The RuII atoms in the crystal structures of two new potential catalyst precursors, [Ru(Tpy-Cl)(CO)2Cl][Ru(CO)3Cl3] and [Ru(Tpy-Cl)(CO)2Cl2] (Tpy-Cl = 4′-chloro 2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine-κ3 N), exhibit distorted octahedral coordination spheres.
Keywords: crystal structure, ruthenium, terpyridine ligand, carbonyl ligand
Abstract
Two ruthenium carbonyl complexes with the 4′-chloro-2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine ligand (tpy-Cl, C15H10ClN3), i.e. [RuCl(tpy-Cl)(CO)2][RuCl3(CO)3] (I) [systematic name: cis-dicarbonylchlorido(4′-chloro-2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine-κ3 N)ruthenium(II) fac-tricarbonyltrichloridoruthenate(II)], and [RuCl2(tpy-Cl)(CO)2] (II) [cis-dicarbonyl-trans-dichlorido(4′-chloro-2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine-κ2 N 1,N 1′)ruthenium(II)], were synthesized and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The RuII atoms in both centrosymmetric structures (I) and (II) display similar, slightly distorted octahedral coordination spheres. The coordination sphere in the complex cation in compound (I) is defined by three N atoms of the tridentate tpy-Cl ligand, two carbonyl carbon atoms and one chlorido ligand; the charge is balanced by an octahedral [Ru(CO)3Cl3]− counter-anion. In the neutral compound (II), the tpy-Cl ligand coordinates to the metal only through two of its N atoms. The coordination sphere of the RuII atom is completed by two carbonyl and two chlorido ligands. In the crystal structures of both (I) and (II), weak C—H⋯Cl interactions are observed.
Chemical context
Ruthenium-carbonyl compounds with polypyridine ligands are known to be active catalysts for several catalytic processes including the reduction of carbon dioxide (Collomb-Dunand-Sauthier et al., 1994 ▸; Chardon-Noblat et al., 2002 ▸; Kuramochi et al., 2015 ▸), water–gas shift reaction (Luukkanen et al., 1999 ▸) and hydroformylation (Alvila et al., 1994 ▸). Many of these systems are metallopolymers obtained by reducing mononuclear precursors either chemically or electrochemically. The 2,2′-bipyridine ligand or its derivatives are the most commonly used ligand systems in these catalysts. It is also reported that possible substituents on polypyridine rings can have a strong impact on the catalytic behaviour of the compounds (Chardon-Noblat et al., 2001 ▸), which could offer a route to tailor the catalytic activity. Compounds with terpyridine and its derivatives as ligands together with carbonyl ligands are less commonly used (Deacon et al., 1984 ▸; Gibson et al., 1997 ▸; Ziessel et al., 2004 ▸), although it has also been shown that these types of compounds can be used to obtain active catalysts. Terpyridines are able to act as strong tridentate ligands because of the arrangement of the pyridine nitrogen atoms. However, bidentate coordination is also known (Deacon et al., 1984 ▸; Kooijman et al., 2007 ▸; Amoroso et al., 2010 ▸).
In this context we report on the two title compounds, [RuCl(tpy-Cl)(CO)2][Ru(CO)3Cl3] (I) and [RuCl2(tpy-Cl)(CO)2] (II) with the 4′-chloro-2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine ligand (tpy-Cl, C15H10ClN3), which show both types of coordination, i.e. tridentate for (I) and bidentate for (II). The title compounds were synthesized by adopting a literature procedure (Homanen et al., 1996 ▸).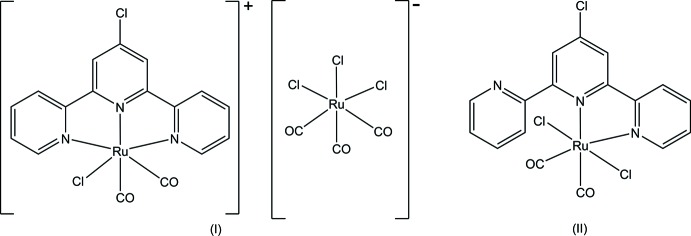
Structural commentary
Compound (I) is a salt and crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with four formula units in the unit cell. The coordination sphere of the RuII atom in the cation is a slightly distorted octahedron. The equatorial positions are occupied by three pyridine N atoms from the Tpy-Cl ligand and by one carbonyl ligand; axial positions are occupied by one chloride and one carbonyl ligand. The charge on the RuII atom is balanced by an octahedrally shaped fac-[Ru(CO)3Cl3]− anion (Fig. 1 ▸). As expected, in the cation the Ru1—N5 bond to the central pyridine ring of the tpy-Cl ligand [2.019 (2) Å] is the shortest of the Ru—N bonds (Gibson et al., 1997 ▸; Ziessel et al., 2004 ▸). The Ru1—N1 [2.097 (2) Å] and Ru1—N15 [2.093 (2) Å] bonds involving the outer pyridine rings are lengthened to relieve strain and to retain a typical terpyridine bite angle of about 79°. Similar structures can be found in other ruthenium(II) complexes containing terpyridine ligands (Gibson et al., 1997 ▸). The Ru1—C2 bond of the equatorial carbonyl group [1.918 (3) Å] is longer than the Ru1—C1 bond [1.893 (3) Å] of the axial carbonyl group, indicating a slightly stronger trans-influence caused by the pyridine N atom. The Ru1—Cl1 distance [2.4279 (7) Å] is in the range of typical Ru—Cl bond lengths (Deacon et al., 1984 ▸; Ziessel et al., 2004 ▸). The corresponding Ru—Cl bond lengths in the [Ru(CO)3Cl3]− counter-anion [2.4129 (7)–2.4212 (7) Å] also fall into the typical range of Ru—Cl bonds (Table 1 ▸).
Figure 1.
The molecular structures of the cation and anion in compound (I). Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å) for (I) .
| Ru1—C1 | 1.893 (3) | Ru2—C20 | 1.902 (3) |
| Ru1—C2 | 1.918 (3) | Ru2—C18 | 1.914 (3) |
| Ru1—N5 | 2.019 (2) | Ru2—Cl4 | 2.4129 (7) |
| Ru1—N15 | 2.093 (2) | Ru2—Cl5 | 2.4199 (7) |
| Ru1—N1 | 2.097 (2) | Ru2—Cl3 | 2.4212 (7) |
| Ru1—Cl1 | 2.4279 (7) | N1—C3 | 1.336 (3) |
| Ru2—C19 | 1.893 (3) |
Compound (II) is a neutral complex and crystallizes in the triclinic space group P
 with two formula units. The coordination sphere around the RuII atom is again a slightly distorted octahedron (Fig. 2 ▸). The four equatorial positions are occupied by two N atoms [Ru1—N1 = 2.105 (2) and Ru1—N2 = 2.157 (2) Å] from the Tpy-Cl ligand and by two carbonyl ligands [Ru1—C2 = 1.877 (3); Ru1—C1 = 1.895 (3) Å]. The chlorido ligands [Ru1—Cl1 = 2.3762 (8); Ru1—Cl2 = 2.4098 (7) Å] are placed at axial positions of the molecule. The Ru1—N2 and Ru1—C1 bond lengths are slightly longer than Ru1—N1 and Ru1—C2 bond lengths due to the steric strain generated by the non-coordinating pyridine ring (Table 2 ▸).
with two formula units. The coordination sphere around the RuII atom is again a slightly distorted octahedron (Fig. 2 ▸). The four equatorial positions are occupied by two N atoms [Ru1—N1 = 2.105 (2) and Ru1—N2 = 2.157 (2) Å] from the Tpy-Cl ligand and by two carbonyl ligands [Ru1—C2 = 1.877 (3); Ru1—C1 = 1.895 (3) Å]. The chlorido ligands [Ru1—Cl1 = 2.3762 (8); Ru1—Cl2 = 2.4098 (7) Å] are placed at axial positions of the molecule. The Ru1—N2 and Ru1—C1 bond lengths are slightly longer than Ru1—N1 and Ru1—C2 bond lengths due to the steric strain generated by the non-coordinating pyridine ring (Table 2 ▸).
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of compound (II). Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Table 2. Selected bond lengths (Å) for (II) .
| Ru1—C2 | 1.877 (3) | Ru1—N2 | 2.157 (2) |
| Ru1—C1 | 1.895 (3) | Ru1—Cl1 | 2.3762 (8) |
| Ru1—N1 | 2.105 (2) | Ru1—Cl2 | 2.4098 (7) |
The Tpy-Cl ligand in compound (I) is non-planar, despite coordination of all its three N atoms [dihedral angles between the mean planes of the central pyridine ring and the adjacent pyridine rings are 5.70 (8) and 13.28 (7)°]. In compound (II), the ring with the non-coordinating N atom is inclined considerably relative to the coordination plane of the two pyridine rings [dihedral angle 57.71 (9)°].
Supramolecular features
The packing of molecules (I) and (II) are dominated by van der Waals interactions; packing plots are displayed in Fig. 3 ▸ for (I) and Fig. 4 ▸ for (II). Only weak hydrogen bonds and π–π contacts can be found in these structures. In both (I) and (II), some non-conventional hydrogen bonds between the aromatic C—H hydrogen atoms and chlorido ligands of neighboring molecules do exist. The shortest contacts are summarized in Tables 3 ▸ and 4 ▸. In addition to these hydrogen bonds, the aromatic rings in structure (I) are involved in weak face-to-face π–π-interactions with considerable offsets. The shortest intermolecular C—C distances range from 3.23 to 3.50 Å. In (II), an edge-to-face contact exists between C3—H3 and C16 of the neighboring molecule. The distance between H3 and C16 is 2.89 Å and the angle C3—H3⋯C16 amounts to 134°. All interactions considered, three-dimensional network structures are obtained both for (I) and (II).
Figure 3.
The crystal packing of (I) in a view along the b axis.
Figure 4.
The crystal packing of (II) in a view along the b axis.
Table 3. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11—H11⋯Cl5i | 0.95 | 2.76 | 3.664 (3) | 158 |
| C16—H16⋯Cl1ii | 0.95 | 2.72 | 3.515 (3) | 142 |
| C5—H5⋯Cl3iii | 0.95 | 2.82 | 3.553 (3) | 134 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Table 4. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C9—H9⋯Cl2i | 0.95 | 2.77 | 3.687 (3) | 163 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Synthesis and crystallization
The title compounds were synthesized using a literature procedure (Homanen et al., 1996 ▸) and both compounds were obtained in a single pot reaction. A solution of [Ru(CO)3Cl2]2 (25.6 mg, 0.05 mmol) in 3 ml of THF was refluxed for 1 h under argon gas. After the reaction time, 26.7 mg (0.1 mmol) of tpy-Cl in 3 ml of THF was added to the above reaction mixture. The resulting mixture was refluxed for another 2 h in air with continuous stirring. During the reaction, the pale yellow solution turned to a reddish solution with a colourless precipitate. The precipitate was collected through centrifugation and the filtrate was evaporated for crystallization. Compound (I) was obtained as a major product originating from the precipitate and compound (II) was collected as a minor product from the filtrate. High-quality crystals of the salt (I) for single-crystal X-ray diffraction were obtained from DMSO solution and those of complex (II) were obtained as brown-coloured crystals from the filtrate.
Refinement details
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 5 ▸. All H atoms were positioned in calculated positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with C—H = 0.95 Å and U iso = 1.2U eq(C). The maximum electron density in complex (I) is located at 0.67 Å from atom C8 and in complex (II) at 1.28 Å from atom N2, respectively. The minimum density in complex (I) is located at 0.77 Å from atom Ru1 and in complex (II) at 0.87 Å from atom Ru1, respectively.
Table 5. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | [RuCl(C15H10ClN3)(CO)2][Ru(CO)3Cl3] | [RuCl2(C15H10ClN3(CO)2] |
| M r | 751.70 | 495.70 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c | Triclinic, P

|
| Temperature (K) | 123 | 123 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 14.3578 (4), 13.9158 (2), 13.2220 (3) | 7.3019 (3), 8.5080 (3), 14.7702 (6) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 114.080 (3), 90 | 101.287 (3), 91.835 (3), 98.144 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 2411.86 (11) | 889.09 (6) |
| Z | 4 | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 1.85 | 1.35 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.34 × 0.08 × 0.06 | 0.30 × 0.08 × 0.05 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Agilent SuperNova, Dual, Cu at zero, Atlas | Agilent SuperNova, Dual, Cu at zero, Atlas |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013 ▸) | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.914, 1.000 | 0.300, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 11072, 4864, 4264 | 7508, 3662, 3405 |
| R int | 0.023 | 0.036 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.625 | 0.630 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.024, 0.050, 1.06 | 0.033, 0.088, 1.07 |
| No. of reflections | 4864 | 3662 |
| No. of parameters | 316 | 235 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.43, −0.48 | 0.74, −1.43 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017003917/wm5367sup1.cif
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| [RuCl2(C15H10ClN3(CO)2] | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 495.70 | F(000) = 488 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.852 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.3019 (3) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 8.5080 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 5231 reflections |
| c = 14.7702 (6) Å | θ = 5.4–76.2° |
| α = 101.287 (3)° | µ = 1.35 mm−1 |
| β = 91.835 (3)° | T = 123 K |
| γ = 98.144 (3)° | Plate, brown |
| V = 889.09 (6) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.08 × 0.05 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova, Dual, Cu at zero, Atlas diffractometer | 3662 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: micro-source | 3405 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.036 |
| Detector resolution: 10.3953 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.6°, θmin = 1.4° |
| φ scans and ω scans with κ offset | h = −8→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlisPro; Agilent, 2013) | k = −7→10 |
| Tmin = 0.300, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −18→18 |
| 7508 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.033 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.088 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0453P)2 + 0.5543P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.07 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3662 reflections | Δρmax = 0.74 e Å−3 |
| 235 parameters | Δρmin = −1.43 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Ru1 | 0.97989 (3) | 0.30538 (2) | 0.20165 (2) | 0.01402 (9) | |
| Cl2 | 1.19336 (10) | 0.26275 (9) | 0.31916 (5) | 0.02134 (16) | |
| Cl3 | 0.53931 (11) | 0.29015 (9) | 0.58174 (5) | 0.02370 (16) | |
| Cl1 | 0.76545 (11) | 0.37329 (9) | 0.09657 (5) | 0.02563 (17) | |
| O1 | 0.9433 (4) | −0.0448 (3) | 0.10113 (17) | 0.0312 (5) | |
| O2 | 1.2842 (4) | 0.3556 (3) | 0.07324 (19) | 0.0380 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.7827 (3) | 0.2976 (3) | 0.30696 (17) | 0.0187 (5) | |
| N1 | 1.0061 (3) | 0.5492 (3) | 0.27105 (17) | 0.0183 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.6478 (4) | −0.1192 (3) | 0.26366 (18) | 0.0226 (5) | |
| C2 | 1.1703 (5) | 0.3368 (4) | 0.1217 (2) | 0.0242 (6) | |
| C13 | 0.6151 (4) | 0.0228 (4) | 0.2446 (2) | 0.0201 (6) | |
| C12 | 0.6700 (4) | 0.1661 (4) | 0.3213 (2) | 0.0190 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.6327 (4) | 0.2955 (4) | 0.4765 (2) | 0.0197 (6) | |
| C16 | 0.5048 (5) | −0.2483 (4) | 0.1144 (2) | 0.0280 (7) | |
| H16 | 0.4700 | −0.3452 | 0.0693 | 0.034* | |
| C9 | 0.7419 (4) | 0.4346 (4) | 0.4621 (2) | 0.0204 (6) | |
| H9 | 0.7662 | 0.5293 | 0.5096 | 0.024* | |
| C11 | 0.5945 (4) | 0.1598 (4) | 0.4060 (2) | 0.0208 (6) | |
| H11 | 0.5186 | 0.0646 | 0.4152 | 0.025* | |
| C7 | 0.9276 (4) | 0.5750 (3) | 0.3533 (2) | 0.0190 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.8142 (4) | 0.4312 (3) | 0.3764 (2) | 0.0176 (5) | |
| C17 | 0.5949 (5) | −0.2517 (4) | 0.1970 (2) | 0.0271 (7) | |
| H17 | 0.6211 | −0.3531 | 0.2076 | 0.032* | |
| C1 | 0.9506 (4) | 0.0845 (4) | 0.1412 (2) | 0.0226 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.5230 (4) | 0.0391 (4) | 0.1639 (2) | 0.0236 (6) | |
| H14 | 0.5002 | 0.1420 | 0.1543 | 0.028* | |
| C6 | 0.9447 (4) | 0.7303 (4) | 0.4081 (2) | 0.0234 (6) | |
| H6 | 0.8917 | 0.7472 | 0.4665 | 0.028* | |
| C15 | 0.4656 (5) | −0.1013 (4) | 0.0977 (2) | 0.0281 (7) | |
| H15 | 0.4004 | −0.0966 | 0.0418 | 0.034* | |
| C3 | 1.0952 (4) | 0.6760 (4) | 0.2401 (2) | 0.0235 (6) | |
| H3 | 1.1461 | 0.6571 | 0.1812 | 0.028* | |
| C5 | 1.0398 (5) | 0.8593 (4) | 0.3764 (2) | 0.0261 (6) | |
| H5 | 1.0533 | 0.9657 | 0.4132 | 0.031* | |
| C4 | 1.1151 (4) | 0.8330 (4) | 0.2910 (2) | 0.0248 (6) | |
| H4 | 1.1790 | 0.9206 | 0.2678 | 0.030* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Ru1 | 0.01375 (13) | 0.01423 (13) | 0.01338 (13) | 0.00090 (9) | 0.00123 (8) | 0.00191 (9) |
| Cl2 | 0.0197 (3) | 0.0204 (3) | 0.0232 (3) | 0.0047 (3) | −0.0033 (3) | 0.0023 (3) |
| Cl3 | 0.0266 (4) | 0.0286 (4) | 0.0179 (3) | 0.0064 (3) | 0.0063 (3) | 0.0069 (3) |
| Cl1 | 0.0278 (4) | 0.0256 (4) | 0.0223 (4) | 0.0028 (3) | −0.0067 (3) | 0.0043 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0374 (14) | 0.0215 (11) | 0.0310 (13) | 0.0025 (10) | 0.0078 (10) | −0.0031 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0325 (14) | 0.0397 (14) | 0.0417 (15) | 0.0039 (11) | 0.0167 (12) | 0.0068 (12) |
| N2 | 0.0167 (11) | 0.0194 (12) | 0.0205 (12) | 0.0036 (9) | 0.0012 (9) | 0.0043 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0172 (12) | 0.0179 (11) | 0.0194 (12) | 0.0015 (9) | −0.0012 (9) | 0.0042 (9) |
| N3 | 0.0228 (13) | 0.0226 (12) | 0.0224 (13) | 0.0033 (10) | 0.0023 (10) | 0.0044 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0289 (16) | 0.0192 (14) | 0.0238 (15) | 0.0035 (12) | 0.0008 (12) | 0.0030 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0175 (13) | 0.0229 (14) | 0.0191 (14) | −0.0009 (11) | 0.0027 (11) | 0.0044 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0177 (13) | 0.0197 (13) | 0.0191 (14) | 0.0010 (11) | −0.0004 (11) | 0.0043 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0205 (14) | 0.0256 (14) | 0.0141 (13) | 0.0069 (11) | 0.0014 (10) | 0.0043 (11) |
| C16 | 0.0315 (17) | 0.0237 (15) | 0.0224 (15) | −0.0075 (13) | 0.0072 (13) | −0.0033 (12) |
| C9 | 0.0210 (14) | 0.0209 (14) | 0.0193 (14) | 0.0059 (11) | −0.0018 (11) | 0.0028 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0188 (14) | 0.0207 (14) | 0.0225 (14) | 0.0012 (11) | −0.0001 (11) | 0.0050 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0164 (13) | 0.0193 (13) | 0.0209 (14) | 0.0026 (11) | −0.0003 (11) | 0.0033 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0159 (13) | 0.0180 (13) | 0.0172 (13) | 0.0027 (10) | −0.0032 (10) | 0.0004 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0279 (16) | 0.0234 (15) | 0.0296 (17) | 0.0032 (13) | 0.0070 (13) | 0.0043 (13) |
| C1 | 0.0208 (14) | 0.0271 (16) | 0.0208 (14) | 0.0037 (12) | 0.0052 (11) | 0.0069 (12) |
| C14 | 0.0248 (15) | 0.0238 (14) | 0.0207 (15) | −0.0008 (12) | −0.0013 (12) | 0.0049 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0237 (15) | 0.0224 (15) | 0.0227 (15) | 0.0030 (12) | 0.0006 (12) | 0.0017 (12) |
| C15 | 0.0309 (17) | 0.0303 (16) | 0.0195 (15) | −0.0057 (14) | −0.0022 (12) | 0.0040 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0204 (14) | 0.0259 (15) | 0.0246 (15) | 0.0018 (12) | 0.0004 (12) | 0.0074 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0246 (15) | 0.0210 (15) | 0.0305 (17) | 0.0022 (12) | −0.0014 (13) | 0.0014 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0211 (14) | 0.0201 (14) | 0.0329 (17) | −0.0008 (12) | −0.0015 (12) | 0.0078 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Ru1—C2 | 1.877 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.376 (5) |
| Ru1—C1 | 1.895 (3) | C16—C15 | 1.387 (5) |
| Ru1—N1 | 2.105 (2) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| Ru1—N2 | 2.157 (2) | C9—C8 | 1.383 (4) |
| Ru1—Cl1 | 2.3762 (8) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| Ru1—Cl2 | 2.4098 (7) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| Cl3—C10 | 1.723 (3) | C7—C6 | 1.395 (4) |
| O1—C1 | 1.135 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.481 (4) |
| O2—C2 | 1.129 (4) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C12 | 1.348 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.390 (4) |
| N2—C8 | 1.361 (4) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C3 | 1.345 (4) | C6—C5 | 1.384 (4) |
| N1—C7 | 1.352 (4) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C13 | 1.344 (4) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C17 | 1.344 (4) | C3—C4 | 1.384 (4) |
| C13—C14 | 1.391 (4) | C3—H3 | 0.9500 |
| C13—C12 | 1.490 (4) | C5—C4 | 1.383 (5) |
| C12—C11 | 1.391 (4) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| C10—C11 | 1.384 (4) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| C10—C9 | 1.387 (4) | ||
| C2—Ru1—C1 | 85.52 (13) | C8—C9—C10 | 117.9 (3) |
| C2—Ru1—N1 | 96.08 (11) | C8—C9—H9 | 121.0 |
| C1—Ru1—N1 | 178.40 (10) | C10—C9—H9 | 121.0 |
| C2—Ru1—N2 | 171.98 (12) | C10—C11—C12 | 118.4 (3) |
| C1—Ru1—N2 | 101.47 (11) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.8 |
| N1—Ru1—N2 | 76.94 (10) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.8 |
| C2—Ru1—Cl1 | 90.26 (10) | N1—C7—C6 | 120.8 (3) |
| C1—Ru1—Cl1 | 93.67 (10) | N1—C7—C8 | 115.5 (3) |
| N1—Ru1—Cl1 | 86.24 (7) | C6—C7—C8 | 123.5 (3) |
| N2—Ru1—Cl1 | 93.17 (7) | N2—C8—C9 | 122.6 (3) |
| C2—Ru1—Cl2 | 92.02 (10) | N2—C8—C7 | 115.3 (3) |
| C1—Ru1—Cl2 | 92.10 (10) | C9—C8—C7 | 122.0 (3) |
| N1—Ru1—Cl2 | 87.93 (7) | N3—C17—C16 | 123.4 (3) |
| N2—Ru1—Cl2 | 83.87 (7) | N3—C17—H17 | 118.3 |
| Cl1—Ru1—Cl2 | 173.94 (3) | C16—C17—H17 | 118.3 |
| C12—N2—C8 | 118.4 (3) | O1—C1—Ru1 | 175.0 (3) |
| C12—N2—Ru1 | 126.9 (2) | C15—C14—C13 | 117.3 (3) |
| C8—N2—Ru1 | 112.57 (19) | C15—C14—H14 | 121.3 |
| C3—N1—C7 | 119.5 (3) | C13—C14—H14 | 121.3 |
| C3—N1—Ru1 | 125.0 (2) | C5—C6—C7 | 119.1 (3) |
| C7—N1—Ru1 | 115.54 (19) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.4 |
| C13—N3—C17 | 116.5 (3) | C7—C6—H6 | 120.4 |
| O2—C2—Ru1 | 179.6 (3) | C16—C15—C14 | 119.1 (3) |
| N3—C13—C14 | 124.5 (3) | C16—C15—H15 | 120.5 |
| N3—C13—C12 | 114.9 (3) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.5 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 120.4 (3) | N1—C3—C4 | 122.3 (3) |
| N2—C12—C11 | 122.1 (3) | N1—C3—H3 | 118.9 |
| N2—C12—C13 | 120.7 (3) | C4—C3—H3 | 118.9 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 117.1 (3) | C4—C5—C6 | 119.8 (3) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 120.4 (3) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.1 |
| C11—C10—Cl3 | 119.0 (2) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.1 |
| C9—C10—Cl3 | 120.6 (2) | C5—C4—C3 | 118.4 (3) |
| C17—C16—C15 | 119.1 (3) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.8 |
| C17—C16—H16 | 120.5 | C3—C4—H4 | 120.8 |
| C15—C16—H16 | 120.5 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C9—H9···Cl2i | 0.95 | 2.77 | 3.687 (3) | 163 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1.
References
- Agilent (2013). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Alvila, L., Pursiainen, J., Kiviaho, J., Pakkanen, T. A. & Krause, O. (1994). J. Mol. Catal. 91, 335–342.
- Amoroso, A. J., Banu, A., Coogan, M. P., Edwards, P. G., Hossain, G. & Malik, K. M. A. (2010). Dalton Trans. 39, 6993–7003. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chardon-Noblat, S., Da Costa, P., Deronzier, A., Maniguet, S. & Ziessel, R. (2002). J. Electroanal. Chem. 529, 135–144.
- Chardon-Noblat, S., Deronzier, A. & Ziessel, R. (2001). Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 66, 207–227.
- Collomb-Dunand-Sauthier, M.-N., Deronzier, A. & Ziessel, R. (1994). J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. pp. 189–191.
- Deacon, G. B., Patrick, J. M., Skelton, B. W., Thomas, N. C. & White, A. H. (1984). Aust. J. Chem. 37, 929–945.
- Gibson, D. H., Sleadd, B. A., Mashuta, M. S. & Richardson, J. F. (1997). Organometallics, 16, 4421–4427.
- Homanen, P., Haukka, M., Pakkanen, T. A., Pursiainen, J. & Laitinen, R. H. (1996). Organometallics, 15, 4081–4084.
- Kooijman, H., Spek, A. L., Mulder, A. & Reinhoudt, D. N. (2007). Private communication (CCDC numbers 666468 and 666615). CCDC, Cambridge, England.
- Kuramochi, Y., Fukaya, K., Yoshida, M. & Ishida, M. (2015). Chem. Eur. J. 21, 10049–10060. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Luukkanen, S., Homanen, P., Haukka, M., Pakkanen, T. A., Deronzier, A., Chardon-Noblat, S., Zsoldos, D. & Ziessel, R. (1999). Appl. Catal. Gen. 185, 157–164.
- Palatinus, L. & Chapuis, G. (2007). J. Appl. Cryst. 40, 786–790.
- Pettersen, E. F., Goddard, T. D., Huang, C. C., Couch, G. S., Greenblatt, D. M., Meng, E. C. & Ferrin, T. E. (2004). J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1605–1612. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Ziessel, R., Grosshenny, V., Hissler, M. & Stroh, C. (2004). Inorg. Chem. 43, 4262–4271. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017003917/wm5367sup1.cif
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report






