Abstract
Proteases play important roles in all living organisms and also have important industrial applications. Family M12A metalloproteases, mainly found throughout the animal kingdom, belong to the metzincin protease family and are synthesized as inactive precursors. So far, only flavastacin and myroilysin, isolated from bacteria, were reported to be M12A proteases, whereas the classification of myroilysin is still unclear due to the lack of structural information. Here, we report the crystal structures of pro-myroilysin from bacterium Myroides sp. cslb8. The catalytic zinc ion of pro-myroilysin, at the bottom of a deep active site, is coordinated by three histidine residues in the conserved motif HEXXHXXGXXH; the cysteine residue in the pro-peptide coordinates the catalytic zinc ion and inhibits myroilysin activity. Structure comparisons revealed that myroilysin shares high similarity with the members of the M12A, M10A, and M10B families of metalloproteases. However, a unique “cap” structure tops the active site cleft in the structure of pro-myroilysin, and this “cap” structure does not exist in the above structure-reported subfamilies. Further structure-based sequence analysis revealed that myroilysin appears to belong to the M12A family, but pro-myroilysin uses a “cysteine switch” activation mechanism with a unique segment, including the conserved cysteine residue, whereas other reported M12A family proteases use an “aspartate switch” activation mechanism. Thus, our results suggest that myroilysin is a new bacterial member of the M12A family with an exceptional cysteine switch activation mechanism. Our results shed new light on the classification of the M12A family and may suggest a divergent evolution of the M12 family.
Keywords: crystal structure, enzyme, inhibition mechanism, metalloprotease, structural biology
Introduction
Proteases play important roles during the life of all organisms, including microbes (1). Intracellular proteases are of great importance for various metabolic processes, such as protein turnover, sporulation, and differentiation (2, 3). Extracellular proteases usually hydrolyze proteins in the environment to provide nutrients to the bacteria (4–7), although some are thought to be involved in pathogenesis (8). Because extracellular proteases are easily obtained, they are also widely applied in various industries and medical fields, including detergent, leather, food, waste treatment, diagnosis of illness, and pharmaceuticals (9–13).
Metalloproteases, a group of important proteases, require a divalent metal cation (usually zinc ion) for activity. The metal ion in metalloprotease is coordinated by several amino acid residues, commonly His, Glu, Asp, or Lys (14). Zinc-dependent metalloproteases contain a signature motif HEXXH, in which the two histidine residues function as the first and second zinc ligands and the glutamate residue plays an outstanding role in catalysis (15). When the third zinc ligand is a glutamate residue, zinc-dependent metalloproteases are called gluzincins, a group that consists of exopeptidases and endopeptidases (14). If the third zinc ligand is a histidine or aspartate residue in the elongated motif HEXXHXXGXX(H/D), the conserved glycine residue is indispensable for forming a β-turn to bring the three zinc ligands together (16). These types of zinc-dependent metalloproteases are known as metzincins because of a conserved methionine residue in a Met-turn (such as SIMHY) that underlies the active site (17) to form a structure that acts as a “hydrophobic pillow.” All metzincins are endopeptidases and are generally synthesized as inactive precursors (14). In some members of the metzincins, such as the M8, M10, M11, and M12 families, a conserved cysteine residue in the pro-peptide can interact with the catalytic zinc ion to prevent the binding of a water molecule and inactivate the protease. This inhibition mechanism is known as a “cysteine switch” (14).
The M12 family is the second largest family of metzincins and can be further divided into two subfamilies: subfamilies M12A and M12B (14). Subfamily M12A is known as the astacin subfamily (18). These metalloproteases from the M12A subfamily contain a conserved aspartate residue (Asp-21) in the pro-peptide, and their activation mechanism is therefore called “aspartate switch” (19). Proteases in the M12A family are mainly found throughout the animal kingdom and only rarely found in bacteria. Flavastacin (20–22) is the only confirmed bacterial protease in this family. Members in subfamily M12B (also called the reprolysin family) employ a cysteine switch mechanism (14). Reprolysin, found in snake venom, is the representative member. A cysteine switch mechanism for the pro-peptide is thought to operate in the inhibition of reprolysin. Proteases in the M12B subfamily are also widely distributed throughout the animal kingdom.
The Myroides sp. cslb8, isolated from silkworm excrement in our laboratory, secretes a 25-kDa protease. Mass spectrometry analysis and BLAST analysis of the amino acid sequence indicated that this protease shares high sequence identity with the reported myroilysin from Methanolobus profundi D25, which was classified as an M12A subfamily protease based on a sequence alignment (23). However, myroilysin is classified into the M10B family in the MEROPS (24) peptidase database without structural information.
The M10 family, like the M12 family, is synthesized as inactive precursor and can be divided into three subfamilies: M10A, M10B, and M10C. The M10A subfamily proteases are mainly found throughout the animal kingdom and activated through a cysteine switch mechanism. The best known examples are the eukaryotic matrix metallopeptidases (MMPs).3 The M10A proteases are also present in plants and bacteria, but the non-animal M10A proteases do not usually employ a cysteine switch activation mechanism (14). Karilysin is a typical bacterial M10A member; it is expressed as a proenzyme with an aspartate in the pro-peptide that may act in a similar manner to proastacin (25, 26). Proteases in the M10B subfamily are mainly from Proteobacteria, including the well studied serralysin (27).
Sequence analysis revealed a cysteine (Cys-26) in the predicted pro-peptide and a typical M-turn (SIMHY) in the amino acid sequences of the myroilysin from Myroides sp. cslb8. We therefore investigated the question: Should myroilysin belong to the M12 or the M10 family?
To elucidate the catalytic mechanism of myroilysin and clarify the classification of myroilysin, genes encoding myroilysin and pro-myroilysin from Myroides sp. cslb8 were cloned and expressed. The 1.89 and 1.6 Å crystal structures of pro-myroilysin were resolved. The structure comparison revealed that myroilysin shares high similarity to the members of the M12A, M10A, and M10B families of metalloprotease; in particular, the cysteine residue in the pro-peptide coordinates the catalytic zinc ion and inhibits the activity of myroilysin. A unique “cap” structure tops the active site cleft in the structure of pro-myroilysin. Further structure-based sequence analyses suggest that myroilysin should be a new bacterial member of the M12A family using a cysteine switch mechanism.
Results and Discussion
Isolation and Characterization of Strain cslb8
Strain cslb8, an orange colony with the largest clear zone on the skim milk plate, was selected for further study. The cells of cslb8 were Gram-negative and rod-shaped. These cells grow well at pH 7–10, with an optimum pH for growth at 7. No acid was produced from glucose, lactose, sucrose, and fructose. To determine the evolutionary relationship of cslb8 to other bacteria, the 16S rDNA was amplified and sequenced. The 16S rRNA gene of strain cslb8 is 1,473 bp (KP282832). The phylogenetic trees were constructed using the neighbor-joining method (28) with 100% bootstrap support. Phylogenetic distances were calculated using the MEGA6 software package. The 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain cslb8 shared the highest identities with the sequences of Myroides odoratimimus LWD09 (98%, GU570427), M. profundi D25 (98%, EU204978), and M. odoratus NBRC 14945 (95%, AB517709) (Fig. 1). These results indicated that the CSLB8 strain could be classified as Myroides, and thus we named it Myroides sp. cslb8 (CGMCC 1.15038).
FIGURE 1.
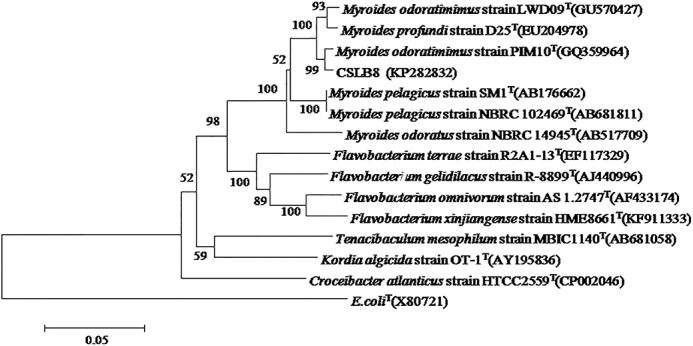
Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showing the phylogenetic positions of strain CSLB8, other Myroides species and representatives of the Flavobacteriaceae family. E. coli (X80721) was used as an out-group. Percentage bootstrap values >50 (1,000 replicates) are indicated at nodes. Scale bar, 0.05 substitutions/nucleotide position.
Purification and Characterization of Protease
The protease was purified stepwise using ammonium sulfate precipitation and various chromatographic methods with monitoring protease activity. The purified enzyme appeared as a single band of ∼25 kDa on 12% SDS-PAGE, indicating that it is the target protein. To further identify the protease, the protein sequence of the purified 25-kDa protein was determined using tandem mass spectrometry. The Mascot peptide fragment search result showed that the matching peptide fragments accounted for 16% (44 of 273) of the deduced amino acids of the zinc-dependent M12 metalloprotease of M. odoratimimus CIP 101113 (EHO09775.1).
To clone the protease-encoding gene, the gene encoding the protease was amplified using primers designed according to the consensus sequences of some bacterial M12 family metalloproteases, cloned into pET24b, and sequenced. The gene is 819 bp long (KR611868), encoding a protein with 273 amino acids and a molecular mass of ∼30 kDa. The deduced protein sequence analysis showed that the amino acid sequence is identical to the M12 family peptidase from M. odoratimimus CCUG 3837 (EKB05810.1) and CCUG 12700 (EPH13478.1), and shares 99% similarity with the peptidase from M. odoratimimus CIP 101113 and the myroilysin from M. profundi D25 (23).
Further sequence analysis showed that a signal peptide consisting of residues 1–31 and a pro-peptide consisting of residues 32–68 are present at the N terminus, and residues 69–273 encode a mature protein (myroilysin) of ∼25 kDa at the C terminus.
Protein Crystallization and Structure Determination
As attempts to obtain diffracted crystals of native mature protein purified from the culture supernatant failed, the gene encoding the mature peptide was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli C43 (DE3). Unfortunately, no target protein was obtained, which may be ascribable to the toxic proteolytic activity of the myroilysin to host cells. Thus, the zymogen (pro-myroilysin) was expressed in E. coli C43 (DE3) and purified for subsequent protein crystallization. However, despite extensive crystallization trials, no crystals were obtained. We noted a relatively large number of lysine residues (14 residues), accounting for 5.79% of the total amino acid residues in pro-myroilysin. Because methylation of the ϵ-amino group of lysine is reported to be helpful for protein crystallization (29–31), reductive methylation was attempted to modify the pro-myroilysin surface. The methylated pro-myroilysin was further purified and crystallized. Large flake-like crystals of the pro-myroilysin were finally obtained.
Because myroilysin is a zinc-dependent metalloprotease, a zinc ion should be present in the active site of pro-myroilysin. A data set at the peak wavelength of zinc (1.2816 Å) was collected to solve the phase. The structure was determined using a single wavelength anomalous dispersion method and refined to 1.89 Å. Another 1.6 Å data set was collected from different conditions (0.1 m BisTris, pH 6.5, 40% PEG 4000), and the structure was determined using the molecular replacement method with the 1.89 Å model as a template. The refined structures correspond well to crystallographic data and anticipated geometric values (Table 1).
TABLE 1.
Data collection and refinement statistics
| Peak | Native | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystallization conditions | 0.1 m HEPES-NaOH, pH 7.5, 1.4 m sodium citrate | 0.1 m BisTris, pH 6.5, 40% PEG 4000 |
| Data collection | ||
| Wavelength (Å) | 1.2816 | 0.9791 |
| Temperature (K) | 100 | 100 |
| Crystal-to-detector distance (mm) | 200 | 200 |
| Rotation range per image (degrees) | 1 | 1 |
| Total rotation range (degrees) | 540 | 360 |
| Space group | P21 | P21 |
| Unit-cell parameters | ||
| a, b, c (Å) | 72.2, 35.5, 93.8 | 51.2, 35.1, 64.3 |
| β (degrees) | 101.4 | 110.1 |
| Resolution range (Å) | 19.90–1.89 (1.99–1.89)a | 19.27–1.6 (1.69–1.60)a |
| Observed reflections | 400,119 (42,953) | 211,175 (30,523) |
| Unique reflections | 37,660 (4,989) | 28,643 (4,143) |
| Multiplicity | 10.6 (8.6) | 7.4 (7.4) |
| Rmerge (%) | 12.8 (70.1) | 10.9 (81.5) |
| Rmeas (%) | 14.3 (78.1) | 11.8 (87.6) |
| Rpim (%) | 4.3 (26) | 4.3 (32) |
| Completeness (%) | 98.6 (91.0) | 99.9 (100) |
| I/σ(I) | 11.9 (3.7) | 11.9 (2.7) |
| Structure refinement | ||
| Total no. of atoms | 4,000 | 2,056 |
| No. of reflections used | 35,832 | 27,216 |
| Rwork (%) | 18.15 | 19.09 |
| Rfree (%) | 22.38 | 23.00 |
| r.m.s.d. bonds (Å) | 0.0067 | 0.0062 |
| r.m.s.d. angles (degrees) | 0.855 | 0.857 |
| Ramachandran plot (%) | ||
| Favored | 98.5 | 96.44 |
| Allowed | 1.5 | 3.56 |
| Outlier | 0 | 0 |
a The highest resolution shell is shown in parenthesis.
Overall Structure
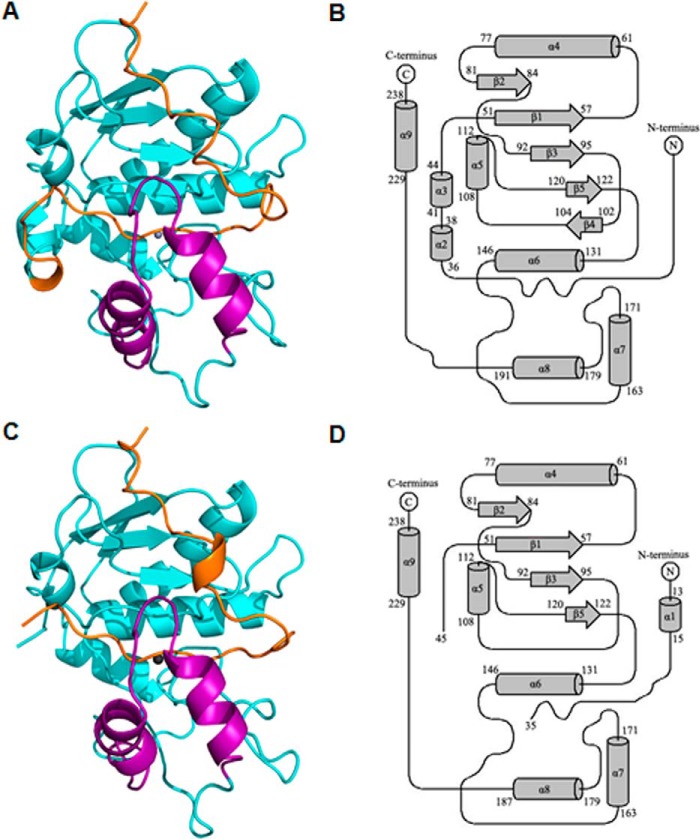
The pro-myroilysin monomer comprises 242 residues and is composed of a pro-peptide consisting of residues 1–37, an N-terminal domain consisting of residues 38–151 and residues 229–242, and a C-terminal domain consisting of residues 152–228. The overall structure indicates that pro-myroilysin is a spherical molecule (Fig. 2, A and C). The crystal structure of pro-myroilysin from the 0.1 m HEPES-NaOH, pH 7.5, 1.4 m sodium citrate condition was refined to 1.89 Å. The topology of pro-myroilysin is shown in Fig. 2B. The crystal belongs to the P21 space group with cell dimensions a = 72.2, b = 35.5, c = 93.8 Å. There are two almost identical molecules of pro-myroilysin with root mean square deviations (r.m.s.d.) of 0.35 Å in the asymmetric unit. In the pro-myroilysin molecule, 23% of residues form nine α-helices, and 8% of residues form five β-strands. The pro-peptide in this model is fully visible (Fig. 2A); it includes a 310-helix (formed by residues 15–17) flanked by coils. The N-terminal domain mainly consists of six α-helices (α2–6 and α9) and a five-stranded (β1–5) parallel β-sheet fragment. The β-sheet fragments pack against the two long α-helices (α4 and α6), and helix α9 is inserted into the cleft between helices α4 and α6. The C-terminal domain is composed of two α-helices (α7–8) and coils. The two helices (α7–8) pack almost perpendicularly against each other and cover the active site.
FIGURE 2.
Overall structure of pro-myroilysin. A, overall structure of pro-myroilysin, solved at 1.89 Å. The pro-peptide is colored orange; the polypeptide chain composed of residues 160–193 is purple; the zinc ion is gray; other parts are cyan. B, topology of the pro-myroilysin structure solved at 1.89 Å. The N-terminal domain is formed by five helices (α3–6 and α9) and four β-strands (β1–5). The C-terminal domain is formed by two helices (α7–8) and coils. C, overall structure of pro-myroilysin solved at 1.6 Å. The pro-peptide is orange; the polypeptide chain composed of residues 160–193 is purple; the zinc ion is gray; other parts are cyan. D, topology of the pro-myroilysin structure solved at 1.6 Å. The N-terminal domain is formed from four helices (α4–6 and α9) and four β-strands (β1–3 and β5). The C-terminal domain is formed from two helices (α7–8) and coils. The diagrams were drawn using TopDraw.
The three-dimensional structure of pro-myroilysin from the 0.1 m BisTris, pH 6.5, 40% PEG 4000 condition was resolved at 1.6 Å with Rwork of 19.1% and Rfree of 23.0%. The crystal belongs to the P21 space group with cell dimensions a = 51.2, b = 35.1, c = 64.3 Å. There is only one molecule of pro-myroilysin in the asymmetric unit. In the pro-myroilysin molecule, 20% of residues form seven α-helices, and 7% of residues form four β-strands (Fig. 2C). Notably, the electron density is invisible for the fragment from residue Thr-36 to Arg-44. The topology of pro-myroilysin is shown in Fig. 2D.
A comparison of the structures obtained from these two conditions revealed that they are almost identical, with an r.m.s.d. of 0.35 Å, but some differences between these two structures were still observed, including the regions from 19 to 23, from 153 to 160, and from 214 to 224 and missing residues 36–44. These differences may stem from the crystal packing caused by intramolecular and intermolecular interactions.
Active Site
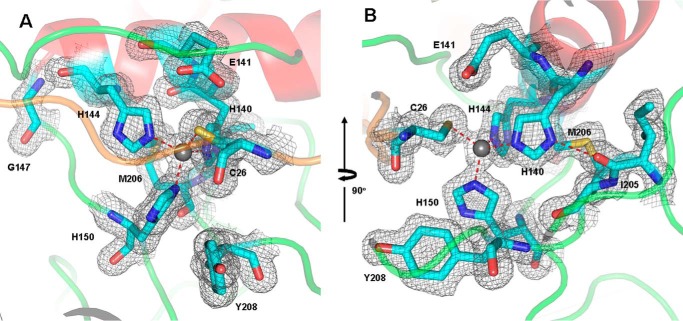
The N-terminal domain and the C-terminal domain form a deep V-shaped cleft, and the active site is located at the bottom of the cleft (Figs. 2 and 3). In the long and deep active site cleft, the catalytic zinc ion at the bottom is coordinated in a triangular pyramidal geometry by three NE2 atoms of His-140 (2.3 Å), His-144 (2.1 Å), and His-150 (2.1 Å), belonging to the signature motif HEXXHXXGXXH. The zinc cation is also coordinated by the SG atom of the side chain of the cysteine residue Cys-26 in the pro-peptide, with a distance of 2.3 Å. The catalytic residue Glu-141, following the first histidine zinc ligand (His-140), is not involved in coordinating the zinc ion, but the OE2 atom of Glu-141 forms a hydrogen bond (3.0 Å) with the SG atom of Cys-26. The side chains of His-140, Glu-141, and His-144 from the central helix α6 project into the deep active site cleft, and the α6 helix extends to Gly-147, where it turns sharply to bring the third coordinator (His-150) of zinc ion to the active site (Fig. 3A). The following Glu-151, the direct neighbor of the third zinc ligand His-150, is thought to be strictly conserved in the members of astacins (32).
FIGURE 3.
Active site of pro-myroilysin. A, active site of pro-myroilysin. The catalytic zinc ion is represented as a gray sphere; the zinc ligands (His-140, His-144, and His-150), the Cys-26 residue of the pro-peptide and the conserved residues Glu-141, Gly-147, Tyr-208 are rendered in cyan sticks; the pro-peptide, helix, and coils are colored orange, red, and green, respectively. B, Ile-205 of the M-turn forms a hydrogen bond with the first zinc ligand His-140. The corresponding electron density (2Fo − Fc) is light gray and contoured at 1.0 σ.
In the other signature motif, SIMHY (residues 204–208), the oxygen atom of the Ile-205 main chain carbonyl group forms a specific interaction with the ND1 atom of the first zinc ligand His-140 through a hydrogen bond (2.7 Å) (Fig. 3B) and is involved in structure stability. However, the side chain of Tyr-208 faces away from the catalytic zinc (Fig. 3), whereas the corresponding tyrosine is engaged in zinc and substrate binding and stabilization in mature astacin and serralysin (27, 33, 34).
Structure Comparison of Pro-myroilysin with Homologues from M12A, M10A, and M10B Subfamilies
A structure similarity search performed with the atomic coordinates of pro-myroilysin using the DALI server yielded the M12 family proastacin (PDB code 3LQ0) (19), pro-meprin (PDB code 4GWM) (35), choriolysin (PDB codes 3VTG and 3LQB) (36), M10 family prokarilysin (PDB code 4R3V) (37), macrophage metalloelastase (PDB code 1UTT) (38), and M12 family astacin (PDB code 1AST) (16), among others.
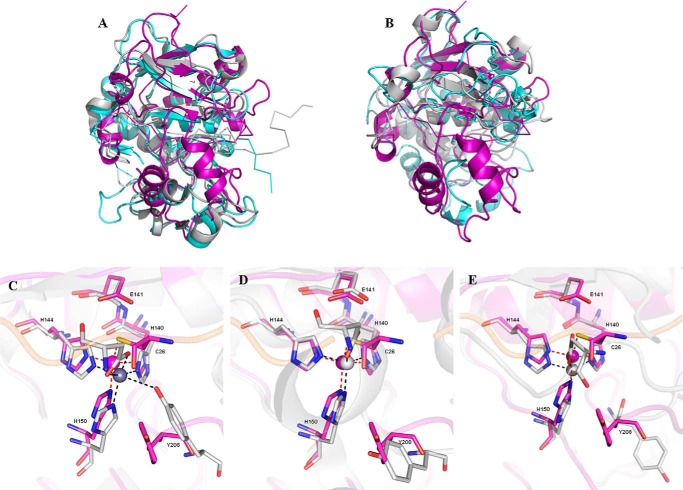
A structural comparison of pro-myroilysin with homologues from M12A, M10A, and M10B subfamilies was also performed. Pro-myroilysin superimposes with the M12 family proteases pro-astacin (PDB code 3LQ0) and pro-meprin (PDB code 4GWM) with an r.m.s.d. of 3.2 Å (for 178 target pairs) and 2.9 Å (for 172 target pairs) and shares amino acid sequence identities of 20 and 21%, respectively. Fig. 4A shows that the N-terminal β1–5 strands of pro-myroilysin partially superimpose onto the corresponding β strands of pro-astacin and pro-meprin homodromously; helices α4, α6, and α9 also partially superimpose onto the corresponding helices of pro-astacin and pro-meprin homodromously. However, the β5 strand of pro-myroilysin is much shorter than the corresponding β-strand of pro-astacin and pro-meprin and instead forms a loop structure protruding outside of the protein. This may be caused by the helix α5 located between β4 and β5. There are also many structural differences between the structures; for example, the α3 helix could not superimpose onto the corresponding helix. The most remarkable structural differences are present at the C terminus. The C-terminal domain of pro-myroilysin consists of coils and two helices (α7 and α8; purple in Fig. 2, A and C); the two helices form the unique cap structure situated above the active site. The C-terminal domains of pro-astacin and pro-meprin have four or five helices and three β strands, but there is no obvious cap structure above the active sites.
FIGURE 4.
Overall structure and active site comparison of pro-myroilysin with that of M12 and M10 family proteases. A, superimposed overall structures of pro-myroilysin (purple), M12 family pro-astacin (aquamarine), and pro-meprin (light gray). B, superimposed active site overall structures of pro-myroilysin (purple) and M10 family pro-karilysin (light gray) and catalytic domain of serralysin (aquamarine). C–E, superimposed active site structures of pro-myroilysin (purple) with pro-astacin, pro-meprin, and pro-karilysin (light gray). The zinc ion of pro-myroilysin is shown as a purple sphere; the zinc ligands of pro-myroilysin are shown as sticks with purple carbon atoms; the zinc ions of pro-astacin, pro-meprin, and pro-karilysin are shown as light gray spheres; the zinc ligands of astacin, pro-meprin, and pro-karilysin are shown as sticks with light gray carbon atoms.
Moreover, pro-myroilysin superimposes onto the M10A family protease pro-karilysin (PDB code 4R3V) with an r.m.s.d. of 2.7 Å (for 179 target pairs) and the M10B family protease serralysin with inhibitor (PDB code 1AF0) with an r.m.s.d. of 3.5 Å (for 154 target pairs); the amino acid sequence identities were 15 and 21%, respectively. As shown in Fig. 4B, the structure of pro-myroilysin also shows similar structural similarity to pro-karilysin and the catalytic domain of serralysin. The helices α4, α6, and α9 of pro-myroilysin partially superimpose onto the corresponding helices of pro-karilysin and the catalytic domain of serralysin homodromously, and β1–5 strands also superimpose well and are located on the surface of both molecules. The C-terminal domain of pro-karilysin and the catalytic domain of serralysin also do not contain a cap structure. Overall, the superimposition of pro-myroilysin with M12A, M10A, and M10B family proteases showed that the N-terminal domain of pro-myroilysin superimposes well with them, whereas the C terminus is evidently structurally different, particularly the cap structure.
Detailed structural and sequence analyses were also performed. As mentioned above, the conserved Gly-147 (equivalent to Gly-99 of astacin and Gly-181 of serralysin) and the M-turn SIMHY are also present, whereas the Tyr-208 (equivalent to Tyr-149 in astacin and Tyr-216 in the serralysin, involved in zinc binding) points away from the zinc in pro-myroilysin (Fig. 3). In addition, the Tyr-239 of pro-myroilysin also perfectly matches the Tyr-194 of astacin and Tyr-246 of serralysin, which are involved in locking the C-terminal helix to the molecular moiety. The 90-loop of pro-myroilysin is exactly equivalent to the loop connecting strands β2 and β3 in astacin and serralysin.
It has been reported that there are two disulfide bonds in astacin and that these two bonds are likely to be conserved among all astacins and contribute to shaping the active site cleft (39). However, no disulfide bond is present in pro-myroilysin, as in serralysin and pro-karilysin.
Inhibition Mechanism
For pro-astacin, pro-meprin, and pro-karilysin, one striking difference could also be observed from pro-myroilysin. The pro-peptides of pro-astacin, pro-meprin, or pro-karilysin, containing 34, 37, or 14 residues, run through the cleft, and a side chain atom of a conserved aspartate residue (Asp-21, Asp-52, or Asp-25) of the pro-peptide is anchored to the catalytic zinc ion to replace the zinc-binding solvent molecule (Fig. 4, C–E). This is the “aspartate switch” activation mechanism (19). For pro-myroilysin, the pro-peptide consisting of 37 residues runs through and occupies the active site cleft to prevent access to peptide substrates. Instead of an aspartate residue, the side chain sulfur atom of Cys-26 of the pro-peptide coordinates the catalytic zinc ion to expel the catalytic water molecule from the activity site, allowing the inhibition of pro-myroilysin catalysis and its so-called “cysteine switch” mechanism (Figs. 3 and 4 (C–E)). Other than this difference, the direction of binding in the pro-peptide of the active site cleft of pro-myroilysin is the same as that seen in the pro-astacin structure (Fig. 4A).
Interestingly, the segment including the conserved “cysteine switch” is unique in pro-myroilysin; the AKVCKDV motif has never been reported, whereas PRCGXPD is conserved in MMPs, PKMCGV in ADAMs (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase), HRCIHD in leishmanolysins, and CG in pappalysins (17).
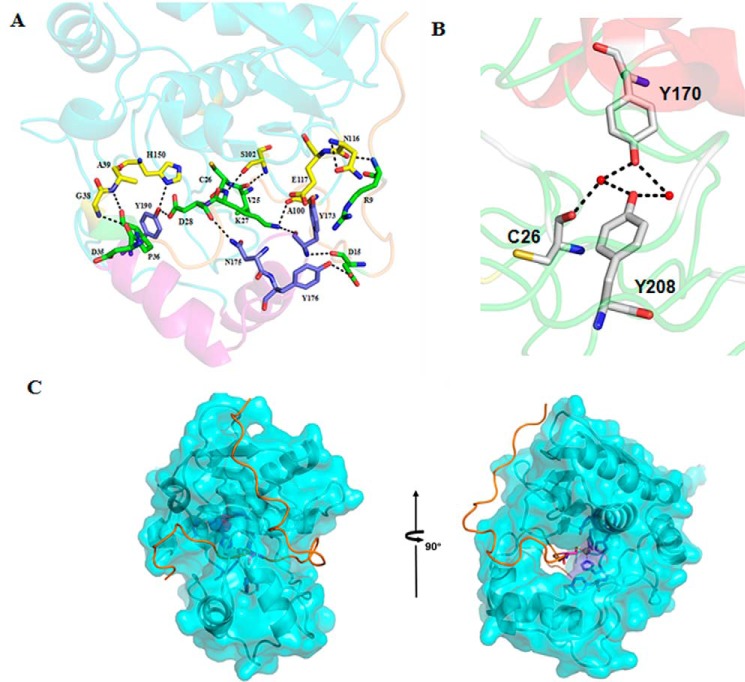
PISA (40) was used to analyze the interactions between the pro-peptide and the mature peptide of pro-myroilysin. The pro-peptide main chain, consisting of 37 residues, extends along the spherical molecule surface of the mature peptide to the active site pocket. Starting at Arg-9, the residues bind the surface of the mature enzyme; from Ala-23, the main chain runs through the active site pocket. The pro-peptide of pro-myroilysin is firmly bound to the mature peptide through several intramolecular interactions, such as hydrogen bonds and salt bridges. Eleven hydrogen bonds are formed between the eight residues (Arg-9, Asp-15, Val-25, Cys-26, Lys-27, Asp-28, Asp-35, and Pro-36) of the pro-peptide and the 11 residues (Gly-38, Ala-39, Ala-100, Ser-102, Asn-116, Glu-117, His-150, Tyr-173, Asn-175, Tyr-176, and Tyr-190) of the mature peptide (Fig. 5A); two salt bridges form between the Cys-26 of the pro-peptide and Tyr-170 and Tyr-208 of the mature peptide (Fig. 5B). In addition, the cysteine residue of the pro-peptide itself (Cys-26) is tightly bound to the catalytic zinc ion (Fig. 3). Therefore, the pro-peptide is firmly fixed in the active site pocket.
FIGURE 5.
The interaction of the pro-peptide and mature peptide in pro-myroilysin. A, the pro-peptide forms interactions with the mature peptide in pro-myroilysin. The residues shown as sticks with green carbon atoms belong to the pro-peptide; residues shown as sticks with carbon atoms colored yellow belong to mature peptide, except for the cap structure; the residues shown as sticks with carbon atoms colored sky blue belong to the cap structure. B, Cys-26 forms interactions with Tyr-170 and Tyr-208 though water-mediated hydrogen bonds. Water molecules are shown as red spheres; Cys-26, Tyr-170, and Tyr-208 are shown as light gray sticks. C, surface contour image showing access to the active site pocket of pro-myroilysin.
In the reported mature enzymes of the M10 and M12 family of proteases, the catalytic water molecule is anchored by the glutamate residue following the first histidine zinc ligand (41) and is thought to be responsible for the nucleophilic attack to the carbon atom of the carbonyl group of the substrate peptide bond (14). However, in pro-myroilysin the catalytic water molecule is absent, and instead a cysteine residue (Cys-26) in the pro-peptide coordinates the zinc ion. Cys-26 also forms a hydrogen bond with the catalytic Glu-141 residue (Fig. 3). Thus, the presence of Cys-26 expels the catalytic water molecule away from the active site and results in inhibition of protease activity.
A Unique Cap Structure in Pro-myroilysin May Be Involved in Substrate Binding
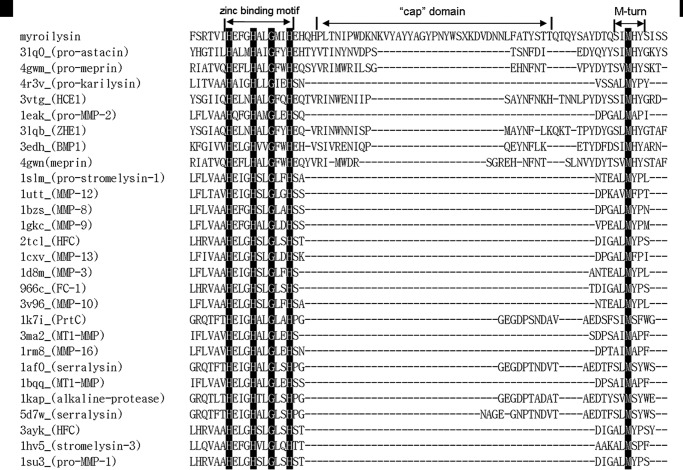
Structure-based sequence alignment of pro-myroilysin with other proteases with Z scores >10 indicate that these proteases belong to the M10 or M12 subfamily, especially the M12A, M10A, and M10B subfamilies. However, the insert between the two conserved motifs of pro-myroilysin (HEXXHXXGXXH and M-turn SIMHY) are much longer than in other homologs (Fig. 6). This fragment (residues 160–193) includes the helices α7 and α8, forming the cap in the pro-myroilysin structure (Fig. 2, A and C).
FIGURE 6.
Structure-based sequence alignment of pro-myroilysin with members of the M12 and M10 families. Aligned sequences are representative members of the M12 and M10 families obtained from the Dali server result. The strictly conserved residues are highlighted. Conserved zinc binding motif, M-turn, and unique cap structure are indicated. HCE1, high choriolytic enzyme 1; ZHE1, zebrafish hatching enzyme 1; BMP1, bone morphogenetic protein 1; FC-1, fibroblast collagenase 1; MT1-MMP, membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase; HFC, human fibroblast collagenase; ProMMP-2, pro-matrix metalloproteinase-2.
Work by Chen showed that myroilysin has broad specificity and high elastinolytic activity, indicating that the active cleft of myroilysin is opened before the substrate accesses it (23). The unique cap structure in pro-myroilysin, which does not exist in the other structure-reported members of the M12 or M10 family, may help to stabilize the pro-peptide through hydrogen bonds (Fig. 5A). Tyr-170 and Tyr-190 are two unique amino acid residues in the cap structure. The oxygen atom of Tyr-190 forms a hydrogen bond (2.9 Å) with the third histidine zinc ligand (His-150), and therefore the Tyr-190 residue seems to stabilize the conformation of the third histidine and the pro-peptide of pro-myroilysin (Fig. 5A). Furthermore, the Tyr-170 residue in the cap could also stabilize the pro-peptide through water-mediated hydrogen bonds (Fig. 5B).
In our pro-myroilysin structure, the cap domain covers the pro-peptide and forms a tunnel that holds the pro-peptide inside (Fig. 5C). If the tunnel exists throughout the entire catalytic cycle, the substrate must be inserted into the tunnel for cleavage. However, because the tunnel is not wide enough to directly let the substrate get into the tunnel, we hypothesized that there is a conformational change to expose the active site, with the cap moving away from the active site after the N-terminal pro-peptide of pro-myroilysin is proteolytically removed.
In addition, it has been reported that the Glu-103 of astacin, the amino acid residue just after the third zinc-binding His in the HEXXHXXGXXH motif, is important for structural stability due to its water-mediated salt bridge to the N-terminal Ala-1 after the pro-peptide is cleaved (42). The main chain of astacin rotates 180° around the Ψ main chain angle of the new N-terminal residue to allow the N terminus to bury into the mature enzyme body to maintain the structural features. The removal of the pro-segment would offer sufficient space for the activation domain to enclose its substrate (39). This Glu is thought to be the family-specific residue of astacin family (M12A) proteases, whereas the corresponding residue is a proline or serine in the serralysin family of protease (M10B) or MMPs (M10A) (17, 32). Inspection of the mature N termini of representative astacin family members also showed that N-terminal residues are almost exclusively alanine or asparagine (39). Glu-151 is the corresponding amino acid residue in the HEXXHXXGXXH motif of pro-myroilysin. However, the Glu-151 is far from the Gly-38, the first amino acid residue of the mature myroilysin (23) in the structure of pro-myroilysin. Instead, Glu-151 can form hydrogen bonds with Thr-195 and Gln-196 just after the α7 and α8 helices (cap structure), which do not exist in astacin, and keeps the Glu-151 from the Gly-38 in the pro-myroilysin (Fig. 7). This may imply that the unique cap structure in pro-myroilysin might change the structure arrangement. However, the real role of the cap structure in the mature form of myroilysin is still unknown.
FIGURE 7.
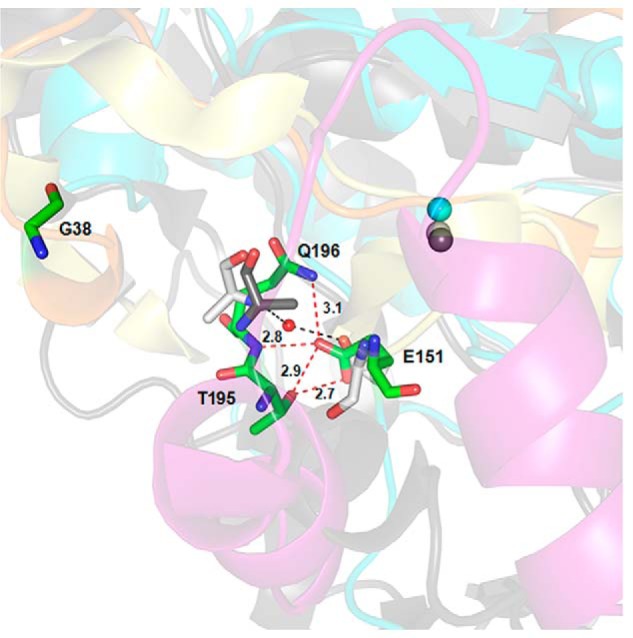
The conserved Glu-151 just after the third zinc-binding His in the HEXXHXXGXXH motif of pro-myroilysin interacts with Thr-195 and Gln-196 just after the cap structure. The conserved Glu-151 forms hydrogen bonds with Thr-195 and Gln-196 and distances itself far from Gly-38 (the first amino acid residue in myroilysin) in pro-myroilysin. In contrast, the Ala-1 of proastacin is much closer to the corresponding residue Glu-101 and forms water-mediated salt bridges to the N-terminal Ala-1 after the pro-peptide is cleaved. The pro-peptide, the cap structure, and the rest of pro-myroilysin (including the zinc ion) are in orange, purple, and cyan, respectively; Gly-38, Glu-151, Thr-195, and Gln-196 of pro-myroilysin are rendered in green sticks; the pro-peptide and the rest of pro-astacin are light yellow and gray, respectively. Glu-101 (light gray) and Ala-1 of astacin (light gray) and Ala-1 in pro-astacin (dark gray) are shown as sticks; the zinc ions in pro-astacin and astacin are shown in dark gray and light gray, respectively; water molecules are shown in red.
The structure of mature myroilysin would answer the question, but unfortunately, we failed to obtain diffractable myroilysin crystals of native mature myroilysin from the culture supernatant of cslb8 and failed to obtain myroilysin expressed in E. coli. This may imply that myroilysin with proteolytic activity is toxic to E. coli cells.
Structure and Sequence Analysis Suggest That Myroilysin Is a Bacterial M12 Family Protease
The M10 and M12 families of proteases are two major families of metzincins. They share quite high sequence similarity, zymogen activation, and catalytic mechanisms, including the signature conserved motifs HEXXHXXGXX(H/D) and Met-turn (14).
The M12 family is the second largest family in the metzincins, and proteases in this family are mainly found throughout the animal kingdom and rarely in bacteria. Although quite a few structures from the M12 family have been solved, no structural information is available for M12 family proteases from bacteria. The flavastacin from Flavobacterium meningosepticum (20–22) is the only reported bacterial proteases in this family. Myroilysin is a newly identified metazincin from M. profundi D25, and amino acid sequence analysis showed that it belongs to the M12A family of proteases (23). However, myroilysin is classified in the M10B family in the peptidase database MEROPS.
Here, we report the crystal structures of pro-myroilysin in two different crystal forms from Myroides sp. cslb8. A structural comparison of pro-myroilysin with some M12 and M10 family proteases, including astacin, meperin, karilysin, and serralysin, is shown in Fig. 4. The overall structural comparison with these M12 and M10 family proteases showed that the N-terminal domain of pro-myroilysin superimposes well, whereas the C-terminal domain is structurally different. The signature motif HEXXHXXGXXH and the M-turn (SIMHY) of pro-myroilysin are strictly conserved (Fig. 6). The three histidine residues belonging to the HEXXHXXGXXH motif of these three proteins are structurally conserved and function as zinc ligands (Fig. 4, C–E).
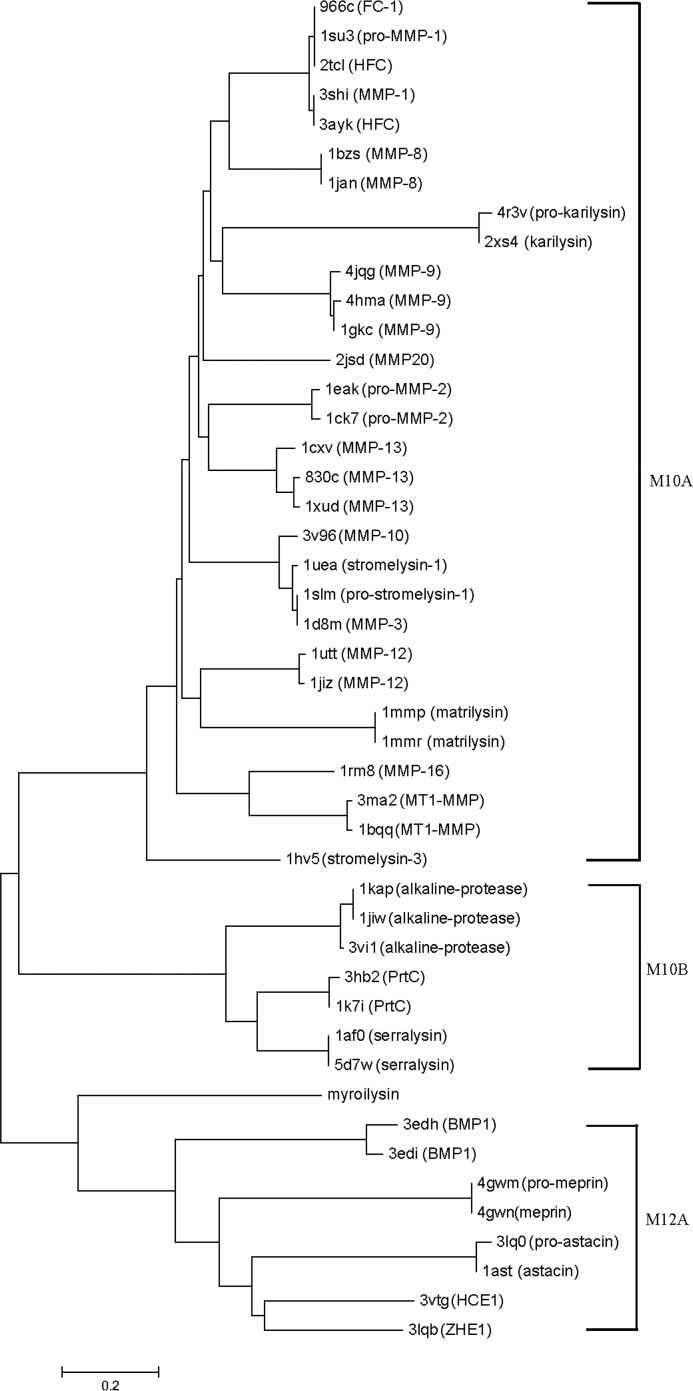
The Dali server results showed that the structure of pro-myroilysin shares some similarity with M12A, M10A, and M10B family proteases, such as pro-astacin, pro-meperin and serralysin. The phylogenetic tree of the myroilysin structure-based homologs based on the Dali server (Z > 10) was then constructed. Fig. 8 shows that distinct clusters form for M10 and M12 family proteases; pro-myroilysin is clearly more closely related to M12A family proteases than M10B family proteases or M10A family proteases. The above results have showed a conserved Glu residue just after the third zinc-binding His in the HEXXHXXGXXH motif, which is thought to be a family-specific residue of the astacin family; non-animal M10A proteases do not usually employ a cysteine switch activation mechanism (as in pro-karilysin). We conclude that pro-myroilysin should belong to the M12A family rather than the M10 family. However, pro-myroilysin also forms a distinct branch with structurally determined M12A family proteases in the phylogenetic tree and has a different activation mechanism (cysteine switch mechanism) from the M12A family. In addition, due to a special cap structure, different N terminus amino acid residues in the mature enzyme, a different binding character of Glu151, and its function in pro-myroilysin, we also conclude that myroilysin should be a new member of the M12A family of proteases or may even form a new M12 subfamily. In summary, our crystal structures and structural comparison with M12 and M10 family proteases contribute new insights into the classification of the M12 metalloprotease family and may imply a divergent evolution of this family.
FIGURE 8.
Structure-based phylogenetic tree illustrating the relationship between the pro-myroilysin and its homologs. The data set of these homologs was obtained from DALI by selecting proteins with Z score >10 when compared with pro-myroilysin. For the sake of clarity, only 46 proteins are shown in the phylogenetic tree. Scale bar, phylogenetic distance. PDB codes and protein names are listed. ZHE1, zebrafish hatching enzyme 1; HCE1, high choriolytic enzyme 1; BMP1, bone morphogenetic protein 1; ProMMP-2, pro-matrix metalloproteinase-2; HFC, human fibroblast collagenase; FC-1, fibroblast collagenase 1; MT1-MMP, membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase; MMP20, enamelysin; MMP-11, stromelysin-3.
Materials and Methods
Biological Material and Culture Conditions
Bacterial strain cslb8 was isolated from silkworm feces on the LB medium (1% NaCl, 1% tryptone, and 0.5% yeast extract) with a 2% skim milk plate. Strain cslb8 was inoculated in LB medium on a rotary shaker at 180 rpm at 28 °C for 12 h and then transferred into 1 liter of LB medium at 28 °C for another 12 h. The culture was centrifuged at 8,000 rpm, and the supernatant was then used for protein isolation and purification.
16S rDNA Sequencing
The 16S rDNA gene of CSLB8 was amplified by PCR using the genomic DNA as template with the common primers, and the PCR product was then cloned and sequenced. Multiple alignment of the sequence was performed using the ClustalW program (44).
Protein Purification and Sequence Determination
All of the following purification procedures were performed at 4 °C if not otherwise indicated. Ammonium sulfate was added to the culture supernatant to reach 80% saturation. The precipitate was collected after centrifugation at 15,000 rpm for 30 min. The precipitate was dissolved in 40 mm KH2PO4/K2HPO4 (pH 7.6) and diluted with an equal volume of 2 m ammonium sulfate solution. After centrifugation, the sample was then loaded onto an octyl-Sepharose 4 fast flow chromatography column (2-ml bed volume) pre-equilibrated with binding buffer (20 mm KH2PO4/K2HPO4, pH 7.6, and 1 m (NH4)2SO4). After washing with 5 bed volumes of binding buffer, the protein was eluted with a linear gradient of 1 to 0 m ammonium sulfate. The eluted protease was then concentrated by the Amicon Ultra15 centrifugal filter unit with a 10 kDa molecular mass cut-off (Merck Millipore) and further purified by the Sephadex G200 gel filtration column pre-equilibrated with 20 mm Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 300 mm NaCl. The purified protein was then eluted with the same buffer. The purified protein was then inspected on 12% SDS-PAGE. The protein concentration was measured using the PerkinElmer Life Sciences Lambda 25 UV-visible spectrometer at 280 nm.
After SDS-PAGE separation and gel staining, the single protein band was cut off from the gel; the protein was then sequenced by an ultrafleXtreme MALDI-TOF/TOF mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltonics). Peptide sequences were identified by searching the peak list against the Mass Spectrometry Protein Sequence Database using the Mascot version 2.1 search engine (45).
Gene Amplification and Cloning
To amplify the gene encoding the purified protease, a pair of degenerated primers, 5′-gacgcatATGAAATTACACCACAAGATCC (upstream primer 1) and 5′-cagctcgagGTTTCTTGGATAMACTGTTGC (downstream primer 2), were designed according to the result of the mass spectrometry and the sequence alignment of the genes encoding M12 family metalloproteases from bacteria. The restriction sites (NdeI and XhoI) are underlined. PCR amplification was carried out with Pfu DNA polymerase (Thermo Fermentas) using the genomic DNA of cslb8 as template. The PCR product was then cloned into the pET24b and sequenced by the Beijing Luhe Technology Co. Ltd.
Protein Expression and Purification
For expression and purification of myroilysin and pro-myroilysin, the genes encoding the two proteins were amplified through PCR with the chromosomal DNA of Myroides sp. cslb8 as template. PCR was performed with Pfu DNA polymerase and the following primers: myroilysin_forward (5′-atcgcatatgGGGGCTGTTGTCAGAAGTACAAAG-3′) and myroilysin_reverse (5′-cagctcgaggtttcttggatamactgttgc-3′), pro-myroilysin_forward (5′-tacgcatatgAGTAGTAAGGGGCTAAAAGAATTAAG-3′), and myroilysin_reverse. The amplified genes and the pET24b vector were digested with NdeI and XhoI restriction enzymes and ligated. The recombinant plasmids (pET24b_myroilysin and pET24b_pro-myroilysin) were verified by restriction reaction and DNA sequencing, and the correct recombinant plasmids were then each transformed into expression strain E. coli C43 (DE3).
The fresh transformants were grown in LB medium containing kanamycin (30 μg/ml) at 37 °C until the A600 reached 0.7. The cells were cooled to 25 °C and then induced with 0.1 mm isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside by incubating at 25 °C for another 5 h. The induced cells were harvested, carefully resuspended in binding buffer (50 mm KH2PO4/K2HPO4, pH 7.6, 300 mm NaCl, 5 mm imidazole, 10% (v/v) glycerol) supplemented with 1 mm PMSF, and then sonicated in an ice bath. After removing insoluble materials and unbroken cells by centrifugation, the supernatant was applied to a 2-ml bed volume nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid (GE Life Sciences) column, which was pre-equilibrated with 6 bed volumes of binding buffer. After washing the column with the buffers containing different concentrations of imidazole (5, 20, and 50 mm, 6 bed volumes each), the pro-myroilysin was eluted with buffer containing 100 mm imidazole.
The buffer of eluted protein was exchanged with 50 mm KH2PO4/K2HPO4, pH 7.6, 300 mm NaCl, and 10% (v/v) glycerol using a desalting column, and then the target protein was concentrated to 8 mg/ml for the subsequent methylation (according to a methylation protocol (Hampton Research)). Methylation was carefully performed by dimethylamine borane complex and formaldehyde, as reported previously (46). The methylated pro-myroilysin was concentrated to ∼1 ml using an Amicon Ultra-10 filter (Millipore) and then loaded onto a Superdex 200 column pre-equilibrated with 20 mm Tris-Cl, pH 8.5, 300 mm NaCl, and 10% (v/v) glycerol. The column was then carefully eluted with 1.2 bed volumes of the pre-equilibrated buffer. The elution pattern showed that there was only a single peak, which was further analyzed by SDS-PAGE to check the purity of pro-myroilysin. Pro-myroilysin was pooled together and concentrated to 20 mg/ml for crystallization.
Protein Crystallization
Crystallization was performed with the commercial kits from Hampton Research and Microlytic using the sitting drop vapor diffusion method at 4 and 22 °C. The initial screen yielded flake-like crystals at 22 °C from the 0.1 m BisTris, pH 6.5, 40% PEG 4000 condition and flaky crystals at 4 °C from the following three conditions: 0.1 m HEPES-NaOH, pH 7.5, 1.4 m sodium citrate; 1.6 m sodium citrate; and 0.1 m Tris-Cl, pH 8.5, 1.25 m sodium citrate. Because flake-like crystals at the 0.1 m BisTris, pH 6.5, 40% PEG 4000 condition grow better and need a short time to grow to full size (about 7 days), this condition was chosen for further optimization. A systematic grid screening of precipitant concentrations, pH, and protein concentrations was set up to optimize the crystal. The best condition was then optimized with the commercial additive screening kit (Hampton Research).
Data Collection, Structure Determination, and Refinement
The crystal was carefully looped out from the crystallization drop and quickly cooled in liquid nitrogen. Data collection was performed at 100 K. X-ray diffraction data sets were collected at beamline BL17U1 of the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (47). The crystal from the 0.1 m HEPES-NaOH, pH 7.5, 1.4 m sodium citrate condition was diffracted to 1.89 Å. A full data set of 540 frames was collected at the peak wavelength (1.2816 Å) of zinc ion. Each frame was exposed with a rotation range of 1.0 for 1.2 s. Diffraction data were processed with XDS (48). The structure of pro-myroilysin was solved using the SAS protocol of Auto-Rickshaw: the EMBL-Hamburg automated crystal structure determination platform (49). The input diffraction data were prepared and converted for use in Auto-Rickshaw using programs of the CCP4 suite (50). FA (the estimated substructure structure factors) values were calculated using the program SHELXC (51). Based on an initial analysis of the data, the maximum resolution for substructure determination and initial phase calculation was set to 2.4 Å. Both of the two heavy atoms requested were found using the program SHELXD (52). 84.30% of the model was built using the program ARP/wARP (53, 54). The crystal from the 0.1 m BisTris, pH 6.5, 40% PEG 4000 condition was diffracted to 1.6 Å. A data set of 360 frames was collected at wavelength 0.9791 Å. The crystal structure of pro-myroilysin from this condition was solved with the molecular replacement method with Phaser using the 1.89 Å crystal structure of pro-myroilysin (55). The structure model was manually adjusted with Coot (56), and structure refinement was performed with REFMAC and Phenix (57, 58). The models were validated with MolProbity (59). All figures were drawn with PyMOL (60) and TopDraw (61). Data processing and refinement statistics are summarized in Table 1.
Sequence Alignment
Structure-based amino acid sequence alignment of members of the M12 family was performed with the Dali server and then redrawn with ClustalX version 1.81 (62) and GENEDOC (43).
Author Contributions
W. W., D. X., and T. R. conceived the study. D. X., J. Z., X. L., and T. R. conducted the experiments. J. H. and all other authors participated in data analysis and wrote the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff of the BL17B/BL18U1/BL19U1 beamlines at the National Center for Protein Sciences Shanghai and the staff of beamline BL17U of the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility for assistance during data collection.
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China Grants 31400055, 31170686, and 31100028; Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province Grant BK20140690; and Youth Science and Technology Innovation Fund from Nanjing Agricultural University Grant KJ2013027. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
The atomic coordinates and structure factors (codes 5CZW and 5GWD) have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank (http://wwpdb.org/).
- MMP
- matrix metallopeptidase
- BisTris
- 2-[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol
- r.m.s.d.
- root mean square deviation(s)
- PDB
- Protein Data Bank
- M-turn
- Met-turn.
References
- 1. Gupta R., Beg Q. K., and Lorenz P. (2002) Bacterial alkaline proteases: molecular approaches and industrial applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 59, 15–32 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Sastry K. J., Srivastava O. P., Millet J., FitzJames P. C., and Aronson A. I. (1983) Characterization of Bacillus subtilis mutants with a temperature-sensitive intracellular protease. J. Bacteriol. 153, 511–519 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Reysset G., and Millet J. (1972) Characterization of an intracellular protease in B. subtillus during sporulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 49, 328–334 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Okujo N., Akiyama T., Miyoshi S., Shinoda S., and Yamamoto S. (1996) Involvement of vulnibactin and exocellular protease in utilization of transferrin- and lactoferrin-bound iron by Vibrio vulnificus. Microbiol. Immunol. 40, 595–598 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Fleming A. B., Tangney M., Jørgensen P. L., Diderichsen B., and Priest F. G. (1995) Extracellular enzyme synthesis in a sporulation-deficient strain of Bacillus licheniformis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61, 3775–3780 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Nishina Y., Miyoshi S., Nagase A., and Shinoda S. (1992) Significant role of an exocellular protease in utilization of heme by Vibrio vulnificus. Infect. Immun. 60, 2128–2132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Frankena J., Koningstein G. M., Vanverseveld H. W., and Stouthamer A. H. (1986) Effect of different limitations in chemostat cultures on growth and production of exocellular protease by Bacillus licheniformis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24, 106–112 [Google Scholar]
- 8. Miyoshi S., and Shinoda S. (2000) Microbial metalloproteases and pathogenesis. Microbes Infect. 2, 91–98 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Ichida J. M., Krizova L., LeFevre C. A., Keener H. M., Elwell D. L., and Burtt E. H. (2001) Bacterial inoculum enhances keratin degradation and biofilm formation in poultry compost. J. Microbiol. Methods 47, 199–208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Maeda H. (1996) Role of microbial proteases in pathogenesis. Microbiol. Immunol. 40, 685–699 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Cheng S. W., Hu H. M., Shen S. W., Takagi H., Asano M., and Tsai Y. C. (1995) Production and characterization of keratinase of a feather-degrading Bacillus licheniformis PWD-1. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 59, 2239–2243 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Aehle W., Sobek H., Amory A., Vetter R., Wilke D., and Schomburg D. (1993) Rational protein engineering and industrial application: structure prediction by homology and rational design of protein variants with improved “washing performance”: the alkaline protease from Bacillus alcalophilus. J. Biotechnol. 28, 31–40 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Zhu W. S., Wojdyla K., Donlon K., Thomas P. A., and Eberle H. I. (1990) Extracellular proteases of Aspergillus flavus: fungal keratitis, proteases, and pathogenesis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 13, 491–497 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Rawlings N. D., and Barrett A. J. (2013) Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes Introduction: Metallopeptidases and Their Clans, pp. 325–1740, Elsevier, London [Google Scholar]
- 15. Tallant C., Marrero A., and Gomis-Rüth F. X. (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases: fold and function of their catalytic domains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1803, 20–28 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Bode W., Gomis-Rüth F. X., Huber R., Zwilling R., and Stöcker W. (1992) Structure of astacin and implications for activation of astacins and zinc-ligation of collagenases. Nature 358, 164–167 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Stöcker W., Grams F., Baumann U., Reinemer P., Gomis-Rüth F. X., McKay D. B., and Bode W. (1995) The metzincins: topological and sequential relations between the astacins, adamalysins, serralysins, and matrixins (collagenases) define a superfamily of zinc-peptidases. Protein Sci. 4, 823–840 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Mac Sweeney A., Gil-Parrado S., Vinzenz D., Bernardi A., Hein A., Bodendorf U., Erbel P., Logel C., and Gerhartz B. (2008) Structural basis for the substrate specificity of bone morphogenetic protein 1/tolloid-like metalloproteases. J. Mol. Biol. 384, 228–239 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Guevara T., Yiallouros I., Kappelhoff R., Bissdorf S., Stöcker W., and Gomis-Rüth F. X. (2010) Proenzyme structure and activation of astacin metallopeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 13958–13965 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Tarentino A. L., Quinones G., Grimwood B. G., Hauer C. R., and Plummer T. H. Jr. (1995) Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of flavastacin: an O-glycosylated prokaryotic zinc metalloendopeptidase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 319, 281–285 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Reinhold B. B., Hauer C. R., Plummer T. H., and Reinhold V. N. (1995) Detailed structural analysis of a novel, specific O-linked glycan from the prokaryote Flavobacterium meningosepticum. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 13197–13203 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Plummer T. H. Jr., Tarentino A. L., and Hauer C. R. (1995) Novel, specific O-glycosylation of secreted Flavobacterium meningosepticum proteins: Asp-Ser and Asp-Thr-Thr consensus sites. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 13192–13196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Chen X. L., Xie B. B., Bian F., Zhao G. Y., Zhao H. L., He H. L., Zhou B. C., and Zhang Y. Z. (2009) Ecological function of myroilysin, a novel bacterial M12 metalloprotease with elastinolytic activity and a synergistic role in collagen hydrolysis, in biodegradation of deep-sea high-molecular-weight organic nitrogen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75, 1838–1844 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Rawlings N. D., Barrett A. J., and Finn R. (2016) Twenty years of the MEROPS database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, D343–D350 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Guevara T., Ksiazek M., Skottrup P. D., Cerdà-Costa N., Trillo-Muyo S., de Diego I., Riise E., Potempa J., and Gomis-Rüth F. X. (2013) Structure of the catalytic domain of the Tannerella forsythia matrix metallopeptidase karilysin in complex with a tetrapeptidic inhibitor. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 69, 472–476 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Cerdà-Costa N., Guevara T., Karim A. Y., Ksiazek M., Nguyen K. A., Arolas J. L., Potempa J., and Gomis-Rüth F. X. (2011) The structure of the catalytic domain of Tannerella forsythia karilysin reveals it is a bacterial xenologue of animal matrix metalloproteinases. Mol. Microbiol. 79, 119–132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Wu D., Ran T., Wang W., and Xu D. (2016) Structure of a thermostable serralysin from Serratia sp. FS14 at 1.1 Å resolution. Acta Crystallogr. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 72, 10–15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Saitou N., and Nei M. (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Sun L. L., Chen Y. X., Rajendran C., Mueller U., Panjikar S., Wang M. T., Mindnich R., Rosenthal C., Penning T. M., and Stoockigt J. (2012) Crystal structure of perakine reductase, founding member of a novel aldo-keto reductase (AKR) subfamily that undergoes unique conformational changes during NADPH binding. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 11213–11221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Walter T. S., Meier C., Assenberg R., Au K. F., Ren J., Verma A., Nettleship J. E., Owens R. J., Stuart D. I., and Grimes J. M. (2006) Lysine methylation as a routine rescue strategy for protein crystallization. Structure 14, 1617–1622 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Rayment I. (1997) Reductive alkylation of lysine residues to alter crystallization properties of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 276, 171–179 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Bode W., Gomis-Rüth F. X., and Stöckler W. (1993) Astacins, serralysins, snake venom and matrix metalloproteinases exhibit identical zinc-binding environments (HEXXHXXGXXH and Met-turn) and topologies and should be grouped into a common family, the “metzincins”. FEBS Lett. 331, 134–140 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Grams F., Dive V., Yiotakis A., Yiallouros I., Vassiliou S., Zwilling R., Bode W., and Stöcker W. (1996) Structure of astacin with a transition-state analogue inhibitor. Nat. Struct. Biol. 3, 671–675 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Baumann U., Wu S., Flaherty K. M., and McKay D. B. (1993) Three-dimensional structure of the alkaline protease of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a two-domain protein with a calcium binding parallel β roll motif. EMBO J. 12, 3357–3364 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Arolas J. L., Broder C., Jefferson T., Guevara T., Sterchi E. E., Bode W., Stöcker W., Becker-Pauly C., and Gomis-Rüth F. X. (2012) Structural basis for the sheddase function of human meprin β metalloproteinase at the plasma membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109, 16131–16136 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Okada A., Sano K., Nagata K., Yasumasu S., Ohtsuka J., Yamamura A., Kubota K., Iuchi I., and Tanokura M. (2010) Crystal structure of zebrafish hatching enzyme 1 from the zebrafish Danio rerio. J. Mol. Biol. 402, 865–878 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. López-Pelegrin M., Ksiazek M., Karim A. Y., Guevara T., Arolas J. L., Potempa J., and Gomis-Rüth F. X. (2015) A novel mechanism of latency in matrix metalloproteinases. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 4728–4740 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Morales R., Perrier S., Florent J. M., Beltra J., Dufour S., De Mendez I., Manceau P., Tertre A., Moreau F., Compere D., Dublanchet A. C., and O'Gara M. (2004) Crystal structures of novel non-peptidic, non-zinc chelating inhibitors bound to MMP-12. J. Mol. Biol. 341, 1063–1076 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Gomis-Rüth F. X., Trillo-Muyo S., and Stöcker W. (2012) Functional and structural insights into astacin metallopeptidases. Biol. Chem. 393, 1027–1041 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Krissinel E., and Henrick K. (2007) Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. J. Mol. Biol. 372, 774–797 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Gomis-Rüth F. X., Stöcker W., Huber R., Zwilling R., and Bode W. (1993) Refined 1.8 Å X-ray crystal structure of astacin, a zinc-endopeptidase from the crayfish Astacus astacus L.: structure determination, refinement, molecular structure and comparison with thermolysin. J. Mol. Biol. 229, 945–968 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Yiallouros I., Kappelhoff R., Schilling O., Wegmann F., Helms M. W., Auge A., Brachtendorf G., Berkhoff E. G., Beermann B., Hinz H. J., König S., Peter-Katalinic J., and Stöcker W. (2002) Activation mechanism of pro-astacin: role of the propeptide, tryptic and autoproteolytic cleavage and importance of precise amino-terminal processing. J. Mol. Biol. 324, 237–246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Nicholas K. B., Nicholas H. B., Deerfield D. W. I., Nicholas K. B., Nicholas H. B., and Deerfield D. W. I. (1997) GeneDoc: analysis and visualization of genetic variation. Embnew News 4, 1–4 [Google Scholar]
- 44. Larkin M. A., Blackshields G., Brown N. P., Chenna R., McGettigan P. A., McWilliam H., Valentin F., Wallace I. M., Wilm A., Lopez R., Thompson J. D., Gibson T. J., and Higgins D. G. (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23, 2947–2948 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Liu L., Xu L., Yan F., Yan R., Song X., and Li X. (2009) Immunoproteomic analysis of the second-generation merozoite proteins of Eimeria tenella. Vet. Parasitol. 164, 173–182 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Rosenthal C., Mueller U., Panjikar S., Sun L., Ruppert M., Zhao Y., and Stöckigt J. (2006) Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of perakine reductase, a new member of the aldo-keto reductase enzyme superfamily from higher plants. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 62, 1286–1289 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Wang Q. S., Yu F., Huang S., Sun B., Zhang K. H., Liu K., Wang Z. J., Xu C. Y., Wang S. S., Yang L. F., Pan Q. Y., Li L., Zhou H., Cui Y., Xu Q., et al. (2015) The macromolecular crystallography beamline of SSRF. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 26, 12–17 [Google Scholar]
- 48. Kabsch W. (2010) XDS. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 125–132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Panjikar S., Parthasarathy V., Lamzin V. S., Weiss M. S., and Tucker P. A. (2005) Auto-rickshaw: an automated crystal structure determination platform as an efficient tool for the validation of an X-ray diffraction experiment. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 61, 449–457 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Dodson E. J., Winn M., and Ralph A. (1997) Collaborative Computational Project, number 4: providing programs for protein crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 277, 620–633 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Sheldrick G. M. (2008) A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A 64, 112–122 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Schneider T. R., and Sheldrick G. M. (2002) Substructure solution with SHELXD. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 58, 1772–1779 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Perrakis A., Morris R., and Lamzin V. S. (1999) Automated protein model building combined with iterative structure refinement. Nat. Struct. Biol. 6, 458–463 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Morris R. J., Zwart P. H., Cohen S., Fernandez F. J., Kakaris M., Kirillova O., Vonrhein C., Perrakis A., and Lamzin V. S. (2004) Breaking good resolutions with ARP/wARP. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 11, 56–59 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. McCoy A. J., Grosse-Kunstleve R. W., Adams P. D., Winn M. D., Storoni L. C., and Read R. J. (2007) Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 40, 658–674 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Emsley P., and Cowtan K. (2004) Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2126–2132 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Murshudov G. N., Skubák P., Lebedev A. A., Pannu N. S., Steiner R. A., Nicholls R. A., Winn M. D., Long F., and Vagin A. A. (2011) REFMAC5 for the refinement of macromolecular crystal structures. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 67, 355–367 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Adams P. D., Afonine P. V., Bunkóczi G., Chen V. B., Davis I. W., Echols N., Headd J. J., Hung L. W., Kapral G. J., Grosse-Kunstleve R. W., McCoy A. J., Moriarty N. W., Oeffner R., Read R. J., Richardson D. C., et al. (2010) PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 213–221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Chen V. B., Arendall W. B. 3rd, Headd J. J., Keedy D. A., Immormino R. M., Kapral G. J., Murray L. W., Richardson J. S., and Richardson D. C. (2010) MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D 66, 12–21 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Bramucci E., Paiardini A., Bossa F., and Pascarella S. (2012) PyMod: sequence similarity searches, multiple sequence-structure alignments, and homology modeling within PyMOL. BMC Bioinformatics 10.1186/1471-2105-13-S4-S2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Potterton L., McNicholas S., Krissinel E., Gruber J., Cowtan K., Emsley P., Murshudov G. N., Cohen S., Perrakis A., and Noble M. (2004) Developments in the CCP4 molecular-graphics project. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2288–2294 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Thompson J. D., Gibson T. J., Plewniak F., Jeanmougin F., and Higgins D. G. (1997) The CLUSTAL_X Windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 4876–4882 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]