In the two title Schiff base derivatives, the (E)-N′-[(1H-indol-3-yl)methylidene]isonicotinohydrazide molecules and (E)-N-methyl-2-[1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)ethylidene]hydrazinecarbothioamide molecules form a tape structure and a helical chain structure, respectively, through hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: crystal structure, Schiff base derivatives, isonicotinohydrazide, hydrazinecarbothioamide
Abstract
The crystal structures of two title Schiff base derivatives, C15H12N4O·C2H6O (1·EtOH) and C13H13N3O2S (2), were determined at 110 and 100 K, respectively. In the crystal of compound 1·EtOH, the (E)-N′-[(1H-indol-3-yl)methylidene]isonicotinohydrazide and ethanol molecules are linked by O—H⋯O, N—H⋯O and N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming a tape structure running along the b-axis direction. The tapes are weakly linked via a C—H⋯N interaction. In the crystal of compound 2, (E)-N-methyl-2-[1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)ethylidene]hydrazinecarbothioamide molecules are linked via N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a helical chain along the b-axis direction. The chains are further linked into a layer expanding parallel to (102) through C—H⋯S interactions.
Chemical context
Schiff base derivatives are a biologically versatile class of compounds possessing diverse activities, such as anti-oxidant (Haribabu, Subhashree et al., 2015 ▸, 2016 ▸), anti-inflammatory (Alam et al., 2012 ▸), anti-cancer (Creaven et al., 2010 ▸; Haribabu, Jeyalakshmi et al., 2015 ▸, 2016 ▸), anti-bacterial (Sondhi et al., 2006 ▸), anti-fungal (Jarrahpour et al., 2007 ▸), anti-convulsant (Bhat & Al-Omar, 2011 ▸). Schiff bases have gained special attention in pharmacophore research and in the development of several bioactive lead molecules. They are widely used as catalysts, corrosion inhibitors and intermediates in organic synthesis, and also play a potential role in the development of coordination chemistry (Muralisankar et al., 2016 ▸). As part of our studies in this area, we have synthesized the title Schiff base compounds, 1·EtOH and 2, and determined their crystal structures.
Structural commentary
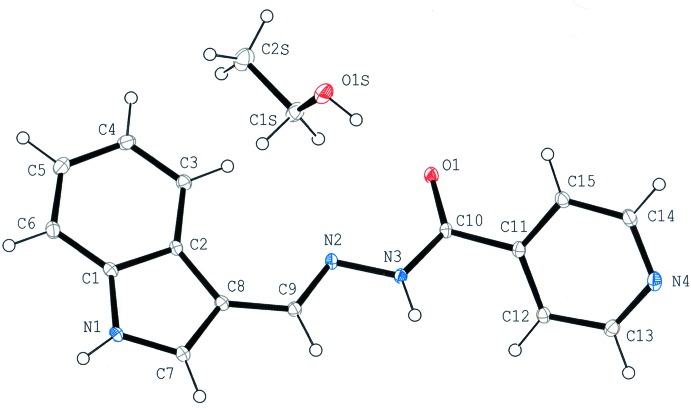
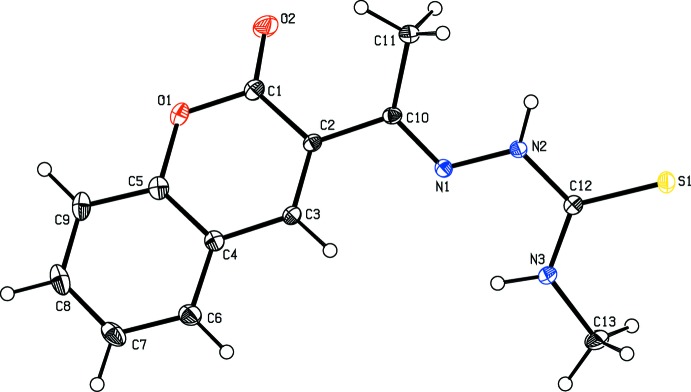
The molecular structures ((Figs. 1 ▸ and 2 ▸) of both 1 and 2 are non-planar, as evidenced by the torsion angles N3—C10—C11—C12 [42.5 (3)°] in 1 and C1—C2—C10—N1 [−152.0 (2)°] in 2. The mean plane of the central chain C9/N2/N3/C10/O1 in 1 makes dihedral angles of 6.91 (12) and 42.71 (13)°, respectively, with the C1–C8/N1 ring system and the pyridine C11–C15/N4 ring. In molecule 2, the dihedral angle between the C1–C9/O1 ring system and the mean plane of the C10/N1/N2/C12/N3/C13 chain is 30.36 (9)°.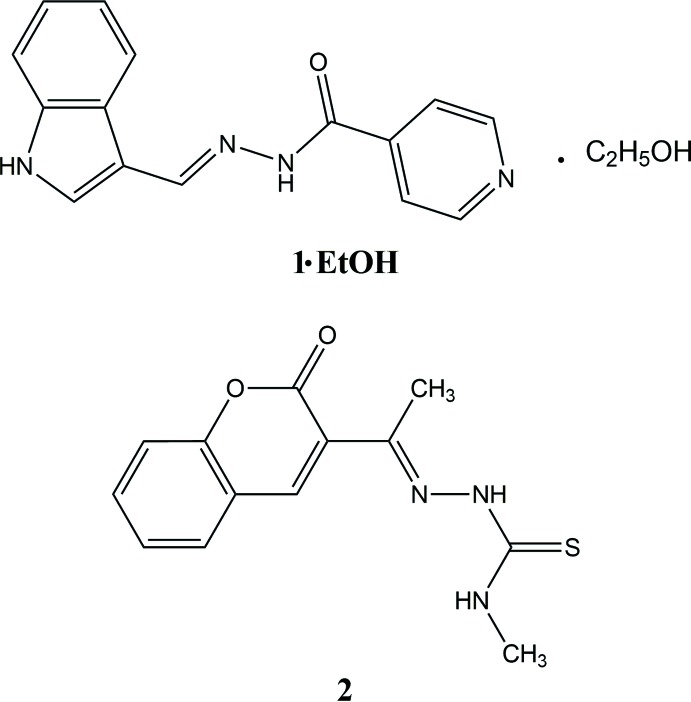
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of compound 1·EtOH, with the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids of non-H atoms are drawn at 30% probability level.
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of compound 2, with the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids of non-H atoms are drawn at 30% probability level.
Supramolecular features
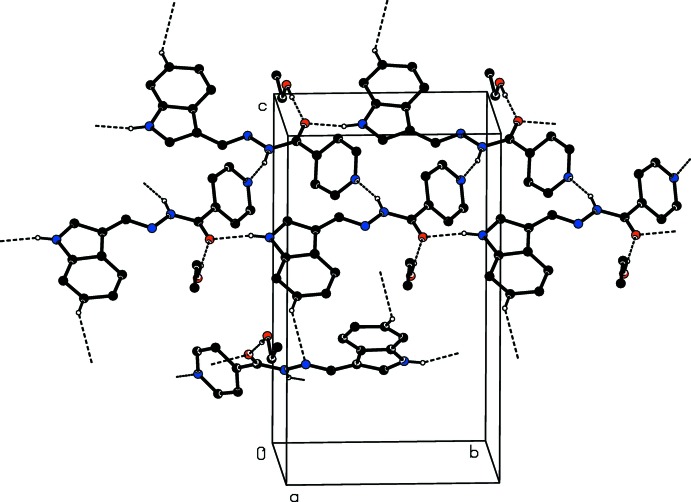
The crystal packing of 1·EtOH features O—H⋯O, N—H⋯O and N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸), which link the molecules into a tape structure running along the b-axis direction (Fig. 3 ▸). The tapes are weakly linked via a C—H⋯N interaction (Table 1 ▸). In the N—H⋯O and N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, atoms N1 and N3 act as donors to atoms O1 and N4, respectively, generating C(9) and C(7) chain motifs. The C—H⋯N interaction generates a C(8) chain. Atom O1S of the ethanol molecule acts as a donor in forming the O—H⋯O hydrogen bond with atom O1, which acts as a double acceptor.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for 1·EtOH .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1i | 0.88 | 2.05 | 2.871 (3) | 156 |
| N3—H3⋯N4ii | 0.88 | 2.14 | 2.979 (3) | 159 |
| C5—H5⋯N2iii | 0.95 | 2.62 | 3.236 (3) | 123 |
| O1S—H1S⋯O1 | 0.84 | 1.90 | 2.742 (3) | 177 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii) 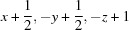 .
.
Figure 3.
A packing diagram of compound 1·EtOH, viewed along the a axis, showing the O—H⋯O, N—H⋯O, N—H⋯N and C—H⋯N interactions (dashed lines). For clarity, H atoms not involved in these interactions have been omitted.
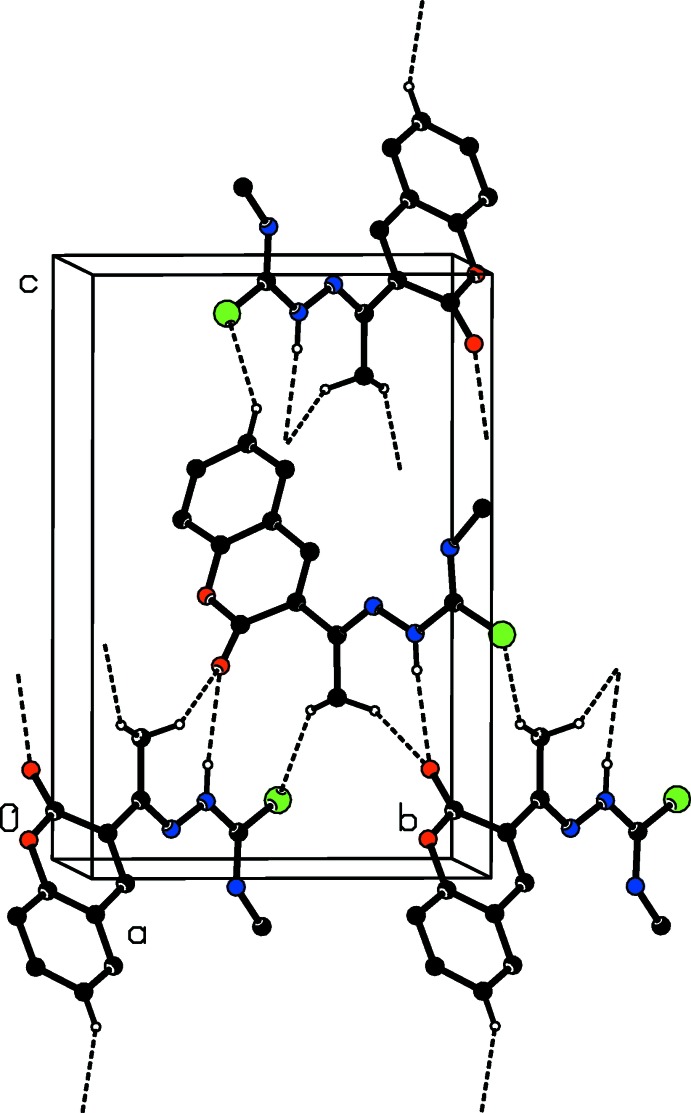
In 2, the crystal packing features N—H⋯O, C—H⋯O and C—H⋯S interactions (Table 2 ▸). The molecules are linked via N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a helical chain along the b-axis direction (Fig. 4 ▸). The chains are further linked via C—H⋯S interactions, forming a layer expanding parallel to (102). Atoms N2 and C11 act as donors to the double acceptor O2, generating C(7) and C(6) chains, respectively. As a result of these two hydrogen bonds, an 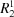 (7) ring motif is generated. In the C—H⋯S interactions, atoms C7 and C11 act as donors to the double acceptor S1, generating C(11) and C(7) chains, respectively.
(7) ring motif is generated. In the C—H⋯S interactions, atoms C7 and C11 act as donors to the double acceptor S1, generating C(11) and C(7) chains, respectively.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for 2 .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2⋯O2i | 0.88 | 2.39 | 3.269 (3) | 175 |
| C11—H11A⋯O2i | 0.98 | 2.47 | 3.109 (3) | 123 |
| C7—H7⋯S1ii | 0.95 | 2.85 | 3.711 (3) | 151 |
| C11—H11B⋯S1iii | 0.98 | 2.87 | 3.728 (3) | 146 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii) 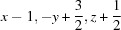 ; (iii)
; (iii) 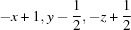 .
.
Figure 4.
A crystal packing view of 2 along the a axis, showing the intermolecular hydrogen-bonded network formed by N—H⋯O, C—H⋯O and C—H⋯S interactions (dashed lines). For clarity, H atoms not involved in these interactions have been omitted.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for the substructures 1 and 2 revealed several related Schiff base derivatives, including those with refcodes ADEKAW, ACIPIN, ADEZAL02 and APAQEP reported by Qiu et al. (2006 ▸), Lobana et al. (2012 ▸), Ilies et al. (2013 ▸) and Chainok et al. (2016 ▸), respectively.
Synthesis and crystallization
Compound 1 was synthesized by condensing equimolar amounts of 1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde (145 mg, 1 mmol) with nicotinic acid hydrazide (137 mg, 1 mmol) in ethanol. The reaction mixture was then refluxed on a water bath for 5 h and poured into crushed ice. The corresponding solid Schiff base that formed was filtered, washed several times with distilled water and dried under vacuum. The compound was recrystallized from an ethanol–chloroform (1:3) solvent mixture, yielding the ethanol solvate compound, 1·EtOH. Similarly, compound 2 was synthesized from equimolar amounts of 3-acetyl-2H-chromen-2-one (188 mg, 1 mmol) with N-methylhydrazinecarbothioamide (105 mg, 1 mmol) in ethanol. Compound 2 was also recrystallized from an ethanol–chloroform (1:3) solvent mixture.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. H atoms were refined as riding with N—H = 0.88, C—H = 0.95 or 0.98 Å and U iso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5U eq(parent atom). For 1·EtOH, the methylene H atoms of the ethanol solvent molecule were refined independently under strong bond-length and angle restraints using DFIX to avoid a large residual electron-density peak near the methylene C atom caused by the usual riding treatment of the H atoms. In 2, TWINABS was employed to correct the data for absorption effects, as well as to separate hkl files for the domains with major and minor components; the twin ratio was observed to be 91:9. In the refinement, only the data of the major domain were used.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| 1·EtOH | 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C15H12N4O·C2H6O | C13H13N3O2S |
| M r | 310.35 | 275.32 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P212121 | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 110 | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 9.4692 (18), 9.9821 (19), 16.682 (3) | 9.289 (4), 9.616 (4), 14.474 (6) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 90.825 (4), 90 |
| V (Å3) | 1576.9 (5) | 1292.8 (9) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.09 | 0.25 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.50 × 0.37 × 0.13 | 0.49 × 0.46 × 0.31 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD | Bruker APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▸) | Multi-scan (TWINABS; Bruker, 2012 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.618, 0.681 | 0.534, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 39878, 3616, 3527 | 5480, 2902, 2285 |
| R int | 0.054 | 0.044 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.651 | 0.651 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.043, 0.119, 0.98 | 0.048, 0.116, 1.10 |
| No. of reflections | 3616 | 2902 |
| No. of parameters | 216 | 174 |
| No. of restraints | 3 | 0 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 1.50, −0.36 | 0.30, −0.35 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 1491 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) | – |
| Absolute structure parameter | −0.2 (3) | – |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) Global, 2, 1.EtOH. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901700411X/is5471sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 1.EtOH. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901700411X/is54711.EtOHsup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 2. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901700411X/is54712sup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901700411X/is54711.EtOHsup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901700411X/is54712sup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
GD thanks the UGC–SAP and DST–FIST for funding to Centre of Advanced Study in Crystallography and Biophysics, University of Madras.
supplementary crystallographic information
(1.EtOH) (E)-N'-[(1H-Indol-3-yl)methylidene]isonicotinohydrazide ethanol monosolvate . Crystal data
| C15H12N4O·C2H6O | Dx = 1.307 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 310.35 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Cell parameters from 9846 reflections |
| a = 9.4692 (18) Å | θ = 2.4–27.5° |
| b = 9.9821 (19) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 16.682 (3) Å | T = 110 K |
| V = 1576.9 (5) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.50 × 0.37 × 0.13 mm |
| F(000) = 656 |
(1.EtOH) (E)-N'-[(1H-Indol-3-yl)methylidene]isonicotinohydrazide ethanol monosolvate . Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3527 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | Rint = 0.054 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | θmax = 27.6°, θmin = 2.4° |
| Tmin = 0.618, Tmax = 0.681 | h = −12→12 |
| 39878 measured reflections | k = −12→12 |
| 3616 independent reflections | l = −21→21 |
(1.EtOH) (E)-N'-[(1H-Indol-3-yl)methylidene]isonicotinohydrazide ethanol monosolvate . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.077P)2 + 0.9574P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.119 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.004 |
| S = 0.98 | Δρmax = 1.50 e Å−3 |
| 3616 reflections | Δρmin = −0.36 e Å−3 |
| 216 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 1491 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 3 restraints | Absolute structure parameter: −0.2 (3) |
(1.EtOH) (E)-N'-[(1H-Indol-3-yl)methylidene]isonicotinohydrazide ethanol monosolvate . Special details
| Experimental. SADABS-2014/3 (Bruker, 2014) was used for absorption correction. wR2(int) was 0.1205 before and 0.0824 after correction. The Ratio of minimum to maximum transmission is 0.9082. The λ/2 correction factor is not present. |
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. 1. Fixed Uiso; at 1.2 times of: all C(H) groups, all N(H) groups and at 1.5 times of: C2S(H2SA, H2SB, H2SC) and O(H) groups 2. a. Aromatic/amide H refined with riding coordinates: N1(H1), N3(H3), C3(H3A), C4(H4), C5(H5), C6(H6), C7(H7), C9(H9), C12(H12), C13(H13), C14(H14), C15(H15) b. Idealised Me refined as rotating group: C11(H11A, H11B, H11C) 3. Strong restraints with DFIX were employed for methylene hydrogen atoms of the ethanol solvent molecule. |
(1.EtOH) (E)-N'-[(1H-Indol-3-yl)methylidene]isonicotinohydrazide ethanol monosolvate . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.41425 (19) | 0.67417 (16) | 0.63518 (11) | 0.0184 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.4971 (2) | −0.05011 (19) | 0.64904 (12) | 0.0157 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.492857 | −0.137698 | 0.654508 | 0.019* | |
| N2 | 0.3980 (2) | 0.40446 (18) | 0.66721 (11) | 0.0140 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.2999 (2) | 0.49844 (19) | 0.69437 (12) | 0.0137 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.228694 | 0.472947 | 0.724635 | 0.016* | |
| N4 | −0.0322 (2) | 0.8812 (2) | 0.74337 (13) | 0.0195 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.5943 (2) | 0.0185 (2) | 0.60295 (13) | 0.0143 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.5644 (2) | 0.1570 (2) | 0.60882 (13) | 0.0135 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.6449 (3) | 0.2483 (2) | 0.56436 (14) | 0.0166 (5) | |
| H3A | 0.625228 | 0.341561 | 0.566138 | 0.020* | |
| C4 | 0.7543 (3) | 0.1987 (3) | 0.51768 (15) | 0.0201 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.809673 | 0.259218 | 0.486964 | 0.024* | |
| C5 | 0.7852 (3) | 0.0605 (3) | 0.51472 (15) | 0.0204 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.862792 | 0.030250 | 0.483480 | 0.024* | |
| C6 | 0.7048 (3) | −0.0316 (2) | 0.55637 (14) | 0.0185 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.723861 | −0.124959 | 0.553456 | 0.022* | |
| C7 | 0.4091 (2) | 0.0393 (2) | 0.68452 (14) | 0.0156 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.333452 | 0.016491 | 0.719368 | 0.019* | |
| C8 | 0.4453 (2) | 0.1688 (2) | 0.66264 (13) | 0.0140 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.3669 (2) | 0.2839 (2) | 0.68918 (13) | 0.0142 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.289165 | 0.270747 | 0.724287 | 0.017* | |
| C10 | 0.3146 (2) | 0.6275 (2) | 0.67420 (13) | 0.0133 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.1947 (2) | 0.7155 (2) | 0.70049 (14) | 0.0139 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.1325 (2) | 0.7050 (2) | 0.77589 (14) | 0.0156 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.165590 | 0.641316 | 0.813786 | 0.019* | |
| C13 | 0.0204 (2) | 0.7902 (2) | 0.79444 (14) | 0.0185 (5) | |
| H13 | −0.021080 | 0.783377 | 0.846143 | 0.022* | |
| C14 | 0.0301 (3) | 0.8902 (2) | 0.67103 (15) | 0.0196 (5) | |
| H14 | −0.005725 | 0.954149 | 0.634104 | 0.023* | |
| C15 | 0.1435 (2) | 0.8117 (2) | 0.64711 (15) | 0.0168 (5) | |
| H15 | 0.185233 | 0.823122 | 0.595771 | 0.020* | |
| O1S | 0.6541 (2) | 0.6025 (2) | 0.55370 (12) | 0.0279 (4) | |
| H1S | 0.582293 | 0.623623 | 0.580387 | 0.042* | |
| C1S | 0.7704 (3) | 0.5902 (2) | 0.60520 (14) | 0.0246 (5) | |
| H1SA | 0.757 (3) | 0.4957 (4) | 0.6166 (9) | 0.037* | |
| H1SB | 0.776 (4) | 0.6301 (9) | 0.6581 (2) | 0.037* | |
| C2S | 0.9016 (3) | 0.5715 (3) | 0.5560 (2) | 0.0314 (6) | |
| H2SA | 0.889630 | 0.494186 | 0.520487 | 0.047* | |
| H2SB | 0.982242 | 0.556124 | 0.591660 | 0.047* | |
| H2SC | 0.918511 | 0.652049 | 0.523841 | 0.047* |
(1.EtOH) (E)-N'-[(1H-Indol-3-yl)methylidene]isonicotinohydrazide ethanol monosolvate . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0179 (8) | 0.0109 (7) | 0.0262 (8) | −0.0002 (6) | 0.0061 (7) | −0.0001 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0189 (9) | 0.0099 (8) | 0.0183 (9) | −0.0004 (7) | 0.0013 (7) | 0.0009 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0137 (8) | 0.0113 (8) | 0.0169 (9) | 0.0022 (7) | 0.0002 (7) | −0.0012 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0120 (8) | 0.0116 (8) | 0.0177 (9) | 0.0004 (7) | 0.0025 (7) | −0.0003 (7) |
| N4 | 0.0150 (9) | 0.0153 (9) | 0.0282 (10) | 0.0019 (8) | 0.0009 (8) | −0.0020 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0156 (10) | 0.0125 (10) | 0.0147 (9) | −0.0009 (8) | −0.0034 (8) | 0.0008 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0138 (10) | 0.0122 (10) | 0.0143 (9) | 0.0011 (7) | −0.0018 (8) | −0.0001 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0182 (11) | 0.0137 (10) | 0.0178 (10) | −0.0015 (8) | 0.0003 (9) | −0.0003 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0207 (11) | 0.0219 (12) | 0.0177 (10) | −0.0021 (10) | 0.0046 (9) | 0.0005 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0181 (11) | 0.0250 (13) | 0.0180 (10) | 0.0025 (9) | 0.0018 (9) | −0.0022 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0213 (11) | 0.0158 (10) | 0.0184 (11) | 0.0043 (9) | −0.0012 (9) | −0.0016 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0168 (10) | 0.0130 (10) | 0.0171 (10) | 0.0004 (8) | −0.0004 (8) | 0.0005 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0139 (10) | 0.0129 (10) | 0.0153 (9) | −0.0004 (8) | −0.0011 (8) | 0.0005 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0133 (9) | 0.0135 (10) | 0.0157 (10) | 0.0000 (8) | 0.0002 (8) | 0.0003 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0138 (10) | 0.0118 (9) | 0.0143 (10) | 0.0014 (8) | −0.0011 (8) | −0.0020 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0126 (9) | 0.0110 (9) | 0.0181 (10) | −0.0012 (8) | −0.0006 (8) | −0.0029 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0151 (10) | 0.0134 (10) | 0.0183 (10) | 0.0001 (8) | −0.0004 (8) | −0.0007 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0165 (10) | 0.0186 (10) | 0.0204 (11) | −0.0007 (9) | 0.0032 (9) | −0.0021 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0180 (10) | 0.0144 (10) | 0.0263 (11) | 0.0018 (9) | −0.0003 (9) | 0.0028 (9) |
| C15 | 0.0162 (10) | 0.0132 (10) | 0.0212 (11) | −0.0007 (8) | 0.0006 (9) | 0.0011 (8) |
| O1S | 0.0224 (9) | 0.0324 (10) | 0.0288 (10) | 0.0047 (8) | 0.0065 (7) | −0.0004 (8) |
| C1S | 0.0269 (13) | 0.0223 (12) | 0.0246 (12) | −0.0020 (10) | 0.0061 (10) | −0.0072 (10) |
| C2S | 0.0208 (12) | 0.0312 (14) | 0.0423 (16) | −0.0029 (11) | 0.0077 (12) | −0.0042 (12) |
(1.EtOH) (E)-N'-[(1H-Indol-3-yl)methylidene]isonicotinohydrazide ethanol monosolvate . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C10 | 1.238 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.386 (3) |
| N1—C7 | 1.357 (3) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C1 | 1.381 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.437 (3) |
| N1—H1 | 0.8800 | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C9 | 1.292 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.501 (3) |
| N2—N3 | 1.396 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.393 (3) |
| N3—C10 | 1.339 (3) | C11—C15 | 1.396 (3) |
| N3—H3 | 0.8800 | C12—C13 | 1.395 (3) |
| N4—C13 | 1.341 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| N4—C14 | 1.346 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C6 | 1.397 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.388 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.414 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.401 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C8 | 1.446 (3) | O1S—C1S | 1.402 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.387 (3) | O1S—H1S | 0.8400 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9500 | C1S—C2S | 1.500 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.411 (4) | C1S—H1SA | 0.9700 (2) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C1S—H1SB | 0.9700 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.381 (3) | C2S—H2SA | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C2S—H2SB | 0.9800 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C2S—H2SC | 0.9800 |
| C7—N1—C1 | 109.00 (18) | N2—C9—H9 | 118.7 |
| C7—N1—H1 | 125.5 | C8—C9—H9 | 118.7 |
| C1—N1—H1 | 125.5 | O1—C10—N3 | 125.0 (2) |
| C9—N2—N3 | 112.49 (18) | O1—C10—C11 | 120.7 (2) |
| C10—N3—N2 | 119.74 (19) | N3—C10—C11 | 114.30 (19) |
| C10—N3—H3 | 120.1 | C12—C11—C15 | 118.7 (2) |
| N2—N3—H3 | 120.1 | C12—C11—C10 | 122.7 (2) |
| C13—N4—C14 | 116.9 (2) | C15—C11—C10 | 118.6 (2) |
| N1—C1—C6 | 129.1 (2) | C11—C12—C13 | 118.5 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 108.2 (2) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.8 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 122.6 (2) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.8 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.3 (2) | N4—C13—C12 | 123.6 (2) |
| C3—C2—C8 | 134.4 (2) | N4—C13—H13 | 118.2 |
| C1—C2—C8 | 106.20 (19) | C12—C13—H13 | 118.2 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 118.1 (2) | N4—C14—C15 | 124.0 (2) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 120.9 | N4—C14—H14 | 118.0 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 120.9 | C15—C14—H14 | 118.0 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.6 (2) | C14—C15—C11 | 118.3 (2) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.2 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.2 | C11—C15—H15 | 120.9 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.3 (2) | C1S—O1S—H1S | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.4 | O1S—C1S—C2S | 109.0 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.4 | O1S—C1S—H1SA | 96.0 (14) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 117.0 (2) | C2S—C1S—H1SA | 95.2 (13) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 121.5 | O1S—C1S—H1SB | 124.6 (19) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 121.5 | C2S—C1S—H1SB | 120 (2) |
| N1—C7—C8 | 110.3 (2) | H1SA—C1S—H1SB | 103.2 (9) |
| N1—C7—H7 | 124.9 | C1S—C2S—H2SA | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 124.9 | C1S—C2S—H2SB | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 122.4 (2) | H2SA—C2S—H2SB | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C2 | 106.3 (2) | C1S—C2S—H2SC | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C2 | 131.2 (2) | H2SA—C2S—H2SC | 109.5 |
| N2—C9—C8 | 122.6 (2) | H2SB—C2S—H2SC | 109.5 |
| C9—N2—N3—C10 | −177.7 (2) | C3—C2—C8—C9 | 0.1 (4) |
| C7—N1—C1—C6 | 179.6 (2) | C1—C2—C8—C9 | −178.0 (2) |
| C7—N1—C1—C2 | −1.0 (3) | N3—N2—C9—C8 | 174.45 (19) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −177.2 (2) | C7—C8—C9—N2 | −178.1 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 2.2 (3) | C2—C8—C9—N2 | −1.6 (4) |
| N1—C1—C2—C8 | 1.3 (2) | N2—N3—C10—O1 | −3.5 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C8 | −179.3 (2) | N2—N3—C10—C11 | 174.32 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.8 (3) | O1—C10—C11—C12 | −139.5 (2) |
| C8—C2—C3—C4 | −179.8 (2) | N3—C10—C11—C12 | 42.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.3 (4) | O1—C10—C11—C15 | 40.6 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 2.0 (4) | N3—C10—C11—C15 | −137.4 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.6 (4) | C15—C11—C12—C13 | 0.7 (3) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | 178.8 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −179.2 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.5 (3) | C14—N4—C13—C12 | −1.1 (3) |
| C1—N1—C7—C8 | 0.2 (3) | C11—C12—C13—N4 | 0.7 (4) |
| N1—C7—C8—C9 | 177.8 (2) | C13—N4—C14—C15 | 0.0 (4) |
| N1—C7—C8—C2 | 0.6 (3) | N4—C14—C15—C11 | 1.4 (4) |
| C3—C2—C8—C7 | 177.1 (2) | C12—C11—C15—C14 | −1.7 (3) |
| C1—C2—C8—C7 | −1.1 (2) | C10—C11—C15—C14 | 178.2 (2) |
(1.EtOH) (E)-N'-[(1H-Indol-3-yl)methylidene]isonicotinohydrazide ethanol monosolvate . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.88 | 2.05 | 2.871 (3) | 156 |
| N3—H3···N4ii | 0.88 | 2.14 | 2.979 (3) | 159 |
| C5—H5···N2iii | 0.95 | 2.62 | 3.236 (3) | 123 |
| O1S—H1S···O1 | 0.84 | 1.90 | 2.742 (3) | 177 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y−1, z; (ii) −x, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (iii) x+1/2, −y+1/2, −z+1.
(2) (E)-N'-Methyl-2-[1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)ethylidene]hydrazinecarbothioamide . Crystal data
| C13H13N3O2S | F(000) = 576 |
| Mr = 275.32 | Dx = 1.415 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.289 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 4293 reflections |
| b = 9.616 (4) Å | θ = 2.2–27.3° |
| c = 14.474 (6) Å | µ = 0.25 mm−1 |
| β = 90.825 (4)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1292.8 (9) Å3 | Block, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.49 × 0.46 × 0.31 mm |
(2) (E)-N'-Methyl-2-[1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)ethylidene]hydrazinecarbothioamide . Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2285 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | Rint = 0.044 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (TWINABS; Bruker, 2012) | θmax = 27.6°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Tmin = 0.534, Tmax = 0.746 | h = −12→12 |
| 5480 measured reflections | k = −12→12 |
| 2902 independent reflections | l = 0→18 |
(2) (E)-N'-Methyl-2-[1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)ethylidene]hydrazinecarbothioamide . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.116 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0375P)2 + 0.711P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.10 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 2902 reflections | Δρmax = 0.30 e Å−3 |
| 174 parameters | Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3 |
(2) (E)-N'-Methyl-2-[1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)ethylidene]hydrazinecarbothioamide . Special details
| Experimental. For component 1: wR2(int) was 0.1337 before and 0.0605 after correction. The ratio of minimum to maximum transmission is 0.72. The λ/2 correction factor is not presentFinal HKLF 4 output contains 20988 reflections, Rint = 0.0871 (9738 with I > 3sig(I), Rint = 0.0747) |
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. The absorption correction program TWINABS2 was employed to correct the data for absorption effects, as well as to separate hkl files for the domains with major component, which was used for further analysis.1. Fixed Uiso; at 1.2 times of: All C(H) groups, all N(H) groups at 1.5 times of: all C(H, H, H) groups 2. a. Aromatic/amide H refined with riding coordinates: N2(H2), N3(H3), C3(H3A), C6(H6), C7(H7), C8(H8), C9(H9) b. Idealised Me refined as rotating group: C11(H11A, H11B, H11C), C13(H13A, H13B, H13C) |
(2) (E)-N'-Methyl-2-[1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)ethylidene]hydrazinecarbothioamide . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.80937 (6) | 1.04558 (5) | 0.39682 (4) | 0.02114 (16) | |
| O1 | 0.21617 (15) | 0.36330 (14) | 0.44249 (10) | 0.0215 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.37162 (18) | 0.38370 (16) | 0.33164 (11) | 0.0314 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.52878 (17) | 0.75100 (17) | 0.43518 (11) | 0.0160 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.61381 (18) | 0.84670 (17) | 0.39257 (11) | 0.0173 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.6171 | 0.8510 | 0.3319 | 0.021* | |
| N3 | 0.67181 (19) | 0.92800 (18) | 0.53607 (11) | 0.0197 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.6007 | 0.8755 | 0.5554 | 0.024* | |
| C1 | 0.3192 (2) | 0.4382 (2) | 0.39822 (14) | 0.0200 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.3575 (2) | 0.5745 (2) | 0.43650 (13) | 0.0158 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.3017 (2) | 0.6138 (2) | 0.51797 (13) | 0.0164 (4) | |
| H3A | 0.3296 | 0.7005 | 0.5441 | 0.020* | |
| C4 | 0.2019 (2) | 0.5287 (2) | 0.56577 (13) | 0.0182 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.1581 (2) | 0.4043 (2) | 0.52496 (14) | 0.0193 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.1375 (2) | 0.5677 (2) | 0.64904 (14) | 0.0256 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.1641 | 0.6528 | 0.6780 | 0.031* | |
| C7 | 0.0363 (2) | 0.4834 (3) | 0.68876 (15) | 0.0311 (6) | |
| H7 | −0.0071 | 0.5099 | 0.7452 | 0.037* | |
| C8 | −0.0026 (2) | 0.3591 (3) | 0.64601 (16) | 0.0310 (6) | |
| H8 | −0.0720 | 0.3010 | 0.6743 | 0.037* | |
| C9 | 0.0567 (2) | 0.3179 (2) | 0.56388 (15) | 0.0256 (5) | |
| H9 | 0.0289 | 0.2332 | 0.5349 | 0.031* | |
| C10 | 0.4546 (2) | 0.6670 (2) | 0.38477 (13) | 0.0164 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.4552 (3) | 0.6675 (3) | 0.28152 (14) | 0.0309 (6) | |
| H11A | 0.4431 | 0.7630 | 0.2590 | 0.046* | |
| H11B | 0.3760 | 0.6097 | 0.2579 | 0.046* | |
| H11C | 0.5470 | 0.6302 | 0.2599 | 0.046* | |
| C12 | 0.6937 (2) | 0.9357 (2) | 0.44612 (13) | 0.0159 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.7581 (2) | 1.0010 (2) | 0.60437 (14) | 0.0273 (5) | |
| H13A | 0.8603 | 0.9825 | 0.5938 | 0.041* | |
| H13B | 0.7326 | 0.9689 | 0.6663 | 0.041* | |
| H13C | 0.7399 | 1.1011 | 0.5994 | 0.041* |
(2) (E)-N'-Methyl-2-[1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)ethylidene]hydrazinecarbothioamide . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0185 (3) | 0.0218 (3) | 0.0231 (3) | −0.0043 (2) | 0.0011 (2) | 0.0012 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0192 (8) | 0.0158 (7) | 0.0295 (8) | −0.0012 (6) | −0.0026 (6) | −0.0015 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0320 (9) | 0.0280 (9) | 0.0343 (9) | −0.0001 (7) | 0.0055 (7) | −0.0140 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0141 (8) | 0.0183 (9) | 0.0155 (8) | 0.0000 (7) | −0.0004 (6) | 0.0013 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0162 (8) | 0.0225 (9) | 0.0130 (8) | −0.0038 (7) | −0.0018 (6) | 0.0010 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0206 (9) | 0.0219 (9) | 0.0164 (9) | −0.0043 (7) | −0.0021 (7) | −0.0015 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0168 (10) | 0.0206 (11) | 0.0226 (11) | 0.0015 (9) | −0.0033 (8) | −0.0010 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0133 (9) | 0.0178 (10) | 0.0161 (10) | 0.0009 (8) | −0.0036 (7) | −0.0009 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0138 (10) | 0.0181 (10) | 0.0173 (10) | 0.0009 (8) | −0.0036 (7) | 0.0001 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0138 (10) | 0.0235 (11) | 0.0171 (10) | 0.0018 (8) | −0.0053 (7) | 0.0054 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0140 (10) | 0.0200 (10) | 0.0237 (11) | 0.0045 (8) | −0.0051 (8) | 0.0066 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0212 (11) | 0.0361 (13) | 0.0195 (11) | −0.0010 (10) | −0.0027 (8) | 0.0017 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0218 (12) | 0.0522 (16) | 0.0193 (11) | −0.0009 (11) | −0.0017 (9) | 0.0119 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0171 (11) | 0.0420 (14) | 0.0339 (13) | −0.0039 (10) | −0.0045 (9) | 0.0221 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0172 (11) | 0.0237 (11) | 0.0356 (13) | −0.0026 (9) | −0.0070 (9) | 0.0114 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0149 (10) | 0.0193 (10) | 0.0151 (10) | 0.0015 (8) | −0.0009 (7) | −0.0019 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0347 (14) | 0.0419 (14) | 0.0162 (11) | −0.0165 (11) | 0.0014 (9) | −0.0042 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0131 (9) | 0.0162 (10) | 0.0184 (10) | 0.0035 (8) | −0.0027 (7) | 0.0008 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0269 (12) | 0.0347 (13) | 0.0202 (11) | −0.0033 (11) | −0.0069 (9) | −0.0041 (9) |
(2) (E)-N'-Methyl-2-[1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)ethylidene]hydrazinecarbothioamide . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C12 | 1.674 (2) | C4—C6 | 1.404 (3) |
| O1—C1 | 1.365 (2) | C5—C9 | 1.382 (3) |
| O1—C5 | 1.375 (3) | C6—C7 | 1.374 (3) |
| O2—C1 | 1.206 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C10 | 1.282 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.392 (4) |
| N1—N2 | 1.366 (2) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C12 | 1.367 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.375 (3) |
| N2—H2 | 0.8800 | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C12 | 1.323 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C13 | 1.446 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.494 (3) |
| N3—H3 | 0.8800 | C11—H11A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.464 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.349 (3) | C11—H11C | 0.9800 |
| C2—C10 | 1.479 (3) | C13—H13A | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.423 (3) | C13—H13B | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9500 | C13—H13C | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.392 (3) | ||
| C1—O1—C5 | 122.86 (16) | C6—C7—H7 | 120.1 |
| C10—N1—N2 | 118.48 (16) | C8—C7—H7 | 120.1 |
| N1—N2—C12 | 118.61 (16) | C9—C8—C7 | 121.8 (2) |
| N1—N2—H2 | 120.7 | C9—C8—H8 | 119.1 |
| C12—N2—H2 | 120.7 | C7—C8—H8 | 119.1 |
| C12—N3—C13 | 123.65 (18) | C8—C9—C5 | 117.6 (2) |
| C12—N3—H3 | 118.2 | C8—C9—H9 | 121.2 |
| C13—N3—H3 | 118.2 | C5—C9—H9 | 121.2 |
| O2—C1—O1 | 116.07 (18) | N1—C10—C2 | 114.68 (17) |
| O2—C1—C2 | 126.37 (19) | N1—C10—C11 | 123.86 (18) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 117.55 (17) | C2—C10—C11 | 121.29 (17) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.16 (18) | C10—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C10 | 121.28 (18) | C10—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C10 | 119.56 (17) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.67 (18) | C10—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 119.2 | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 119.2 | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C6 | 117.92 (19) | N3—C12—N2 | 115.66 (17) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.43 (18) | N3—C12—S1 | 124.32 (15) |
| C6—C4—C3 | 123.51 (19) | N2—C12—S1 | 120.02 (15) |
| O1—C5—C9 | 117.38 (19) | N3—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| O1—C5—C4 | 119.94 (18) | N3—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C9—C5—C4 | 122.7 (2) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C4 | 120.3 (2) | N3—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.9 | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C4—C6—H6 | 119.9 | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.7 (2) | ||
| C10—N1—N2—C12 | −179.56 (18) | C5—C4—C6—C7 | 1.0 (3) |
| C5—O1—C1—O2 | 172.55 (18) | C3—C4—C6—C7 | 176.49 (19) |
| C5—O1—C1—C2 | −6.3 (3) | C4—C6—C7—C8 | −0.1 (3) |
| O2—C1—C2—C3 | −171.9 (2) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.7 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 6.9 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C5 | 0.5 (3) |
| O2—C1—C2—C10 | 8.9 (3) | O1—C5—C9—C8 | −179.46 (18) |
| O1—C1—C2—C10 | −172.34 (17) | C4—C5—C9—C8 | 0.4 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −2.7 (3) | N2—N1—C10—C2 | −175.51 (16) |
| C10—C2—C3—C4 | 176.51 (17) | N2—N1—C10—C11 | −0.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −2.2 (3) | C3—C2—C10—N1 | 28.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C6 | −177.73 (19) | C1—C2—C10—N1 | −152.03 (18) |
| C1—O1—C5—C9 | −178.67 (18) | C3—C2—C10—C11 | −146.7 (2) |
| C1—O1—C5—C4 | 1.5 (3) | C1—C2—C10—C11 | 32.4 (3) |
| C6—C4—C5—O1 | 178.71 (18) | C13—N3—C12—N2 | 172.14 (19) |
| C3—C4—C5—O1 | 3.0 (3) | C13—N3—C12—S1 | −8.2 (3) |
| C6—C4—C5—C9 | −1.1 (3) | N1—N2—C12—N3 | −5.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C9 | −176.87 (18) | N1—N2—C12—S1 | 174.97 (13) |
(2) (E)-N'-Methyl-2-[1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)ethylidene]hydrazinecarbothioamide . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···O2i | 0.88 | 2.39 | 3.269 (3) | 175 |
| C11—H11A···O2i | 0.98 | 2.47 | 3.109 (3) | 123 |
| C7—H7···S1ii | 0.95 | 2.85 | 3.711 (3) | 151 |
| C11—H11B···S1iii | 0.98 | 2.87 | 3.728 (3) | 146 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) x−1, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (iii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
References
- Alam, M. S., Choi, J. & Lee, D. (2012). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 20, 4103–4108. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bhat, M. A. & Al-Omar, M. A. (2011). Acta Pol. Pharm. 68, 375–380. [PubMed]
- Bruker (2013). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2012). TWINABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chainok, K., Makmuang, S. & Kielar, F. (2016). Acta Cryst. E72, 980–983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Creaven, B. S., Duff, B., Egan, D. A., Kavanagh, K., Rosair, G., Thangella, V. R. & Walsh, M. (2010). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 363, 4048–4058.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Haribabu, J., Jeyalakshmi, K., Arun, Y., Bhuvanesh, N. S. P., Perumal, P. T. & Karvembu, R. (2015). RSC Adv. 5, 46031–46049.
- Haribabu, J., Jeyalakshmi, K., Arun, Y., Bhuvanesh, N. S. P., Perumal, P. T. & Karvembu, R. (2016). J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. doi: 10.1007/s00775-016-1424-1. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Haribabu, J., Subhashree, G. R., Saranya, S., Gomathi, K., Karvembu, R. & Gayathri, D. (2015). J. Mol. Struct. 1094, 281–291.
- Haribabu, J., Subhashree, G. R., Saranya, S., Gomathi, K., Karvembu, R. & Gayathri, D. (2016). J. Mol. Struct. 1110, 185–195.
- Ilies, D.-C., Pahontu, E., Shova, S., Gulea, A. & Rosu, T. (2013). Polyhedron, 51, 307–315.
- Jarrahpour, A., Khalili, D., De Clercq, E., Salmi, C. & Brunel, J. M. (2007). Molecules, 12, 1720–1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lobana, T. S., Sharma, R., Hundal, G., Castineiras, A. & Butcher, R. J. (2012). Polyhedron, 47, 134–142.
- Muralisankar, M., Haribabu, J., Bhuvanesh, N. S. P., Karvembu, R. & Sreekanth, A. (2016). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 449, 82–95.
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.-Y., Fang, X.-N., Liu, W.-S. & Zhu, H.-L. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o2685–o2686.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Sondhi, S. M., Singh, N., Kumar, A., Lozach, O. & Meijer, L. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 14, 3758–3765. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 9–18. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) Global, 2, 1.EtOH. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901700411X/is5471sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 1.EtOH. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901700411X/is54711.EtOHsup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 2. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901700411X/is54712sup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901700411X/is54711.EtOHsup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901700411X/is54712sup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report