Abstract
Oxytocin is a key modulator of emotional processing and social cognitive function. In line with this, polymorphisms of genes involved in oxytocin signaling, like the oxytocin receptor (OXTR) gene, are known to influence social behavior in various species. However, to date, no study has investigated environmental factors possibly influencing the epigenetic variation of the OXTR gene and its behavioral effects in dogs. Pet dogs form individualized and strong relationships with their owners who are central figures in the social environment of their dogs and therefore might influence the methylation levels of their OXTR gene. Here we set out to investigate whether DNA methylation within the OXTR promoter region of pet dogs is linked to their owner’s interaction style and to the social behavior of the dogs. To be able to do so, we collected buccal epithelial cells and, in Study 1, we used pyrosequencing techniques to look for differentially methylated CpG sites in the canine OXTR promoter region on a heterogeneous sample of dogs and wolves of different ages and keeping conditions. Four identified sites (at positions -727, -751, -1371, and -1383 from transcription start site) showing more than 10% methylation variation were then, in Study 2, measured in triplicate in 217 pet Border Collies previously tested for reactions to an adverse social situation (i.e., approach by a threatening human) and with available data on their owners’ interaction styles. We found that CpG methylation was significantly associated with the behavior of the dogs, in particular with the likelihood that dogs would hide behind their owner or remain passive when approached by a threatening human. On the other hand, CpG methylation was not related to the owners’ behavior but to dog sex (at position -1371). Our findings underpin the complex relationship between epigenetics and behavior and highlight the importance of including epigenetic methods in the analysis of dog behavioral development. Further research is needed to investigate which environmental factors influence the epigenetic variation of the OXTR gene.
Keywords: dog, DNA methylation, epigenetics, social behavior, oxytocin receptor gene, ownership style, oxytocin
Introduction
Social interactions are central to the life of all social species, and genetic variation across individuals has been associated with mechanisms regulating these interactions. In particular, associations have been found between the genetic variation of different genes involved in the oxytocinergic system and a variety of social phenotypes in different mammalian species, e.g., mice (see Caldwell et al., 2016 for a review), primates (Staes et al., 2014), cats (Arahori et al., 2015), humans (see Ebstein et al., 2012 for a review), and dogs (Kis et al., 2014). For example, polymorphisms in the oxytocin receptor (OXTR) gene were associated with dogs’ proximity seeking with the owner (Kis et al., 2014), rough temperament in cats (Arahori et al., 2015), and sociability in humans (Li et al., 2015). Furthermore, oxytocin has been associated with social fear (Kirsch et al., 2005), aggression toward unfamiliar individuals (Stallen et al., 2012) and social anxiety (Grillon et al., 2013) in humans, and friendliness toward a threatening human in dogs (Hernádi et al., 2015). In particular, Hernádi et al. (2015) showed that dogs, after intranasal oxytocin administration, showed less friendliness toward the owner approaching them in a threatening way (in the so-called Threatening Approach test, originally developed and validated by Vas et al. (2005, 2008) and looked more at their owners standing behind them than a control group of dogs who received a placebo. These results, taken together with the associations between OXTR polymorphisms and dog friendliness and proximity seeking toward the owner found by Kis et al. (2014) during the same test, highlight a potential dual role of the oxytocinergic system: regulating a dog’s behavioral response toward a social threat and expressing the relationship between the dog and the owner present in such a situation.
The relationship dogs build with their owners (at least in western societies) has been defined as analogous to the infant-mother attachment bond (Topál et al., 1998), and it has been shown that the presence of the owner influences the coping strategy of a dog exposed to such social threats (Horváth et al., 2007) and attachment-related behaviors like proximity seeking (Gácsi et al., 2013). This latter behavior has been interpreted as dogs seeing their owners as a “safe haven,” a concept introduced by Bowlby (1969) in the frame of the attachment theory. The safe haven effect is activated by distress and fear, when a child (or a dog) seeks for proximity to the caregiver in order to find protection and safety. However, it is important to notice that not all dogs seek proximity in the same way, suggesting that individual differences might play a role in shaping the relationship between a dog and its owner. In fact, it has been shown that the reactions of dogs during the Threatening Approach test are strictly associated with the interaction styles of their owners (Cimarelli et al., 2016), supporting the idea that owners can indeed serve as a safe haven for their dogs, but only if they show specific behavioral characteristics. Specifically, only if previous experiences provided the dog with the information that the caregiver was present and responsive.
Similarly, in human infants, the caregivers’ parenting style strongly influences the children’s attachment styles (that is, their behavioral reaction to separation from and reunion with the caregiver), and it has been proposed that epigenetic modifications of the genome are the biological mechanisms that mediate this link between caregiver and child behavior (Champagne and Curley, 2009). In fact, epigenetic modifications of the DNA, that affect gene expression but do not alter the primary sequence itself, are known to be influenced by various biological and environmental factors (Powledge, 2011; Tammen et al., 2013). One of their best known mechanisms is DNA methylation that in mammals occurs predominantly on cytosine residues that are followed by guanine (CpG sites). Although DNA methylation can exert opposite effects on transcription efficiency depending on the genomic context and extent of methylation, basically it represses gene expression. This is especially true for promoter regions where DNA methylation is considered as a major factor influencing gene expression (e.g., in tissue-specific transcriptional inactivation, Goldberg et al., 2007; Portela and Esteller, 2010). Studies in rodents show that the social environment in which individuals grow up, and as such, also caregiving quality, has a high impact on DNA methylation (Weaver et al., 2004; McGowan et al., 2011). In child development it has been suggested that epigenetic modifications of specific genes caused by environmental factors result in changes in emotion regulation and, in turn, in behavior (van Ijzendoorn et al., 2011). For example, it has been shown that methylation levels in the hippocampus of suicidal victims who had experienced abuse was higher than in individuals who committed suicide but had no history of abuse (McGowan et al., 2009). Also, children with mothers reporting a warmer and more affectionate caregiving style had lower methylation levels in the glucocorticoid receptor gene (Bick et al., 2012). Regarding the role of the oxytocinergic system in the epigenetic modification of social behavior, it seems that this system is influenced by early experience (e.g., Unternaehrer et al., 2015), and it has been suggested that methylation of the OXTR gene mediates the effect of parental care on psychosocial development in humans (MacDonald, 2012; MacDonald and Feifel, 2013; Shalev and Ebstein, 2013; Feldman, 2015) and in rodents (Zhang et al., 2010; Bales and Perkeybile, 2012). In humans, a possible role of OXTR methylation in behavioral neuroscience is also underpinned by functional gene expression studies (Kusui et al., 2001) and by observations on the relationship between OXTR methylation and psychosocial traits (Kumsta et al., 2013). In particular, OXTR methylation has been linked to autism (Gregory et al., 2009), social perception (Jack et al., 2012), callous-unemotional traits (Dadds et al., 2014), anxiety/depression (Chagnon et al., 2015) as well as anger and fear perception (Puglia et al., 2015). OXTR methylation levels have also been shown to change dynamically upon acute psychosocial stress (Unternaehrer et al., 2012).
Here we suggest that epigenetic mechanisms are also likely to play a role in mediating the effects of the owner behavior on the social behavior of pet dogs. We have shown that dog owners’ interaction styles vary along three components that are analogous to components of human parenting styles and that they are associated with how dogs cope with a socially stressful situation (Cimarelli et al., 2016). We hypothesize that methylation of the OXTR gene may play a role in mediating such a link between owner and dog behavior. Investigating possible causes and effects of differential methylation patterns in the dog OXTR gene is not only relevant for the field of anthrozoology or canine behavior but could represent a valid model of human caregiving behavior and its effects on the social behavior of cared individuals (either children or dogs). In fact, the vast majority of animal studies have so far focused mainly on laboratory rodents that live in environments not comparable to that of humans. Also, rodent maternal behavior, albeit possibly analogous the human parenting, still has a rather different biological function. It has been pointed out that it is difficult to retrieve useful information from comparing the “reproductive and parenting strategies of humans and other species” (Galbally et al., 2015, p. 2). In contrast, in pet dogs we can directly investigate the effects of human caregiving on dog social behavior. Furthermore, dogs share their environment with humans, not only in terms of habitat and nutrition but also of communication and social interactions (Hare and Tomasello, 2005; Tomasello and Kaminski, 2009; Miklósi and Topál, 2013). Therefore, pet dogs might provide a more relevant animal model than laboratory rodents for studying associations between epigenetic variables and behavior. Finally, this species is also genetically uniquely suited to investigate the genetic background and gene-related associations of various behavior traits (Hejjas et al., 2007). Purebred dogs show a genetic diversity that is intermediate between two extremes represented by the genetically highly variable humans and the genetically nearly homogeneous laboratory animal strains. This intermediate genetic diversity can facilitate the identification of genetic factors underlying phenotypic variation (Ostrander, 2005; Boyko, 2011; Parker, 2012). Despite of these advantages, to date few studies have investigated epigenetic variation in the domestic dog (Maeda et al., 2014; Tomiyasu et al., 2014; Berglund et al., 2015; Montrose et al., 2015; Yamaya et al., 2015) and none of them focused on associations between the OXTR gene and behavioral phenotype.
Here, in Study 1, we explored differentially methylated CpG sites within the canine OXTR promoter region in a heterogeneous sample of dogs and wolves living in different social environments in order to describe the epigenetic variation of the canine OXTR promoter. Then, in Study 2, considering the hypothesis that different owner interaction styles might have an effect on dog behavior through OXTR methylation, first we investigated possible relationships between methylation levels on specific regions of the OXTR promoter and the dogs’ behavioral reactions to an unpleasant social situation (including experimenter-directed behaviors and owner-directed behaviors, e.g., proximity seeking) in a large sample of pet Border Collies. Second, in the same dogs we investigated whether dog-directed interaction styles of the owners are associated with DNA methylation levels of OXTR gene promoter of the dogs.
Materials and Methods
Ethics Statement
No special permission for non-invasive sample taking and socio-cognitive testing of animals is required either in Austria (Tierversuchsgesetz 2012 – TVG 2012) or in Hungary (Act XXVIII of 1998 on the protection and welfare of animals). In accordance with GPS guidelines and national legislation, the experimental procedures of Study 2 were approved by the Ethical Committee for the use of animals in experiments at the University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna (Ref: 09/10/97/2012 and 10/10/97/2012). Owners of the pet dogs participated in the study on a voluntary basis and gave their consent to the genetic analyses as well as the behavioral testing of their dogs.
Sample Collection and DNA Isolation
DNA samples were collected from the inner cheek of the animals using cotton-tipped swabs. Genomic DNA was isolated by a traditional, salting-out procedure as described earlier (Boor et al., 2002). Briefly, collection swabs were incubated overnight at 56°C in 450 μl cell lysis buffer (0.2 g/l Proteinase K, 0.1 M NaCl, 0.5% SDS, 0.01 M Tris buffer pH = 8.0), RNase treated at room temperature, protein precipitated with saturated NaCl (6 M) and centrifuged. DNA was obtained by precipitating the supernatants with isopropanol. Following ethanol purification, pellets were resuspended in 50 μl of Tris-EDTA (0.01 M Tris, 0.001 M EDTA, pH = 8.0) and stored at -20°C prior to bisulfite conversion.
DNA Methylation Analysis
Two hundred nanograms genomic DNA quantified by a NanoDrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Wilmington, DE, USA) was bisulfite converted using the EZ DNA Methylation-GoldTM Kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Bisulfite converted DNA was kept at -80°C until further used. Primers were designed to bisulfite converted regions of an approximately 1000 base pairs (bp) long CpG island shore stretch at the canine OXTR promoter/ 5′ untranslated region (UTR) by the PyroMark Q24 Software (Qiagen NV, Venlo, Netherlands). CpG island localization was determined by an in-house MS-DOS application using the traditional definition of a CpG island as a ≥ 200 bp long region with a GC percentage >50% and an observed-to-expected (O/E) CpG ratio greater than 60%. The OXTR promoter was located according to genome assembly CanFam 3.1 (GCA_000002285.2) and CpG sites investigated were numbered according to transcription start site (+1) of transcript variant NM_001198659.1 (ENSCAFT00000008950.3; genomic coordinate Chr20:9358932) (Aken et al., 2016). For polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, the 25 μl reaction mixture contained 0.625 units EpiMark Hot Start Taq DNA Polymerase (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA), 1x EpiMark Hot Start Taq Reaction Buffer (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA), 0.2 mM deoxynucleotide trisphosphate (dNTP), 10 μM of an unmodified forward primer and a biotin-labeled reverse primer (for sequences see Table 1) and about 15–20 ng bisulfite converted DNA template. All samples were amplified in triplicate on the same PCR machine (Bio-Rad T100TM). Cycling conditions were as follows: Step 1: (95°C/ 1 min)/1 cycle; Step 2: (95°C/30 s, 58°C/1 min, 68°C/45 s)/45 cycles; Step 3: (68°C/5 min)/1 cycle; Step 4: 8°C hold. Successful PCR amplification of a single fragment was verified using agarose gel electrophoresis for each sample and replicate. Pyrosequencing was performed on a PyroMark Q24 platform using sequencing primers indicated in Table 1 with PyroMark Gold Q24 Reagents (Qiagen NV, Venlo, Netherlands). Totally methylated and absolutely unmethylated control DNA were obtained by SSSI methyltransferase treatment (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA) and whole genome amplification (REPLI-g Mini Kit, Qiagen NV, Venlo, Netherlands), respectively, according to the manufacturers’ protocols. Measurements reported as unreliable by the PyroMark software were removed from the database. Epigenotypes reported are an average of triplicate measurements (outliers, i.e., values deviating more than 3% were removed).
Table 1.
Primers used for the exploration of differentially methylated CpG sites in the canine OXTR promoter.
| Primer Name | Sequence | Genomic coordinates (Chromosome 20) | Type | Quality score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1_F | 5′ TGA TGT AAT TTT TAA GGG TAA GAA AAA GAT A 3′ | 9357389 : 9357419 | Amp | – |
| P1_R | 5′ TTT AAA TAC ATT CTT CCT CCT AAC ATT TCC TTT C 3′ | 9357608 : 9357641 | Amp | – |
| P1_S1 | 5′ AAT TTT TAA TTT TTT TTA ATG TTG T 3′ | 9357419 : 9357442 | Seq | 74 |
| P1_S2 | 5′ TTA ATT AGA ATT TTG GGA TT 3′ | 9357476 : 9357495 | Seq | 76 |
| P1_S3 | 5′ GGT ATA GGG TTG TAA TTG 3′ | 9357530 : 9357547 | Seq | 79 |
| P2_F1 | 5′ AGG GTG ATG AAG TTG TAA AAG T 3′ | 9358139 : 9358160 | Amp | – |
| P2_F2 | 5′ AGG GAA AGA TTT TAA GAA AAG ATA AGA AAG 3′ | 9357913 : 9357938 | Amp | – |
| P2_R | 5′ ACA TTT CAT CTT CCT TTA ACA TCA TAT A 3′ | 9357788 : 9357815 | Amp | – |
| P2_S1 | 5′ ATG AAG TTG TAA AAGTAT TTA ATT G 3′ | 9358130 : 9358154 | Seq | 71∗ |
| P2_S2 | 5′ TAA GTA AAT GTT TGT TTT GGA GTA 3′ | 9358026 : 9358049 | Seq | 68∗ |
| P2_S3 | 5′ AAT TTA TTT TTA TTT TAA AGT GAT T 3′ | 9357875 : 9357899 | Seq | 80# |
| P3_F | 5′ GG TTT TTG GAT GGG GAT AGG A 3′ | 9358485 : 9358505 | Amp | – |
| P3_R | 5′ ACT TCA TCA CCC TCT TCT CA 3′ | 9358148 : 9358167 | Amp | – |
| P3_S1 | 5′ TTT TTG GAT GGG GAT AGG 3′ | 9358486 : 9358503 | Seq | 68 |
| P3_S2 | 5′ GGT AGG AGG TAA AAA AAA G 3′ | 9358450 : 9358468 | Seq | 68 |
| P3_S3 | 5′ GTT GGG GAG AGT TTT TTT GTA GT 3′ | 9358416 : 9358438 | Seq | 69 |
| P3_S4 | 5′ GTA TAG TTT TAA GGG GTT ATT GGG 3′ | 9358378 : 9358401 | Seq | 72 |
| P3_S5 | 5′ ATT TTT AGA TTA GGG TTA GTT TGG A 3′ | 9358330 : 9358354 | Seq | 72 |
| P3_S6 | 5′ AAT TAG TAG TTT TAT TTT ATT TAA G 3′ | 9358288 : 9358312 | Seq | 69 |
| P3_S7 | 5′ GGT TTT TTT TTT TTT TGG TTT AGA A 3′ | 9358217 : 9358241 | Seq | 63 |
Genomic coordinates are according to CanFam3.1 (GCA_000002285.2). Quality scores (<40: poor; 40–59: low; 60–87: medium; > 88: high quality) are assigned as by the PyroMark Assay Design Software and refer to primer sets (including forward, reverse and sequencing). Amp: amplifying; Seq: sequencing. ∗For amplification, P2_F1 forward primer was used. #For amplification, P2_F2 forward primer was used.
Study 1: Identification of Differentially Methylated CpG Sites in the Canine OXTR Promoter
The aim of Study 1 was to identify differentially methylated CpG sites in the promoter of the OXTR that show a variation between individuals higher than 10%. As no prior information was available regarding localization of differentially methylated CpG sites in the canine OXTR gene, the DNA methylation profiles needed to be explored first. A diverse sample set including both wolves and dogs of different breeds, sex, age and keeping conditions were used during this pilot study to gain more insight into the methylation levels of the canine OXTR promoter region. The rationale behind choosing a heterogeneous population for this goal was that in a homogeneous sample, potential variably methylated sites are more likely to be missed, especially if the sample size is small. Given that methylation status of promoter-associated CpG islands and their immediate flanking regions, the CpG island shores, often influences gene expression and because the latter have been shown to be frequently differentially methylated (Doi et al., 2009; Portela and Esteller, 2010; Deaton and Bird, 2011), we focused on identifying differentially methylated CpGs at near promoter CpG island shore.
Subjects
Twelve animals (nine dogs and three timber wolves, six females and six males, mean age ± SD = 47.94 ± 37.84 months; see Table 2 for all details about the subjects of Study 1) were involved in the present study. All wolves and two dogs were born in captivity and were hand-raised in peer-groups at the Wolf Science Center1 after being separated from their mothers before they were 10 days old. Among the remaining seven dogs, one lived at a Hungarian dog school as guarding dog, six were kept as pet dogs and among them four lived inside the house and two lived mainly outside.
Table 2.
Animals involved in the identification of the differentially methylated CpG sites (Study 1).
| Sub-species | Breed | Living conditions | Sex | Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wolf | Timber | Hand-raised at the WSC | Male | 6 years |
| Wolf | Timber | Hand-raised at the WSC | Male | 2 years |
| Wolf | Timber | Hand-raised at the WSC | Female | 4 years |
| Dog | Mix breed | Hand-raised at the WSC | Female | 2 years |
| Dog | Mix breed | Hand-raised at the WSC | Female | 3 weeks |
| Dog | Mix breed | Pet dog (kept inside) | Female | 7 years |
| Dog | Shetland Sheepdog | Pet dog (kept inside) | Female | 2 years |
| Dog | Caucasian Shepherd | Guard dog at dog school | Male | 7 years |
| Dog | Boxer | Pet dog (kept inside) | Male | 6 months |
| Dog | Central Asian Shepherd | Pet dog (kept outside) | Male | 2 weeks |
| Dog | West Highland White Terrier | Pet dog (kept inside) | Male | 9 years |
| Dog | Beagle | Pet dog (kept outside) | Female | 5 years |
Data Analysis
We used the traditional CpG island definition (at least 200 bp long DNA stretch with a G+C content of at least 50% and a ratio of observed to statistically expected CpG frequencies of at least 0.6) to identify CpG islands.
Results
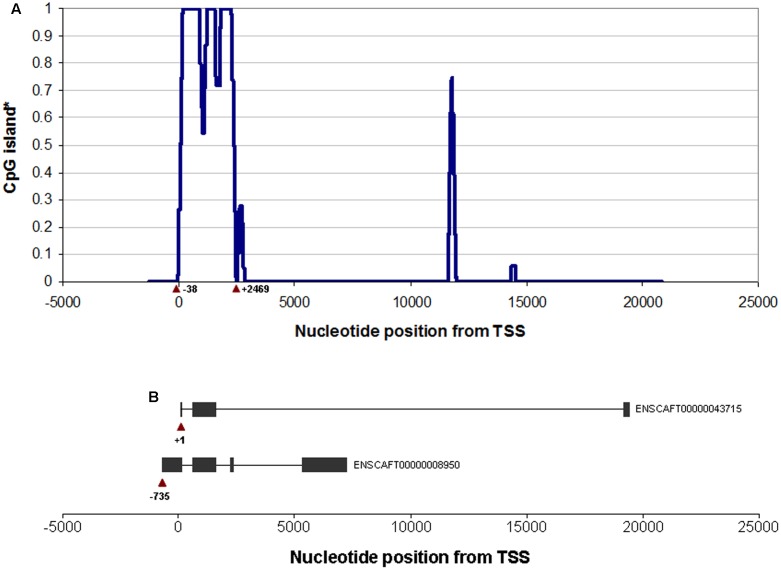
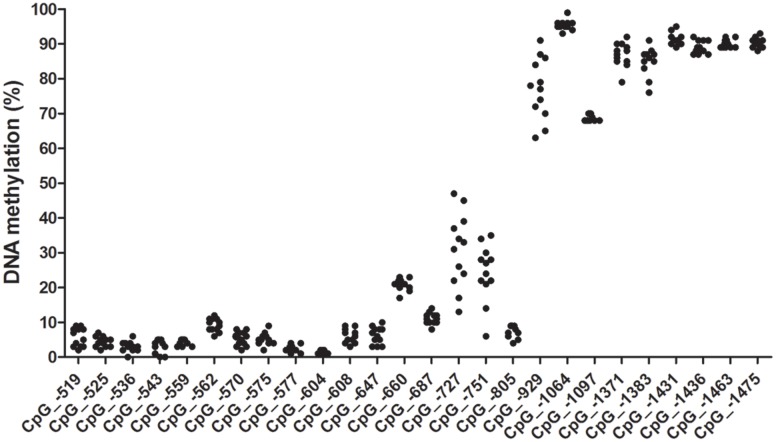
We identified a CpG island located right at the 5′ UTR of the canine OXTR gene (Figure 1). Accordingly, an 1117 bp long segment located at a CpG island shore in the canine OXTR promoter was investigated for variably methylated CpG sites. Range of methylation levels for given CpG sites are shown in Figure 2 (not all CpG sites were covered by pyrosequencing analysis due to difficulties of designing effective primers for bisulfite converted DNA). Out of the 26 CpG sites analyzed, four were found that showed at least 10% variation in their methylation levels among the subjects, presented with accurate methylation levels for the 0 and 100% methylated controls and their different ratio mixtures (between 10 and 90%) as well as gave high peaks in the chromatogram even in the case of low (10–12 ng) initial (pre-PCR) DNA quantities. These four CpG sites were located -727, -751, -1371, and -1383 bp relative to transcription start site of transcript variant NM_001198659.1 (ENSCAFT00000008950.3), see Figure 3, with their genomic coordinates being Chr20:9358205, Chr20:9358181, Chr20:9357561, and Chr20:9357549, respectively, according to genome assembly CanFam3.1 (GCA_000002285.2). These four CpG sites were then analyzed in Study 2 (see below). Genomic alignment of the canine OXTR promoter segment investigated to the corresponding human sequence is shown in Supplementary Figure 1.
FIGURE 1.
CpG island structure of the canine OXTR gene. (A) Nucleotide positions according to transcription start site of transcript variant NM_001198659.1 (ENSCAFT00000008950.3) to which the traditional CpG island definition applies (“an at least 200 bp long DNA stretch with a ≥ 50% G+C content and a ≥ 0.6 observed-to-expected CpG ratio”). ∗Y axis shows the proportion of all possible different 200 bp long DNA stretches containing the same nucleotide to which the described CpG island definition applies. Positions of nucleotides at the beginning and the end of the CpG island located right at the beginning of the OXTR gene are indicated with respect to +1 as the transcription start site of transcript variant NM_001198659.1 (ENSCAFT00000008950.3). (B) Schematic structure of the transcript variants ENSCAFT00000008950.3 (NM_001198659.1) and ENSCAFT00000043715.1. Boxes represent exons, lines represent introns. Nucleotide positions of the transcription sites are indicated relative to transcription start site of NM_001198659.1 (ENSCAFT00000008950.3).
FIGURE 2.
CpG methylation levels in the canine OXTR promoter. Methylation ranges indicated are as observed in the exploratory sample set of 12 animals of different subspecies, breed, sex, age and keeping conditions. CpG numbering is according to transcription start site of +1 of transcript variant NM_001198659.1. Methylation levels for CpGs –451 to –489 are not indicated due to poor sequence quality, but apparently they were all in the low methylation level range. CpG –590 was not covered by any sequencing primers.
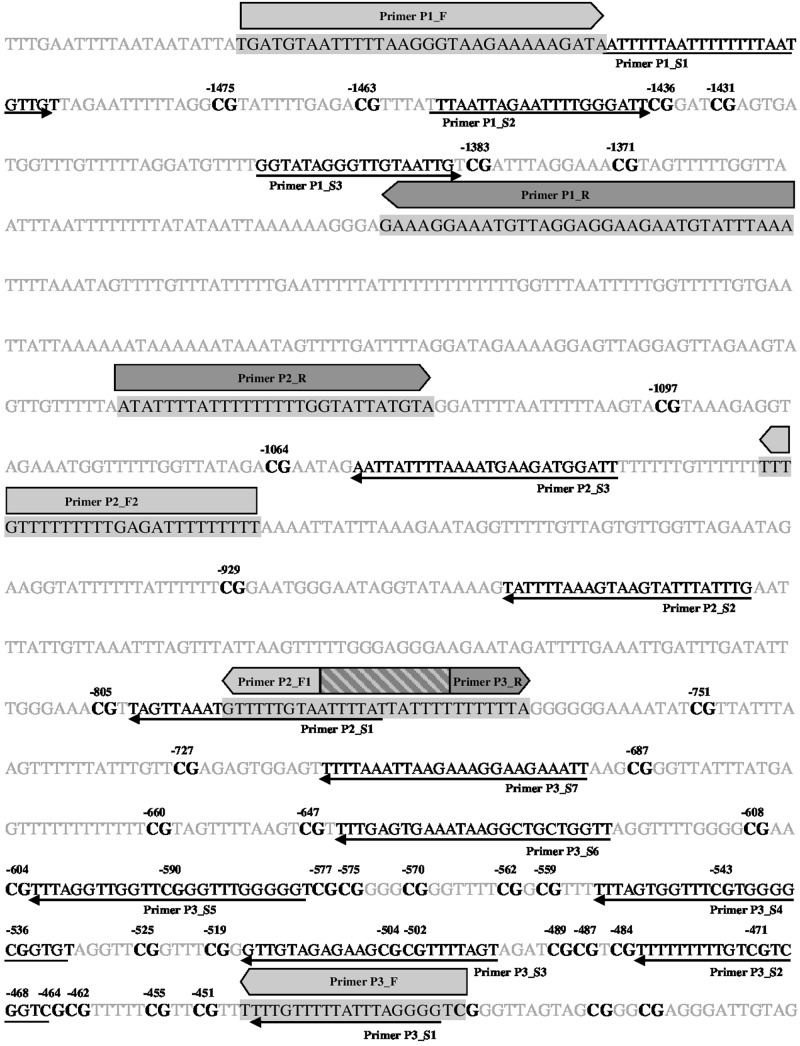
FIGURE 3.
Localization of primers and CpG sites covered. Bisulfite converted sequence of forward strand is indicated. Primer pairs P2_F1/ P2_F2 & P2_R as well as P3_F & P3_R were designed to the reverse strand. Forward and reverse amplifying primers are indicated by filled light and darks arrows, respectively, as well as by black letters in the sequence highlighted by a gray background; sequencing primers are indicated by thin arrows as well as black italics letter in the sequence. Overlap region of forward primer P2_F1 and reverse primer P3_R is indicated by a striped box. CpG sites are shown in bold black letters. CpGs covered by sequencing primers are numbered according to transcription start site of +1 of transcript variant NM_001198659.1 [ENSCAFT00000008950.3; genomic coordinate: CanFam3.1 (GCA_000002285.2) Chr20:9358932].
Study 2: Associations between Owner Interaction Style, Dog Behavior, and Methylation of the OXTR Promoter
Subjects
Study 2 originally involved 220 pure bred Border Collies but three individuals were excluded from the present analyses since it was not possible to obtain DNA samples from them. A single breed was involved to minimize background genetic variability. The 217 dogs (135 females (45 neutered) and 95 males (32 neutered); mean age ± SD = 48.07 ± 42.43 months) involved in the study were all kept as pets in Vienna (Austria) and surroundings. These subjects, together with their owners, participated in a behavioral test battery accompanied by buccal DNA sample collection. All subjects were tested at the Clever Dog Lab (Vienna, Austria) between September 2010 and November 2013. The owners were recruited from the database of volunteer participants of the Clever Dog Lab.
Behavioral Test Battery
The behavioral data were collected as part of a bigger project, and the methods and some of the results have been described by Cimarelli et al. (2016). In summary, the pet Border Collies (N = 217) participated in a modified version of the Threatening Approach test (Vas et al., 2005; Gácsi et al., 2013; Hernádi et al., 2015): the owner stood motionless behind the dog and held the leash. The experimenter (E), initially standing five meters away from the owner-dog dyad, started walking toward the dog slowly (approximately 1 step/4 s) with the upper body bent toward the dog and staring in the eyes of the dog. The test was over when E reached the dog, the dog approached E in a friendly manner, or when the dog showed strong signs of aggression and/or fear (i.e., snapped at E or hid behind the owner). At the end of the test, E crouched down and talked gently to the dog to resolve the situation. We analyzed whether the dog showed any of the following behaviors before E crouched down (recorded as binomial variables): friendly (approaching E wagging the tail), appeasing (approaching E with the tail between the legs, ears pulled back and tense body posture), aggressive (growling, snarling or snapping at E), passive (no visible reaction) and hiding behind the owner (withdrawing in a way that the owner would be positioned between the dogs and E). In addition, we also scored the final reaction of the dogs showed when E made the last step toward them (1 = retreat behind the owner; 2 = passive behavior; 3 = appeasing/friendly approach; 4 = aggressive approach).
Aside from analyzing the dogs’ behavior in this test, the owners’ interaction style with their dog was also characterized (Owner interaction style test). The behavior of the owner toward her/his dog was observed and coded in a set of 8 experimental tasks. The tasks included: (1) showing a preference toward one of two plates to the dog (“Food choice”); (2) holding the dog while the experimenter was taking a buccal sample from the inner mouth of the dog (“DNA sample”); (3) greeting after a short period of separation (“Greeting”); (4) playing with the dog using a rope in a tug-of-war game (“Tug-of-war”); (5) putting a T-shirt on a dog (“T-shirt”); (6) commanding the dog to perform three simple behaviors (i.e., sit, lay down, stay; “Commands”); (7) demonstrating the dog how to remove the lid from a bin to get a piece of food (“Teaching”); (8) playing a retrieval game using a ball (“Ball”). The following variables were measured: communication style (4-point scale, in Food choice and Teaching tests), warmth (4-point scale, in the Greeting test), enthusiasm (4-point scale, in the Tug-of-war and Ball test), social support (4-point scale, in DNA sample and T-shirt test), authoritarian behaviors (0 = none, 1 = the owner raises the tone of voice, 2 = the owner forces the dog in a determined position in the Commands test). Furthermore, the number of commands, attention sounds (e.g., clapping the hands), vocal praises and petting were counted in the DNA sample, Tug-of-war, Commands and Ball tests. Previous analyses showed that the behavioral variables analyzed during this test grouped in three factors, namely the “Owner Warmth” (characterized by a positive and warm communication and interaction style showed in positive contexts, e.g., play), “Owner Social Support” (characterized by the number of petting and praising given by the owner in stressful situations, e.g., DNA sample test) and “Owner Control” [mainly characterized by the number of commands; for a detailed description see (Cimarelli et al., 2016)].
Statistical Analysis
In order to estimate whether the methylation levels of the adjacent sites identified in Study 1 were correlated, Pearson correlations between sites were calculated. To investigate whether the Owner interaction styles and the demographic characteristics of the dog (i.e., sex, age, and neutered status) were associated with the methylation levels of the CpG sites identified in Study 1, we ran Generalized Least Squares models (GLSs) with the methylation levels as dependent variable and the Owner interaction styles and the dog demographic variables as predictors [R package nlme (Pinheiro et al., 2007), function gls]. Furthermore, to investigate associations between the methylation levels and dog behavior during the Threatening Approach test, we ran Generalized Linear Models (GZLM) with binomial distributions. We ran models with the methylation levels of the different CpG sites as predictors and the following variables as response variables: “Aggression,” “Appeasing,” “Friendly,” “Hide behind the owner,” and “Passive.” Furthermore, we ran a Multinomial Regression Model with the “Reaction at the end of the test” as dependent variable and the methylation levels as predictors. We selected the best model using model reduction based on p-values. Non-significant predictors (p > 0.05) were removed from the model and are not reported in the results. Model residuals were tested for normality using the Shapiro-Wilk normality test and homoscedasticity was assessed via plots of residuals against fitted values. We accounted for multiple testing using post hoc sequential Bonferroni (Holm, 1979). All statistical tests were conducted using R version 3.1.1 (R Development Core Team). See Supplementary Materials for a complete correlation matrix between all variables included in the present study.
Results
Characteristics of OXTR Promoter CpG Site Methylation
The four sites identified in Study 1 were further investigated in the Border Collie group (N = 217). The degree of methylation of these CpGs in the Border Collie population ranged between 9.0 and 58.7% (-727), 15.5 and 46.5% (-751), 80.5 and 89.7% (-1371), and 76.5 and 94.0% (-1383). Sites -1383 and -1371 were found to be moderately correlated (r210 = 0.23, p < 0.01) while sites -727 and -751 were strongly correlated (r210 = 0.69, p < 0.01).
Associations of Methylation Levels with Sex, Age, Neutered Status, Sex∗Neutered Status Interaction and Owner Interaction Scores
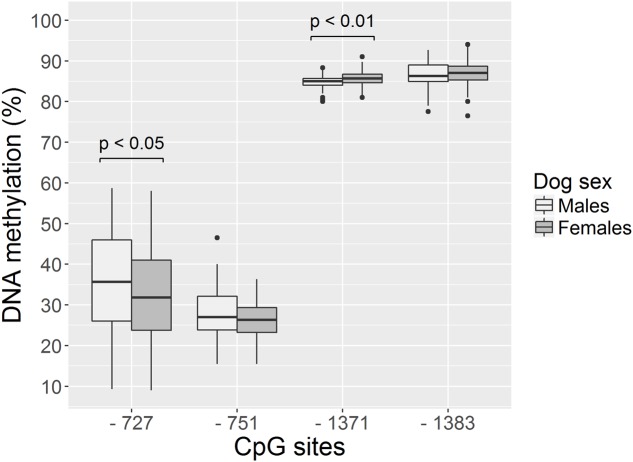
The three Owner interaction style factors, together with the dogs’ sex, age, neutered status and sex∗neutered status were investigated as predictors for methylation levels of the three CpG sites. We found that the none of the predictors was significantly associated with the methylation level of sites –751 and -1383 (p > 0.05, Table 3 and Figure 4). On the other hand, the sex of the dog was associated with the methylation level in site -1367 and -723. In particular, female dogs had higher methylation levels than males in position -1371 (GLS, estimate ± SD = 0.81 ± 0.24, t210 = 3.31, p < 0.01, significant after correcting for multiple testing; Table 3 and Figure 4), while males seemed to have higher methylation levels than females in position -727 (GLS, estimate ± SD = -3.53 ± 1.66, t210 = -2.12, p = 0.03; no longer significant when correcting for multiple testing; Table 3 and Figure 4).
Table 3.
Factors affecting the methylation levels of the CpG sites analyzed in Study 2.
| Dependent variable | Predictor | Estimate ± SE | DF | t value | p-value | Effect size (Pearson’s r) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -727 | Age | 0.01 ± 0.02 | 1 | 0.55 | 0.58 | 0.01 |
| Sex | -3.53 ± 1.66 | 1 | -2.12 | 0.03 | 0.15 | |
| Neutered status | 1.55 ± 1.87 | 1 | 0.83 | 0.41 | 0.05 | |
| Sex∗Neutered status | -2.38 ± 3.86 | 1 | -0.62 | 0.54 | 0.04 | |
| Owner Warmth | -0.75 ± 1.16 | 1 | -0.65 | 0.52 | 0.06 | |
| Owner Social Support | -1.12 ± 1.10 | 1 | -1.06 | 0.29 | 0.08 | |
| Owner Control | -1.14 ± 1.11 | 1 | -1.03 | 0.30 | 0.05 | |
| -751 | Age | 0.00 ± 0.01 | 1 | 0.43 | 0.67 | 0.03 |
| Sex | -1.22 ± 0.73 | 1 | -1.67 | 0.09 | 0.12 | |
| Neutered status | 0.69 ± 0.75 | 1 | 0.92 | 0.36 | 0.06 | |
| Sex∗Neutered status | -1.90 ± 1.53 | 1 | -1.24 | 0.22 | 0.08 | |
| Owner Warmth | 0.30 ± 0.50 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.95 | 0.02 | |
| Owner Social Support | -0.49 ± 0.47 | 1 | -1.06 | 0.29 | 0.05 | |
| Owner Control | 0.18 ± 0.48 | 1 | 0.38 | 0.71 | 0.03 | |
| -1383 | Age | 0.00 ± 0.01 | 1 | 0.86 | 0.39 | 0.06 |
| Sex | 0.37 ± 0.46 | 1 | 0.81 | 0.42 | 0.03 | |
| Neutered status | -0.73 ± 0.49 | 1 | -1.51 | 0.13 | 0.06 | |
| Sex∗Neutered status | 0.03 ± 0.95 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.97 | 0.00 | |
| Owner Warmth | 0.27 ± 0.31 | 1 | 0.88 | 0.38 | 0.07 | |
| Owner Social Support | -0.06 ± 0.30 | 1 | -0.20 | 0.84 | 0.02 | |
| Owner Control | 0.00 ± 0.31 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.99 | 0.04 | |
| -1371 | Age | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.97 | 0.08 |
| Sex | 0.81 ± 0.24 | 1 | 3.31 | 0.001* | 0.22 | |
| Neutered status | -0.49 ± 0.26 | 1 | -1.90 | 0.06 | 0.12 | |
| Sex∗Neutered status | -0.34 ± 0.58 | 1 | -0.58 | 0.56 | 0.04 | |
| Owner Warmth | 0.03 ± 0.17 | 1 | 0.16 | 0.87 | 0.07 | |
| Owner Social Support | 0.19 ± 0.16 | 1 | 1.18 | 0.24 | 0.02 | |
| Owner Control | -0.07 ± 0.17 | 1 | -0.42 | 0.67 | 0.04 | |
∗Significant after post hoc sequential Bonferroni correction for multiple testing.
FIGURE 4.
Sex differences for methylation levels –727, –751, –1371, –1383 in dogs involved in Study 2. Females have higher methylation levels than males at position –1371 while males have higher methylation levels than females at position –727. Horizontal bars represent medians, the bottom and the top of the boxes represent the lower and the upper quartiles, respectively, whiskers represent the interquartile range and filled circles represent outliers.
Associations of Methylation Levels with Dog Reaction in Males and Females
As methylation levels were found to differ by dog sex, the association between different methylation levels and the dog behavior was analyzed separately in female and male dogs. We found that males who hid behind the owner had higher methylation levels in site -751 than those who did not hide behind the owner (GZLM, estimate ± SD = 0.13 ± 0.05, z70 = 2.59, p < 0.01, significant after correcting for multiple testing; Table 4 and Figure 5) and that males remaining passive or retreating at the end of the test tended to have lower methylation levels in site -727 than males approaching the experimenter in an appeasing or aggressive manner (Multinomial Regression Model, X2 = 8.30, df = 3, p = 0.04; no longer significant when correcting for multiple testing; Table 5 and Figure 6). Furthermore, females who approached the experimenter in an appeasing way tended to have higher levels of methylation in site -1383 (GZLM, estimate ± SD = 0.14 ± 0.07, z104 = 1.97, p = 0.04, no longer significant after correcting for multiple testing; Table 4 and Figure 7) than those who did not show any sign of appeasement, contrary to the males who approached the experimenter in an appeasing manner which tended to have lower methylation levels in site -1383 than those who did not (GZLM, estimate ± SD = -0.16 ± 0.08, z70 = -2.09, p = 0.04, no longer significant after correcting for multiple testing; Table 4 and Figure 7). On the other hand, males who remained passive till the end of the Threatening Approach test had higher methylation levels in site -1383 than those who showed any other reaction (GZLM, estimate ± SD = 0.43 ± 0.15, z77 = 2.81, p < 0.01, significant after correcting for multiple testing; Table 4 and Figure 8). All non-significant associations are reported in Tables 4, 5.
Table 4.
Factors affecting male and female dogs’ reaction during the Threatening Approach test (Study 2).
| Dependent variable | Predictor | Sex | Estimate + SE | DF | z value | p-value | Effect size (Pearson’s r) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aggression | -727 | Males | -0.00 ± 0.05 | 1 | -0.02 | 0.99 | 0.07 |
| Females | 0.00 ± 0.03 | 1 | 0.05 | 0.96 | 0.07 | ||
| -751 | Males | -0.05 ± 0.06 | 1 | -0.92 | 0.36 | 0.08 | |
| Females | -0.00 ± 0.08 | 1 | -0.04 | 0.97 | 0.04 | ||
| -1371 | Males | -0.17 ± 0.16 | 1 | -0.01 | 0.31 | 0.13 | |
| Females | 0.21 ± 0.16 | 1 | 1.31 | 0.19 | 0.10 | ||
| -1383 | Males | 0.01 ± 0.11 | 1 | 0.09 | 0.93 | 0.06 | |
| Females | -0.12 ± 0.10 | 1 | -1.18 | 0.24 | 0.08 | ||
| Friendly | -727 | Males | -0.04 ± 0.06 | 1 | -0.70 | 0.48 | 0.14 |
| Females | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 1 | 1.50 | 0.13 | 0.15 | ||
| -751 | Males | 0.01 ± 0.41 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.98 | 0.10 | |
| Females | 0.05 ± 0.09 | 1 | 0.54 | 0.59 | 0.16 | ||
| -1371 | Males | 0.14 ± 0.46 | 1 | 0.31 | 0.75 | 0.03 | |
| Females | 0.33 ± 0.19 | 1 | 1.71 | 0.09 | 0.13 | ||
| -1383 | Males | -0.11 ± 0.45 | 1 | -0.24 | 0.81 | 0.11 | |
| Females | -0.03 ± 0.16 | 1 | -0.19 | 0.85 | 0.12 | ||
| Appeasing | -727 | Males | -0.00 ± 0.04 | 1 | -0.07 | 0.94 | 0.14 |
| Females | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 1 | 1.21 | 0.23 | 0.18 | ||
| -751 | Males | -0.01 ± 0.04 | 1 | -0.19 | 0.85 | 0.08 | |
| Females | -0.06 ± 0.06 | 1 | -1.01 | 0.31 | 0.05 | ||
| -1371 | Males | 0.03 ± 0.16 | 1 | 0.18 | 0.86 | 0.06 | |
| Females | 0.05 ± 0.14 | 1 | 0.39 | 0.69 | 0.02 | ||
| -1383 | Males | -0.16 ± 0.08 | 1 | -2.09 | 0.04 | 0.28 | |
| Females | 0.14 ± 0.07 | 1 | 1.97 | 0.05 | 0.22 | ||
| Passive | -727 | Males | -0.02 ± 0.04 | 1 | -0.51 | 0.61 | 0.11 |
| Females | -0.03 ± 0.03 | 1 | -1.09 | 0.27 | 0.04 | ||
| -751 | Males | 0.03 ± 0.11 | 1 | 0.30 | 0.76 | 0.09 | |
| Females | 0.07 ± 0.09 | 1 | 0.78 | 0.43 | 0.01 | ||
| -1371 | Males | -0.37 ± 0.24 | 1 | -1.55 | 0.12 | 0.04 | |
| Females | -0.09 ± 0.21 | 1 | -0.44 | 0.66 | 0.04 | ||
| -1383 | Males | 0.43 ± 0.15 | 1 | 2.81 | 0.005* | 0.31 | |
| Females | 0.17 ± 0.11 | 1 | 1.54 | 0.12 | 0.13 | ||
| Hide behind | -727 | Males | -0.03 ± 0.03 | 1 | -0.91 | 0.36 | 0.20 |
| Females | -0.01 ± 0.02 | 1 | -0.33 | 0.74 | 0.04 | ||
| -751 | Males | 0.13 ± 0.05 | 1 | 2.59 | 0.009* | 0.35 | |
| Females | 0.03 ± 0.07 | 1 | 0.4 | 0.69 | 0.00 | ||
| -1371 | Males | -0.14 ± 0.19 | 1 | -0.72 | 0.47 | 0.10 | |
| Females | -0.02 ± 0.13 | 1 | -0.16 | 0.87 | 0.05 | ||
| -1383 | Males | 0.03 ± 0.13 | 1 | 0.22 | 0.82 | 0.04 | |
| Females | 0.05 ± 0.10 | 1 | 0.51 | 0.61 | 0.03 | ||
∗Significant after post hoc sequential Bonferroni correction for multiple testing.
FIGURE 5.
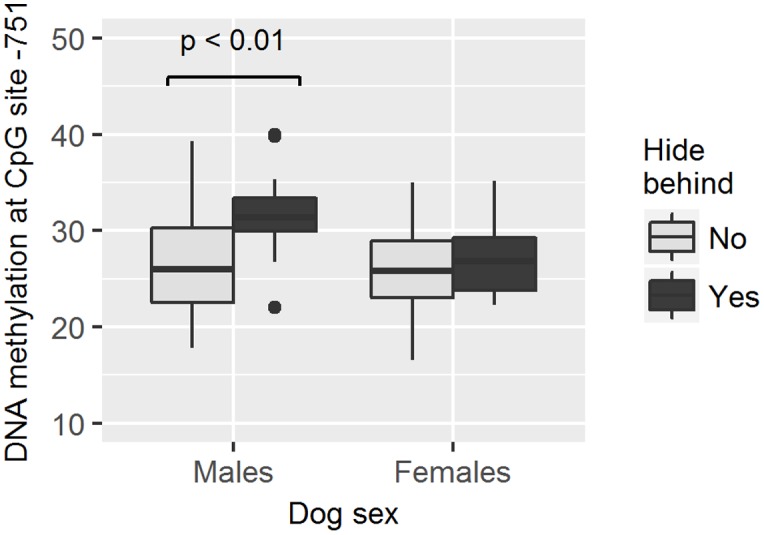
Association between methylation levels at position –751 and the likelihood of dogs to hide behind the owner during the Threatening Approach test. Males hiding behind the owner had higher methylation levels than males not hiding behind the owner. Horizontal bars represent medians, the bottom and the top of the boxes represent the lower and the upper quartiles, respectively, whiskers represent the interquartile range and filled circles represent outliers.
Table 5.
Factors affecting dog’s reaction at the end of the Threatening Approach test (Study 2).
| Dependent variable | Predictor | Sex | Level: Estimate ± SE | DF | X2 | p-value | Effect size (Pearson’s r) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reaction at the end of the test | -727 | Males | (1) -0.01 ± 0.04 | 3 | 8.30 | 0.04 | 0.19 |
| (2) -0.05 ± 0.03 | |||||||
| (3) -0.06 ± 0.02 | |||||||
| Females | (1) 0.01 ± 0.03 | 3 | 0.81 | 0.85 | 0.06 | ||
| (2) 0.00 ± 0.02 | |||||||
| (3) 0.01 ± 0.02 | |||||||
| -751 | Males | (1) -0.03 ± 0.08 | 3 | 7.22 | 0.07 | 0.18 | |
| (2) -0.08 ± 0.05 | |||||||
| (3) -0.13 ± 0.05 | |||||||
| Females | (1) 0.00 ± 0.07 | 3 | 1.18 | 0.76 | 0.07 | ||
| (2) -0.05 ± 0.06 | |||||||
| (3) -0.03 ± 0.05 | |||||||
| -1371 | Males | (1) -0.03 ± 0.09 | 3 | 1.99 | 0.57 | 0.10 | |
| (2) 0.07 ± 0.15 | |||||||
| (3) -0.15 ± 0.14 | |||||||
| Females | (1) -0.02 ± 0.09 | 3 | 0.69 | 0.87 | 0.06 | ||
| (2) -0.02 ± 0.09 | |||||||
| (3) 0.07 ± 0.09 | |||||||
| -1383 | Males | (1) 0.20 ± 0.18 | 3 | 3.63 | 0.30 | 0.13 | |
| (2) -0.11 ± 0.10 | |||||||
| (3) -0.02 ± 0.09 | |||||||
| Females | (1) 0.12 ± 0.12 | 3 | 3.04 | 0.39 | 0.12 | ||
| (2) 0.12 ± 0.10 | |||||||
| (3) -0.01 ± 0.09 | |||||||
FIGURE 6.
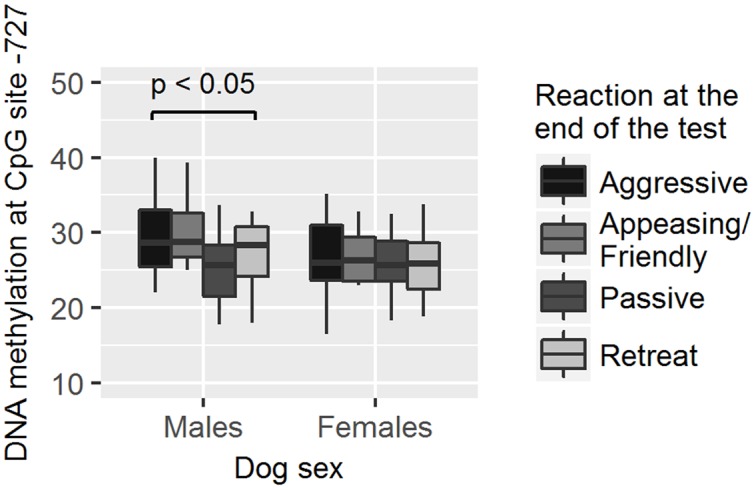
Association between methylation levels at position –727 and their reaction at the end of the Threatening Approach test. Male dogs approaching the experimenter either in an aggressive or in an appeasing/friendly manner had higher methylation levels than male dogs that remained passive or retreated. Horizontal bars represent medians, the bottom and the top of the boxes represent the lower and the upper quartiles, respectively, whiskers represent the interquartile range and filled circles represent outliers.
FIGURE 7.
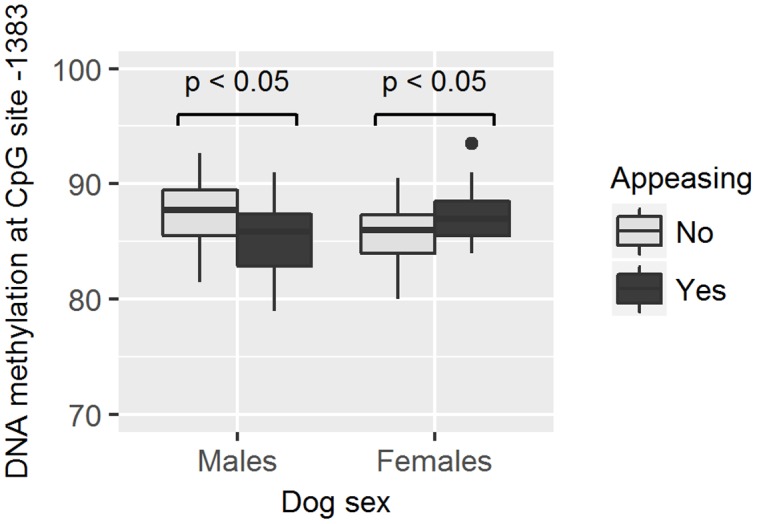
Association between methylation levels at position –1383 and the likelihood of dogs to approach the experimenter in an appeasing way. Males approaching the experimenter in an appeasing way had lower methylation levels than males who did not, while the opposite was true for female dogs. Horizontal bars represent medians, the bottom and the top of the boxes represent the lower and the upper quartiles, respectively, whiskers represent the interquartile range and filled circles represent outliers.
FIGURE 8.
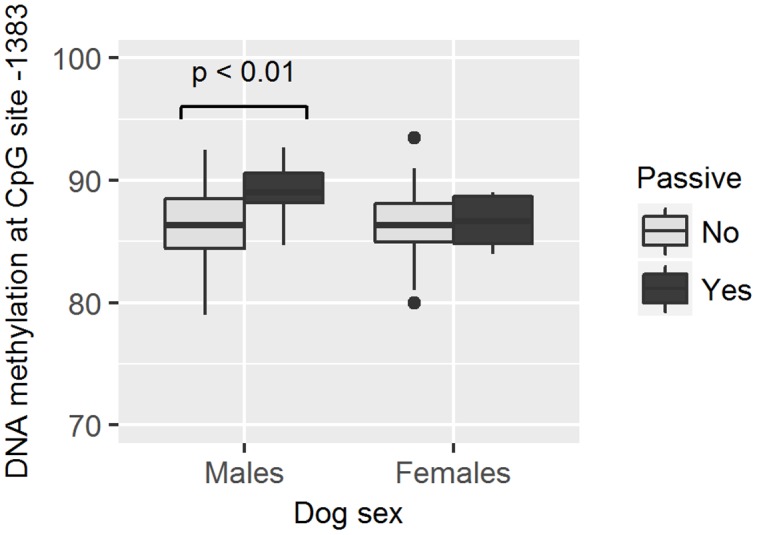
Association between methylation levels at position –1383 and the likelihood of dogs to stay passive during the Threatening Approach test. Males remaining passive had higher methylation levels than males showing any other reaction. Horizontal bars represent medians, the bottom and the top of the boxes represent the lower and the upper quartiles, respectively, whiskers represent the interquartile range and filled circles represent outliers.
Discussion
The present study explored for the first time the DNA methylation patterns in canids and their associations with pet dogs’ social behavior. Specifically, four CpG sites in the OXTR promoter were identified where at least 10% of inter-individual variation in their methylation level was observed. The methylation levels of these CpG sites were different in female and male dogs and were associated with the behavioral reaction dogs showed when exposed to social stress. These results provide the first evidence of an association between epigenetic modifications of OXTR and dog social behavior. In particular, we found higher methylation levels in females than in males at site -1383 and we found a tendency to have lower methylation level at site -727 in females than in males. Moreover, lower methylation levels in this position tended to be associated with a higher likelihood to approach a threatening unfamiliar person (either in an aggressive, appeasing or friendly manner) in males and a lower likelihood to remain passive or hide behind the owner. Regarding the two sites -751 and -1383, males with higher methylation levels were more likely to remain passive or to hide behind the owner than those having lower methylation levels.
It is not surprising that we found different methylation patterns in female and male dogs. Oxytocin is a hormone also with sex-related functions, therefore its receptors are expressed differently in males and females (Alves et al., 2015). It has also been shown that oxytocin administration and oxytocin level influence the social behavior of prairie voles in a sex-specific way (Bales and Carter, 2003; Bales et al., 2007). Similarly, in our study, a tendency for a different association was found in male and female dogs in regards to the appeasing behavior; while females were more likely to approach the experimenter in an appeasing manner if their methylation levels were higher in site -1383, in males we found the opposite relationship. These results might be explained by a differential interplay between the methylation of the OXTR gene and other biological mechanisms (e.g., the expression of sex hormones) and/or reflect a sex-specific response strategy to social threat.
Furthermore, our results suggest that different CpG sites might be differently involved in behavioral regulation. Higher promoter methylation levels generally lead to lower OXTR gene expression, which, in turn, leads to fewer available receptors for the oxytocin to bind. The present study suggests that the different sites might regulate OXTR expression in different manners: for instance, CpG sites -727 might be located in a transcription inhibitory region, where suppression of inhibition by methylation would potentially lead to higher gene expression (Portela and Esteller, 2010), or methylation of this site could trigger the use of an alternate, potentially more active, promoter (Maunakea et al., 2010). In fact, higher methylation levels on -751 or on -1383 were associated with more owner-directed behaviors or a passive state while higher methylation levels on -727 tended to lead to the opposite behavioral outcome.
Naturally, the identified associations can only be genuine if the analyzed biomarker – OXTR promoter methylation at the investigated CpG sites in canine buccal epithelia – reliably refers to neural processes, regulating the OXTR gene expression in the brain. A direct experimental verification of such a biological connection is unfortunately highly challenging, mainly because of the limited accessibility of brain tissues of (pet) dogs. Still, indirect evidence suggests that OXTR promoter methylation levels as measured in buccal epithelium could indeed be of physiological relevance for behavior. Human-related studies identified strong correlation between brain and surrogate tissue DNA methylation levels regarding functionally important OXTR promoter CpG sites (Gregory et al., 2009; Jack et al., 2012; Bell et al., 2015; Chagnon et al., 2015; Puglia et al., 2015). As buccal epithelium is of the same germ layer origin as neural tissues (Tam and Behringer, 1997), it is plausible that the inherited component of DNA methylation states remains relatively similar during embryonic development, when basic DNA methylation patterns are established (Reik and Walter, 2001). In later life, these patterns are modified both by environmental factors and stochastic effects (Kaminsky et al., 2009; Aguilera et al., 2010; Choi and Friso, 2010). How different tissues could react to environmental stimuli in similar manners in terms of DNA methylation is yet to be elucidated. However, it has been reported in humans that, even in the case of white blood cells, dynamic changes in OXTR promoter methylation can be observed in response to social stimuli (Unternaehrer et al., 2012). Given that OXTR protein is also expressed in squamous epithelial cells according to The Human Protein Atlas (Uhlen et al., 2010, 2015), it is feasible that nerves innervating the oral epithelium directly mediate epigenetic communication between brain and buccal tissues (Kress et al., 2006; Kim et al., 2009; da Silva et al., 2015). It is important to mention, however, that it has been shown that OXTR promoter methylation in rodents brain affects transcription efficiency in a region-specific manner (Harony-Nicolas et al., 2014). Future studies should investigate associations between OXTR methylation in brain tissues and in buccal cells and tissue-specific oxytocin expression in order to fully inform the psychophysiological role of OXTR methylation in the buccal epithelium in dogs.
Contrary to our predictions, in the present study, we could not find any association between owner behavior and methylation levels of the OXTR gene of their dogs. It might be that the methylation profiles of the CpG sites investigated in the present study are mostly inherited (Reik and Walter, 2001) and/or not be representative of the methylation levels of the OXTR gene in brain tissues that could still be potentially affected by the environment. In addition, it is possible that the owner interaction styles analyzed in the present study were factors not strong enough for such methylation changes. Indeed, the present analyses were carried out in a rather uniform population of purebred Border Collies kept as pets, and it would be necessary to investigate different breeds and/or dogs living in different social environments (e.g., in shelters or as stray dogs) in order to further investigate the role of the environment in shaping dog social behavior through epigenetic modifications. Further on, in this study we focused on the promoter of the OXTR gene, and we cannot exclude the possibility that owners’ interaction styles might affect other regulatory regions in other genes.
It is important to notice that the OXTR methylation might not be the only factor to influence dog behavior, it is possibly also mediated by which SNPs the dog was carrying (Smearman et al., 2016). In fact, some studies highlighted a correlation between degree of methylation and SNPs (Bell et al., 2012; Smith et al., 2015). In our study, we did not take into account the genetic background of our subjects, but future studies should address the interaction between environment, SNPs, DNA methylation and behavior in order to have a better understanding of the mechanisms regulating dog social behavior. Epigenetic modifications other than DNA methylation should also be investigated. It is also important to note that the pyrosequencing technique used for DNA methylation assessment is not suitable for differentiating between 5-methylcytosines and 5-hydroxymethylcytosines (Guibert and Weber, 2013), so it cannot be ascertained yet if (some of) the observed relationships are not linked to hydroxymethylation. Another important issue is that even when considering only a single epigenetic mark (DNA methylation) and a single gene, it would be useful to obtain data regarding the whole gene and all of its regulatory regions, i.e., not only a limited number of CpG sites in the promoter region. The present tissue choice (buccal epithelia) is unfortunately not suitable for such a comprehensive analysis mainly because of the obtainable DNA yield. Though buccal tissue has the major advantage of offering non-invasive sample taking and thus easy accessibility and keeping physiological effects of the sample taking procedure itself to a minimum, future studies should consider the use of other tissues as well in order to ensure investigation of a larger number of CpG sites within the same population.
Social behavior is a complex and multi factorial phenotype regulated by various interacting mechanisms: genetic background as well as inherited and environmentally induced epigenetic modifications of the individuals. The present study focused on only one of the possible mechanisms, namely the methylation of a single gene promoter, without clearly disentangling between inherited or environmentally influenced epigenetic patterns. As such, our results can provide an initial contribution to shedding light on the complex processes shaping social behavior. In particular, by indicating epigenetic analyses as a novel tool for the understanding of the mechanisms regulating dog behavior and ultimately suggesting pet dogs as good models for the field of human epigenetics. Future studies would need to investigate the interactions between the methylation levels and the polymorphisms of OXTR, the correspondence between buccal DNA methylation states of the CpG analyzed here and those in different regions of the brain, the effect of methylation in those areas on nervous system functions and on dog behavior, and other environmental factors possibly influencing epigenetic modifications.
Author Contributions
GC, ZB, ZV, ZR, and MS-S designed the study. GC, ZB, BT, ZV, ZR, and MS-S prepared the study material and data acquisition. GC, ZB, and BT entered the data and prepared it for statistical analyses. GC, ZB, and BT analyzed the data. GC, ZB, BT, and ZV interpreted the data. ZV, ZR, and MS-S obtained funding. GC and ZB wrote the first draft of the manuscript. GC, BT, ZB, and ZV critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors gave final approval of the manuscript version to be published and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all dogs and owners participating in the study, Professor Ilona Kovalszky, head of Molecular Diagnostics Laboratory at the 1st Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research of Semmelweis University, for providing access to their PyroMark Q24 platform, as well as to Dr. Zsófia Nemoda and Dr. Péter Hollósi for helpful advice in pyrosequencing. In addition, we thank Ludwig Huber and Friederike Range for their support, Karin Bayer, Jennifer Bentlage, and Aleksandar Orlic for administrative help and Peter Füreder and Wolfgang Berger for technical support at the Clever Dog Lab.
Funding. This research was supported by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) project I 1271-B24 and the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund project OTKA-ANN 107726. Furthermore, we are thankful to Royal Canin for supporting the Clever Dog Lab.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00549/full#supplementary-material
References
- Aguilera O., Fernandez A. F., Munoz A., Fraga M. F. (2010). Epigenetics and environment: a complex relationship. J. Appl. Physiol. 109 243–251. 10.1152/japplphysiol.00068.2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aken B. L., Ayling S., Barrell D., Clarke L., Curwen V., Fairley S., et al. (2016). The Ensembl gene annotation system. Database 2016:baw093 10.1093/database/baw093 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alves E., Fielder A., Ghabriel N., Sawyer M., Buisman-Pijlman F. T. A. (2015). Early social environment affects the endogenous oxytocin system: a review and future directions. Front. Endocrinol. 6:32 10.3389/fendo.2015.00032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arahori M., Hori Y., Saito A., Chijiiwa H., Takagi S., Ito Y., et al. (2015). The oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) polymorphism in cats (Felis catus) is associated with “Roughness” assessed by owners. J. Vet. Behav. Clin. Appl. Res. 11 109–112. 10.1016/j.jveb.2015.07.039 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bales K. L., Carter C. S. (2003). Sex differences and developmental effects of oxytocin on aggression and social behavior in prairie voles (Microtus ochrogaster). Horm. Behav. 44 178–184. 10.1016/S0018-506X(03)00154-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bales K. L., Perkeybile A. M. (2012). Developmental experiences and the oxytocin receptor system. Horm. Behav. 61 313–319. 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2011.12.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bales K. L., Plotsky P. M., Young L. J., Lim M. M., Grotte N., Ferrer E., et al. (2007). Neonatal oxytocin manipulations have long-lasting, sexually dimorphic effects on vasopressin receptors. Neuroscience 144 38–45. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.09.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell A. F., Carter C. S., Steer C. D., Golding J., Davis J. M., Steffen A. D., et al. (2015). Interaction between oxytocin receptor DNA methylation and genotype is associated with risk of postpartum depression in women without depression in pregnancy. Front. Genet. 6:243 10.3389/fgene.2015.00243 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. T., Tsai P.-C., Yang T.-P., Pidsley R., Nisbet J., Glass D., et al. (2012). Epigenome-wide scans identify differentially methylated regions for age and age-related phenotypes in a healthy ageing population. PLoS Genet. 8:e1002629 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002629 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berglund J., Quilez J., Arndt P. F., Webster M. T. (2015). Germline methylation patterns determine the distribution of recombination events in the dog genome. Genome Biol. Evol. 7 522–530. 10.1093/gbe/evu282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bick J., Naumova O., Hunter S., Barbot B., Lee M., Luthar S. S., et al. (2012). Childhood adversity and DNA methylation of genes involved in the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis and immune system: whole-genome and candidate-gene associations. Dev. Psychopathol. 24 1417–1425. 10.1017/S0954579412000806 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boor K., Ronai Z., Nemoda Z., Gaszner P., Sasvari-Szekely M., Guttman A., et al. (2002). Noninvasive genotyping of dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4) using nanograms of DNA from substance-dependent patients. Curr. Med. Chem. 9 793–797. 10.2174/0929867024606821 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowlby J. (1969). Attachment and Loss, Vol. 1 New York, NY: Basic Books [Google Scholar]
- Boyko A. R. (2011). The domestic dog: man’s best friend in the genomic era. Genome Biol. 12:216 10.1186/gb-2011-12-2-216 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. K., Aulino E. A., Freeman A. R., Miller T. V., Witchey S. K. (2016). Oxytocin and behavior: lessons from knockout mice. Dev. Neurobiol. 77 190–201. 10.1002/dneu.22431 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chagnon Y. C., Potvin O., Hudon C., Préville M. (2015). DNA methylation and single nucleotide variants in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and oxytocin receptor (OXTR) genes are associated with anxiety/depression in older women. Front. Genet. 6:230 10.3389/fgene.2015.00230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champagne F. A., Curley J. P. (2009). Epigenetic mechanisms mediating the long-term effects of maternal care on development. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 33 593–600. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.10.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi S.-W., Friso S. (2010). Epigenetics: a new bridge between nutrition and health. Adv. Nutr. 1 8–16. 10.3945/an.110.1004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimarelli G., Turcsán B., Bánlaki Z., Range F., Virányi Z. (2016). Dog owners’ interaction styles: their components and associations with reactions of pet dogs to a social threat. Front. Psychol. 7:1979 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01979 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva V. A. M., Dantas M. D. S., Silva L. A. D. C., Carneiro J. G., Schamber-Reis B. L. F. (2015). Testosterone depletion induces demethylation of murine reelin promoter CpG dinucleotides: a preliminary study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015 286369 10.1155/2015/286369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dadds M. R., Moul C., Cauchi A., Dobson-Stone C., Hawes D. J., Brennan J., et al. (2014). Methylation of the oxytocin receptor gene and oxytocin blood levels in the development of psychopathy. Dev. Psychopathol. 26 33–40. 10.1017/S0954579413000497 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deaton A. M., Bird A. (2011). CpG islands and the regulation of transcription. Genes Dev. 25 1010–1022. 10.1101/gad.2037511 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi A., Park I.-H., Wen B., Murakami P., Aryee M. J., Irizarry R., et al. (2009). Differential methylation of tissue- and cancer-specific CpG island shores distinguishes human induced pluripotent stem cells, embryonic stem cells and fibroblasts. Nat. Genet. 41 1350–1353. 10.1038/ng.471 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebstein R. P., Knafo A., Mankuta D., Chew S. H., Lai P. S. (2012). The contributions of oxytocin and vasopressin pathway genes to human behavior. Horm. Behav. 61 359–379. 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2011.12.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. (2015). The neurobiology of mammalian parenting and the biosocial context of human caregiving. Horm. Behav. 77 3–17. 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.10.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gácsi M., Maros K., Sernkvist S., Faragó T., Miklósi Á. (2013). Human analogue safe haven effect of the owner: behavioural and heart rate response to stressful social stimuli in dogs. PLoS ONE 8:e58475 10.1371/journal.pone.0058475 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbally M., Lewis A. J., Ijzendoorn M. V., Permezel M. (2015). The role of oxytocin in mother-infant relations: a systematic review of human studies. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 19 1–14. 10.3109/10673229.2011.549771 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. D., Allis C. D., Bernstein E. (2007). Epigenetics: a landscape takes shape. Cell 128 635–638. 10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory S. G., Connelly J. J., Towers A. J., Johnson J., Biscocho D., Markunas C. A., et al. (2009). Genomic and epigenetic evidence for oxytocin receptor deficiency in autism. BMC Med. 7:62 10.1186/1741-7015-7-62 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillon C., Krimsky M., Charney D. R., Vytal K., Ernst M., Cornwell B. (2013). Oxytocin increases anxiety to unpredictable threat. Mol. Psychiatry 18 958–960. 10.1038/mp.2012.156 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guibert S., Weber M. (2013). Functions of DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation in mammalian development. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 104 47–83. 10.1016/B978-0-12-416027-9.00002-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hare B., Tomasello M. (2005). Human-like social skills in dogs? Trends Cogn. Sci. 9 439–444. 10.1016/j.tics.2005.07.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harony-Nicolas H., Mamrut S., Brodsky L., Shahar-Gold H., Barki-Harrington L., Wagner S. (2014). Brain region-specific methylation in the promoter of the murine oxytocin receptor gene is involved in its expression regulation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 39 121–131. 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.10.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hejjas K., Vas J., Topal J., Szantai E., Ronai Z., Szekely A., et al. (2007). Association of polymorphisms in the dopamine D4 receptor gene and the activity-impulsivity endophenotype in dogs. Anim. Genet. 38 629–633. 10.1111/j.1365-2052.2007.01657.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernádi A., Kis A., Kanizsár O., Tóth K., Miklósi B., Topál J. (2015). Intranasally administered oxytocin affects how dogs (Canis familiaris) react to the threatening approach of their owner and an unfamiliar experimenter. Behav. Processes 119 1–5. 10.1016/j.beproc.2015.07.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm S. (1979). A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand. J. Stat. 6 65–70. 10.2307/4615733 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Horváth Z., Igyártó B.-Z., Magyar A., Miklósi Á. (2007). Three different coping styles in police dogs exposed to a short-term challenge. Horm. Behav. 52 621–630. 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2007.08.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack A., Connelly J. J., Morris J. P. (2012). DNA methylation of the oxytocin receptor gene predicts neural response to ambiguous social stimuli. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 6:280 10.3389/fnhum.2012.00280 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminsky Z. A., Tang T., Wang S.-C., Ptak C., Oh G. H. T., Wong A. H. C., et al. (2009). DNA methylation profiles in monozygotic and dizygotic twins. Nat. Genet. 41 240–245. 10.1038/ng.286 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M.-S., Kondo T., Takada I., Youn M.-Y., Yamamoto Y., Takahashi S., et al. (2009). DNA demethylation in hormone-induced transcriptional derepression. Nature 461 1007–1012. 10.1038/nature08456 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch P., Esslinger C., Chen Q., Mier D., Lis S., Siddhanti S., et al. (2005). Oxytocin modulates neural circuitry for social cognition and fear in humans. J. Neurosci. 25 11489–11493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kis A., Bence M., Lakatos G., Pergel E., Turcsán B., Pluijmakers J., et al. (2014). Oxytocin receptor gene polymorphisms are associated with human directed social behavior in dogs (Canis familiaris). PLoS ONE 9:e83993 10.1371/journal.pone.0083993 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress C., Thomassin H., Grange T. (2006). Active cytosine demethylation triggered by a nuclear receptor involves DNA strand breaks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 11112–11117. 10.1073/pnas.0601793103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumsta R., Hummel E., Chen F. S., Heinrichs M. (2013). Epigenetic regulation of the oxytocin receptor gene: implications for behavioral neuroscience. Front. Neurosci. 7:83 10.3389/fnins.2013.00083 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusui C., Kimura T., Ogita K., Nakamura H., Matsumura Y., Koyama M., et al. (2001). DNA methylation of the human oxytocin receptor gene promoter regulates tissue-specific gene suppression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 289 681–686. 10.1006/bbrc.2001.6024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Zhao Y., Li R., Broster L. S., Zhou C., Yang S. (2015). Association of oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) rs53576 polymorphism with sociality: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 10:e0131820 10.1371/journal.pone.0131820 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald K., Feifel D. (2013). Helping oxytocin deliver: considerations in the development of oxytocin-based therapeutics for brain disorders. Front. Neurosci. 7:35 10.3389/fnins.2013.00035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald K. S. (2012). Sex, receptors, and attachment: a review of individual factors influencing response to oxytocin. Front. Neurosci. 6:194 10.3389/fnins.2012.00194 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda S., Ohno K., Fujiwara-Igarashi A., Tomiyasu H., Fujino Y., Tsujimoto H. (2014). Methylation of TNFRSF13B and TNFRSF13C in duodenal mucosa in canine inflammatory bowel disease and its association with decreased mucosal IgA expression. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 160 97–106. 10.1016/j.vetimm.2014.04.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maunakea A. K., Nagarajan R. P., Bilenky M., Ballinger T. J., D’Souza C., Fouse S. D., et al. (2010). Conserved role of intragenic DNA methylation in regulating alternative promoters. Nature 466 253–257. 10.1038/nature09165 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan P. O., Sasaki A., D’Alessio A. C., Dymov S., Labonté B., Szyf M., et al. (2009). Epigenetic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor in human brain associates with childhood abuse. Nat. Neurosci. 12 342–348. 10.1038/nn.2270 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan P. O., Suderman M., Sasaki A., Huang T. C. T., Hallett M., Meaney M. J., et al. (2011). Broad epigenetic signature of maternal care in the brain of adult rats. PLoS ONE 6:e14739 10.1371/journal.pone.0014739 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miklósi Á., Topál J. (2013). What does it take to become “best friends”? Evolutionary changes in canine social competence. Trends Cogn. Sci. 17 287–294. 10.1016/j.tics.2013.04.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montrose L., Noonan C. W., Cho Y. H., Lee J., Harley J., O’Hara T., et al. (2015). Evaluating the effect of ambient particulate pollution on DNA methylation in Alaskan sled dogs: potential applications for a sentinel model of human health. Sci. Total Environ. 51 489–494. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrander E. A. (2005). The canine genome. Genome Res. 15 1706–1716. 10.1101/gr.3736605 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker H. G. (2012). Genomic analyses of modern dog breeds. Mamm. Genome 23 19–27. 10.1007/s00335-011-9387-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro J., Bates D., DebRoy S., Sarkar D. (2007). nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. Available at: http://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&btnG=Search&q=intitle:nlme:+Linear+and+nonlinear+mixed+effects+models#3 [Google Scholar]
- Portela A., Esteller M. (2010). Epigenetic modifications and human disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 28 1057–1068. 10.1038/nbt.1685 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powledge T. M. (2011). Behavioral epigenetics: how nurture shapes nature. Bioscience 61 588–592. 10.1525/bio.2011.61.8.4 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Puglia M. H., Lillard T. S., Morris J. P., Connelly J. J. (2015). Epigenetic modification of the oxytocin receptor gene influences the perception of anger and fear in the human brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112 3308–3313. 10.1073/pnas.1422096112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik W., Walter J. (2001). Genomic imprinting: parental influence on the genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2 21–32. 10.1038/35047554 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalev I., Ebstein R. P. (2013). Frontiers in oxytocin science: from basic to practice. Front. Neurosci. 7:250 10.3389/fnins.2013.00250 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smearman E. L., Almli L. M., Conneely K. N., Brody G. H., Sales J. M., Bradley B., et al. (2016). Oxytocin receptor genetic and epigenetic variations: association with child abuse and adult psychiatric symptoms. Child Dev. 87 122–134. 10.1111/cdev.12493 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. K., Kilaru V., Klengel T., Mercer K. B., Bradley B., Conneely K. N., et al. (2015). DNA extracted from saliva for methylation studies of psychiatric traits: evidence tissue specificity and relatedness to brain. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 168 36–44. 10.1002/ajmg.b.32278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staes N., Stevens J. M. G., Helsen P., Hillyer M., Korody M., Eens M. (2014). Oxytocin and vasopressin receptor gene variation as a proximate base for inter- and intraspecific behavioral differences in bonobos and chimpanzees. PLoS ONE 9:e113364 10.1371/journal.pone.0113364 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallen M., De Dreu C. K. W., Shalvi S., Smidts A., Sanfey A. G. (2012). The herding hormone. Psychol. Sci. 23 1288–1292. 10.1177/0956797612446026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam P. P., Behringer R. R. (1997). Mouse gastrulation: the formation of a mammalian body plan. Mech. Dev. 68 3–25. 10.1016/S0925-4773(97)00123-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tammen S. A., Friso S., Choi S.-W. (2013). Epigenetics: the link between nature and nurture. Mol. Aspects Med. 34 753–764. 10.1016/j.mam.2012.07.018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasello M., Kaminski J. (2009). Like infant, like dog. Science 325 1213–1214. 10.1126/science.1179670 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomiyasu H., Fujiwara-Igarashi A., Goto-Koshino Y., Fujino Y., Ohno K., Tsujimoto H. (2014). Evaluation of DNA methylation profiles of the CpG island of the ABCB1 gene in dogs with lymphoma. Am. J. Vet. Res. 75 835–841. 10.2460/ajvr.75.9.835 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topál J., Miklósi Á, Csányi V., Dóka A. (1998). Attachment behavior in dogs (Canis familiaris): a new application of Ainsworth’s (1969) strange situation test. J. Comp. Psychol. 112 219–229. 10.1037//0735-7036.112.3.219 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlen M., Fagerberg L., Hallstrom B. M., Lindskog C., Oksvold P., Mardinoglu A., et al. (2015). Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 347:1260419 10.1126/science.1260419 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlen M., Oksvold P., Fagerberg L., Lundberg E., Jonasson K., Forsberg M., et al. (2010). Towards a knowledge-based human protein atlas. Nat. Biotechnol. 28 1248–1250. 10.1038/nbt1210-1248 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unternaehrer E., Luers P., Mill J., Dempster E., Meyer A. H., Staehli S., et al. (2012). Dynamic changes in DNA methylation of stress-associated genes (OXTR, BDNF) after acute psychosocial stress. Transl. Psychiatry 2:e150 10.1038/tp.2012.77 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unternaehrer E., Meyer A. H., Burkhardt S. C. A., Dempster E., Staehli S., Theill N., et al. (2015). Childhood maternal care is associated with DNA methylation of the genes for brain-derived neurotrophic factor ( BDNF ) and oxytocin receptor (OXTR) in peripheral blood cells in adult men and women. Stress 18 451–461. 10.3109/10253890.2015.1038992 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ijzendoorn M. H., Bakermans-Kranenburg M. J., Ebstein R. P. (2011). Methylation matters in child development: toward developmental behavioral epigenetics. Child Dev. Perspect. 5 305–310. 10.1111/j.1750-8606.2011.00202.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Vas J., Topál J., Gácsi M., Miklósi Á., Csányi V. (2005). A friend or an enemy? Dogs’ reaction to an unfamiliar person showing behavioural cues of threat and friendliness at different times. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 94 99–115. 10.1016/j.applanim.2005.02.001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Vas J., Topál J., Gyõri B., Miklósi Á. (2008). Consistency of dogs’ reactions to threatening cues of an unfamiliar person. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 112 331–344. 10.1016/j.applanim.2007.09.002 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver I. C. G., Cervoni N., Champagne F. A., D’Alessio A. C., Sharma S., Seckl J. R., et al. (2004). Epigenetic programming by maternal behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 7 847–854. 10.1038/nn1276 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaya Y., Sugiya H., Watari T. (2015). Methylation of free-floating deoxyribonucleic acid fragments in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of dogs with chronic bronchitis exposed to environmental tobacco smoke. Ir. Vet. J. 68 7 10.1186/s13620-015-0035-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang T.-Y., Hellstrom I. C., Bagot R. C., Wen X., Diorio J., Meaney M. J. (2010). Maternal care and DNA methylation of a glutamic acid decarboxylase 1 promoter in rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 30 13130–13137. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1039-10.2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.