Figure 4.
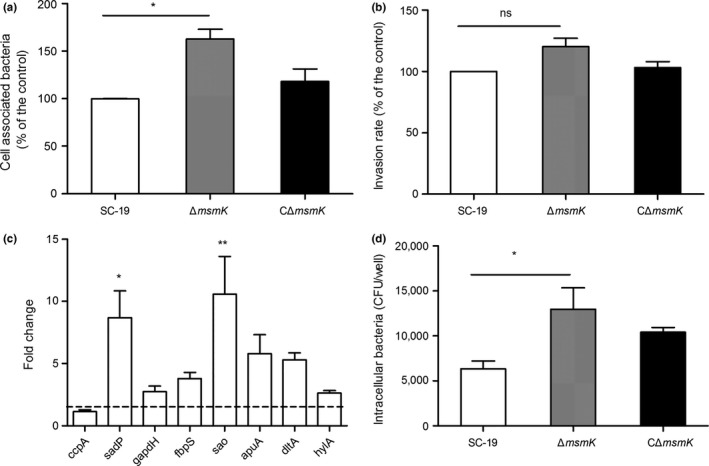
msmK absence promotes adhesion to Hep‐2 cells and susceptibility to macrophages. (a) Cell‐associated bacteria recovered after incubation with HEp‐2 cells. The number of the recovered SC‐19 serves as the control, which was regarded as 100% cell association. Up to 100% cell association represents 83,600 colony‐forming unit (CFU)/well. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. *, p ≤ 0.05. (b) Pathogen invasion of HEp‐2 cells. Extracellular bacteria were eradicated through antibiotic treatment. The number of the recovered intracellular SC‐19 serves as the control, which was regarded as 100% cell invasion. Up to 100% cell invasion represents the entry of 3,060 CFU/well. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. ns, p > 0.05. (c) Gene expression analysis of adherence‐related genes of ΔmsmK compared with SC‐19. The dotted line means +2‐fold change. The height of the bars indicates the mean values for the relative expression data ± SEM. *, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01. (d) Phagocytosis of SS2 strains by RAW264.7 cells. Phagocytosed bacteria were recovered after antibiotic treatment. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *, p ≤ 0.05
