The molecular and crystal structures of two N-(furylmethyl)propan-2-aminium salts – the products of interaction between maleic acid and N-R-furfurylamines – were studied by X-ray diffraction and correlated with their lack of reactivity in [4 + 2] cycloaddition reactions.
Keywords: furans, Diels–Alder reaction, maleates, crystal structure, synchrotron radiation
Abstract
The title molecular salts, C15H20NO+·C4H3O4 −, (I), and C9H15INO+·C4H3O4 −, (II), have very similar molecular geometries for both cation and anion. The anions of both (I) and (II) are practically planar (r.m.s. deviations = 0.062 and 0.072 Å, respectively) and adopt a rare symmetrical geometry with the hydroxy H atom approximately equidistant from the two O atoms. In their crystals, the cations and anions in both (I) and (II) form tight ionic pairs via strong N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, with a roughly perpendicular disposition of the anion to the furan ring of the cation. This ion-pair conformation appears to correlate with the lack of reactivity of these salts in [4 + 2] cycloaddition reactions. In the extended structures of (I) and (II), the ion pairs form hydrogen-bonded chains propagating along [010] and [001], respectively, via N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Chemical context
Owing to the fact that the furan ring contains a system of conjugated double bonds, it usually acts as an effective diene in intra- and intermolecular Diels–Alder reactions with electron-deficient dienophiles. The [4 + 2] cycloaddition of furans with maleic acid leading to structurally diverse 7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptenes has been investigated for a long time (Diels & Alder, 1931 ▸; Berson & Swidler, 1953 ▸, 1954 ▸; Eggelte et al., 1973 ▸; Sprague et al., 1985 ▸). However, there are only fragmentary data concerning the reactions of halogen- or aryl-substituted furans with maleic acid (Sheinkman et al., 1972 ▸; Shih et al., 1975 ▸). It is known that the interaction between maleic acid and furfurylamines leads usually to the formation of the salts, but is not accompanied by the [4 + 2] cycloaddition (Clitherow, 1983 ▸; Price et al., 1985 ▸; Brown, 1986 ▸; Pelosi et al., 2002 ▸; Craig et al., 2008 ▸; Metsger et al., 2010 ▸).
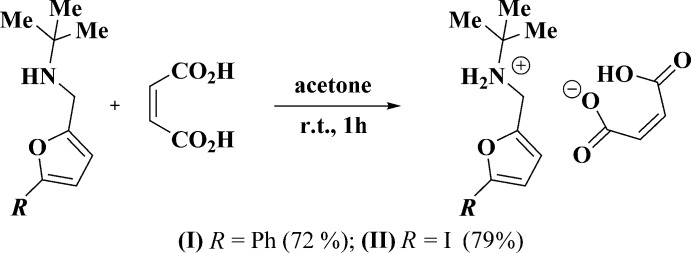
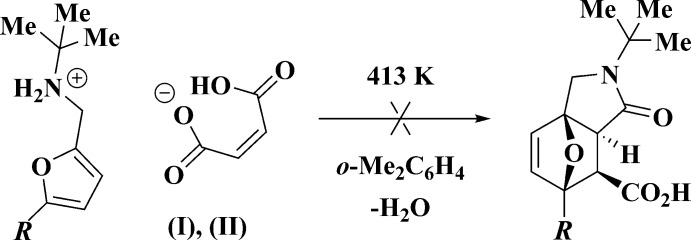
The main goal of this work was to study the cycloaddition reaction between 5-R-furfuryl-tert-butylamines and maleic acid. The interaction between the corresponding amines and maleic acid at room temperature leads to the salts (I) and (II) only (Fig. 1 ▸). Unexpectedly, attempts to achieve thermal cyclization of salts (I) and (II) did not result in isolation of the targeted 7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptenes: the initial maleates remained unchanged at temperatures up to 413 K (Fig. 2 ▸). In order to explain this fact by an understanding of their stereochemical features, an X-ray diffraction study of compounds (I) and (II) was undertaken.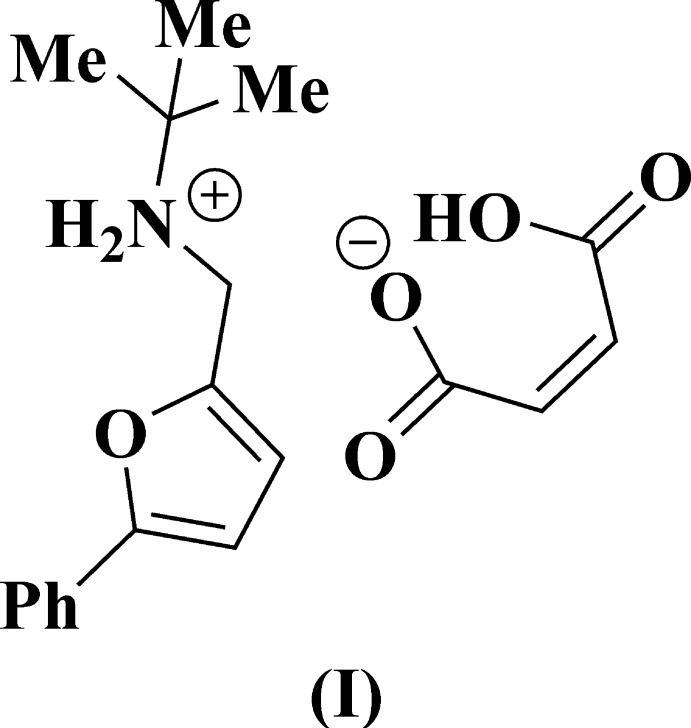
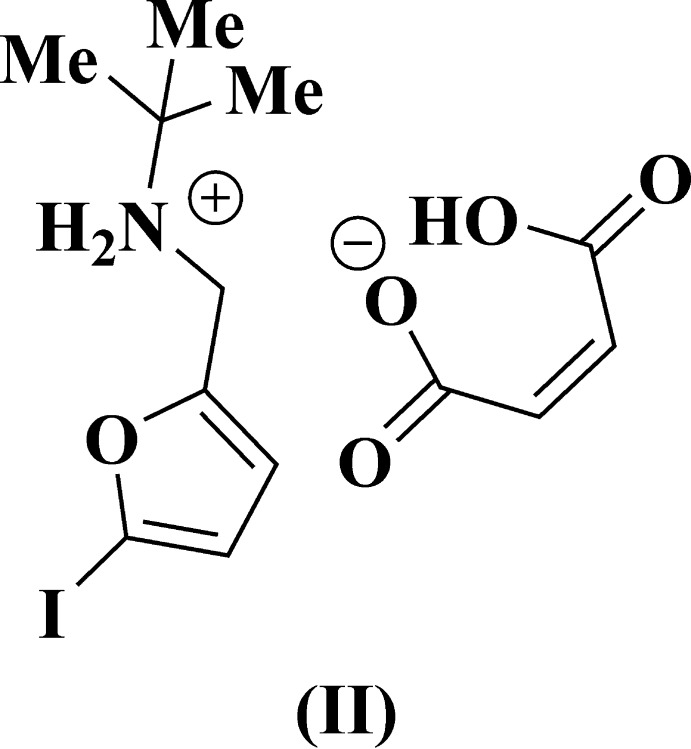
Figure 1.
Synthesis of maleic salts (I) and (II) from N-[(5-R-furan-2-yl)methyl]-2-methylpropan-2-amines.
Figure 2.
The attempted thermal cyclization of salts (I) (R = Ph) and (II) (R = I).
Structural commentary
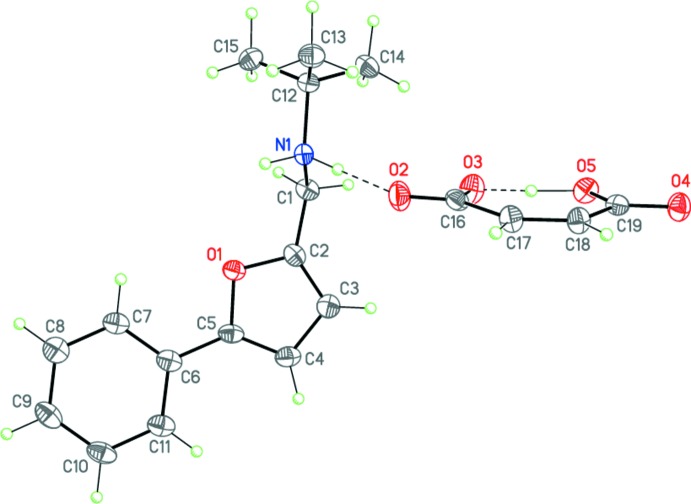
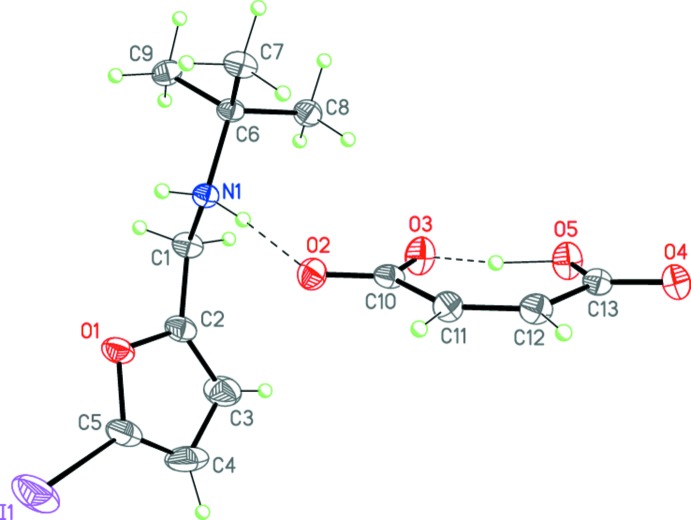
Compounds (I), C15H20NO+·C4H3O4 −, and (II), C9H15INO+·C4H3O4 −, represent secondary amine salts of maleic acid and have very similar molecular geometries (Figs. 3 ▸ and 4 ▸) for both cation and anion. The saturated C2–C1–N1–C(t-Bu) backbone of the ammonium cation is twisted by 72.66 (7) and 63.2 (2)° relative to the furan ring in (I) and (II), respectively. The phenyl substituent of the cation in (I) is almost coplanar to the furan ring (r.m.s. deviation is 0.006 Å). The anions of (I) and (II) are practically planar (r.m.s. deviations are 0.062 and 0.072 Å, respectively). It interesting to note that the hydrogen atom of the hydroxy group of the anion is arranged at almost equal distances from the two oxygen atoms in both (I) and (II) (Tables 1 ▸ and 2 ▸, Figs. 3 ▸ and 4 ▸). Thus, the anions of (I) and (II) adopt a rare symmetrical geometry.
Figure 3.
The molecular structure of salt (I). Displacement ellipsoids are shown at the 50% probability level. H atoms are presented as small spheres of arbitrary radius. Dashed lines indicate the intramolecular O—H⋯O and intermolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Figure 4.
The molecular structure of salt (II). Displacement ellipsoids are shown at the 50% probability level. H atoms are presented as small spheres of arbitrary radius. Dashed lines indicate the intramolecular O—H⋯O and intermolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O5—H5O⋯O3 | 1.160 (17) | 1.257 (17) | 2.4142 (14) | 175.3 (15) |
| N1—H1A⋯O2i | 0.968 (15) | 1.790 (15) | 2.7547 (15) | 174.9 (13) |
| N1—H1B⋯O4ii | 0.936 (15) | 1.860 (15) | 2.7803 (14) | 167.4 (13) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O5—H5O⋯O3 | 1.18 (5) | 1.25 (5) | 2.425 (3) | 172 (4) |
| N1—H1A⋯O2 | 0.88 (4) | 1.97 (4) | 2.828 (3) | 167 (3) |
| N1—H1B⋯O4i | 0.88 (4) | 1.92 (4) | 2.792 (4) | 172 (3) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Importantly, the cations and anions in both (I) and (II) form tight ion pairs via strong N1—H1A⋯O2 hydrogen bonds (Tables 1 ▸ and 2 ▸, Figs. 3 ▸ and 4 ▸). Within the tight ion pairs, the anion is roughly perpendicular to the furan ring of the cation, the interplanar angles being 72.01 (4) and 67.94 (12)° in (I) and (II), respectively. Apparently, the formation of the robust tight ion pairs with a definite cation–anion conformation inhibits the desired cyclization reaction, preventing the closure of the cations and anions.
Supramolecular features
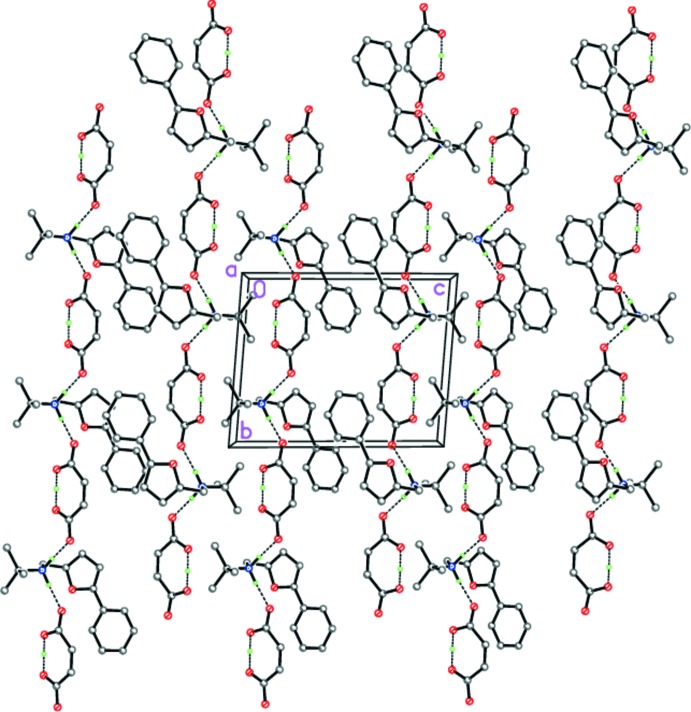
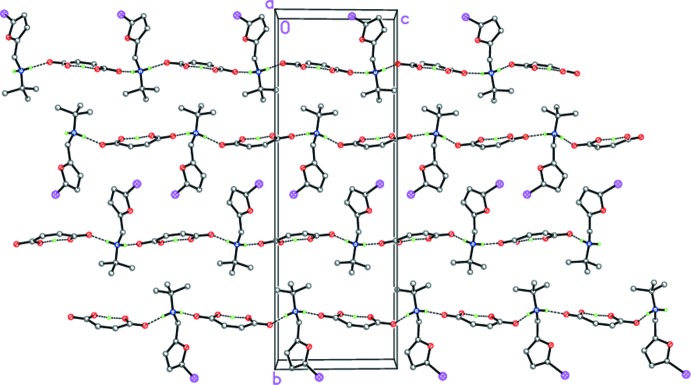
Despite the sterically different substituents at the furyl ring of the aminium cations, compounds (I) and (II) organize similar supramolecular structures in the solid state. So, in the crystal of (I), the tight ion pairs form hydrogen-bonded chains propagating along [010] via strong N1—H1B⋯O4 links (Table 1 ▸, Fig. 5 ▸). In the crystal of (II), the analogous hydrogen-bonded chains propagate along [001] (Table 2 ▸, Fig. 6 ▸). In both (I) and (II), the chains are further packed in stacks along [100] (Figs. 5 ▸ and 6 ▸).
Figure 5.
The crystal structure of (I), illustrating the hydrogen-bonded chains propagating along [010]. Dashed lines indicate the intramolecular O—H⋯O and intermolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Figure 6.
The crystal structure of (II), illustrating the hydrogen-bonded chains propagating along [001]. Dashed lines indicate the intramolecular O—H⋯O and intermolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Synthesis and crystallization
The starting N-[(5-R-furan-2-yl)methyl]-2-methylpropan-2-amines were synthesized according to the procedure described recently (Zubkov et al., 2016 ▸).
General procedure. A solution of the corresponding amine (1 mmol) and maleic acid (0.12 g, 1.1 mmol) in acetone (5 ml) was stirred for 1 h. The precipitated crystals were filtered off and recrystallized from an i-PrOH–DMF mixture [for (I)] or MeOH [for (II)] to give the analytically pure maleates (I) and (II).
2-Methyl- N -[(5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methyl]propan-2-aminium (2 Z )-3-carboxyacrylate (I). Colourless prisms. Yield 0.26 g (72%). M.p. = 485.1–486.1 K (i-PrOH–DMF). IR (KBr), ν (cm−1): 1591, 1630, 3435. 1H NMR (DMSO, 600 MHz, 301 K): δ = 1.36 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 4.30 (s, 2H, CH2—N), 6.04 (s, 2H, –CH=CH–), 6.74 (d, 1H, H3, furyl, J = 3.4), 7.00 (d, 1H, H4, furyl, J = 3.4), 7.34 (br t, 1H, H4, Ph, J = 7.6), 7.46 (ddd, 2H, H3 and H5, Ph, J = 8.2, J = 7.6, J = 1.4), 7.76 (dd, 2H, H2 and H6, Ph, J = 8.2, J = 1.4), 8.89 (br s, 1H, CO2H). 13C NMR (CDCl3, 150.9 MHz, 301 K): δ = 25.7 (3C, CH3), 38.0 (CH2—N), 57.3 (N—C), 100.0 (2C, –CH=CH–), 107.4 (C4, furyl), 114.3 (C3, furyl), 124.2, 128.5, 129.5, 130.3, 136.7 (C1, Ph), 146.6 (C2, furyl), 154.5 (C5, furyl), 167.8 (2C, CO2). MS (APCI): m/z = 230 [M − 115]+.
N -[(5-Iodofuran-2-yl)methyl]-2-methylpropan-2-aminium (2 Z )-3-carboxyprop-2-enoate (II). Colourless needles. Yield 0.31 g (79%). M.p. = 452.1–453.3 K (CH3OH). IR (KBr), ν (cm−1): 1576, 1631, 2800, 3012. 1H NMR (DMSO, 600 MHz, 301 K): δ = 1.26 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 4.19 (s, 2H, CH2—N), 5.99–6.00 (m, 2H, –CH=CH–), 6.54 (d, 1H, H3, furyl, J = 3.3), 6.73 (d, 1H, H4, furyl, J = 3.3), 8.89 (br s, 1H, CO2H). 13C NMR (CDCl3, 150.9 MHz, 301 K): δ = 25.6 (3C, CH3), 37.4 (CH2—N), 57.3 (N—C), 100.0 (C5, furyl), 115.3 (C4, furyl), 121.8 (C3, furyl), 136.6 (2C, —CH=CH—), 151.1 [C2, furyl], 167.7 (2C, CO2). MS (APCI): m/z = 280 [M − 115]+.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. X-ray diffraction studies for (II) were carried out on the ‘Belok’ beamline of the National Research Center "Kurchatov Institute" (Moscow, Russian Federation).
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C15H20NO+·C4H3O4 − | C9H15INO+·C4H3O4 − |
| M r | 345.38 | 395.18 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P

|
Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 120 | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 7.5177 (4), 9.8339 (6), 12.1951 (7) | 5.7501 (12), 28.272 (6), 9.6402 (19) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 94.387 (1), 94.552 (1), 91.578 (1) | 90, 93.17 (3), 90 |
| V (Å3) | 895.57 (9) | 1564.8 (6) |
| Z | 2 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Synchrotron, λ = 0.96990 Å |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.09 | 4.69 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.20 | 0.30 × 0.05 × 0.03 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD | Rayonix SX165 CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2003 ▸) | Multi-scan (SCALA; Evans, 2006 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.966, 0.977 | 0.460, 0.860 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 14165, 6555, 3947 | 21875, 3146, 2714 |
| R int | 0.047 | 0.068 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.760 | 0.641 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.053, 0.122, 1.00 | 0.040, 0.100, 1.02 |
| No. of reflections | 6555 | 3146 |
| No. of parameters | 238 | 194 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.31, −0.26 | 0.94, −1.21 |
The hydrogen atoms of the amino and hydroxy groups were localized in a difference-Fourier map and refined isotropically with fixed displacement parameters [U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(N) and 1.5U eq(O)]. All other hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions with C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å and refined using the riding model with fixed isotropic displacement parameters [U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C) for the CH3 groups and 1.2U eq(C) for all other atoms].
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017003541/hb7663sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017003541/hb7663Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017003541/hb7663IIsup3.hkl
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
(I) 2-Methyl-N-[(5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methyl]propan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyacrylate . Crystal data
| C15H20NO+·C4H3O4− | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 345.38 | F(000) = 368 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.281 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.5177 (4) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 9.8339 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 2186 reflections |
| c = 12.1951 (7) Å | θ = 2.6–31.5° |
| α = 94.387 (1)° | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 94.552 (1)° | T = 120 K |
| γ = 91.578 (1)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 895.57 (9) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm |
(I) 2-Methyl-N-[(5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methyl]propan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyacrylate . Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3947 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.047 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 32.7°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2003) | h = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.966, Tmax = 0.977 | k = −14→14 |
| 14165 measured reflections | l = −18→18 |
| 6555 independent reflections |
(I) 2-Methyl-N-[(5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methyl]propan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyacrylate . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.053 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.122 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.00 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0454P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 6555 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 238 parameters | Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3 |
(I) 2-Methyl-N-[(5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methyl]propan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyacrylate . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
(I) 2-Methyl-N-[(5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methyl]propan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyacrylate . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.92461 (12) | 0.90909 (9) | 0.24482 (7) | 0.0223 (2) | |
| N1 | 1.20595 (14) | 0.76402 (11) | 0.11610 (9) | 0.0175 (2) | |
| H1A | 1.2498 (18) | 0.6949 (15) | 0.1627 (12) | 0.021* | |
| H1B | 1.2370 (19) | 0.8484 (15) | 0.1545 (12) | 0.021* | |
| C1 | 1.00641 (17) | 0.74679 (14) | 0.09978 (11) | 0.0223 (3) | |
| H1C | 0.9596 | 0.8102 | 0.0461 | 0.027* | |
| H1D | 0.9736 | 0.6525 | 0.0691 | 0.027* | |
| C2 | 0.92419 (17) | 0.77432 (13) | 0.20536 (11) | 0.0216 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.84120 (18) | 0.69612 (15) | 0.27361 (12) | 0.0264 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.8233 | 0.5998 | 0.2652 | 0.032* | |
| C4 | 0.78576 (19) | 0.78600 (15) | 0.36059 (12) | 0.0272 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.7229 | 0.7610 | 0.4210 | 0.033* | |
| C5 | 0.83939 (17) | 0.91370 (14) | 0.34107 (11) | 0.0222 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.82740 (17) | 1.04880 (14) | 0.39825 (11) | 0.0229 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.89734 (18) | 1.16539 (15) | 0.35647 (12) | 0.0262 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.9550 | 1.1572 | 0.2898 | 0.031* | |
| C8 | 0.88348 (19) | 1.29304 (16) | 0.41130 (12) | 0.0296 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.9325 | 1.3716 | 0.3824 | 0.036* | |
| C9 | 0.79823 (19) | 1.30640 (16) | 0.50820 (12) | 0.0302 (3) | |
| H9 | 0.7881 | 1.3940 | 0.5454 | 0.036* | |
| C10 | 0.72778 (19) | 1.19148 (16) | 0.55059 (11) | 0.0286 (3) | |
| H10 | 0.6689 | 1.2005 | 0.6167 | 0.034* | |
| C11 | 0.74308 (18) | 1.06376 (16) | 0.49678 (11) | 0.0260 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.6960 | 0.9854 | 0.5269 | 0.031* | |
| C12 | 1.30888 (17) | 0.75667 (13) | 0.01359 (11) | 0.0200 (3) | |
| C13 | 1.50545 (18) | 0.75962 (15) | 0.05686 (12) | 0.0265 (3) | |
| H13A | 1.5326 | 0.8418 | 0.1067 | 0.040* | |
| H13B | 1.5804 | 0.7604 | −0.0053 | 0.040* | |
| H13C | 1.5294 | 0.6785 | 0.0969 | 0.040* | |
| C14 | 1.25942 (19) | 0.62298 (14) | −0.05538 (12) | 0.0262 (3) | |
| H14A | 1.1346 | 0.6240 | −0.0853 | 0.039* | |
| H14B | 1.2751 | 0.5465 | −0.0089 | 0.039* | |
| H14C | 1.3368 | 0.6126 | −0.1163 | 0.039* | |
| C15 | 1.26620 (19) | 0.88007 (15) | −0.05105 (12) | 0.0262 (3) | |
| H15A | 1.2918 | 0.9639 | −0.0029 | 0.039* | |
| H15B | 1.1397 | 0.8753 | −0.0779 | 0.039* | |
| H15C | 1.3397 | 0.8804 | −0.1139 | 0.039* | |
| O2 | 0.34880 (14) | 0.57638 (10) | 0.25174 (8) | 0.0310 (2) | |
| O3 | 0.19310 (13) | 0.40290 (11) | 0.15970 (8) | 0.0306 (2) | |
| O4 | 0.34720 (13) | −0.00091 (10) | 0.23666 (8) | 0.0279 (2) | |
| O5 | 0.19913 (12) | 0.15695 (10) | 0.14960 (8) | 0.0255 (2) | |
| H5O | 0.190 (2) | 0.2747 (18) | 0.1531 (13) | 0.038* | |
| C16 | 0.31067 (18) | 0.45314 (14) | 0.23545 (11) | 0.0226 (3) | |
| C17 | 0.40964 (18) | 0.36056 (14) | 0.30859 (11) | 0.0235 (3) | |
| H17 | 0.4830 | 0.4061 | 0.3680 | 0.028* | |
| C18 | 0.41217 (18) | 0.22465 (14) | 0.30440 (11) | 0.0226 (3) | |
| H18 | 0.4888 | 0.1892 | 0.3602 | 0.027* | |
| C19 | 0.31356 (17) | 0.11924 (14) | 0.22580 (11) | 0.0210 (3) |
(I) 2-Methyl-N-[(5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methyl]propan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyacrylate . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0221 (5) | 0.0253 (5) | 0.0199 (5) | 0.0034 (4) | 0.0041 (4) | 0.0016 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0174 (5) | 0.0160 (5) | 0.0189 (5) | 0.0008 (4) | −0.0002 (4) | 0.0010 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0167 (6) | 0.0276 (7) | 0.0217 (6) | 0.0006 (5) | −0.0003 (5) | −0.0016 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0178 (6) | 0.0236 (7) | 0.0225 (6) | 0.0032 (5) | −0.0012 (5) | −0.0011 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0246 (7) | 0.0266 (7) | 0.0281 (7) | 0.0009 (6) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0025 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0254 (7) | 0.0333 (8) | 0.0242 (7) | 0.0024 (6) | 0.0068 (6) | 0.0056 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0181 (6) | 0.0320 (7) | 0.0172 (6) | 0.0057 (5) | 0.0023 (5) | 0.0039 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0183 (6) | 0.0309 (7) | 0.0197 (6) | 0.0072 (5) | −0.0001 (5) | 0.0022 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0242 (7) | 0.0325 (8) | 0.0223 (7) | 0.0043 (6) | 0.0039 (5) | 0.0022 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0276 (7) | 0.0318 (8) | 0.0293 (8) | 0.0040 (6) | 0.0008 (6) | 0.0020 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0289 (7) | 0.0348 (8) | 0.0252 (7) | 0.0090 (6) | −0.0028 (6) | −0.0064 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0252 (7) | 0.0417 (9) | 0.0189 (7) | 0.0105 (6) | 0.0005 (5) | −0.0004 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0227 (7) | 0.0359 (8) | 0.0197 (7) | 0.0077 (6) | 0.0006 (5) | 0.0038 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0189 (6) | 0.0220 (6) | 0.0193 (6) | 0.0012 (5) | 0.0031 (5) | 0.0007 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0207 (6) | 0.0299 (8) | 0.0291 (7) | 0.0013 (6) | 0.0037 (6) | 0.0026 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0260 (7) | 0.0261 (7) | 0.0257 (7) | 0.0021 (6) | 0.0042 (6) | −0.0051 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0287 (7) | 0.0276 (7) | 0.0229 (7) | 0.0005 (6) | 0.0025 (6) | 0.0062 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0433 (6) | 0.0204 (5) | 0.0294 (6) | 0.0081 (4) | 0.0000 (5) | 0.0026 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0296 (5) | 0.0296 (6) | 0.0318 (6) | 0.0042 (4) | −0.0079 (4) | 0.0075 (4) |
| O4 | 0.0333 (6) | 0.0196 (5) | 0.0301 (5) | −0.0014 (4) | −0.0006 (4) | −0.0001 (4) |
| O5 | 0.0256 (5) | 0.0284 (5) | 0.0215 (5) | −0.0018 (4) | −0.0041 (4) | 0.0021 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0233 (6) | 0.0250 (7) | 0.0203 (6) | 0.0077 (5) | 0.0039 (5) | 0.0025 (5) |
| C17 | 0.0254 (7) | 0.0222 (7) | 0.0217 (7) | 0.0024 (5) | −0.0045 (5) | −0.0003 (5) |
| C18 | 0.0225 (6) | 0.0226 (7) | 0.0218 (6) | 0.0029 (5) | −0.0042 (5) | 0.0021 (5) |
| C19 | 0.0206 (6) | 0.0230 (7) | 0.0191 (6) | −0.0007 (5) | 0.0031 (5) | 0.0000 (5) |
(I) 2-Methyl-N-[(5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methyl]propan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyacrylate . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C2 | 1.3747 (16) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| O1—C5 | 1.3796 (15) | C12—C15 | 1.5247 (19) |
| N1—C1 | 1.5007 (16) | C12—C14 | 1.5259 (18) |
| N1—C12 | 1.5198 (16) | C12—C13 | 1.5279 (18) |
| N1—H1A | 0.968 (15) | C13—H13A | 0.9800 |
| N1—H1B | 0.936 (15) | C13—H13B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.4817 (18) | C13—H13C | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1C | 0.9900 | C14—H14A | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1D | 0.9900 | C14—H14B | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.352 (2) | C14—H14C | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.424 (2) | C15—H15A | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C15—H15B | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.353 (2) | C15—H15C | 0.9800 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | O2—C16 | 1.2351 (17) |
| C5—C6 | 1.4609 (19) | O3—C16 | 1.2866 (17) |
| C6—C7 | 1.396 (2) | O3—H5O | 1.257 (17) |
| C6—C11 | 1.4022 (19) | O4—C19 | 1.2300 (16) |
| C7—C8 | 1.387 (2) | O5—C19 | 1.2979 (16) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | O5—H5O | 1.160 (17) |
| C8—C9 | 1.388 (2) | C16—C17 | 1.4947 (19) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | C17—C18 | 1.3343 (18) |
| C9—C10 | 1.387 (2) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9500 | C18—C19 | 1.4952 (18) |
| C10—C11 | 1.384 (2) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| C10—H10 | 0.9500 | ||
| C2—O1—C5 | 106.85 (10) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.7 |
| C1—N1—C12 | 117.49 (10) | C6—C11—H11 | 119.7 |
| C1—N1—H1A | 108.0 (8) | N1—C12—C15 | 108.92 (10) |
| C12—N1—H1A | 108.0 (8) | N1—C12—C14 | 109.41 (11) |
| C1—N1—H1B | 109.6 (9) | C15—C12—C14 | 111.64 (11) |
| C12—N1—H1B | 106.5 (9) | N1—C12—C13 | 105.08 (10) |
| H1A—N1—H1B | 106.6 (12) | C15—C12—C13 | 111.28 (11) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 111.02 (10) | C14—C12—C13 | 110.29 (11) |
| C2—C1—H1C | 109.4 | C12—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1C | 109.4 | C12—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1D | 109.4 | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1D | 109.4 | C12—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| H1C—C1—H1D | 108.0 | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—O1 | 109.83 (12) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 134.49 (13) | C12—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| O1—C2—C1 | 115.65 (12) | C12—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 106.78 (13) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 126.6 | C12—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 126.6 | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 107.10 (12) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 126.4 | C12—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 126.4 | C12—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—O1 | 109.43 (12) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 134.61 (13) | C12—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| O1—C5—C6 | 115.96 (12) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C11 | 118.51 (13) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.38 (12) | C16—O3—H5O | 111.3 (7) |
| C11—C6—C5 | 120.11 (13) | C19—O5—H5O | 111.7 (8) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 120.65 (13) | O2—C16—O3 | 123.38 (13) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.7 | O2—C16—C17 | 116.77 (12) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.7 | O3—C16—C17 | 119.85 (12) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.20 (15) | C18—C17—C16 | 130.78 (13) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.9 | C18—C17—H17 | 114.6 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.9 | C16—C17—H17 | 114.6 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 119.80 (14) | C17—C18—C19 | 130.28 (12) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 120.1 | C17—C18—H18 | 114.9 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.1 | C19—C18—H18 | 114.9 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 120.17 (13) | O4—C19—O5 | 123.00 (12) |
| C11—C10—H10 | 119.9 | O4—C19—C18 | 117.33 (12) |
| C9—C10—H10 | 119.9 | O5—C19—C18 | 119.67 (12) |
| C10—C11—C6 | 120.67 (14) | ||
| C12—N1—C1—C2 | −172.59 (11) | C11—C6—C7—C8 | 0.0 (2) |
| C5—O1—C2—C3 | 0.25 (14) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 179.45 (13) |
| C5—O1—C2—C1 | 178.57 (11) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.6 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −109.20 (17) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.4 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2—O1 | 73.02 (14) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.3 (2) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.17 (15) | C9—C10—C11—C6 | −0.9 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −177.70 (14) | C7—C6—C11—C10 | 0.8 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.53 (16) | C5—C6—C11—C10 | −178.73 (12) |
| C3—C4—C5—O1 | 0.70 (16) | C1—N1—C12—C15 | 67.55 (14) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −178.87 (14) | C1—N1—C12—C14 | −54.73 (14) |
| C2—O1—C5—C4 | −0.60 (14) | C1—N1—C12—C13 | −173.13 (11) |
| C2—O1—C5—C6 | 179.06 (11) | O2—C16—C17—C18 | −172.20 (14) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −179.94 (15) | O3—C16—C17—C18 | 7.4 (2) |
| O1—C5—C6—C7 | 0.51 (18) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | −1.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C11 | −0.5 (2) | C17—C18—C19—O4 | 176.22 (14) |
| O1—C5—C6—C11 | 179.98 (11) | C17—C18—C19—O5 | −3.2 (2) |
(I) 2-Methyl-N-[(5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methyl]propan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyacrylate . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O5—H5O···O3 | 1.160 (17) | 1.257 (17) | 2.4142 (14) | 175.3 (15) |
| N1—H1A···O2i | 0.968 (15) | 1.790 (15) | 2.7547 (15) | 174.9 (13) |
| N1—H1B···O4ii | 0.936 (15) | 1.860 (15) | 2.7803 (14) | 167.4 (13) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y, z; (ii) x+1, y+1, z.
(II) N-[(5-Iodofuran-2-yl)methyl]-2-methylpropan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyprop-2-enoate . Crystal data
| C9H15INO+·C4H3O4− | F(000) = 784 |
| Mr = 395.18 | Dx = 1.678 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Synchrotron radiation, λ = 0.96990 Å |
| a = 5.7501 (12) Å | Cell parameters from 600 reflections |
| b = 28.272 (6) Å | θ = 3.5–35.0° |
| c = 9.6402 (19) Å | µ = 4.69 mm−1 |
| β = 93.17 (3)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1564.8 (6) Å3 | Needle, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.30 × 0.05 × 0.03 mm |
(II) N-[(5-Iodofuran-2-yl)methyl]-2-methylpropan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyprop-2-enoate . Data collection
| Rayonix SX165 CCD diffractometer | 2714 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ scan | Rint = 0.068 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (Scala; Evans, 2006) | θmax = 38.5°, θmin = 3.5° |
| Tmin = 0.460, Tmax = 0.860 | h = −7→7 |
| 21875 measured reflections | k = −36→36 |
| 3146 independent reflections | l = −11→11 |
(II) N-[(5-Iodofuran-2-yl)methyl]-2-methylpropan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyprop-2-enoate . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.100 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0377P)2 + 3.P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.02 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3146 reflections | Δρmax = 0.94 e Å−3 |
| 194 parameters | Δρmin = −1.21 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015a), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: difference Fourier map | Extinction coefficient: 0.0047 (5) |
(II) N-[(5-Iodofuran-2-yl)methyl]-2-methylpropan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyprop-2-enoate . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
(II) N-[(5-Iodofuran-2-yl)methyl]-2-methylpropan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyprop-2-enoate . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| I1 | 0.75296 (5) | 0.48487 (2) | 0.86223 (3) | 0.05279 (17) | |
| O1 | 0.4289 (4) | 0.56119 (7) | 0.7766 (3) | 0.0273 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.6669 (4) | 0.62755 (8) | 0.4628 (2) | 0.0250 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.4201 (4) | 0.64214 (9) | 0.2824 (3) | 0.0284 (5) | |
| O4 | 0.7068 (4) | 0.65296 (8) | −0.1219 (2) | 0.0242 (5) | |
| O5 | 0.4335 (4) | 0.65188 (8) | 0.0330 (3) | 0.0272 (5) | |
| H5O | 0.434 (7) | 0.6447 (14) | 0.153 (5) | 0.041* | |
| N1 | 0.3606 (4) | 0.65833 (8) | 0.6639 (3) | 0.0172 (5) | |
| H1A | 0.436 (6) | 0.6486 (12) | 0.592 (4) | 0.021* | |
| H1B | 0.462 (7) | 0.6587 (12) | 0.735 (4) | 0.021* | |
| C1 | 0.1674 (5) | 0.62389 (10) | 0.6907 (4) | 0.0227 (7) | |
| H1C | 0.1109 | 0.6293 | 0.7845 | 0.027* | |
| H1D | 0.0355 | 0.6289 | 0.6219 | 0.027* | |
| C2 | 0.2549 (5) | 0.57433 (10) | 0.6802 (4) | 0.0247 (7) | |
| C3 | 0.2006 (7) | 0.53816 (12) | 0.5920 (5) | 0.0379 (9) | |
| H3 | 0.0876 | 0.5385 | 0.5163 | 0.045* | |
| C4 | 0.3478 (8) | 0.49932 (12) | 0.6355 (5) | 0.0425 (10) | |
| H4 | 0.3511 | 0.4687 | 0.5950 | 0.051* | |
| C5 | 0.4796 (6) | 0.51500 (11) | 0.7450 (4) | 0.0307 (9) | |
| C6 | 0.2890 (5) | 0.71010 (10) | 0.6427 (3) | 0.0189 (7) | |
| C7 | 0.5174 (5) | 0.73740 (10) | 0.6298 (4) | 0.0236 (7) | |
| H7A | 0.6151 | 0.7339 | 0.7157 | 0.035* | |
| H7B | 0.4829 | 0.7710 | 0.6137 | 0.035* | |
| H7C | 0.6001 | 0.7248 | 0.5516 | 0.035* | |
| C8 | 0.1369 (5) | 0.71450 (11) | 0.5089 (4) | 0.0241 (7) | |
| H8A | 0.2219 | 0.7025 | 0.4310 | 0.036* | |
| H8B | 0.0968 | 0.7478 | 0.4926 | 0.036* | |
| H8C | −0.0061 | 0.6961 | 0.5171 | 0.036* | |
| C9 | 0.1632 (5) | 0.72673 (10) | 0.7693 (4) | 0.0225 (7) | |
| H9A | 0.0164 | 0.7094 | 0.7744 | 0.034* | |
| H9B | 0.1308 | 0.7607 | 0.7611 | 0.034* | |
| H9C | 0.2618 | 0.7208 | 0.8537 | 0.034* | |
| C10 | 0.6235 (5) | 0.63160 (9) | 0.3358 (4) | 0.0198 (7) | |
| C11 | 0.8219 (5) | 0.62384 (10) | 0.2425 (3) | 0.0213 (7) | |
| H11 | 0.9625 | 0.6131 | 0.2884 | 0.026* | |
| C12 | 0.8311 (5) | 0.62967 (10) | 0.1049 (4) | 0.0225 (7) | |
| H12 | 0.9776 | 0.6225 | 0.0690 | 0.027* | |
| C13 | 0.6458 (5) | 0.64577 (10) | −0.0025 (3) | 0.0196 (6) |
(II) N-[(5-Iodofuran-2-yl)methyl]-2-methylpropan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyprop-2-enoate . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| I1 | 0.0535 (2) | 0.04314 (19) | 0.0625 (3) | 0.02765 (12) | 0.00979 (16) | 0.01596 (12) |
| O1 | 0.0296 (12) | 0.0202 (10) | 0.0322 (15) | 0.0075 (9) | 0.0039 (11) | 0.0029 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0267 (12) | 0.0268 (11) | 0.0221 (14) | 0.0022 (9) | 0.0057 (10) | 0.0000 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0182 (11) | 0.0421 (13) | 0.0254 (14) | 0.0036 (9) | 0.0057 (10) | 0.0003 (10) |
| O4 | 0.0217 (11) | 0.0293 (11) | 0.0218 (13) | −0.0005 (8) | 0.0017 (10) | 0.0046 (9) |
| O5 | 0.0164 (10) | 0.0397 (13) | 0.0257 (14) | 0.0047 (9) | 0.0030 (9) | 0.0035 (10) |
| N1 | 0.0150 (12) | 0.0167 (11) | 0.0201 (15) | 0.0015 (9) | 0.0032 (11) | 0.0001 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0178 (14) | 0.0199 (14) | 0.031 (2) | −0.0007 (11) | 0.0050 (13) | 0.0017 (13) |
| C2 | 0.0235 (15) | 0.0194 (14) | 0.032 (2) | −0.0016 (11) | 0.0062 (14) | 0.0039 (13) |
| C3 | 0.042 (2) | 0.0239 (16) | 0.046 (3) | −0.0080 (14) | −0.0075 (18) | 0.0007 (16) |
| C4 | 0.054 (2) | 0.0180 (15) | 0.056 (3) | −0.0022 (16) | 0.011 (2) | −0.0060 (17) |
| C5 | 0.0343 (18) | 0.0207 (15) | 0.038 (2) | 0.0063 (12) | 0.0127 (17) | 0.0074 (14) |
| C6 | 0.0180 (14) | 0.0159 (13) | 0.0231 (19) | 0.0027 (10) | 0.0033 (13) | −0.0002 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0210 (15) | 0.0182 (13) | 0.032 (2) | 0.0006 (11) | 0.0046 (14) | 0.0021 (13) |
| C8 | 0.0237 (15) | 0.0224 (14) | 0.0260 (19) | 0.0045 (11) | −0.0001 (14) | 0.0007 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0198 (14) | 0.0214 (13) | 0.0267 (19) | 0.0024 (11) | 0.0046 (13) | −0.0040 (13) |
| C10 | 0.0189 (14) | 0.0144 (12) | 0.026 (2) | −0.0001 (10) | 0.0054 (13) | 0.0007 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0180 (14) | 0.0229 (14) | 0.0232 (19) | 0.0023 (11) | 0.0034 (13) | 0.0016 (13) |
| C12 | 0.0164 (14) | 0.0230 (14) | 0.029 (2) | 0.0026 (11) | 0.0065 (13) | 0.0003 (13) |
| C13 | 0.0172 (13) | 0.0181 (13) | 0.0235 (19) | −0.0005 (10) | 0.0014 (13) | 0.0007 (12) |
(II) N-[(5-Iodofuran-2-yl)methyl]-2-methylpropan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyprop-2-enoate . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| I1—C5 | 2.068 (4) | C4—C5 | 1.341 (6) |
| O1—C5 | 1.376 (4) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| O1—C2 | 1.379 (4) | C6—C8 | 1.523 (5) |
| O2—C10 | 1.241 (4) | C6—C9 | 1.527 (4) |
| O3—C10 | 1.287 (4) | C6—C7 | 1.535 (4) |
| O3—H5O | 1.25 (5) | C7—H7A | 0.9800 |
| O4—C13 | 1.238 (4) | C7—H7B | 0.9800 |
| O5—C13 | 1.297 (3) | C7—H7C | 0.9800 |
| O5—H5O | 1.18 (5) | C8—H8A | 0.9800 |
| N1—C1 | 1.510 (4) | C8—H8B | 0.9800 |
| N1—C6 | 1.531 (4) | C8—H8C | 0.9800 |
| N1—H1A | 0.88 (4) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| N1—H1B | 0.88 (4) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.494 (4) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1C | 0.9900 | C10—C11 | 1.507 (4) |
| C1—H1D | 0.9900 | C11—C12 | 1.340 (5) |
| C2—C3 | 1.355 (5) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.435 (6) | C12—C13 | 1.515 (5) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C5—O1—C2 | 105.2 (3) | N1—C6—C7 | 105.5 (2) |
| C10—O3—H5O | 107.7 (19) | C6—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| C13—O5—H5O | 107 (2) | C6—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—C6 | 116.4 (2) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—H1A | 109 (2) | C6—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C6—N1—H1A | 109 (2) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—H1B | 110 (2) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C6—N1—H1B | 105 (2) | C6—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| H1A—N1—H1B | 107 (3) | C6—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—N1 | 109.8 (2) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1C | 109.7 | C6—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1C | 109.7 | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1D | 109.7 | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1D | 109.7 | C6—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| H1C—C1—H1D | 108.2 | C6—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—O1 | 110.7 (3) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 133.1 (3) | C6—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O1—C2—C1 | 116.2 (3) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 106.4 (4) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 126.8 | O2—C10—O3 | 123.0 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 126.8 | O2—C10—C11 | 117.3 (3) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 106.0 (3) | O3—C10—C11 | 119.7 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 127.0 | C12—C11—C10 | 130.2 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 127.0 | C12—C11—H11 | 114.9 |
| C4—C5—O1 | 111.8 (3) | C10—C11—H11 | 114.9 |
| C4—C5—I1 | 132.4 (3) | C11—C12—C13 | 130.5 (3) |
| O1—C5—I1 | 115.7 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 114.8 |
| C8—C6—C9 | 112.1 (3) | C13—C12—H12 | 114.8 |
| C8—C6—N1 | 109.2 (2) | O4—C13—O5 | 122.9 (3) |
| C9—C6—N1 | 108.9 (2) | O4—C13—C12 | 117.4 (3) |
| C8—C6—C7 | 110.1 (3) | O5—C13—C12 | 119.7 (3) |
| C9—C6—C7 | 110.8 (3) | ||
| C6—N1—C1—C2 | 168.5 (3) | C2—O1—C5—C4 | 0.1 (4) |
| C5—O1—C2—C3 | −0.4 (4) | C2—O1—C5—I1 | 175.9 (2) |
| C5—O1—C2—C1 | −179.6 (3) | C1—N1—C6—C8 | −66.1 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −115.3 (4) | C1—N1—C6—C9 | 56.6 (4) |
| N1—C1—C2—O1 | 63.7 (4) | C1—N1—C6—C7 | 175.5 (3) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.5 (4) | O2—C10—C11—C12 | −173.7 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 179.6 (3) | O3—C10—C11—C12 | 6.0 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.5 (4) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.3 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5—O1 | 0.2 (4) | C11—C12—C13—O4 | 172.5 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—I1 | −174.7 (3) | C11—C12—C13—O5 | −6.8 (5) |
(II) N-[(5-Iodofuran-2-yl)methyl]-2-methylpropan-2-aminium (2Z)-3-carboxyprop-2-enoate . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O5—H5O···O3 | 1.18 (5) | 1.25 (5) | 2.425 (3) | 172 (4) |
| N1—H1A···O2 | 0.88 (4) | 1.97 (4) | 2.828 (3) | 167 (3) |
| N1—H1B···O4i | 0.88 (4) | 1.92 (4) | 2.792 (4) | 172 (3) |
Symmetry code: (i) x, y, z+1.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation grant 4.1154.2017.
References
- Battye, T. G. G., Kontogiannis, L., Johnson, O., Powell, H. R. & Leslie, A. G. W. (2011). Acta Cryst. D67, 271–281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Berson, J. A. & Swidler, R. (1953). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 75, 1721–1726.
- Berson, J. A. & Swidler, R. (1954). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 76, 4060–4069.
- Brown, T. H. (1986). Patent US4567176A1.
- Bruker (2001). SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker. (2005). APEX2. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Clitherow, J. W. (1983). Patent US4413135A1.
- Craig, A. S., Ho, T. C. T. & McClure, M. S. (2008). Patent WO2008/154469A1.
- Diels, O. & Alder, K. (1931). Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 490, 257–266.
- Eggelte, T. A., de Koning, H. & Huisman, H. O. (1973). Tetrahedron, 29, 2491–2493.
- Evans, P. (2006). Acta Cryst. D62, 72–82. [DOI] [PubMed]
- MarXperts. (2015). Automar. marXperts GmbH, Norderstedt, Germany.
- Metsger, L., Mittelman, A. & Yurkovski, S. (2010). Pat. US2010/87459A1.
- Pelosi, S. S. Jr, Yu, C.-N. & Calcagno, M. A. (2002). Patent EP1231208A2.
- Price, B. J., Clitherow, J. W., Bradshaw, J., Martin-Smith, M., Judd, D. B. & Hayes, R. (1985). Patent US4524071A1.
- Sheinkman, A. K., Deikalo, A. A., Stupnikova, T. V., Klyuev, N. A. & Mal’tseva, G. A. (1972). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 8, 993–997.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2003). SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Shih, W., Lau, N. & Seltzer, S. (1975). J. Org. Chem. 40, 1269–1274.
- Sprague, P. W., Heikes, J. E., Gougoutas, J. Z., Malley, M. F., Harris, D. N. & Greenberg, R. (1985). J. Med. Chem. 28, 1580–1590. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zubkov, F. I., Golubev, V. D., Zaytsev, V. P., Bakhanovich, O. V., Nikitina, E. V., Khrustalev, V. N., Aysin, R. R., Timofeeva, T. V., Novikov, R. A. & Varlamov, A. V. (2016). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd, 52, 225–236.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017003541/hb7663sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017003541/hb7663Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017003541/hb7663IIsup3.hkl
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report