Abstract
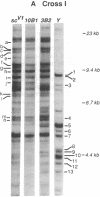
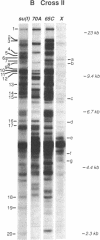
Determining the spatial organization of middle repetitive DNA has proven difficult for several reasons. Repeated arrays are often so large that molecular methods alone cannot resolve their organization, and the lack of phenotypic markers within arrays limits the value of classical genetic analysis. We have characterized the superstructure of one repeated gene family, the ribosomal gene family of Drosophila melanogaster, by a combination of recombinational and molecular analyses of spacer-length variants. The resulting genetic maps demonstrate that some spacer variants are widely dispersed, while others are limited in their distribution. Moreover, exchange among ribosomal DNA (DNA encoding rRNA) arrays was often unequal, leading to a prediction of little or no relationship between physical location in an array and relatedness of gene family members. Extensions of our procedure may be generally useful for mapping the superstructure of repetitive DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Britten R. J., Kohne D. E. Repeated sequences in DNA. Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science. 1968 Aug 9;161(3841):529–540. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3841.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cluster P. D., Marinković D., Allard R. W., Ayala F. J. Correlations between development rates, enzyme activities, ribosomal DNA spacer-length phenotypes, and adaptation in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):610–614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E. S., Thoday J. M., Dover G. Rate of turnover of structural variants in the rDNA gene family of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):564–568. doi: 10.1038/295564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E., Strachan T., Dover G. Dynamics of concerted evolution of ribosomal DNA and histone gene families in the melanogaster species subgroup of Drosophila. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 15;158(1):17–35. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90448-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSalle R., Slightom J., Zimmer E. The molecular through ecological genetics of abnormal abdomen. II. Ribosomal DNA polymorphism is associated with the abnormal abdomen syndrome in Drosophila mercatorum. Genetics. 1986 Apr;112(4):861–875. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.4.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G., Coen E. Springcleaning ribosomal DNA: a model for multigene evolution? Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):731–732. doi: 10.1038/290731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. S., Tartof K. D. The ribosomal DNA of Drosophila melanogaster is organized differently from that of Drosophila hydei. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 25;163(3):499–503. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Dawid I. B. Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:727–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddern R. H. Exchange between the ribosomal RNA genes of X and Y chromosomes in Drosophila melanogaster males. Genet Res. 1981 Aug;38(1):1–7. doi: 10.1017/s001667230002036x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz-Pohl R., Glätzer K. H., Kunz W. Ribosomal RNA genes with an intervening sequence are clustered within the X chromosomal ribosomal DNA of Drosophila hydei. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 5;148(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins L. G., Swanson E. E. Rex-induced recombination implies bipolar organization of the ribosomal RNA genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Dec;120(4):1053–1059. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.4.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roiha H., Glover D. M. Duplicated rDNA sequences of variable lengths flanking the short type I insertions in the rDNA of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5521–5532. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson M. L., Wegnez M. Bipartite structure of the 5S ribosomal gene family in a Drosophila melanogaster strain, and its evolutionary implications. Genetics. 1988 Apr;118(4):685–691. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.4.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartof K. D. Increasing the multiplicity of ribosomal RNA genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1971 Jan 22;171(3968):294–297. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3968.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Dover G. A. Transcription of the tandem array of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster does not terminate at any fixed point. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1267–1273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Hancock J. M., Webb D. A., Tautz C., Dover G. A. Complete sequences of the rRNA genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol. 1988 Jul;5(4):366–376. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. M., Furnier G. R., Fuog E., Strobeck C. Evolution of the ribosomal DNA spacers of Drosophila melanogaster: different patterns of variation on X and Y chromosomes. Genetics. 1987 Jun;116(2):225–232. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. M., Kennison J. A., Robbins L. G., Strobeck C. Reciprocal recombination and the evolution of the ribosomal gene family of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1989 Jul;122(3):617–624. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.3.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagura T., Yagura M., Muramatsu M. Drosophila melanogaster has different ribosomal RNA sequences on S and Y chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 9;133(4):533–547. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90406-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]