxygen in C-19 hydroxylations. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6772–6777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morand P., Williamson D. G., Layne D. S., Lompa-Krzymien L., Salvador J. Conversion of an androgen epoxide into 17beta-estradiol by human placental microsomes. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 11;14(3):635–638. doi: 10.1021/bi00674a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa Y., Shibata K., Rohrer D., Weeks C., Duax W. L. Letter: Reassignment of the absolute configuration of 19-substituted 19-hydroxysteroids and stereomechanism of estrogen biosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Jul 23;97(15):4400–4402. doi: 10.1021/ja00848a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYAN K. J. Biological aromatization of steroids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Feb;234(2):268–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. N., Moore P. H., Jr, Peterson D. M., Tcholakian R. K. Synthesis of new steroid haptens for radioimmunoassay--part V. 19-O-carboxymethyl ether derivative of testosterone. A highly specific antiserum for immunoassay of testosterone from both male and female plasma without chromatography. J Steroid Biochem. 1978 Jun;9(6):539–545. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(78)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Ohno S. Kinetic properties of human placental aromatase. Application of an assay measuring 3H2O release from 1beta,2beta-3H-androgens. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1625–1631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santen R. J. Potential clinical role of new aromatase inhibitors. Steroids. 1987 Oct-Dec;50(4-6):575–593. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(87)90040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzel W. C., Kruggel W. G., Brodie H. J. Studies on the mechanism of estrogen biosynthesis. 8. The development of inhibitors of the enzyme system in human placenta. Endocrinology. 1973 Mar;92(3):866–880. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-3-866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. A., Jr, Siiteri P. K. Utilization of oxygen and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate by human placental microsomes during aromatization of androstenedione. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5364–5372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsley J. D., Brodie H. J. Studies on the mechanism of estrogen biosynthesis. 3. The stereochemistry of aromatization of C19 and C18 steroids. Biochemistry. 1968 Jan;7(1):33–40. doi: 10.1021/bi00841a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


