Abstract
Selection experiments and protein engineering were used to identify an amino acid position in integral membrane alkane hydroxylases (AHs) that determines whether long-chain-length alkanes can be hydroxylated by these enzymes. First, substrate range mutants of the Pseudomonas putida GPo1 and Alcanivorax borkumensis AP1 medium-chain-length AHs were obtained by selection experiments with a specially constructed host. In all mutants able to oxidize alkanes longer than C13, W55 (in the case of P. putida AlkB) or W58 (in the case of A. borkumensis AlkB1) had changed to a much less bulky amino acid, usually serine or cysteine. The corresponding position in AHs from other bacteria that oxidize alkanes longer than C13 is occupied by a less bulky hydrophobic residue (A, V, L, or I). Site-directed mutagenesis of this position in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv AH, which oxidizes C10 to C16 alkanes, to introduce more bulky amino acids changed the substrate range in the opposite direction; L69F and L69W mutants oxidized only C10 and C11 alkanes. Subsequent selection for growth on longer alkanes restored the leucine codon. A structure model of AHs based on these results is discussed.
The alkane hydroxylases (AHs) of Pseudomonas putida GPo1 and other eubacteria are of great interest for biocatalytic (37) and environmental studies (35) and as prototypes of a large family of integral membrane non-heme iron oxygenases which includes desaturases and xylene monooxygenases (24). In addition, AHs occur in pathogens such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Legionella pneumophila, in which they have unknown roles.
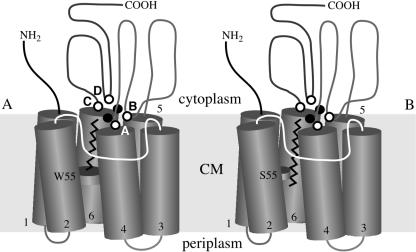
The P. putida GPo1 AH catalyzes the hydroxylation of linear and branched aliphatic, alicyclic, and alkylaromatic compounds (7, 20, 31); oxidation of terminal alcohols to the corresponding aldehydes; demethylation of branched methyl ethers; sulfoxidation of thioethers; and epoxidation of terminal olefins (12, 13, 18, 19) and allyl alcohol derivatives (6). One of the substrate range studies was used to estimate the approximate dimensions of the substrate-binding site (31). However, our attempts to determine the three-dimensional structure of the integral membrane AH failed, and three-dimensional structures of related proteins are not available, either. Figure 1 shows a schematic topology model of P. putida GPo1 AlkB based on an analysis of the hydrophobicity and gene fusions with alkaline phosphatase and β-galactosidase (34). Transmembrane (TM) helices 1 and 2, 3 and 4, and 5 and 6 are likely to form pairs because the loops connecting the three helix pairs on the periplasmic side are very short. However, nothing is known about the spatial arrangement and relative angles of the TM helices or the presence or absence of kinks. AlkB contains two iron atoms that are liganded to histidine residues located in four highly conserved, short sequence motifs (26, 28). The four sequence motifs are indicated in Fig. 1 and are located near the ends of TM helices 4 and 6. Alanine scanning has shown that the eight conserved histidines in motifs A, B, and D are indeed essential for the activity of AlkB (25). The single conserved histidine in motif C (NYXEHYG) was identified as an additional potential ligand because it is conserved in all AH sequences (28, 33). In addition, the corresponding histidine in P. putida mt-2 xylene monooxygenase was found to be essential for activity (M. Wubbolts, personal communication). Amino acids lining the substrate-binding pocket have not been identified.
FIG. 1.
Topology model of the P. putida GPo1 AH. The TM helices are represented by straight cylinders and numbered 1 through 6, and the connecting peptides are indicated by lines between the cylinders (not to scale). The N- and C-terminal ends of the protein are located in the cytoplasm, and the TM helices are connected by three short peptides on the periplasmic side of the membrane. About 60 to 65% of AlkB is located in the cytoplasm (34). (A) Wild-type enzyme (W55) binding dodecane; (B) W55S mutant enzyme binding hexadecane. The open circles denote the approximate locations of the four conserved histidine-containing sequence motifs (motif A, H138EXXHK143; motif B, E167HXXGHH173; motif C, N269YXEHYG275; and motif D, L309QRHXDHHA317), two of which (motifs A and C) are located at the ends of TM helices 4 and 6, close to the surface of the cytoplasmic membrane. Filled circles denote the approximate locations of the two iron atoms liganded by the conserved histidine-containing sequence motifs.
In this study, we used selection experiments to identify an amino acid position that affects the substrate range of the P. putida GPo1 and Alcanivorax borkumensis AP1 AHs. Based on these results, we carried out site-directed mutagenesis of the equivalent position in the M. tuberculosis H37Rv AH, which confirmed the role of the identified position.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains, plasmids, and media.
Strains used in this study are listed in Table 1. Luria-Bertani broth (22) and E2 medium (15) supplemented with carbon sources or antibiotics were used throughout. MT trace elements (15) were added to minimal media. Escherichia coli recombinants harboring plasmids were grown with appropriate antibiotics (tetracycline, 12.5 μg/ml; ampicillin, 100 μg/ml; and gentamicin, 10 μg/ml). For Pseudomonas fluorescens KOB2Δ1 recombinants, gentamicin was used at 100 μg/ml. For P. putida GPo12 recombinants, tetracycline (12.5 μg/ml) and gentamicin (25 μg/ml) were used. Recombinants were grown on solid agar E2 media with C5 to C16 alkanes as the sole C and energy source, as described previously (27).
TABLE 1.
Strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strain or plasmid | Relevant characteristic(s) | Reference(s), source, or source strain |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli GEc137 | E. coli DH1 fadR | 5 |
| E. coli DH10B | Cloning strain | Invitrogen |
| M. tuberculosis H37Rv | Virulent strain, possibly degrades alkanes | ATCC 27294 |
| P. fluorescens CHA0 | C10 to C28n-alkane-degrading biocontrol strain | 9 |
| P. fluorescens KOB2Δ1 | P. fluorescens CHA0 alkB knockout | 27 |
| P. putida GPo1 | C5 to C12n-alkane-degrading strain | 23, 33 |
| P. putida GPo12 | P. putida GPo1 cured of OCT | 14 |
| pCom8 | Expression vector, PalkB GmroriT alkS | 29 |
| pKKPalk | Expression vector, PalkB Apr | 29 |
| RK600 | Helper plasmid for triparental matings | 3 |
| pGEc47ΔB | ΔB derivative of pGEc47 | 34 |
| pCom8-alkB-GPo1 | pCom8 with alkB from P. putida GPo1 | 27 |
| pCom8-alkB-GPo1-H273A | pCom8-alkB-GPo1 with H273A mutation | This study |
| pCom8-alkB-GPo1-H273Q | pCom8-alkB-GPo1 with H273Q mutation | This study |
| pCom8-alkB-GPo1-W55S | pCom-alkB-GPo1 with W55S mutation | This study |
| pCom8-alkB-GPo1-W55C | pCom-alkB-GPo1 with W55C mutation | This study |
| pKKPalk-alkB-GPo1 | pKKPalk with alkB from P. putida GPo1 | This study |
| pKKPalk-alkB-GPo1-W55S | pKKPalk-alkB-GPo1 with W55S mutation | This study |
| pKKPalk-alkB-GPo1-W55C | pKKPalk-alkB-GPo1 with W55C mutation | This study |
| pCom8-alkB1-AP1 | pCom8 with alkB1 from A. borkumensis AP1 | 27, 32 |
| pCom8-alkB1-AP1-W58S | pCom8-alkB1-AP1 with W55S mutation | This study |
| pCom8-alkB1-AP1-W58C | pCom8-alkB1-AP1 with W55C mutation | This study |
| pCom8-alkB1-AP1-W58L | pCom8-alkB1-AP1 with W55L mutation | This study |
| pCom8-alkB1-AP1-W58G | pCom8-alkB1-AP1 with W55G mutation | This study |
| pCom8-alkB-H37Rv | pCom8 with alkB from M. tuberculosis H37Rv | 27 |
| pCom8-alkB-H37Rv-L69F | pCom8-alkB-H37Rv with L69F mutation | This study |
| pCom8-alkB-H37Rv-L69W | pCom8-alkB-H37Rv with L69W mutation | This study |
To determine the growth rates of Pseudomonas recombinants reported in Table 2 and/or to select for mutations in the alkB genes that would allow growth, 5-ml Luria-Bertani broth precultures with appropriate antibiotics were inoculated with single colonies resulting from electroporation or triparental matings of plasmids containing wild-type or mutant alkB genes. Main cultures (500-ml baffled Erlenmeyer flasks with 100 ml of E2 medium and 0.5% [vol/vol] n-alkanes as a carbon source) were inoculated with 1 ml of the precultures and incubated with shaking at 130 rpm and at 30°C. Citrate (0.02%) was added to P. fluorescens cultures. The cell densities in the cultures were estimated from the optical density at 450 nm (36).
TABLE 2.
Growth rates of P. fluorescens CHA0, P. fluorescens KOB2Δ1, P. putida GPo1, P. putida GPo12(pGEc47ΔB), and derived recombinants on n-alkanes ranging from C6 (hextane) to C16 (hexadecane)
| Strain or plasmidc | Growth rate (h−1) ona:
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6 | C8 | C10c | C11c | C12 | C13 | C14 | C16 | |
| GPo1 | 0.49 | 0.31 | 0.20 | 0.094 | 0.063 | 0.018 | 0 | 0 |
| GPo12(pCom8-alkB-GPo1) | 0.41 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.087 | 0.056 | 0.017 | 0 | 0 |
| GPo12(pCom8-alkB-GPo1-W55S) | 0.38 | 0.28 | 0.20 | 0.11 | 0.092 | 0.047 | 0 | 0 |
| GPo12(pCom8-alkB-GPo1-W55C) | 0.35 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.090 | 0.046 | 0 | 0 |
| GPo12(pCom8-alkB1-AP1) | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.081 | 0.0087 | 0 | 0 | ||
| CHA0b | 0.019 | 0.019 | 0.053 | |||||
| KOB2Δ1(pCom8-alkB-GPo1) | 0.009 | 0.013 | 0.0069 | 0.0020 | 0 | 0 | ||
| KOB2Δ1(pCom8-alkB-GPo1-W55S) | 0.0083 | 0.012 | 0.0068 | 0.0075 | 0.011 | 0.012 | ||
| KOB2Δ1(pCom8-alkB-GPo1-W55C) | 0.0087 | 0.012 | 0.0070 | 0.0077 | 0.012 | 0.013 | ||
| KOB2Δ1(pCom8-alkB1-AP1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| KOB2Δ1*(pCom8-alkB1-AP1) | 0.028 | 0.021 | 0.026 | 0.0091 | 0 | 0 | ||
| KOB2Δ1*(pCom8-alkB1-AP1-W58S) | 0.018 | 0.023 | 0.027 | 0.017 | 0.035 | 0.017 | ||
| KOB2Δ1*(pCom8-alkB1-AP1-W58L) | 0.014 | 0.024 | 0.022 | 0.0076 | 0.0051 | 0 | ||
| KOB2Δ1(pCom8-alkB-H37Rv) | 0.025 | 0.027 | 0.043 | 0.043 | 0.041 | 0.038 | ||
| KOB2Δ1(pCom8-alkB-H37Rv-L69F) | 0.024 | 0.0081 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| KOB2Δ1(pCom8-alkB-H37Rv-L69W) | 0.011 | 0.0053 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
Average growth rates of two parallel cultures inoculated from the same preculture (in all cases, the difference in growth rate was less than 10%). To reduce the toxicity of C10 and C11 to KOB2Δ1 recombinants, these alkanes were diluted in heptamethylnonane (1:3 for C10 and 1:1 for C11).
Data are from reference 27.
*, uncharacterized mutation in KOB2Δ1 that allows functional expression of AP1 AlkB1.
Cultures that did not start to grow within a week were further incubated with shaking at 130 rpm and at 30°C for as long as was necessary to obtain growth (several weeks to several months). Once growth started, the optical density at 450 nm was monitored until the stationary phase, 1 ml from the cultures was used to inoculate new cultures, which were grown to the stationary phase, and plasmid was isolated and sequenced to identify mutations in the alkB gene. All cultures were carried out at least in duplicate.
DNA manipulations.
E. coli strains were transformed by electroporation according to the method of Dower et al. (4). P. fluorescens KOB2Δ1 was transformed by electroporation according to the method of Højberg et al. (11). Plasmids were transferred to P. putida GPo12(pGEc47ΔB) by triparental matings (27). Plasmid DNA was isolated with a Roche highly pure plasmid isolation kit or according to the method of Birnboim and Doly (2) for Pseudomonas recombinants. The P. putida GPo1 alkB gene was amplified from pGEc47 (5) with primers B5-Eco (GGAGAATTCCAAATGCTTGAG [EcoRI site is underlined]) and B3-Hind (TTTGTGAAAGCTTTCAACGCC [HindIII site is underlined]) and was cloned between the EcoRI and HindIII sites of pCom8 (29). The M. tuberculosis H37Rv and A. borkumensis AP1 alkB genes were cloned in pCom8 as described previously (27). Mutations were introduced in the H37Rv alkB gene by using the QuikChange method and the primers MT-L69F-fw (TCGGACCGATCCTGTTCTACGTaTTGTTGCCGCTTCT) and MT-L69W-fw (CTGTGGATCGGACCaATCCTGtggTACGTCTTGTTGCC). The primers introduce a SnaBI site and a BstXI site (underlined), respectively, to facilitate the screening of the mutants. H273A and H273Q mutations were introduced in the GPo1 alkB gene by using primers GPo1-H273A-fw (GCGAACTATATTGAAgcTTACGGCTTGCTCCGT) and GPo1-H273Q-fw (ACTATATTGAACAGTACGGtcTaCTCCGTCAAAAA). Lowercase letters indicate changed bases. These primers also introduce HindIII and AccI sites (underlined). Both strands of the pCom8 inserts were sequenced on a Li-Cor 4000L sequencer with the Amersham Thermosequenase cycle sequencing kit and IRD800-labeled PalkFw3 (GCCAGCTCGTGTTTTTCCAGCAGACG) and pKKRev (GAGTTCGGCATGGGGTCAGGTG) (MWG-Biotech). Nucleotide and amino acid sequences were analyzed and compared using LASERGENE Navigator software from DNASTAR. Nucleotide and amino acid sequences were compared with the EMBL, Swiss-Prot, and GenBank databases by using the BLAST application (1). BLAST searches were carried out at the NCBI website (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/).
RESULTS
Selection for the hydroxylation of long-chain-length n-alkanes by the P. putida GPo1 and A. borkumensis AP1 AHs.
Growth experiments using baffled Erlenmeyer flasks showed that P. putida GPo1 is able to grow well on alkanes ranging from C6 to C13, with growth rates ranging from 0.49 h−1 (doubling time, 1.7 h) for C6 to 0.018 h−1 (doubling time, 40 h) for C13 (Table 2). Selection experiments to obtain mutants of P. putida GPo1 able to grow on alkanes longer than C13 failed also in the presence of a gratuitous inducer of the alk genes, dicyclopropylketone (8), and/or biosurfactants to facilitate alkane uptake by the strain, such as rhamnolipids (0.01%) or Triton X-100 (0.1%), failed to facilitate alkane uptake by this strain. This result indicates that the host P. putida does not allow selection for mutants that are able to oxidize longer alkanes, presumably because an uptake system for such alkanes is lacking in this strain. Therefore, the P. putida GPo1 alkB gene was expressed in P. fluorescens KOB2Δ1, an alkB1 knockout derivative of P. fluorescens CHA0 that is able to take up alkanes up to C28 but is unable to grow on C10 to C16 alkanes unless an AH that is able to oxidize these alkanes is expressed in this strain (27). To this end, the GPo1 alkB gene encoding the integral membrane monooxygenase component of the AH system was cloned in the broad-host-range expression vector pCom8 (29) and transferred to P. fluorescens KOB2Δ1. For details on plasmids and host strains, see Table 1.
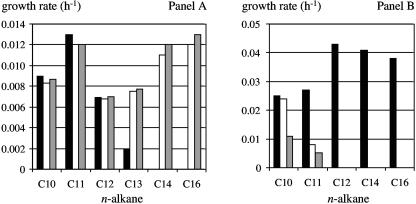
Recombinant strain KOB2Δ1(pCom8-alkB-GPo1) was tested for growth on alkanes in liquid cultures, and C10 to C13 alkanes were found to support the growth of the recombinant. C14 and C16 did not support growth (Table 2; Fig. 2A). However, after 3 to 4 weeks, the latter cultures did start to grow. New cultures inoculated with these long-term cultures started to grow immediately. To investigate whether mutations in the alkB gene had occurred, the inserts of plasmids isolated from seven independent C14 and C16 cultures were sequenced, which revealed point mutations in all cases in tryptophan codon W55, which had changed to a serine (TGG→TCG) or cysteine (TGG→TGC or TGT) codon. The fact that three different codon changes were found indicates that these mutants are not siblings that were already present in the precultures that were used to inoculate the long-term cultures. Mutations in other positions were not found. Two mutated plasmids, pCom8-alkB-GPo1-W55S and pCom8-alkB-GPo1-W55C, were retransferred to KOB2Δ1. The resulting recombinants were able to grow on C14 and C16 immediately, while the growth rate of those on C13 had tripled (Table 2; Fig. 2A).
FIG. 2.
(A) Growth rates on alkanes of P. fluorescens KOB2Δ1 containing the P. putida GPo1 alkB wild-type gene (black bars) or the alkB W55S and W55C mutant genes (white and grey bars, respectively). (B) Growth rates of P. fluorescens KOB2Δ1 containing the M. tuberculosis H37Rv alkB wild-type gene (black bars) and the L69F and/or L69W mutant gene (white bars and grey bars, respectively).
Similar selection experiments with P. fluorescens KOB2Δ1 were also carried out with A. borkumensis AP1 AlkB1, which oxidizes C5 to C12 alkanes. In this case, selection of mutants was not possible with the original strain, because A. borkumensis AP1 contains multiple AHs with overlapping substrate ranges (32). Here, we observed that the KOB2Δ1 recombinant containing plasmid pCom8-alkB1-AP1 initially did not grow on any of the alkanes. Cultures with C14 and C16 as C sources did not start to grow, even after several months. However, KOB2Δ1(pCom8-alkB1-AP1) cultures started to grow on C10 and C12, with delays of 1 to 2 months. Sequencing of the AP1 alkB1 gene from the C10 and C12 cultures revealed no changes. Retransfer of the plasmids to KOB2Δ1 yielded recombinants that, again, did not grow on alkanes for 1 to 2 months, suggesting that one or more mutations in the host were required to obtain functional expression of AP1 alkB1. These recombinants were not further investigated. KOB2Δ1(pCom8-alkB1-AP1) cells from the above-mentioned C10 and C12 cultures [now named KOB2Δ1*(pCom8-alkB1-AP1)] did start to grow on C13, C14, and C16 after 2 to 3 weeks, and sequencing of eight alkB1 genes from these cultures showed that tryptophan codon W58 (corresponding to W55 in GPo1 AlkB) had changed to serine (three cases), cysteine (three cases), glycine (one case), and leucine (one case). Recombinants containing W58S, W58C, and W58G mutations grew on C10 to C16 alkanes, while the W58L mutant allowed relatively weak growth on alkanes up to C14 but no growth on C16 (Table 2). Here, the growth rates of the recombinants could not be compared with those of the wild-type strain A. borkumensis AP1 because of the strong wall growth and clumping of this strain (32).
Effects of the W55S and W55C mutations on the growth of P. putida GPo12 recombinants on alkanes.
To investigate (i) why we failed to obtain substrate range mutants of P. putida GPo1, (ii) if the activity on short- and medium-chain-length alkanes remains the same, and (iii) whether the substrate range changes upon the mutation of codon W55, two mutant GPo1 alkB genes (a W55S mutant and a W55C mutant) and the wild-type alkB gene, all in pCom8, were transferred to P. putida GPo12(pGEc47ΔB). This recombinant is a derivative of GPo1 in which the OCT plasmid (carrying all the alk genes) is replaced by the pGEc47ΔB plasmid (carrying all the alk genes except alkB) (27). In liquid cultures, P. putida GPo12(pGEc47ΔB) recombinants containing pCom8-GPo1-alkB-W55S or pCom8-GPo1-alkB-W55C showed growth rates on C6 to C10 similar to, and growth rates on C11 to C13 higher than, those obtained with the wild-type alkB gene (Table 2). However, recombinants containing pCom8-GPo1-alkB-W55S or pCom8-GPo1-alkB-W55C did not grow on C14 or C16, even after induction with dicyclopropylketone and in the presence of 0.01% rhamnolipids or Triton X-100. In combination with the observation that we were not able to obtain substrate range mutants with GPo1, this result indicates that GPo1 and derived recombinants lack an uptake system for alkanes longer than C13.
Mutagenesis of the M. tuberculosis H37Rv AH.
To test the hypothesis that the position corresponding to W55 in AlkB-GPo1 affects the substrate range in long-chain-length AHs as well as in medium-chain-length AHs, we carried out site-directed mutagenesis of this position of the M. tuberculosis H37Rv AH, which was previously shown to oxidize C10 to C16 alkanes in KOB2Δ1 (27). Two mutants (the L69F and L69W mutants) were constructed and transferred to KOB2Δ1. The resulting recombinants grew on C10 and C11 but failed to grow on C12 to C16 alkanes, unlike the recombinant containing the wild-type sequence (Table 2; Fig. 2B). L69F and L69W mutant cultures started to grow on C12 to C16 alkanes after 2 to 3 weeks due to mutations changing the F69 and W69 codons to leucine (six cases) or serine (one case) codons.
As the L69F and L69W mutations limit the length of the accepted alkane to C11 and not C13, as was the case with wild-type GPo1 AlkB, the substrate range of the H37Rv AlkB mutants was within the range that can be tested well in P. putida. In this host, we found that growth rates of recombinants containing the wild-type sequence and the L69F mutants were identical on C9; the L69F mutant grew on C10 slightly slower, while the L69F recombinant initially did not grow on C12 to C13. In all cases, cultures eventually started to grow, and the L69F mutant reverted to L69 (three mutants were sequenced).
Mutagenesis of position H273 in the P. putida GPo1 AH.
H273A and H273Q mutant proteins of the P. putida GPo1 AH were constructed to test whether H273 in conserved histidine motif C is essential for activity. P. putida GPo12(pGEc47ΔB) recombinants containing pCom8-GPo1-alkB-H273A or -H273Q failed to grow on any of the alkanes tested, although the protein was expressed to normal levels (data not shown).
DISCUSSION
Medium- and long-chain-length AHs have been previously cloned and functionally expressed from several sources, including A. borkumensis AP1, a marine hydrocarbonoclastic γ-proteobacterium that makes up a large part of the biomass (up to 30%) in oil-polluted marine environments (10); M. tuberculosis H37Rv, the causative agent of tuberculosis; and P. putida GPo1, which expresses the prototype integral membrane alkane hydroxylase and is a useful biocatalyst (5, 17, 27, 32). These studies have allowed us to start investigating structure-function relationships. However, we have found that sequence alignments alone do not enable us to identify positions involved in substrate binding; other methods based on the selection of mutants with different substrate ranges must be applied. In this work, we show that point mutations at position W55 in P. putida GPo1 AlkB or at position W58 in A. borkumensis AP1 AlkB1 obtained by such selection experiments are sufficient to allow medium-chain-length AHs to oxidize alkanes longer than C13. Because P. putida GPo1 appears to lack an uptake system for such alkanes (27) and A. borkumensis AP1 contains multiple AHs (32), the mutations could be obtained only by transferring the medium-chain-length AHs to a host that is able to take up long-chain-length alkanes but no longer possesses an AH that oxidizes these substrates: P. fluorescens KOB2Δ1 (27).
Close to 40 full-length AH gene sequences are now available, many of which have now been shown to encode functional AHs (17, 21, 27, 30). With a few exceptions, the encoded protein sequences show more than 40% sequence identity to each other. All contain the six hydrophobic stretches proposed to be TM helices in GPo1 AlkB, the level of sequence identity being somewhat lower than the average in these stretches. Residue W55 of the GPo1 AH is located close to the middle of TM helix 2. Figure 3 shows a multiple sequence alignment for this helix. In the highly homologous medium-chain-length AHs of P. putida P1 (28, 33) and AlkB1 of A. borkumensis AP1 (32), the corresponding position is also occupied by a tryptophan residue. In contrast, the other AHs have an alanine, a valine, a leucine, or an isoleucine residue at the corresponding position. Eleven of these other AHs were shown to oxidize alkanes that had up to at least 16 carbon atoms (17, 21, 27, 30) (Fig. 3). Not one of these enzymes was limited to the medium-chain-length alkanes.
FIG. 3.
Sequence alignment of TM helix 2 and comparison of properties. The first column contains the strain and AH names. M. smegmatis, Mycobacterium smegmatis; P. rugosa, Prauserella rugosa; R. erythropolis, Rhodococcus erythropolis; B. cepacia, Burkholderia cepacia; A. calcoaceticus, Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. The second column contains the upper end of the respective AH substrate ranges. Asterisks indicate that C16 was the longest alkane tested, but it is likely that the substrate range extends to longer alkanes. n.d., not determined; —, no activity could be detected. The third column shows the alignment of TM helix 2, with the position of the first and last residues indicated above (GPo1 AlkB position). TM helix 2 runs from the periplasm to the cytoplasm. Position 55 (GPo1 AlkB position) is indicated by the letter V. The W55 residue in the GPo1 AH and the L69 residue in the M. tuberculosis H37Rv AH are framed in black. The degree of conservation within TM helix 2 is shown below as a bar graph created by Clustal X.
The length of a C13 molecule in an extended (linear) conformation is about 19 Å. Assuming that the six TM segments of integral membrane AHs fold as perfect α-helices, with a pitch of 1.5 Å per residue, a C13 molecule corresponds to 12 to 13 amino acids in an α-helix. Comparisons of the TM stretches indicate that W55 is located about 11 residues from the cytoplasmic (C-terminal) end of the hydrophobic core sequence or about 10 and 14 residues from the conserved histidines at the ends of TM helices 4 and 6, respectively, approximately the correct distance to position the activated oxygen near the end of an extended C13 molecule. Therefore, the W55 residue may limit the lengths of the substrate alkanes, as shown schematically in Fig. 1. More evidence for this notion was obtained by changing residue L69 of the M. tuberculosis H37Rv AH, which corresponds to W55 in GPo1 AlkB, to F or W. The resulting mutants still oxidized C10 and C11 alkanes but no longer oxidized C12 to C16 alkanes, confirming the importance of this position. In almost all integral membrane AHs that have not been characterized with respect to substrate range, the position corresponding to W55 in the P. putida GPo1 AH is a small residue, which suggests that, by far, most members of this enzyme family act on alkanes longer than those with 12 carbon atoms. The P. putida AHs and their close homologs from other closely related γ-proteobacteria, such as A. borkumensis, are exceptions in this enzyme family in that they have high activity with C5 to C10 alkanes and do not oxidize alkanes longer than those with 12 or 13 carbon atoms.
To confirm that the conserved histidine in sequence motif C, at the end of TM helix 6, may play a role in binding the two iron atoms in AlkB or in catalysis, we replaced this residue with alanine and glutamine. Both mutations resulted in a complete loss of activity, suggesting that H273 is essential, like the eight histidines studied previously by Shanklin and Whittle (25).
The model shown in Fig. 1 implies that alkanes interact with the halves of the TM helices closest to the cytoplasm. The C-terminal half of TM helix 2 may be involved because the position corresponding to W55 in the AlkB protein of GPo1 is located in this TM helix, while the C-terminal halves of TM helices 4 and 6 may interact with the substrate, as two of the conserved histidine motifs are located at the ends of these two TM helices. TM helices 1 and 2 of the integral membrane AHs are absent in desaturases, enzymes that are distantly related to AHs (26). Recent studies with desaturase chimeras of the Δ6 fatty acid and Δ8 sphingolipid desaturases from Borago officinalis indicate that TM helices 1 and 2 of these enzymes, which correspond to TM helices 3 and 4 in the AHs, form at least part of the substrate-binding site of these enzymes (16). Therefore, TM helices 3 and 4 in the AHs may play a similar role. Further site-directed mutagenesis and selection experiments will be used to clarify this question.
With these results, we have for the first time obtained insight into the substrate-binding pocket of the integral membrane AHs, enzymes that appear to be crucial in natural crude oil degradation, which is interesting for biocatalytic applications, but that also play an unknown role in pathogens such as M. tuberculosis and L. pneumophila.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Swiss Priority Program in Biotechnology of the Swiss National Science Foundation, project no. 5002-037023.
REFERENCES
- 1.Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Birnboim, H. C., and J. Doly. 1979. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening of recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 7:1513-1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ditta, G., S. Stanfield, D. Corbin, and D. R. Helinski. 1980. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:7347-7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dower, W. J., J. F. Miller, and C. W. Ragsdale. 1988. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 16:6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Eggink, G., R. G. Lageveen, B. Altenburg, and B. Witholt. 1987. Controlled and functional expression of Pseudomonas oleovorans alkane utilizing system in Pseudomonas putida and Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 262:17712-17718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fu, H., M. Newcomb, and C. H. Wong. 1991. Pseudomonas oleovorans monooxygenase catalyzed asymmetric epoxidation of allyl alcohol derivatives and hydroxylation of a hypersensitive radical probe with the radical ring opening state exceeding the oxygen rebound state. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113:5878-5880. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fukuda, M., T. Nishi, M. Igarashi, T. Kondo, M. Takagi, and K. Yano. 1989. Degradation of ethylbenzene by Pseudomonas putida harboring OCT plasmid. Agric. Biol. Chem. 53:3293-3299. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Grund, A., J. Shapiro, M. Fennewald, P. Bacha, J. Leahy, K. Markbreiter, M. Nieder, and M. Toepfer. 1975. Regulation of alkane oxidation in Pseudomonas putida. J. Bacteriol. 123:546-556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Haas, D., C. Blumer, and C. Keel. 2000. Biocontrol ability of fluorescent pseudomonads genetically dissected: importance of positive feedback regulation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 11:290-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Harayama, S., H. Kishira, Y. Kasai, and K. Shutsubo. 1999. Petroleum biodegradation in marine environments. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1:63-70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Højberg, O., U. Schnider, H. V. Winteler, J. Sørensen, and D. Haas. 1999. Oxygen-sensing reporter strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens for monitoring the distribution of low-oxygen habitats in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65:4085-4093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Katopodis, A. G., H. A. Smith, and S. W. May. 1988. New oxyfunctionalization capabilities for ω-hydroxylases: asymmetric aliphatic sulfoxidation and branched ether demethylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 110:897-899. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Katopodis, A. G., K. Wimalasena, J. Lee, and S. W. May. 1984. Mechanistic studies on non-heme iron monooxygenase catalysis: epoxidation, aldehyde formation, and demethylation by the ω-hydroxylation system of Pseudomonas oleovorans. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 106:7928-7935. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kok, M. 1988. Alkane utilization by Pseudomonas oleovorans. Ph.D. thesis. University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 15.Lageveen, R. G., G. W. Huisman, H. Preusting, P. Ketelaar, G. Eggink, and B. Witholt. 1988. Formation of polyesters by Pseudomonas oleovorans: effect of substrates on formation and composition of poly-(R)-3-hydroxyalkanoates and poly-(R)-3-hydroxyalkenoates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54:2924-2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Libisch, B., L. V. Michaelson, M. J. Lewis, P. R. Shewry, and J. A. Napier. 2000. Chimeras of Δ6-fatty acid and Δ8-sphingolipid desaturases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 279:779-785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Marín, M. M., T. H. M. Smits, J. B. van Beilen, and F. Rojo. 2001. The alkane hydroxylase gene of Burkholderia cepacia RR10 is under catabolite repression control. J. Bacteriol. 183:4202-4209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.May, S. W., and B. J. Abbott. 1972. Enzymatic epoxidation. I. Alkane epoxidation by the ω-hydroxylation system of Pseudomonas oleovorans. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 48:1230-1234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.May, S. W., and A. G. Katopodis. 1986. Oxygenation of alcohol and sulphide substrates by a prototypical non-haem iron monooxygenase: catalysis and biotechnological potential. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 8:17-21. [Google Scholar]
- 20.McKenna, E. J., and M. J. Coon. 1970. Enzymatic ω-oxidation. IV. Purification and properties of the ω-hydroxylase of Pseudomonas oleovorans. J. Biol. Chem. 245:3882-3889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ratajczak, A., W. Geiβdörfer, and W. Hillen. 1998. Alkane hydroxylase from Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP-1 is encoded by alkM and belongs to a new family of bacterial integral-membrane hydrocarbon hydroxylases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64:1175-1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sambrook, J., E. F. Fritsch, and T. Maniatis. 1989. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
- 23.Schwartz, R. D., and C. J. McCoy. 1973. Pseudomonas oleovorans hydroxylation-epoxidation system: additional strain improvements. Appl. Microbiol. 26:217-218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shanklin, J., and E. B. Cahoon. 1998. Desaturation and related modifications of fatty acids. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 49:611-641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Shanklin, J., and E. Whittle. 2003. Evidence linking the Pseudomonas oleovorans alkane omega-hydroxylase, an integral membrane diiron enzyme, and the fatty acid desaturase family. FEBS Lett. 545:188-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shanklin, J., E. Whittle, and B. G. Fox. 1994. Eight histidine residues are catalytically essential in a membrane-associated iron enzyme, stearoyl-CoA desaturase, and are conserved in alkane hydroxylase and xylene monooxygenase. Biochemistry 33:12787-12794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Smits, T. H. M., S. B. Balada, B. Witholt, and J. B. van Beilen. 2002. Functional analysis of alkane hydroxylases from gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 184:1733-1742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Smits, T. H. M., M. Röthlisberger, B. Witholt, and J. B. van Beilen. 1999. Molecular screening for alkane hydroxylase genes in gram-negative and gram-positive strains. Environ. Microbiol. 1:307-318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Smits, T. H. M., M. A. Seeger, B. Witholt, and J. B. van Beilen. 2001. New alkane-responsive expression vectors for E. coli and Pseudomonas. Plasmid 46:16-24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tani, A., T. Ishige, Y. Sakai, and N. Kato. 2001. Gene structures and regulation of the alkane hydroxylase complex in Acinetobacter sp. strain M-1. J. Bacteriol. 183:1819-1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.van Beilen, J. B., J. Kingma, and B. Witholt. 1994. Substrate specificity of the alkane hydroxylase of Pseudomonas oleovorans GPo1. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 16:904-911. [Google Scholar]
- 32.van Beilen, J. B., M. Marín, T. H. M. Smits, M. Röthlisberger, A. Franchini, B. Witholt, and F. Rojo. 2004. Characterization of two alkane hydroxylase genes from the marine hydrocarbonoclastic bacterium Alcanivorax borkumensis. Environ. Microbiol. 6:264-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.van Beilen, J. B., S. Panke, S. Lucchini, A. G. Franchini, M. Röthlisberger, and B. Witholt. 2001. Analysis of Pseudomonas putida alkane degradation gene clusters and flanking insertion sequences: evolution and regulation of the alk-genes. Microbiology 147:1621-1630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.van Beilen, J. B., D. Penninga, and B. Witholt. 1992. Topology of the membrane-bound alkane hydroxylase of Pseudomonas oleovorans. J. Biol. Chem. 267:9194-9201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Whyte, L. G., A. Schultz, J. B. van Beilen, A. P. Luz, D. Pellizari, D. Labbé, and C. W. Greer. 2002. Prevalence of alkane monooxygenase genes in arctic and antarctic hydrocarbon-contaminated and pristine soils. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 41:141-150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Witholt, B. 1972. Method for isolating mutants overproducing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and its precursors. J. Bacteriol. 109:350-364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Witholt, B., M. J. de Smet, J. Kingma, J. B. van Beilen, M. Kok, R. G. Lageveen, and G. Eggink. 1990. Bioconversions of aliphatic compounds by Pseudomonas oleovorans in multiphase bioreactors: background and economic potential. Trends Biotechnol. 8:46-52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]