SUMMARY:
Malignant gliomas are characterized by infiltrative growth of tumor cells, including along white matter tracts. This may result in clinical cranial neuropathy due to direct involvement of a cranial nerve rather than by leptomeningeal spread along cranial nerves. Gliomas directly involving cranial nerves III–XII are rare, with only 11 cases reported in the literature before 2014, including 8 with imaging. We present 8 additional cases demonstrating direct infiltration of a cranial nerve by a glioma. Asymmetric cisternal nerve expansion compared with the contralateral nerve was noted with a mean length of involvement of 9.4 mm. Based on our case series, the key imaging feature for recognizing direct cranial nerve involvement by a glioma is the detection of an intra-axial mass in the pons or midbrain that is directly associated with expansion, signal abnormality, and/or enhancement of the adjacent cranial nerves.
Gliomas are the most common intra-axial primary brain tumors, with World Health Organization (WHO) grade IV glioblastoma multiforme representing the most common subtype.1–4 Malignant gliomas are characterized by infiltrative growth of tumor cells, including along white matter tracts.3,5–8 The cranial nerve nuclei are within the brain parenchyma and have glial cells extending into the root entry zone and proximal cisternal segments with gradual replacement by Schwann cells of >1–9 mm.9–11 Therefore, infiltrating growth patterns as seen along white matter tracts intra-axially may potentially occur with known or suspected gliomas. This imaging appearance may simulate nerve sheath tumors, intracranial perineural spread of head and neck tumors, or leptomeningeal spread of disease, all of which are well-described and relatively more common disease processes.12–15
If we exclude cranial nerve involvement in the setting of diffuse leptomeningeal spread of tumor, 11 unique cases of gliomas directly infiltrating cranial nerves have been reported in the literature before 2014, 8 with imaging.9,16–25 Through our MR imaging glioma data base, we have identified 8 additional cases of pathologically confirmed gliomas with imaging findings indicating direct involvement of the cranial nerves. One of our cases (case 1) has since recently been separately reported in the neurosurgery literature.10 The purpose of our study was to characterize the clinical and imaging features of cranial nerve involvement by gliomas and to improve recognition and understanding of this entity.
Case Series
This study was performed under institutional review board approval and was compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. Individual cases of gliomas directly involving a cranial nerve were retrospectively identified through a search of our teaching file data base and radiology reporting system. Cases of cranial nerve involvement in the setting of diffuse leptomeningeal spread, as determined by the presence of other areas where the brain surface was coated with tumor, were excluded. Additionally, direct involvement of the olfactory (cranial nerve [CN] I) or optic (CN II) nerves was specifically excluded because anatomically and histologically, these nerves are white matter tract extensions of the brain and, as such, are not true cranial nerves.
Eight individual cases of pathologically proved infiltrating glioma involving the cisternal segment of ≥1 cranial nerve were identified (Table) from 2000 to 2013. The mean patient age was 41 years (range, 9–67 years). There were 4 male and 4 female patients. Five of the 8 (63%) cases involved the trigeminal nerve (CN V); 1, the oculomotor nerve (CN III); 1, the ipsilateral trigeminal and facial nerves (CN VII); and 1, the ipsilateral trigeminal and vestibulocochlear nerves (CN VIII). Three cases were direct involvement from unifocal gliomas, and 5 cases were in the setting of multifocal advanced glioma. In 2 of the patients with unifocal tumors (cases 1 and 8) and in 1 of the patients with advanced multifocal tumors (case 4), cranial neuropathy was a feature of the patients' tumor presentations. The third patient with a unifocal tumor (case 3) had evidence of cranial neuropathy that became more apparent with time. Six of the cases were found at biopsy to be glioblastomas (WHO grade IV). One case had previously been determined to be WHO grade III (case 3); and 1 case, WHO grade II (case 7), which had likely dedifferentiated into a higher grade glioma as evidenced by contrast-enhancing tumor on follow-up imaging. The mean maximal thickness of the involved cisternal cranial nerve (5.9 mm) was statistically significantly thicker (P < .01, 2-tailed t test) than the mean thickness of the contralateral uninvolved nerve (1.5 mm), with a mean length of involvement of 9.4 mm. Involvement of the adjacent midbrain or pons deep to the root entry zone of the cranial nerves by a lesion contiguous with and matching the cranial nerve involvement in signal characteristics and enhancement pattern was present in all cases and was a key imaging feature in identifying the intra-axial origin of disease.
Case series of patients with gliomas involving cranial nerves
| Case | Age (yr) | Sex | Location | Grade (WHO) | Neuropathy | Maximal Thickness, Involved CN (mm) | Maximal Thickness, Contralateral CN (mm) | Maximal Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 67 | M | R pons to trigeminal nerve | IV | Yes | 6 | 2 | 8 |
| 2 | 53 | F | R pons to trigeminal and vestibulocochlear nerves; separate R frontal tumor | IV | No | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| 3 | 67 | F | L pons to trigeminal nerve | II | Yes | 4 | 1 | 13 |
| 4 | 49 | F | R midbrain to R oculomotor nerve; separate R frontal tumor | IV | Yes | 14 | 1 | 16 |
| 5 | 22 | M | R pons to trigeminal nerve; separate R frontal and thalamus tumor | IV | No | 4 | 2 | 7 |
| 6 | 9 | M | R pons to trigeminal nerve; separate R thalamus and midbrain tumor | IV | No | 4 | 2 | 4 |
| 7 | 34 | M | R pons to trigeminal nerve; separate R parietal tumor | II | No | 4 | 2 | 8 |
| 8 | 24 | F | R pons to trigeminal and facial nerves | IV | Yes | 8 | 1 | 15 |
| Mean (SD) | 41 (20.3) | 5.9 (3.6) | 1.5 (0.5) | 9.4 (4.7) |
Note:—R indicates right; L, left.
Case 1
A 67-year-old man presented with an 8-week history of right facial numbness, which began in the midface and progressed to complete right facial numbness during 6 weeks. MR imaging (Figs 1 and 2) demonstrated an irregular, peripherally enhancing, T2 FLAIR hyperintense mass centered in the right pons and extending into the trigeminal root entry zone and the cisternal segment of the right trigeminal nerve. Dynamic susceptibility-weighted contrast-enhanced perfusion imaging demonstrated increased relative cerebral blood volume within the brain stem component compared with the contralateral pons. Multivoxel MR spectroscopy demonstrated an elevated choline signal relative to the NAA signal within the brain stem component. Surgical biopsy of the lesion was performed at the root entry zone/proximal cisternal segment of the trigeminal nerve with decompression of an intraneural cyst (Fig 2). Histopathology revealed WHO grade IV glioblastoma arising in the root entry zone of the trigeminal nerve. The patient was treated with external beam radiation therapy and chemotherapy and remains alive with residual disease at 48 weeks since diagnosis.
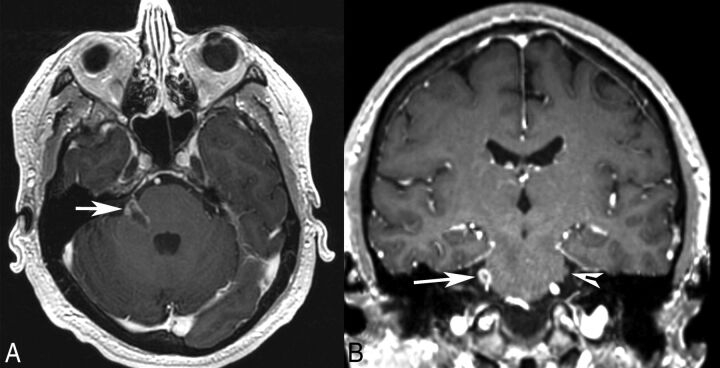
Fig 1.
Patient 1. Axial (A) and coronal (B) postgadolinium T1-weighted MR images demonstrate an irregular enhancing mass involving the right pons, the expected location of trigeminal nuclei, the root entry zone, and the cisternal segment of the right trigeminal nerve (arrow). The normal left trigeminal nerve is marked on the coronal image (arrowhead). This patient presented with right facial numbness.
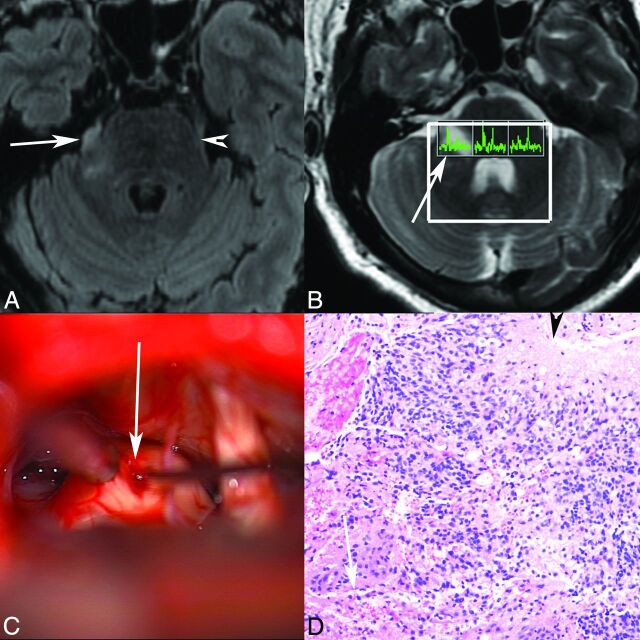
Fig 2.
Patient 1. Axial T2 FLAIR (A) MR image demonstrates abnormal T2 FLAIR signal in the right lateral pons extending into the right trigeminal nerve (arrow marks the site of biopsy, arrowhead marks the normal left trigeminal nerve). B, Multivoxel MR spectroscopy demonstrates increased choline relative to NAA in the right-sided voxel corresponding to the tumor (arrow). C, Operative photograph shows a right retrosigmoid approach to the expanded right trigeminal nerve (arrow), with biopsy being obtained (courtesy of Jonathan D. Breshears, MD). D, Hematoxylin-eosin stained histology slide (original magnification ×20) demonstrates an infiltrative astrocytic neoplasm with nuclear pleomorphism, brisk mitotic activity, microvascular proliferation (arrow), and pseudopalisading necrosis (arrowhead). Pathologic diagnosis was a glioblastoma, WHO grade IV. No peripheral nerve was identified in the specimen despite the biopsy location, likely reflecting the origin from glial cells in the trigeminal root entry zone.
Case 2
A 53-year-old woman with surgical biopsy 9 months prior and I-125 brachytherapy seed placement 6 months prior for residual right frontal WHO grade IV glioblastoma presented for follow-up MR imaging. The patient developed progressive disease with infiltrative T2 FLAIR hyperintensity extending into the brain stem and an irregularly enhancing mass lesion centered in the right pons. The abnormal expansion, T2 FLAIR signal abnormality, and enhancement extended into the root entry zone of the trigeminal nerve and proximal cisternal segment. More subtle signal abnormality and enhancement extended into the right vestibulocochlear nerve complex. No definitive symptoms of cranial neuropathy were reported. The patient had a partial response to chemotherapy and additional radiation therapy but ultimately developed progressive infiltrating glioma.
Case 3
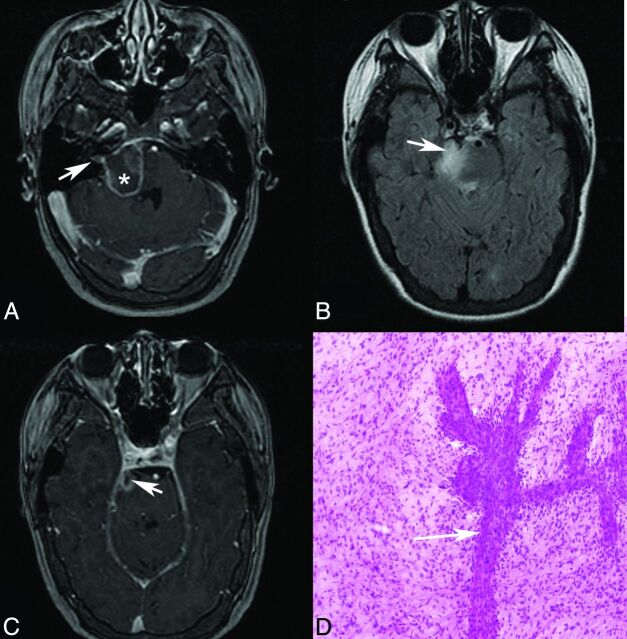
A 67-year-old woman with known neurofibromatosis type 1 presented with headaches, dizziness, and syncope. MR imaging (Fig 3) demonstrated an expansile T2 FLAIR hyperintense, peripherally enhancing mass lesion centered in the left pons with extension into and expansion of the root entry zone of the trigeminal nerve. Surgical biopsy of the contiguous lesion in the pons yielded diffuse astrocytoma, WHO grade II (Fig 3). At presentation, the patient had symptoms referable to the brain stem and cranial nerve nuclei, including abnormal acoustic reflexes and dizziness. With time, the patient developed worsening trigeminal neuropathy as evidenced by abnormal tingling of the left lower face. The patient received radiation therapy and steroids, with an initial response followed eventually by progressive disease.
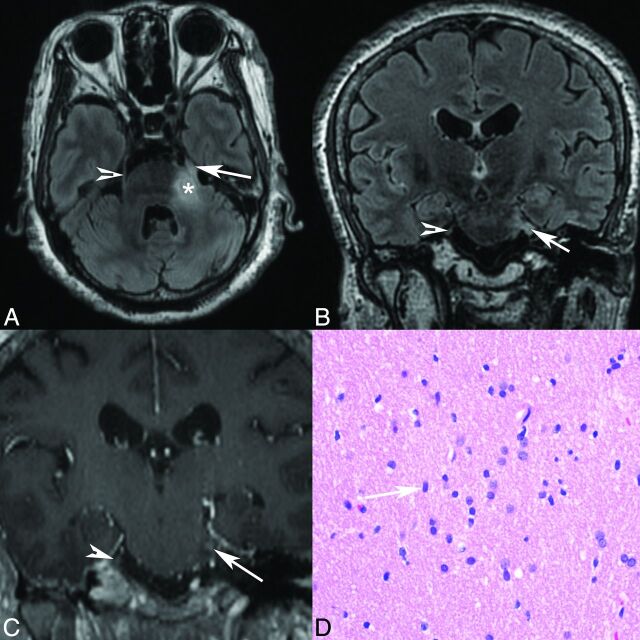
Fig 3.
Patient 3. Axial T2 FLAIR (A), coronal T2 FLAIR (B), and coronal postgadolinium T1 (C) MR images demonstrate abnormal T2 FLAIR signal in the left lateral pons extending into the expanded left trigeminal nerve (arrow), with enhancement shown at the root entry zone (C). The arrowhead marks the normal right trigeminal nerve, and the asterisk marks the approximate site of biopsy in the pons. D, Hematoxylin-eosin stained histology slide (original magnification ×40) demonstrates an infiltrating population of neoplastic astrocytes with irregular ovoid nuclei (arrow) and coarse chromatin and scant eosinophilic cytoplasm. No mitotic activity, microvascular proliferation, or foci of necrosis are present. The pathologic diagnosis was a diffuse astrocytoma, WHO grade II.
Case 4
A 49-year-old pregnant woman presented with diplopia and was found to have right oculomotor nerve palsy (CN III). MR imaging (Fig 4) demonstrated an irregular peripherally enhancing mass lesion extending from the midbrain into the cisternal segment of the right oculomotor nerve. The mass also demonstrated T2 FLAIR hyperintensity and reduced ADC values. The patient had a separate mass in the right frontal lobe with similar imaging characteristics. Surgical biopsy of the right frontal mass was performed, which showed WHO grade IV glioblastoma. The patient underwent external beam radiation therapy with concurrent temozolomide chemotherapy and, at the time of clinical recurrence, was started on bevacizumab (Avastin), but the tumor disseminated widely within the CSF, including to the spinal canal.
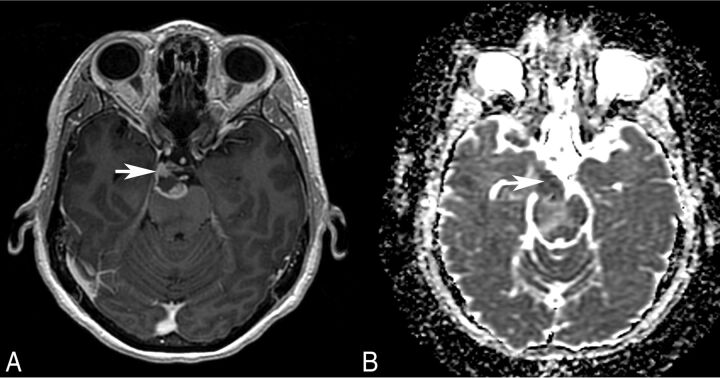
Fig 4.
Patient 4. Axial postgadolinium T1-weighted MR image (A) and ADC map (B) show an irregularly enhancing, mass with restricted diffusion (arrow) involving the root exit zone and the cisternal course of the right oculomotor nerve in the interpeduncular cistern. This patient presented with right oculomotor palsy.
Case 5
A 22-year-old man with a history of a right frontal lobe WHO grade IV glioblastoma, partially resected 18 and 11 months prior, was noted on follow-up imaging to have new right thalamic and right pontine masses. The T2 FLAIR hyperintense mass centered in the right pons demonstrated expansion of the root entry zone of the trigeminal nerve and extension into its cisternal segment. No definitive symptoms of trigeminal neuropathy were noted, though the patient had altered mental status. The patient developed progressive disease despite additional therapy.
Case 6
A 9-year-old boy with a history of a right thalamic WHO grade IV glioblastoma, partially resected 3 months prior, was found to have increasing T2 FLAIR hyperintense signal with associated irregular enhancement extending inferiorly into the right pons with involvement at the root entry zone and proximal cisternal segment of the right trigeminal nerve. The patient did not have any symptoms definitively referable to trigeminal neuropathy; his dysarthria and left-sided facial weakness were presumed to be related to the thalamic tumor. The patient received additional chemotherapy and ultimately developed progressive disease.
Case 7
A 34-year-old man with resection of a right temporal lobe oligodendroglioma 8 years ago and re-resection 32 months prior for recurrent disease re-presented for follow-up MR imaging. Enlarging T2 FLAIR hyperintense signal with associated irregular nodular enhancement was demonstrated in the right pons with new contiguous involvement of the root entry zone and proximal cisternal segment of the right trigeminal nerve. Biopsy of the more accessible right parietal component demonstrated a recurrent WHO grade II oligodendroglioma, though the enhancing portion was not biopsied and the possibility of an undersampled higher grade component could not be excluded. No definitive symptoms of trigeminal neuropathy were present. The patient received additional chemotherapy and ultimately developed progressive disease.
Case 8
A 24-year-old woman presented with ipsilateral trigeminal and facial neuropathies manifesting as right facial numbness and weakness, respectively. MR imaging (Fig 5) demonstrated a T2 FLAIR hyperintense mass with irregular peripheral enhancement involving the right pons, with extension into the right cerebellopontine angle and internal auditory canal along the facial and vestibulocochlear nerve complex and extension into the right trigeminal nerve root entry zone and cisternal segment. Dynamic susceptibility-weighted contrast-enhanced perfusion imaging was performed, which demonstrated increased relative cerebral blood volume within the lesion compared with the contralateral pons. Clinically, there were no features of vestibular or cochlear nerve involvement. Histopathology of the contiguous pontine lesion showed WHO grade IV glioblastoma (Fig 5). This patient received radiation and chemotherapy and ultimately developed progressive disease with right-sided hearing loss later in the course of her disease.
Fig 5.
Patient 8. Axial postgadolinium T1 (A and C) and axial T2 FLAIR (B) MR images demonstrate an irregularly enhancing, T2 FLAIR hyperintense mass involving the right lateral pons and expected origins and intracranial course of both the right facial (A) and the trigeminal (B and C, arrow) nerves. Enhancement also extends into the right internal auditory canal along its anterior and superior aspect where the extra-axial facial nerve courses (A, arrow). Asterisk (A) marks the approximate site of biopsy. D, Hematoxylin-eosin-stained intraoperative smear preparation (original magnification ×10) demonstrates a population of neoplastic astrocytes with nuclear pleomorphism and numerous mitotic figures. A vessel with extensive budding and endothelial proliferation is present (arrow). Pathologic diagnosis was a glioblastoma, WHO grade IV. This patient presented with right facial numbness and weakness, but no clinical evidence of vestibulocochlear nerve involvement until later in the disease course.
Discussion
We have presented a series of 8 cases of direct invasion of a cranial nerve by a glioma. This is a rare phenomenon, with only 11 unique cases reported in the literature before 2014.9,16–25 All 8 cases demonstrated abnormal T2 FLAIR hyperintensity, contrast enhancement, and expansion of a cisternal cranial nerve and its root entry zone contiguous with a brain stem parenchymal lesion.
The literature from 1904 to 2011 describes 11 unique cases of a glial neoplasm involving a cranial nerve.9,16–25 Only 8 of the cases describe imaging findings because 3 of the cases predate modern imaging. In 8 of the reported patients, patient age was available and revealed a mean age of 36 years with a range of 8–70 years. Eight cases were reported to involve the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII); 1 case, to involve the oculomotor nerve (CN III); 1 case, to involve the trigeminal nerve (CN V); and 1 case, to involve the vestibulocochlear, facial, and trigeminal nerves (CNs V, VII, and VIII). The reported histopathology in 9 of the cases was low-grade glioma (WHO grades I–II), and in 2 cases, it was glioblastoma (WHO grade IV).
While the ages of patients in our case series and the literature are similar, our series differs from the prior reported cases in tumor grade and the specific cranial nerve involved. The tumors in our case series are of a higher grade than those identified in the literature, with 6 of 8 (75%) being grade III–IV tumors in our series compared with 2 of 11 (18%) in the prior literature. The most common cranial nerve involved in our series was the trigeminal nerve, which was involved in 7 of 8 cases (88%) compared with 2 of the prior 11 (18%); the most common cranial nerve previously reported in the literature was the vestibulocochlear nerve, which was involved in 9 of 11 cases (82%) in the prior literature compared with being involved in 1 of 8 (13%) in our series. A number of confounding factors may potentially result in these differences. The prior literature has shown an emphasis on gliomas found at surgery for what had been presumed to be a vestibular schwannoma. Our institution is a referral center that uses frequent imaging in patients with known aggressive gliomas. Additionally, modern high-resolution MR imaging techniques make cranial nerve involvement more readily apparent, and this phenomenon might have been under-recognized and under-reported in the past.
Three of the 8 (38%) patients in our series presented with new cranial neuropathy corresponding to the involved nerve, including 1 patient with involvement of 2 cranial nerves. A fourth patient had more subtle evidence of trigeminal neuropathy, which increased with time. Most interesting, 4 of the 8 (50%) patients did not have reported clinical symptomatology referable to cranial nerve involvement. These 4 cases were all in the setting of advanced multifocal glioma with cranial nerve involvement manifesting later in the disease course. Recognizing clinical cranial neuropathy in patients presenting initially with cranial nerve involvement rather than in those developing it later in their disease course may be more likely. Our finding of clinical cranial neuropathy being an inconsistent feature is similar to that seen with perineural spread of head and neck cancer, in which up to 40% of patients are reported to be asymptomatic.14,26 The inconsistency of clinical cranial neuropathy in both situations may be related to the heterogeneous nature of cranial nerve involvement histologically and mechanistically.14,27
The tumors in our case series demonstrated evidence of intra-axial origin and have the typical imaging characteristics of gliomas elsewhere in the central nervous system. The adjacent pons or midbrain was abnormally expanded, with tumor involvement in all cases that was contiguous with the proximal cisternal cranial nerve involvement; this feature was key to recognizing the intra-axial origin of the tumors and helped to differentiate them from other lesions considered at these locations, including nerve sheath tumors, meningiomas, perineural spread of head and neck malignancies, and diffuse neoplastic, infectious, or inflammatory leptomeningeal disease, all of which would be expected to have different imaging findings from those in our cases.
Gliomas directly involving the cranial nerves are rare, with only 11 cases reported in the literature; we have presented an additional 8 cases. These are intra-axial, intraparenchymal tumors, which, despite their unusual locations, demonstrate the imaging features typical of gliomas with the additional feature of extension into and expansion of the cranial nerve. These tumors can cause clinically evident cranial neuropathy, though this was not a consistent feature in our series. Recognition of the intra-axial, intraparenchymal origin of cranial nerve involvement by gliomas is a key imaging feature for the accurate diagnosis and correct management of these patients.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- WHO
World Health Organization
- CN
cranial nerve
Footnotes
Disclosures: Christine M. Glastonbury—UNRELATED: Royalties: Amirsys, Comments: from book and participation in StatDx; Stock/Stock Options: Amirsys.
Marc C. Mabray was supported by a National Institutes of Health T32 training grant (5T32EB001631-10) while working on this research project.
Paper previously presented as a Scientific Exhibit at: Annual Meeting of the American Society of Neuroradiology and the Foundation of the ASNR Symposium, May 17–22, 2014; Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
REFERENCES
- 1. Dolecek TA, Propp JM, Stroup NE, et al. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005–2009. Neuro Oncol 2012;14(suppl 5):v1–49 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, et al. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 2007;114:97–109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Cha S. Update on brain tumor imaging: from anatomy to physiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006;27:475–87 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Omuro A, DeAngelis LM. Glioblastoma and other malignant gliomas: a clinical review. JAMA 2013;310:1842–50 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Barajas RF Jr, Hess CP, Phillips JJ, et al. Super-resolution track density imaging of glioblastoma: histopathologic correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2013;34:1319–25 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Barajas R Jr, Phillips JJ, Parvataneni R, et al. Regional variation in histopathologic features of tumor specimens from treatment-naive glioblastoma correlates with anatomic and physiologic MR imaging. Neuro Oncol 2012;14:942–54 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Giese A, Westphal M. Glioma invasion in the central nervous system. Neurosurgery 1996;39:235–50; discussion 250–52 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Giese A, Kluwe L, Laube B, et al. Migration of human glioma cells on myelin. Neurosurgery 1996;38:755–64 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Arnautovic KI, Husain MM, Linskey ME. Cranial nerve root entry zone primary cerebellopontine angle gliomas: a rare and poorly recognized subset of extraparenchymal tumors. J Neurooncol 2000;49:205–12 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Breshears JD, Ivan ME, Cotter JA, et al. Primary glioblastoma of the trigeminal nerve root entry zone: case report. J Neurosurg 2015;122:78–81 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Bridger MW, Farkashidy J. The distribution of neuroglia and Schwann cells in the 8th nerve of man. J Laryngol Otol 1980;94:1353–62 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Borges A, Casselman J. Imaging the cranial nerves. Part I. Methodology, infectious and inflammatory, traumatic and congenital lesions. Eur Radiol 2007;17:2112–25 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Borges A, Casselman J. Imaging the cranial nerves. Part II. Primary and secondary neoplastic conditions and neurovascular conflicts. Eur Radiol 2007;17:2332–44 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Paes FM, Singer AD, Checkver AN, et al. Perineural spread in head and neck malignancies: clinical significance and evaluation with 18F-FDG PET/CT. Radiographics 2013;33:1717–36 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Muzzafar S, Ketonen L, Weinberg JS, et al. Imaging and clinical features of an intra-axial brain stem schwannoma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2010;31:567–69 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Cushing H. Tumors of the Nervus Acusticus and the Syndrome of the Cerebellopontine Angle. Philadelpia: WB Saunders; 1917 [Google Scholar]
- 17. Panse R. Ein Gliom des Akustikus. Arch Ohr Heilk 1904;61:251–55 [Google Scholar]
- 18. Wu B, Liu W, Zhu H, et al. Primary glioblastoma of the cerebellopontine angle in adults. J Neurosurg 2011;114:1288–93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Mirone G, Schiabello L, Chibbaro S, et al. Pediatric primary pilocytic astrocytoma of the cerebellopontine angle: a case report. Childs Nerv Syst 2009;25:247–51 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Ree A, Jain R, Rock J, et al. Direct infiltration of brainstem glioma along the cranial nerves. J Neuroimaging 2005;15:197–99 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Takada Y, Ohno K, Tamaki M, et al. Cerebellopontine angle pilocytic astrocytoma mimicking acoustic schwannoma. Neuroradiology 1999;41:949–50 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Reifenberger G, Bostrom J, Bettag M, et al. Primary glioblastoma multiforme of the oculomotor nerve: case report. J Neurosurg 1996;84:1062–66 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Beutler AS, Hsiang JK, Moorhouse DF, et al. Pilocytic astrocytoma presenting as an extra-axial tumor in the cerebellopontine angle: case report. Neurosurgery 1995;37:125–28 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Forton G, Verlooy J, Cras P, et al. Problems with flute playing: an otological problem? Case report of a peculiar cerebellar astrocytoma [in Dutch]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg 1992;46:405–10 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Kasantikul V, Palmer JO, Netsky MG, et al. Glioma of the acoustic nerve. Arch Otolaryngol 1980;106:456–59 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Gandhi D, Gujar S, Mukherji SK. Magnetic resonance imaging of perineural spread of head and neck malignancies. Top Magn Reson Imaging 2004;15:79–85 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Binmadi NO, Basile JR. Perineural invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma: a discussion of significance and review of the literature. Oral Oncol 2011;47:1005–10 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]