Abstract
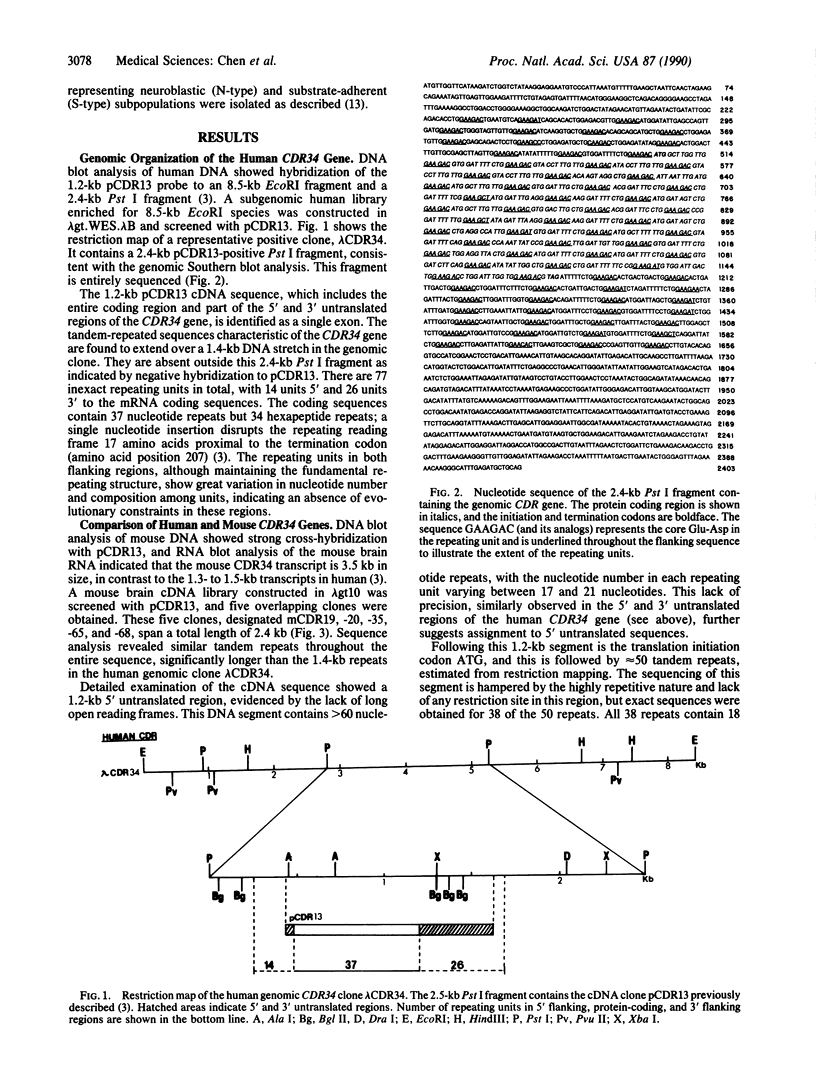
Cerebellar degeneration-related antigen (designated CDR34) was previously cloned by antibody screening of a cDNA library and was shown to be one of the target molecules recognized by autoantibodies in patients with paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration. This molecule is distinctive in that it contains a tandem hexapeptide repetitive structure, presumably the basis for its high immunogenicity. In this study, we cloned the human CDR34 gene and proved that the entire repetitive sequence is encoded by a single exon without introns. We also showed that the nucleotide repeats are preserved only in the protein-coding sequences, suggesting evolutionary constraint in this region of the gene. Corresponding mouse cDNA clones were also isolated, which encoded a larger molecule with very similar hexapeptide repeating units. Comparison of the human and mouse repeats revealed a highly conserved Glu-Asp core in each unit, implicating the functional significance of this motif. Chromosomal mapping by somatic cell hybrid analysis mapped CDR34 to both human and mouse chromosomes X, and in situ hybridization further assigned CDR34 to human Xq24-q27.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson N. E., Rosenblum M. K., Posner J. B. Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration: clinical-immunological correlations. Ann Neurol. 1988 Oct;24(4):559–567. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J. L., Cadena D. L., Ahearn J. M., Jr, Dahmus M. E. A unique structure at the carboxyl terminus of the largest subunit of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7934–7938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dracopoli N. C., Rettig W. J., Whitfield G. K., Darlington G. J., Spengler B. A., Biedler J. L., Old L. J., Kourides I. A. Assignment of the gene for the beta subunit of thyroid-stimulating hormone to the short arm of human chromosome 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1822–1826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dropcho E. J., Chen Y. T., Posner J. B., Old L. J. Cloning of a brain protein identified by autoantibodies from a patient with paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4552–4556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R. L., Green H. Structure and evolution of the human involucrin gene. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):583–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90884-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furneaux H. M., Dropcho E. J., Barbut D., Chen Y. T., Rosenblum M. K., Old L. J., Posner J. B. Characterization of a cDNA encoding a 34-kDa Purkinje neuron protein recognized by sera from patients with paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2873–2877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoggan M. D., Halden N. F., Buckler C. E., Kozak C. A. Genetic mapping of the mouse c-fms proto-oncogene to chromosome 18. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1055–1056. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1055-1056.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Jhanwar S. C., Chaganti R. S., Hayward W. S. Two human c-onc genes are located on the long arm of chromosome 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7842–7846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata Y., Chen Y. T., Stockert E., Old L. J. Structural analysis of TL genes of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5475–5479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig W. J., Dracopoli N. C., Chesa P. G., Spengler B. A., Beresford H. R., Davies P., Biedler J. L., Old L. J. Role of human chromosome 11 in determining surface antigenic phenotype of normal and malignant cells. Somatic cell genetic analysis of eight antigens, including putative human Thy-1. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1603–1619. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig W. J., Dracopoli N. C., Goetzger T. A., Spengler B. A., Biedler J. L., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Somatic cell genetic analysis of human cell surface antigens: chromosomal assignments and regulation of expression in rodent-human hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6437–6441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig W. J., Spengler B. A., Chesa P. G., Old L. J., Biedler J. L. Coordinate changes in neuronal phenotype and surface antigen expression in human neuroblastoma cell variants. Cancer Res. 1987 Mar 1;47(5):1383–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martinville B., Wyman A. R., White R., Francke U. Assignment of first random restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) locus ((D14S1) to a region of human chromosome 14. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Mar;34(2):216–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]