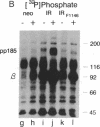
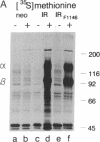
Abstract
We have studied the function of a mutant insulin receptor (IR) molecule in which Tyr-1146, one of the first autophosphorylation sites in the beta subunit, was replaced with phenylalanine (IRF1146). Autophosphorylation of the partially purified IRF1146 was reduced 60-70% when compared to the wild-type IR but was still stimulated by insulin. The phosphotransferase activity of the dephospho form of both the IR and IRF1146 toward exogenous substrates was stimulated 3- to 4-fold by insulin. However, the wild-type IR was activated 12-fold by autophosphorylation, whereas the IRF1146 was activated only 2-fold. When the IRF1146 was expressed in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, insulin binding was normal, whereas autophosphorylation was reduced 80% when compared to cells expressing the wild-type IR. Endogenous substrates of the insulin receptor kinase were not detected during insulin stimulation of CHO cells expressing the IRF1146. Moreover, the IRF1146 did not internalize insulin rapidly or stimulate DNA synthesis in the presence of insulin. In contrast, both the IR and IRF1146 stimulated glycogen synthase equally in CHO cells. These data suggest that activation of the IR tyrosine kinase can be resolved into two components: the first is dependent on insulin binding and the second is dependent on the subsequent insulin-stimulated autophosphorylation cascade. Thus, at least two signal transduction pathways diverging from the IR are implicated in the mechanism of insulin action.
Full text
PDF
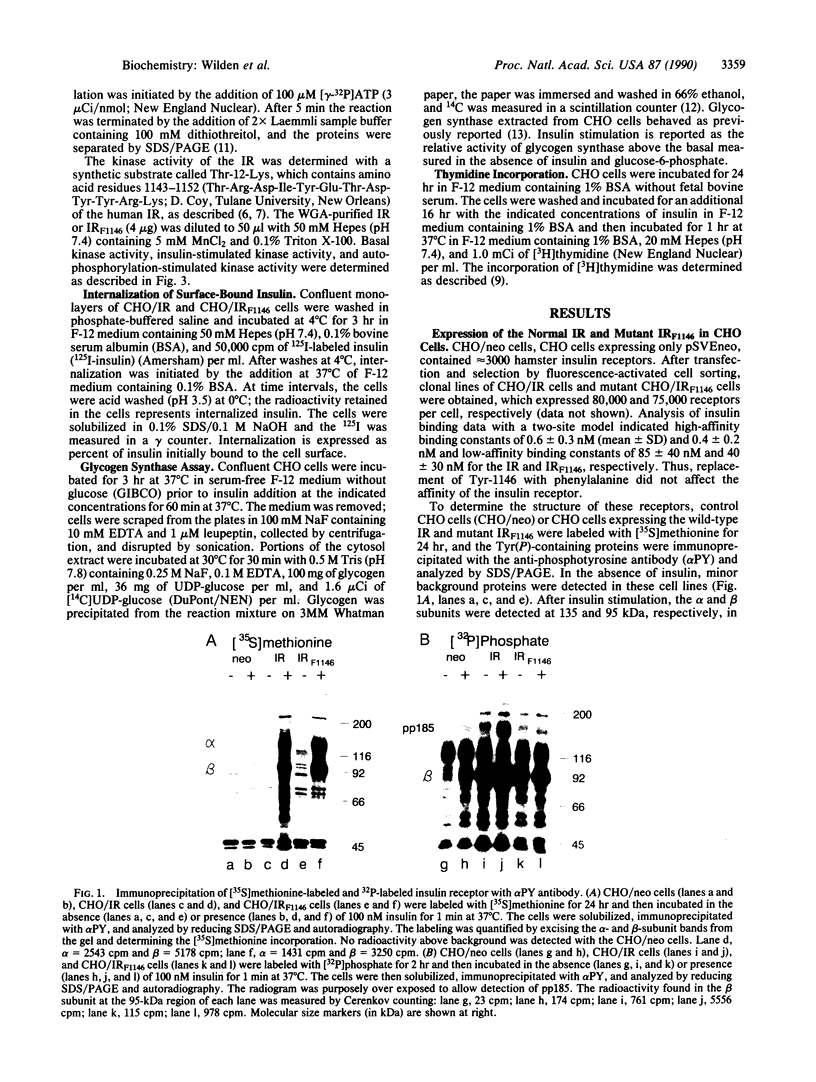
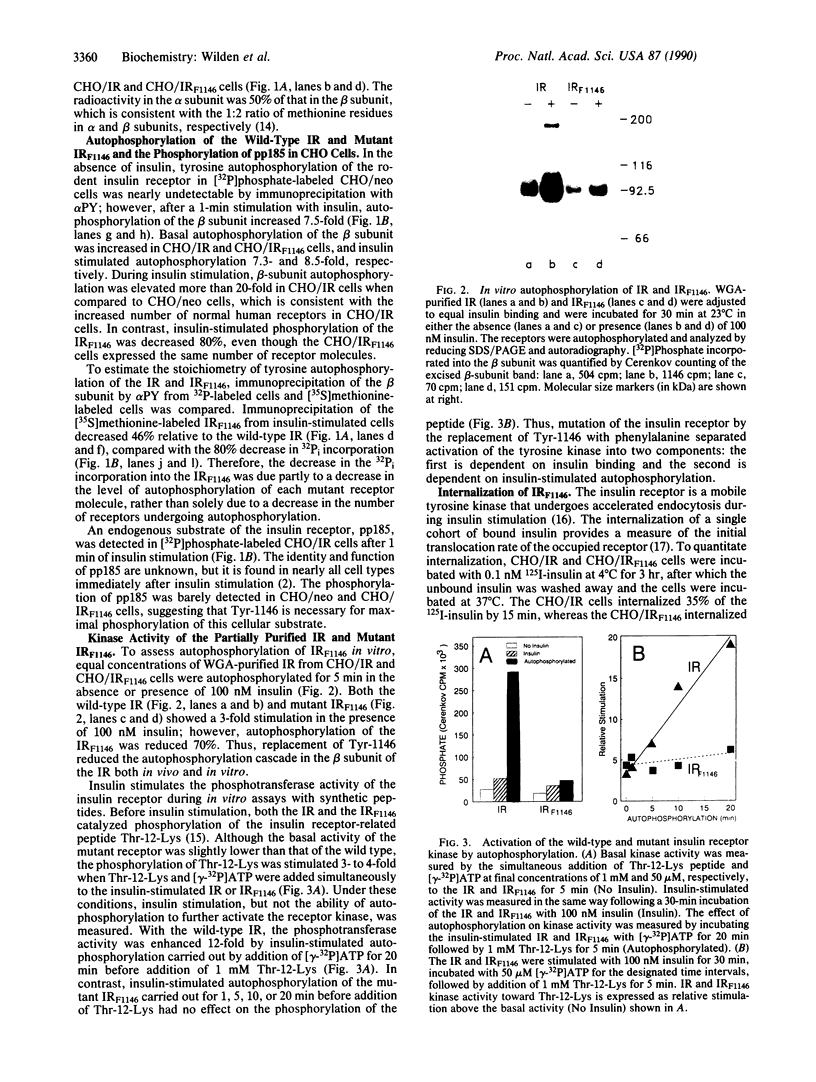
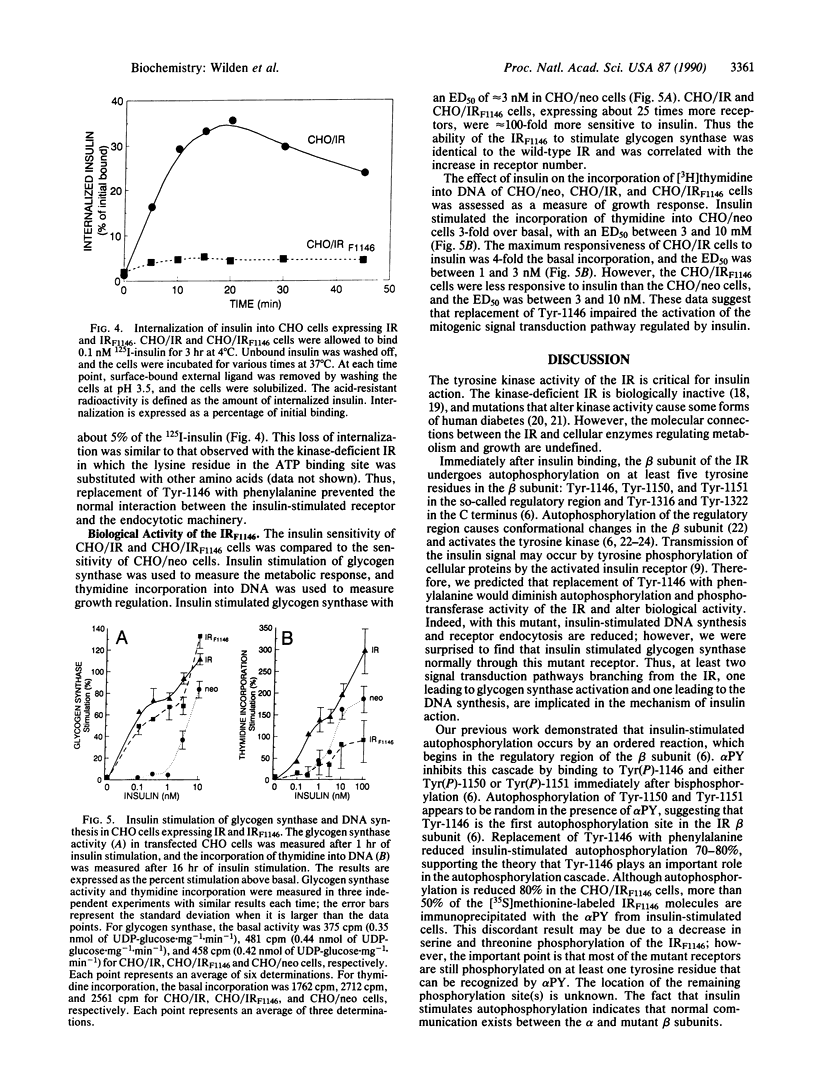

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backer J. M., Kahn C. R., White M. F. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor during insulin-stimulated internalization in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1694–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Kahn C. R., White M. F. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor is not required for receptor internalization: studies in 2,4-dinitrophenol-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3209–3213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K., Larner J. Intracellular mediators of insulin action. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:405–424. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crettaz M., Kahn C. R. Analysis of insulin action using differentiated and dedifferentiated hepatoma cells. Endocrinology. 1983 Oct;113(4):1201–1209. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-4-1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debant A., Clauser E., Ponzio G., Filloux C., Auzan C., Contreres J. O., Rossi B. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 does not alter the mitogenic effect of the hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8032–8036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren H. J., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Separate domains of the insulin receptor contain sites of autophosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 21;26(8):2374–2382. doi: 10.1021/bi00382a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R., Rosen O. M. Autophosphorylation of the insulin receptor in vitro. Designation of phosphorylation sites and correlation with receptor kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):11980–11985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Goldstein B. J. Molecular defects in insulin action. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):13–13. doi: 10.1126/science.2662406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., White M. F. The insulin receptor and the molecular mechanism of insulin action. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1151–1156. doi: 10.1172/JCI113711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maron R., Taylor S. I., Jackson R., Kahn C. R. Analysis of insulin receptors on human lymphoblastoid cell lines by flow cytometry. Diabetologia. 1984 Jul;27 (Suppl):118–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00275665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., Maegawa H., Lee J., Dull T. J., Ulrich A., Olefsky J. M. A mutant insulin receptor with defective tyrosine kinase displays no biologic activity and does not undergo endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14663–14671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odawara M., Kadowaki T., Yamamoto R., Shibasaki Y., Tobe K., Accili D., Bevins C., Mikami Y., Matsuura N., Akanuma Y. Human diabetes associated with a mutation in the tyrosine kinase domain of the insulin receptor. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):66–68. doi: 10.1126/science.2544998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Herrera R., Olowe Y., Petruzzelli L. M., Cobb M. H. Phosphorylation activates the insulin receptor tyrosine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3237–3240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Kapeller R., White M. F., Cantley L. C. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Johnson E. L., Chou C. K., Rosen O. M. The protein-tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor is necessary for insulin-mediated receptor down-regulation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11833–11840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin stimulates the generation from hepatic plasma membranes of modulators derived from an inositol glycolipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. L., Fridovich S. E., Lodish H. F. Kinetics of internalization and recycling of the asialoglycoprotein receptor in a hepatoma cell line. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4230–4237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtmauer L., Rosen O. M. Phosphorylation of synthetic insulin receptor peptides by the insulin receptor kinase and evidence that the preferred sequence containing Tyr-1150 is phosphorylated in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):10000–10005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Livingston J. N., Backer J. M., Lauris V., Dull T. J., Ullrich A., Kahn C. R. Mutation of the insulin receptor at tyrosine 960 inhibits signal transmission but does not affect its tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):641–649. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Maron R., Kahn C. R. Insulin rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a Mr-185,000 protein in intact cells. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):183–186. doi: 10.1038/318183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Shoelson S. E., Keutmann H., Kahn C. R. A cascade of tyrosine autophosphorylation in the beta-subunit activates the phosphotransferase of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2969–2980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Stegmann E. W., Dull T. J., Ullrich A., Kahn C. R. Characterization of an endogenous substrate of the insulin receptor in cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9769–9777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Czech M. P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor beta subunit activates the receptor-associated tyrosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5277–5286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]