Figure 6. Effect of HnRNP-L aberrant expression on prostater cancer apoptosis.
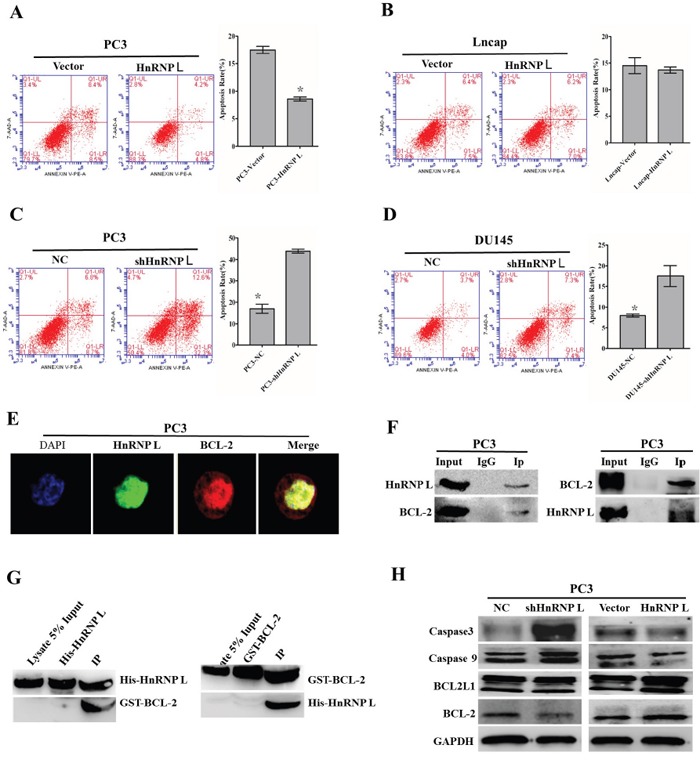
A, B, C and D. Overexpression of HnRNP-L inhibits the apoptosis of PC3 (A) and Lncap (B) cells, whereas HnRNP-L knockdown promotes the apoptosis of PC3 (C) and DU145 (D) cells, which were analyzed by flow cytometry using Annexin V-FITC/PI staining. Statistical analysis of flow cytometry results. The presented columns are given as the means ± SD. *:P<0.05 (vs. control). E. Co-localization of HnRNP-L with BCL-2 in PC3 cells. PC3 cells were immunostained for HnRNP-L (green) and BCL-2 (red), followed by con-focal-microscopic analysis of their co-localization. F. Reciprocal co-immunoprecipitation assays of HnRNP-L and BCL-2 in PC3 cells, which were performed in vitro. IgG group was served as IP antibody control. G. Pull down assays of His-tagged HnRNP-L and GST-tagged BCL-2, which were induced to express abundantly in Rossatte bacteria. The input group and tag-purification (His tag or GST tag) group were treated as negative control in this experiment. H. Western blotting was used to exam the expression of BCL-2, caspase 3 and caspase 9 after the ectopic expression of HnRNP-L. GAPDH was served as a loading control.
