Significance
Salmonella causes many different diseases including gastroenteritis and typhoid fever. For infection to take place, Salmonella must enter the epithelium in the gut by injecting a number of effector proteins that trigger dramatic actin rearrangements and membrane ruffles to engulf the pathogen. In this study we identified a myosin motor protein that translocates along actin filaments as one of the crucial host proteins that are targeted by two Salmonella effector proteins, SopE and SopB, at the onset of infection. SopE and SopB exploit MYO6 to facilitate membrane ruffle formation and phospholipid production at the invasion site to mediate pathogen uptake. Myosin motors are highly druggable targets, and therefore myosin inhibitors are attractive new tools to fight bacterial infections.
Keywords: motor protein, type 3 secretion system, rho GTPase, macropinocytosis, infection
Abstract
To establish infections, Salmonella injects virulence effectors that hijack the host actin cytoskeleton and phosphoinositide signaling to drive pathogen invasion. How effectors reprogram the cytoskeleton network remains unclear. By reconstituting the activities of the Salmonella effector SopE, we recapitulated Rho GTPase-driven actin polymerization at model phospholipid membrane bilayers in cell-free extracts and identified the network of Rho-recruited cytoskeleton proteins. Knockdown of network components revealed a key role for myosin VI (MYO6) in Salmonella invasion. SopE triggered MYO6 localization to invasion foci, and SopE-mediated activation of PAK recruited MYO6 to actin-rich membranes. We show that the virulence effector SopB requires MYO6 to regulate the localization of PIP3 and PI(3)P phosphoinositides and Akt activation. SopE and SopB target MYO6 to coordinate phosphoinositide production at invasion foci, facilitating the recruitment of cytoskeleton adaptor proteins to mediate pathogen uptake.
Mammalian cells use Rho GTPases Rac1, Cdc42, and RhoA as master regulators of the actin cytoskeleton to coordinate the formation of actin-rich structures such as lamellipodia and filopodia at the plasma membrane (1). Rho GTPases are anchored at the membrane by prenylation, where they are activated by guanine-nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) that promote GTP binding to switch the GTPases from an inactive (GDP-bound) to an active (GTP-bound) conformation. GTP-bound Rho GTPases directly activate specific cellular effectors that coordinate the formation of distinct actin structures, e.g., Arp2/3 activators N-WASP and the WAVE complex (1). Rho effectors also include p21-activated kinase (PAK) that controls actin filament turnover by regulating the activity of actin-binding proteins (2). PAK also has been shown to phosphorylate MYO6, a unique member of the myosin superfamily that moves toward the minus end of actin filaments (3, 4). MYO6 has important roles in the endocytic pathway and in the regulation of plasma membrane dynamics and membrane ruffle formation (5, 6).
To establish infections, the intestinal pathogen Salmonella enterica Typhimurium subverts the actin cytoskeleton by injecting a mixture of virulence effector proteins into host epithelial cells to facilitate uptake by macropinocytosis (7–11). Of particular importance is the virulence effector SopE, a Rac1 and Cdc42 GEF that is required for generating membrane ruffles and bacterial macropinocytosis (7, 12). Indeed, deletion of SopE reduces Salmonella invasion by 60%, and in the absence of SopE and the known Salmonella Cdc42 activators SopE2 and SopB, the pathogen cannot activate Rho GTPases or invade host cells (8, 9). Salmonella likely highjacks a number of Rho GTPase effectors, but their identity, how they interact with each other, and how they contribute to Salmonella invasion remain unresolved. Because SopE activates both Rac1 and Cdc42, we set out to reconstitute SopE signaling at model membranes and identify the components of the Rho cytoskeleton network hijacked by Salmonella.
Results
Identification of the Cytoskeleton Protein Network Recruited via SopE.
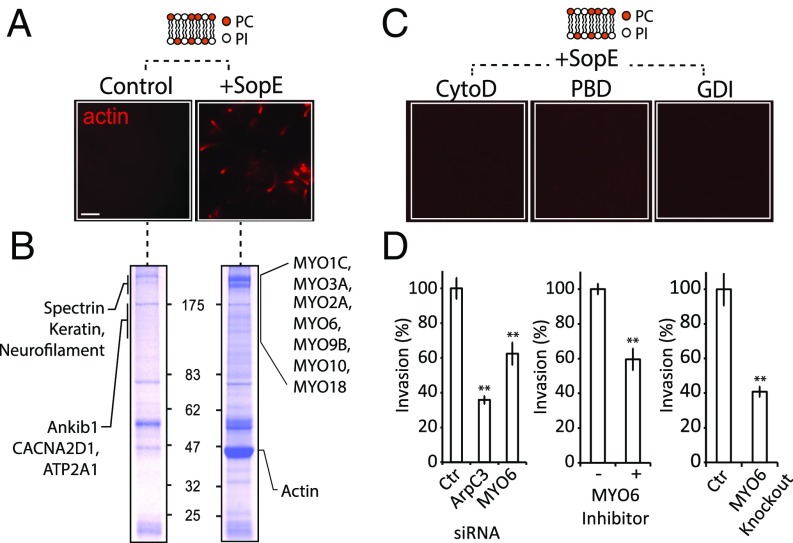
To identify the membrane-associated cytoskeleton network of proteins targeted by SopE, we first reconstituted SopE-mediated actin filament polymerization at immobilized phospholipid membrane bilayers in optimized cell-free brain extract, as previously described (10). Silica microspheres were coated with a phospholipid bilayer composed of equal concentrations of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylinositol (PC:PI), which have been used previously to reconstitute Rho-driven actin assembly (13, 14). When the microspheres were incubated in extract, the control PC:PI beads were unable to polymerize actin (Fig. 1A). In contrast, when the extract was supplemented with purified recombinant SopE, actin filaments were immediately assembled on the membrane surface and propelled the beads through the extract via actin comet tail formation (Fig. 1A). Inhibiting actin polymerization (cytochalasin D) or the Rho GTPases Rac1 and Cdc42 (the PBD domain of PAK or GDI, which binds and sequesters these Rho GTPases) (14) abrogated actin assembly (Fig. 1C). This effect confirmed that SopE-activation of Rho GTPases is necessary for the formation of actin comet tails.
Fig. 1.
Cytoskeleton proteins manipulated by Salmonella SopE. (A) Beads coated with 50% PC and 50% PI (depicted in cartoon) were incubated in cell-free extract containing rhodamine-labeled actin in the presence (+SopE) or absence (Control) of 1 μM SopE. (Scale bar: 5 μm.) (B) SDS/PAGE analysis and Coomassie blue staining of proteins recruited by the beads shown in A. SopE-recruited myosins (Right) are annotated with proteins of equivalent molecular mass recruited by the control (Left). Molecular mass markers are shown in kDa. (C) Experiment performed as A in extract containing inhibitors of actin polymerization (cytochalasin D, 5 μM), or Rho GTPase signaling (PBD or GDI, 1 μM). (Scale bars: 5 μm.) (D) Salmonella invasion into HeLa cells in which MYO6 was depleted by siRNA, inhibited by TIP, or knocked out by CRISPR/CAS9-based engineering. Error bars represent ± SEM; **P < 0.01.
To identify the putative SopE-signaling network, the actin-based motility assays from Fig. 1A were scaled up. Proteins recruited from the cytosol to PC:PI were separated by SDS/PAGE (Fig. 1B) and identified by parallel mass spectrometry. More than 200 proteins were specifically recruited to PC:PI-coated beads directly or indirectly via SopE signaling through Rho GTPases (Table S1), including cellular effectors of Rac1 and Cdc42 that orchestrate actin filament polymerization (1), such as N-WASP and the WAVE complex (comprising Cyfip, Nap1, Abi, WAVE1, and homologs); formins (FMNL1, -2, and DIAPH2); PAK1 and -3; the BAR protein FNBP1; and CEP4/BORG4, as well as its cognate septin-binding partners (summarized in Table S2). Consistent with the presence of Rho GTPase effectors, the Arp2/3 complex and a number of actin-binding proteins that regulate filament dynamics and architecture were also recruited by SopE. In addition seven myosin motor proteins that were absent from control PC:PI beads were recruited in a SopE-dependent manner (Fig. 1B and Tables S1 and S2).
Myosin motors are actin-activated ATPases that translocate along actin filaments and are involved in many different cellular processes by anchoring intracellular cargoes and organelles, by mediating their short-range transport, and also by regulating the architecture of the actin cytoskeleton and plasma membrane dynamics (15). Given the importance of the myosin superfamily in these diverse cellular functions, we sought to address the role of myosin motors in Salmonella macropinocytosis.
MYO6 Facilitates Salmonella Invasion.
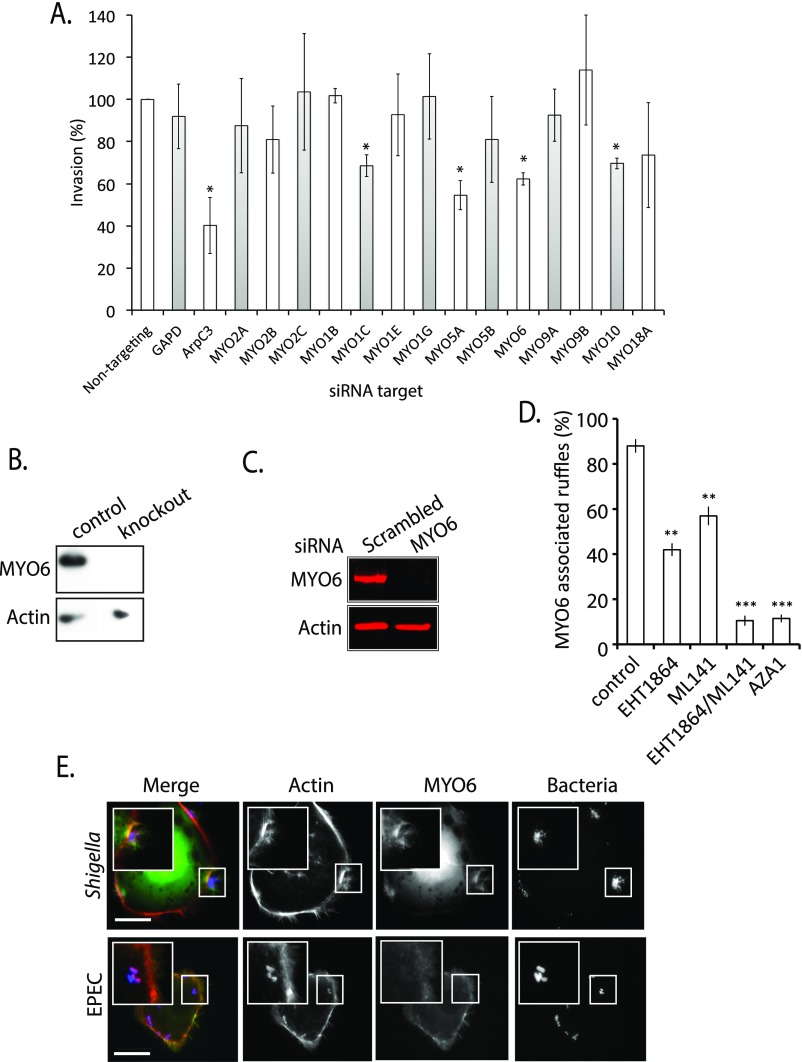
To investigate the importance of these myosin motors in SopE-induced actin filament remodeling, we transfected siRNAs targeting the seven myosins listed in Fig. 1B and an additional six members of the myosin family expressed in HeLa cells (namely myosins 1B, 1E, 1G, 2B, 2C, 5A, and 5C) (16) before assessing Salmonella invasion (Fig. S1 and Table S3). Although we cannot completely exclude a possible role for the other myosins tested, our screen revealed that MYO1C, -5A, -5C, and -6 siRNA transfections significantly impaired invasion relative to cells transfected with a scrambled siRNA. However, only MYO1C and MYO6 were recruited to the PC:PI beads by SopE (Fig. 1B). Because MYO1C was recently reported to be required for Salmonella invasion (17), we further analyzed the requirement for MYO6 in pathogen uptake. Our results clearly demonstrate a key role for MYO6 in Salmonella invasion in cells treated with a small molecule inhibitor of MYO6 (18), in CRISPR-Cas9 MYO6-knockout cells, and in siRNA-transfected MYO6-depleted cells (Fig. 1D). Successful knockout and siRNA-mediated depletion of MYO6 were confirmed by immunoblotting (Fig. S1 B and C).
Fig. S1.
(A) Salmonella invasion into myosin family siRNA cells. Myosin motor proteins were knocked down in 96-well optical plates using siRNAs targeting the indicated myosins and then were infected for 30 min with wild-type Salmonella pM975 encoding SPI2-controlled GFP. Actin was stained with Texas Red-X dye–conjugated phalloidin (red), and nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Invasion was quantified by counting intracellular GFP bacteria using fluorescence microscopy and was normalized to the nontargeting siRNA control. A negative (GAPD) and a positive (ArpC3) control were included also. Error bars represent ±1 SEM; *P < 0.05. (B) Expression of MYO6 in knockout cells. Control and CRISPR-Cas9–engineered MYO6-knockout cells were immunoblotted with antibodies against MYO6 and actin as a control. (C) Knockdown efficiency of MYO6. Cells were transfected with nontargeting (scrambled) or MYO6 siRNA before immunoblotting with antibodies against MYO6 and actin as a control. (D) Localization of GFP-MYO6 to ruffles in CaCo cells infected with wild-type Salmonella and treated with inhibitors of Rac1 (EHT1864), Cdc42 (ML141), or both (AZA1). Bacteria were visualized using Salmonella antibodies and actin filaments with Alexa-Fluor 350-conjugated phalloidin. Error bars represent ± SEM; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (E) Localization of MYO6 to sites of pathogen-induced actin remodeling. Cells were transfected with GFP-tagged MYO6 (green) and were infected with wild-type Shigella flexneri M90T labeled with AlexaFluor-350 (blue) for 5 min to generate a membrane. EPEC E2348/69 were labeled with AlexaFluor-350 (blue) before infection (3 h) and generation of actin pedestals. Actin stained with Texas Red-X dye–conjugated phalloidin (red). (Scale bars: 5 μm.) Insets 2.5× magnify sites of pathogen-induced actin remodeling.
SopE-Dependent Recruitment of MYO6 to Salmonella-Induced Ruffles.
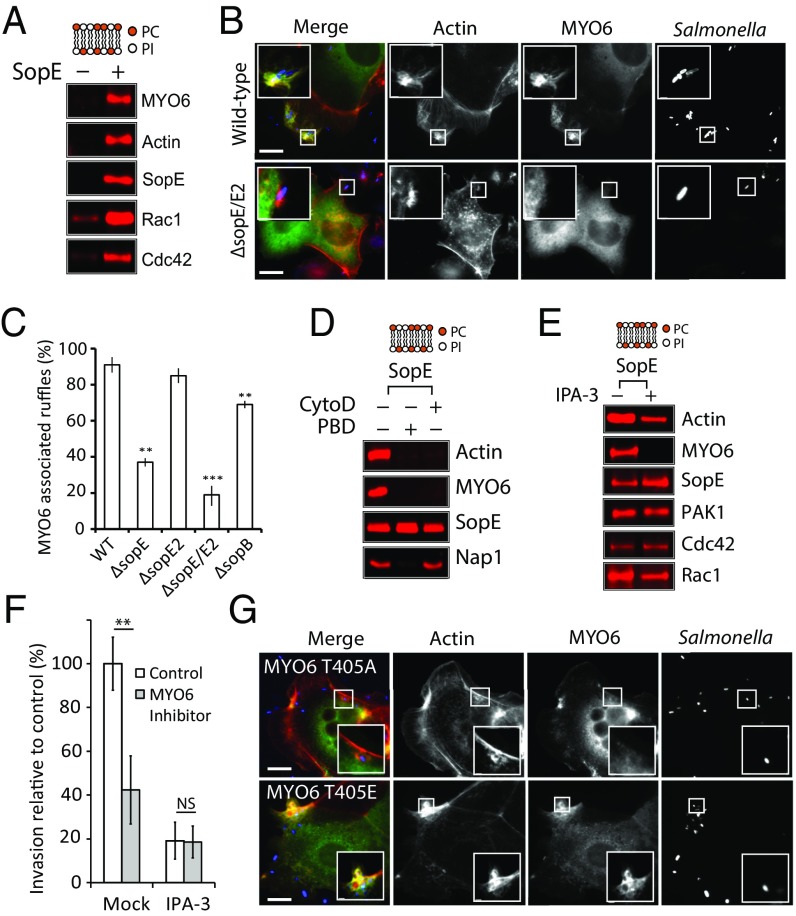
We next examined the recruitment of MYO6 by SopE in more detail. Immunoblotting of PC:PI beads isolated from actin-based motility assays confirmed that SopE (+) triggered the recruitment of MYO6 as well as Cdc42, Rac1, and actin (Fig. 2A), as was consistent with Rho-mediated actin comet tail formation (Fig. 1C). To investigate whether SopE regulated MYO6 localization to actin filaments at the pathogen entry site during invasion, HeLa cells expressing GFP-tagged MYO6 were infected with either wild-type Salmonella or the isogenic ΔsopE mutant (Fig. 2B). Both wild-type and ΔsopE Salmonella induced actin-rich membrane ruffles at pathogen foci (Fig. 2B, Insets), as expected given the role of multiple SPI-1 effectors in cytoskeleton remodeling (19). In cells with wild-type Salmonella, robust MYO6 localization was observed at ∼90% of pathogen-induced ruffles (Fig. 2C). However, when cells were infected with ΔsopE, MYO6 was absent from the majority of ruffles (Fig. 2B), with only ∼35% showing colocalization with MYO6 (Fig. 2C). We next tested whether, in addition to the Rac1/Cdc42 GEF SopE, other effectors such as SopE2 and SopB, which directly and indirectly activate Cdc42, also promote MYO6 localization to ruffles (8, 11). Cells infected with ΔsopE2 showed no reduction in MYO6 recruitment, presumably because of the presence of SopE. However, MYO6 localization at pathogen-induced ruffles was reduced to ∼20% in cells infected with the double mutant ΔsopE/E2 and to ∼70% in cells infected with ΔsopB (Fig. 2C). Consistent with their role in activating Rho GTPases, chemical inhibition of Rac1 and Cdc42 impeded MYO6 recruitment to ruffles induced by wild-type Salmonella (Fig. S1D).
Fig. 2.
SopE manipulation of MYO6 and PAK. (A) PC:PI beads incubated in cell extract in the absence (−) or presence (+) of SopE were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) Localization of GFP-MYO6 (green) in HeLa cells infected with wild-type or ΔsopE Salmonella. Bacteria were visualized using Salmonella antibodies (red) and actin filaments with Alexa-Fluor 350-conjugated phalloidin (blue). (Scale bars: 5 μm.) Insets 3× magnify Salmonella-induced ruffles. (C) Quantification of MYO6 localization to membrane ruffles. The experiment was performed as in B using wild-type, ΔsopE, ΔsopE2, ΔsopE/E2, and ΔsopB Salmonella. Error bars represent ± SEM; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (D) SopE recruitment of MYO6 in the presence (+) or absence (−) of inhibitors of actin polymerization (CytoD) and Rho GTPase signaling (PBD). The experiment was performed as in A. (E) SopE recruitment of MYO6 in the presence (+) or absence (−) of the PAK inhibitor IPA-3. The experiment was performed as in A. (F) Salmonella invasion into HeLa cells in the absence (control) or presence of the MYO6 inhibitor TIP, with or without (Mock) the PAK inhibitor IPA-3 in combination. Error bars represent ± SEM; **P < 0.01. NS, nonsignificant. (G) Localization of GFP-MYO6 (T405A) or phosphomimic (T405E) to Salmonella-induced ruffles. The experiment was performed as in B. Insets 3× magnify Salmonella-induced ruffles. (Scale bars: 5 μm.)
Rho GTPase subversion is a central virulence strategy of many bacterial pathogens. For example, Shigella flexneri also invades host cells using Rho GTPases that trigger membrane ruffling (20), and, indeed, MYO6 also was present in Shigella-induced ruffles (Fig. S1E). Because MYO6 binds actin filaments, it remained possible that this motor is recruited to actin filaments assembled at the plasma membrane independently of Rho signaling, e.g., to actin pedestals generated beneath the extracellular pathogen enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) (21). When we examined MYO6 localization in EPEC-infected host cells, MYO6 was absent from actin pedestals (Fig. S1E), as previously reported (22). Taken together, our data suggest that MYO6 localizes specifically to pathogen foci where Rho GTPases are activated to induce membrane ruffling.
PAK Recruits MYO6 to the Membrane.
Given the importance of Rho GTPases in mediating MYO6 localization, we next addressed the mechanism by which MYO6 is recruited to actin-rich membrane ruffles. Inhibition of Rho GTPases (+PBD) or actin polymerization (+CytoD) in vitro blocked SopE-dependent recruitment of MYO6 to the membrane (Fig. 2D). We noticed that components of the WAVE regulatory complex (i.e., nap1), a Rac1 effector) were still recruited in the presence of cytochalasin D but not in the presence of PBD, indicating that MYO6 targeting is not solely regulated by Rho GTPases or membrane interactions but also requires Rho GTPase-induced actin filaments for recruitment.
Interestingly, our proteomics data also highlight the presence of the PAK family of Rac1 and Cdc42 effectors within the cytoskeleton network recruited by SopE (Tables S1 and S2). Salmonella is known to trigger activation of PAK (23), and PAK also has been reported to phosphorylate MYO6 in the motor domain (4). A potential phosphorylation site is the threonine in position 405 at a conserved site within the head domain of MYO6 (24). To determine whether PAK regulates MYO6 recruitment, actin filament polymerization was triggered at the membrane by SopE in extract supplemented with IPA-3 (Fig. 2E), an inhibitor of PAK1–3 activation. IPA-3 completely ablated SopE recruitment of MYO6 to membranes while still recruiting Rho GTPases and triggering actin polymerization, thereby distinguishing MYO6 recruitment from actin filament formation. Thus, MYO6 recruitment required the combination of actin filaments and Rho GTPase-activated PAK (Fig. 2 D and E). Furthermore, inhibiting PAK with IPA-3 in host cells reduced Salmonella invasion by ∼80% (Fig. 2F). Consistent with PAK regulation of MYO6, no further reduction in invasion was observed when inhibitors of PAK and MYO6 were used in combination (Fig. 2F), showing that PAK and MYO6 mediate pathogen uptake via the same pathway.
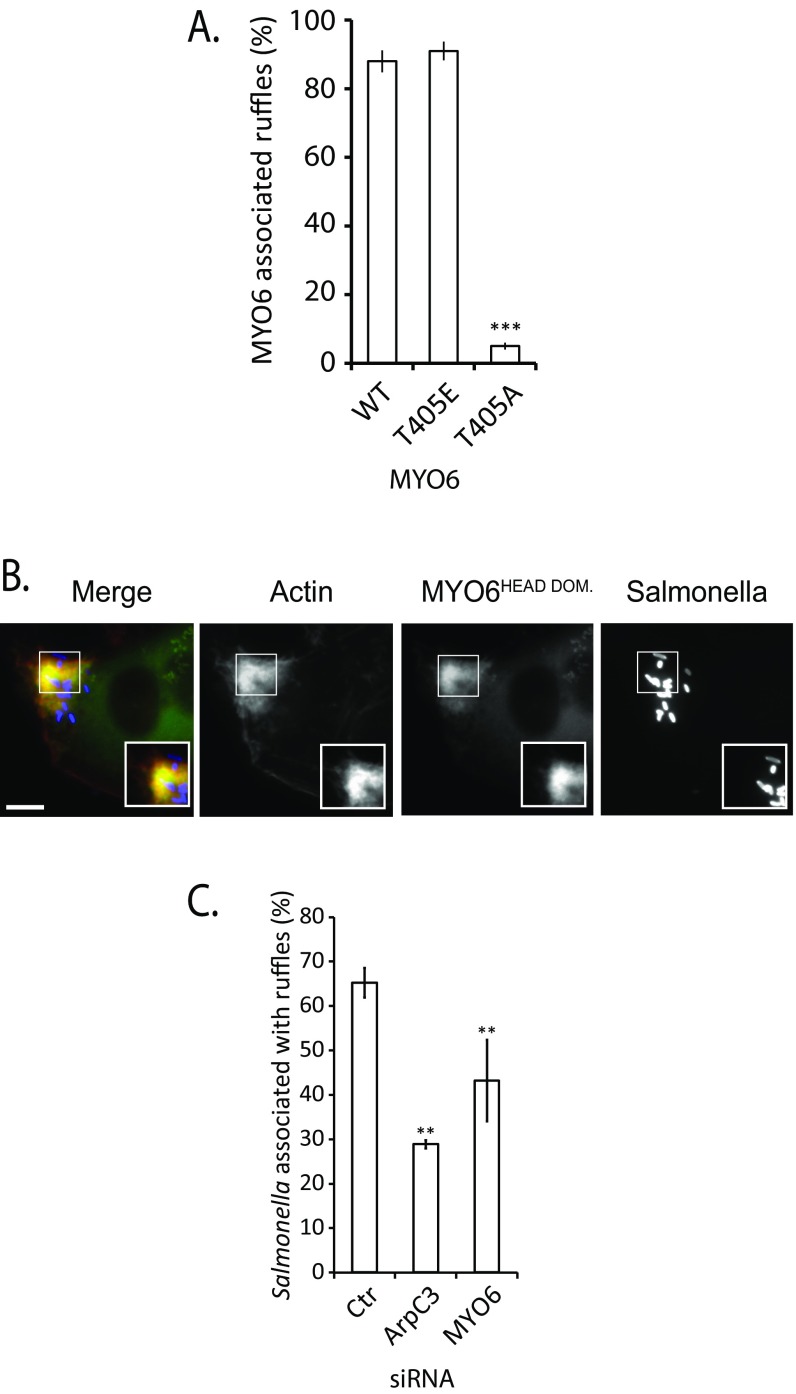
To verify the link between PAK and MYO6, we assessed the significance of the putative MYO6 phosphorylation site at threonine 405 for its localization to Salmonella-induced ruffles (Fig. 2G). GFP-tagged MYO6 mutants mimicking the dephosphorylated (T405A) or phosphorylated (T405E) form were expressed in HeLa cells before Salmonella infection. MYO6 (T405E) was strongly recruited to Salmonella-induced ruffles, but the T405A mutant was not (Fig. 2G and Fig. S2A), demonstrating that PAK-dependent phosphorylation in the motor domain may regulate MYO6 localization to foci of Salmonella invasion. Consistent with this suggestion, only the GFP-MYO6 head domain (residues 1–835), but not the tail domain alone, was recruited into membrane ruffles (Fig. S2B).
Fig. S2.
(A) Quantification of wild-type, dephosphorylated (T405A), or phosphorylated (T405E) GFP-MYO6 localization to Salmonella-induced ruffles. Error bars represent ±1 SEM; ***P < 0.001. Insets 2× magnify Salmonella-induced ruffles. The figure is related to Fig. 2G. (B) HeLa cells transfected with the GFP-tagged head domain (residues 1–835) of MYO6 (green) infected with Alexa-Fluor 350-labeled Salmonella and F-actin labeled with Texas Red-X dye-conjugated phalloidin (red). (Scale bars: 5 μm.) Magnified Insets show pathogen-induced ruffles. (C) Ruffle generation in MYO6-depleted cells. Cells were transfected with scrambled nontargeting (control, Ctr), MYO6, or ArpC3 (positive control) siRNA and were infected for 5 min with Alexa-Fluor 350-labeled Salmonella (blue). Actin was stained using Texas Red-X dye-conjugated phalloidin (red). The number of bacteria associated with membrane ruffles relative to the total number of bacteria were quantified microscopically. Error bars represent ±1 SEM; **P < 0.01.
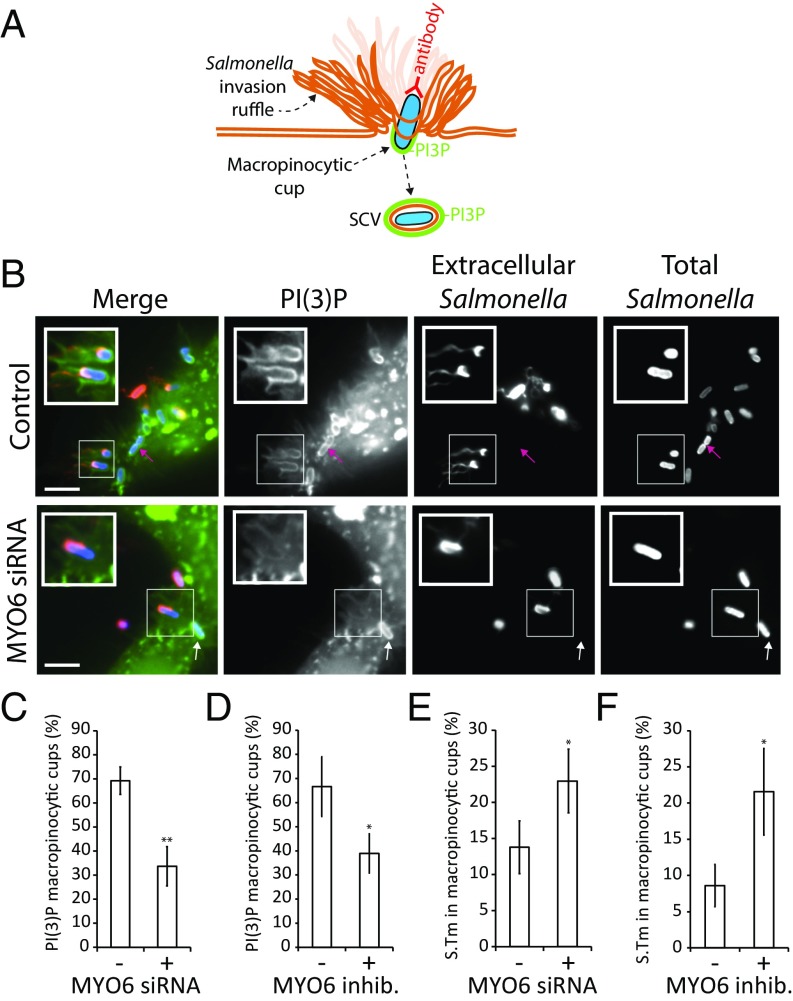
MYO6 Accumulates PI(3)P at Salmonella-Associated Macropinocytic Cups.
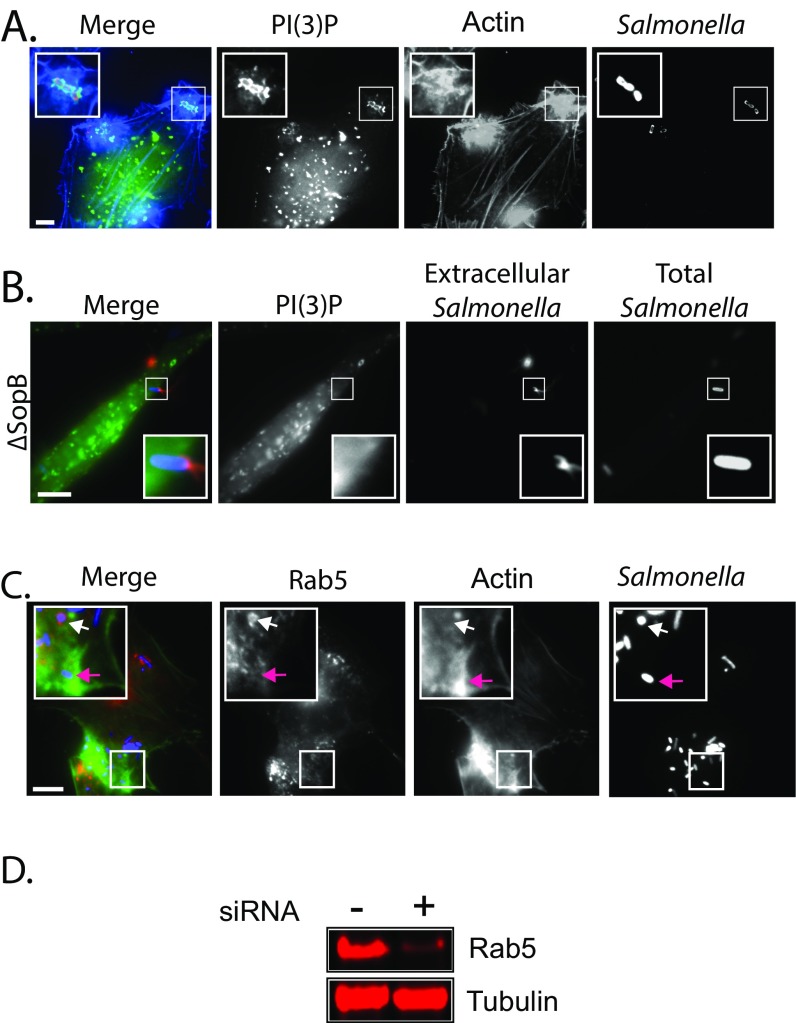
Having established that MYO6 is recruited into membrane ruffles, we next investigated the mechanism by which MYO6 facilitates pathogen invasion. Although the loss of MYO6 reduced the formation of pathogen-induced membrane ruffle (∼65% in the control relative to ∼45% in MYO6-depleted cells), indicating a potential role for MYO6 in regulating actin filament organization (Fig. S2C), Salmonella-induced ruffles were not completely inhibited in the absence of MYO6 (Fig. 2B and Fig. S2C), suggesting that this myosin plays an additional role during pathogen uptake. Actin filament polymerization at sites of Salmonella invasion leads to the formation of a macropinocytic cup, which can be visualized using a GFP-p40-PX domain fusion construct that binds to the phosphoinositide PI(3)P in the macropinocytic cup at the base of invasion ruffles (25) (Fig. S3A).
Fig. S3.
(A) Localization of PI(3)P at actin-rich Salmonella membrane ruffles. Cells were transfected with GFP-p40-PX [PI(3)P] and then were infected with Alexa-Fluor 594-labeled wild-type Salmonella (red) and actin stained with Alexa-Fluor 350-conjugated phalloidin (blue). (Scale bar: 5 μm.) Insets 2× magnify the membrane ruffle and invading Salmonella. (B) PI(3)P enrichment at the macropinocytic cup is dependent on SopB. Cells were transfected with GFP-p40Phox (green) and then were infected for 5 min with Alexa-Fluor 350-labeled ΔsopB Salmonella (blue) and extracellular bacteria labeled with anti-Salmonella antibodies (red). (Scale bar: 5 μm.) Insets 3× magnify the macropinocytic cup. (C) Localization of Rab5 during Salmonella infection. Cells were transfected with RFP-Rab5 and then were infected with Alexa-Fluor 350-labeled wild-type Salmonella (blue) and actin stained with Alexa-Fluor 488-conjugated phalloidin (green). Insets 3× magnify infection foci. Purple arrows indicate an invasion site with no Rab5 localization; white arrows indicate Rab5 on Salmonella-containing vacuoles. (Scale bar: 5 μm.) (D) Knockdown efficiency of Rab5. Cells were transfected with nontargeting (−) or Rab5 (+) siRNA before immunoblotting with antibodies against Rab5 and tubulin as a control.
We decided to examine whether MYO6 influenced the localization of PI(3)P in the macropinocytic cup at invasion ruffles during pathogen uptake (Fig. 3). As depicted in the cartoon (Fig. 3A) and demonstrated experimentally (Fig. 3B), in control cells the PI(3)P-enriched macropinocytic cup formed a tight association with the invading pathogen, which was inaccessible to anti-Salmonella antibodies (Fig. 3B, Inset). Indeed, when Salmonella were in the macropinocytic cup, only the exposed tip of the pathogen and its flagella were accessible to antibodies (extracellular Salmonella). In contrast, the intracellular bacteria within Salmonella-containing vacuoles (SCVs) (pink arrows in Fig. 3B) were completely surrounded by PI(3)P and completely inaccessible to antibodies (Fig. 3 A and B). To our surprise, we observed a striking reduction of PI(3)P at macropinocytic cups in MYO6-depleted cells (Fig. 3B). PI(3)P was reduced from ∼70% in the control to ∼33% in MYO6-depleted cells (Fig. 3C, + MYO6 siRNA) and in cells treated with the MYO6 inhibitor (Fig. 3D, + MYO6 inhibitor). Intriguingly, PI(3)P still surrounded bacteria within intracellular SCVs (white arrows in Fig. 3B). Thus, MYO6 is required for the localization of PI(3)P at the macropinocytic cup but not at the SCV, thus revealing two distinct pools of phosphoinositide PI(3)P associated with the pathogen.
Fig. 3.
MYO6 regulation of the Salmonella macropinocytic cup. (A) Cartoon depicting the macropinocytic cup and SCV labeling for the experiment shown in B. (B) Localization of PI(3)P at Salmonella macropinocytic cups. Cells were transfected with nontargeting siRNA (Control) or MYO6 siRNA before transfection with GFP-p40-PX [PI(3)P, green] and infection with Alexa-Fluor 350-labeled wild-type Salmonella (Total Salmonella, blue). Extracellular Salmonella (red) were visualized by staining nonpermeabilized cells with anti-Salmonella antibodies. (Scale bars: 5 μm.) Insets 2× magnify Salmonella macropinocytic cups. Arrows indicate intracellular SCVs. (C and D) The number of PI(3)P-rich macropinocytic cups was quantified from the experiment shown in B using MYO6 sRNA (C) and in cells treated with the small molecule inhibitor of MYO6 (MyoVI inhib) (D). (E and F) The number of Salmonella (S.Tm)-associated macropinocytic cups relative to the total number of colonizing bacteria was quantified from the experiments in C and D, respectively. Error bars represent ± SEM; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.
The reduction in PI(3)P levels either through MYO6 siRNA transfection or inhibitor treatment caused increased numbers of extracellular bacteria associated with macropinocytic cups at the cell surface (Fig. 3 E and F), suggesting a significant delay in pathogen uptake. In summary, our data suggest that MYO6 facilitates pathogen invasion by promoting membrane ruffling and by triggering localization of PI(3)P at the macropinocytic cup.
MYO6 Cooperates with SopB to Mediate PI3-Kinase Signaling.
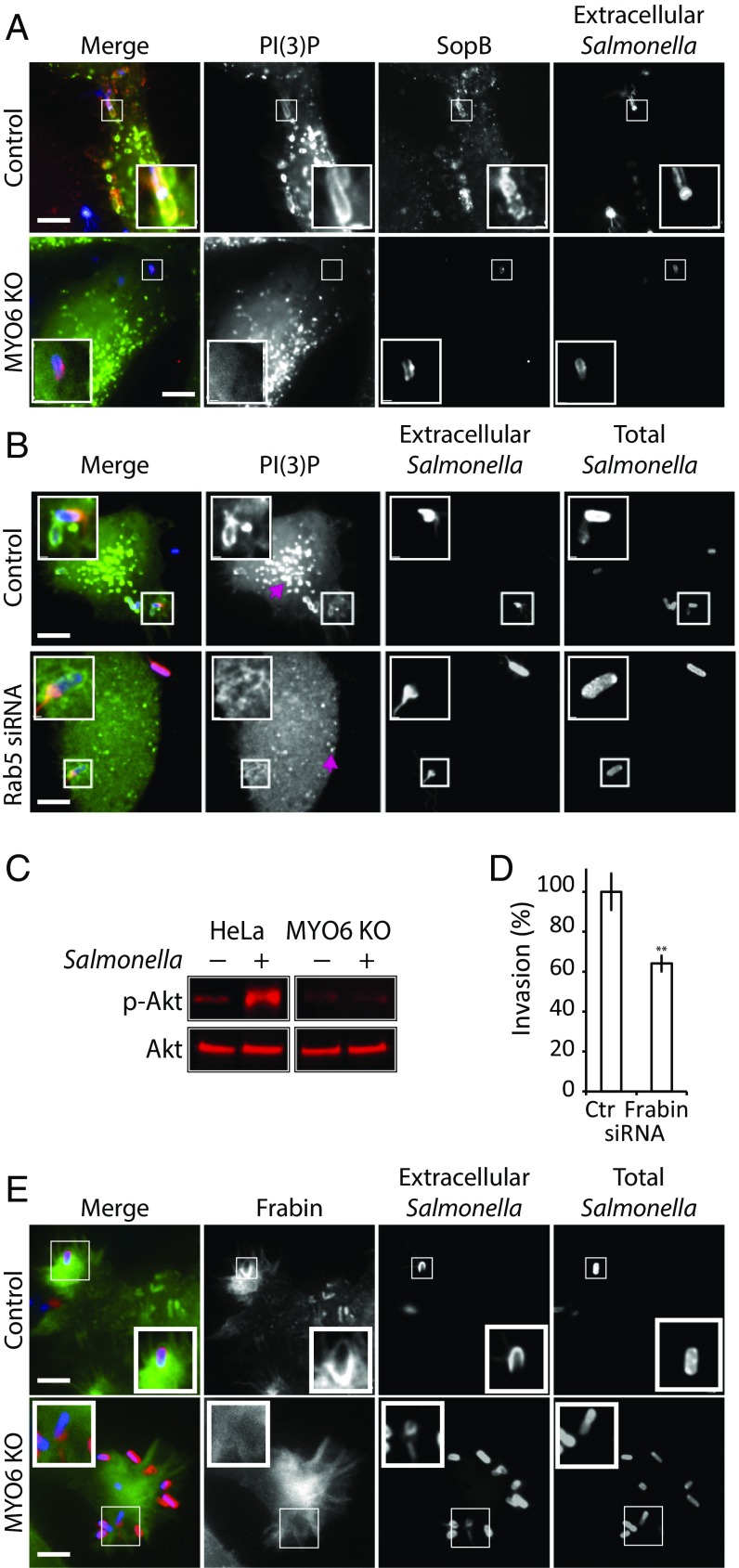
We next addressed how MYO6 facilitated localization of PI(3)P at the macropinocytic cup. It is well established that the generation of PI(3)P by Salmonella is dependent on the bacterial effector SopB, a phosphoinositide phosphatase with PI 4′- and 5′-phosphatase activity (26). SopB is thought to activate distinct classes of PI3-kinases (PI3K) responsible for generating PI(3,4,5)P3 and PI(3,4)P2 (e.g., class I and II) and PI(3)P (class III) (25, 27). Consistent with this activity, Salmonella lacking SopB (ΔsopB) were unable to generate PI(3)P-rich macropinocytic cups (Fig. S3B). We reasoned that MYO6 might control SopB localization and thereby the production of PI(3)P in the macropinocytic cup. In control cells, FLAG-tagged SopB was observed at the macropinocytic cup enriched in PI(3)P (Fig. 4A). In MYO6-knockout cells, SopB retained this localization, but the macropinocytic cup was devoid of PI(3)P (Fig. 4A), showing that MYO6 is not required for SopB localization but inhibits SopB-mediated production of PI(3)P at invasion foci through another mechanism. SopB is known to produce PI(3)P on SCVs via recruitment of Rab5 that activates the class III PI3K Vps34 (25). Consistent with Rab5-dependent endosomal PI(3)P formation, the number and size of PI(3)P-enriched endosomes was reduced in Rab5-depleted cells relative to control cells (Fig. 4B, arrows). However, PI(3)P was still present at the macropinocytic cup in Rab5-depleted cells (Fig. 4B). Indeed, we also found that Rab5-RFP localized to SCVs (Fig. S3C, white arrows), as previously observed (25), but was absent from actin-rich Salmonella invasion sites (Fig. S3C, pink arrow). These findings support our results shown in Fig. 3B and suggests that two distinct pools of PI(3)P are produced by Salmonella, namely a pool at the macropinocytic cup and a pool surrounding SCVs. Thus, PI(3)P is generated at the macropinocytic cup in a MYO6-dependent and Rab5-independent manner.
Fig. 4.
MYO6 regulation of Akt signaling and recruitment of Frabin. (A) Localization of SopB in control or MYO6-knockout HeLa cells expressing GFP-p40-PX [PI(3)P, green] were infected with Salmonella encoding FLAG-tagged SopB. Nonpermeabilized cells were labeled with anti-Salmonella antibodies (blue) before permeabilization and labeling with anti-FLAG antibodies (red). (Scale bars: 5 μm.) Insets 3× magnify the macropinocytic cup. (B) Localization of PI(3)P at Salmonella macropinocytic cups in cells transfected with nontargeting siRNA (Control) or Rab5 siRNA before transfection with GFP-p40-PX [PI(3)P, green] and infection with Alexa-Fluor 350-labeled Salmonella (Total Salmonella, blue). Extracellular Salmonella were visualized by staining nonpermeabilized cells with anti-Salmonella antibodies (Extracellular Salmonella, red). (Scale bars: 5 μm.) Insets 3× magnify Salmonella macropinocytic cups. Arrows indicate PI(3)P-rich endosomes. (C) Control and MYO6-knockout HeLa cells were infected (+) or not (−) with Salmonella. Then whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted for Akt and phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt). (D) Salmonella invasion into HeLa cells where Frabin was depleted by siRNA transfection. Error bars represent ± SEM; **P < 0.01. (E) Localization of CFP-Frabin during Salmonella invasion into control and MYO6-knockout cells. (Scale bars: 5 μm.) The experiment was performed as in B. Insets 2× magnify Salmonella macropinocytic cups.
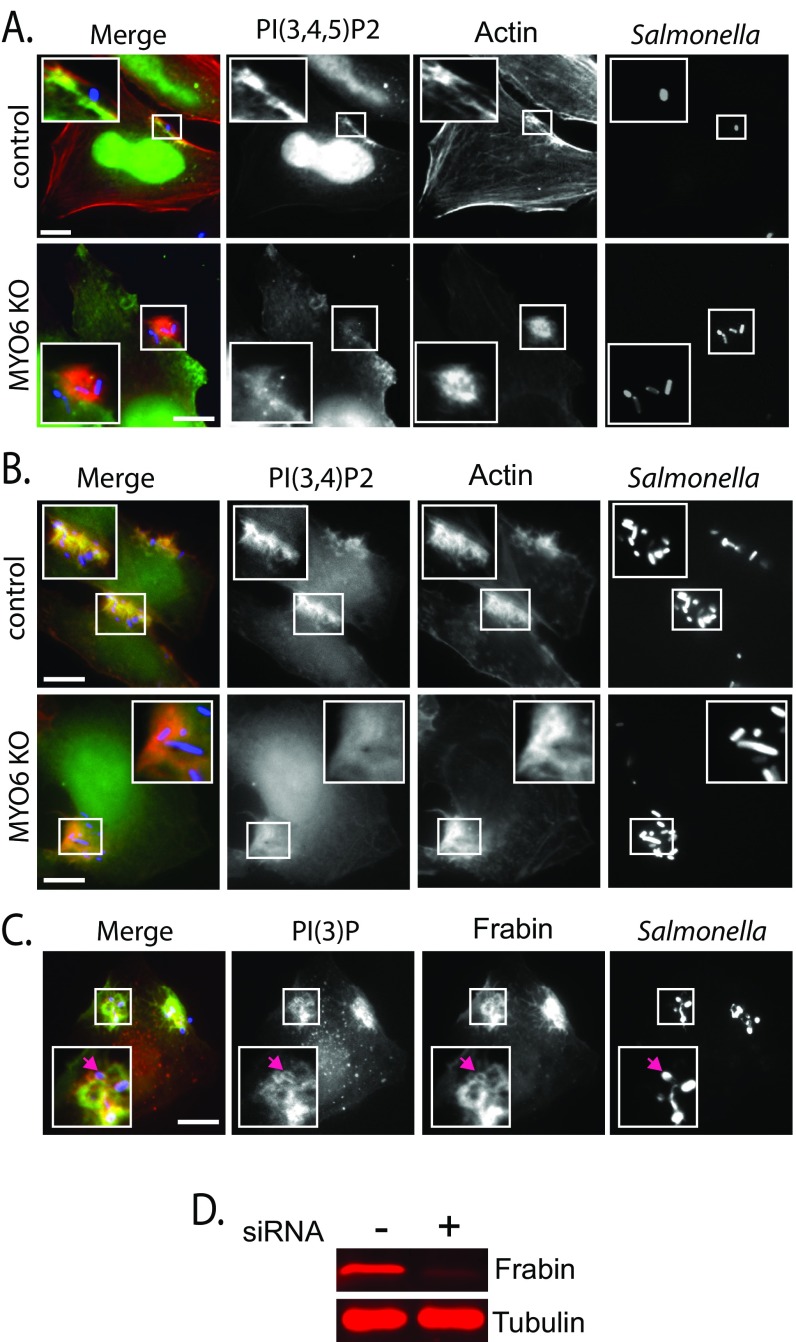
We reasoned that the plasma membrane pool of PI(3)P may derive from MYO6-dependent localization of PI(3,4,5)P3 and PI(3,4)P2 at invasion ruffles and that the plasma membrane pool in turn is dephosphorylated by SopB to generate PI(3)P at the macropinocytic cup. We thus investigated whether MYO6 promotes the localization of PI(3,4,5)P3 and PI(3,4)P2 at Salmonella invasion ruffles by examining the localization of the PH domain of Btk, which binds PI(3,4,5)P3, and that of TAPP1, which binds PI(3,4)P2 (SI Experimental Procedures). In control cells YFP-Btk and GFP-TAPP1 were enriched throughout the invasion ruffle, but this localization was markedly reduced in MYO6-depleted cells (Fig. S4 A and B, Insets). An established measure of downstream of PI3K activity is Akt phosphorylation, which is triggered during infection upon production of PI(3,4,5)P3 and PI(3,4)P2 (27, 28). To address whether MYO6 is required for the activation of PI3K, we examined Akt phosphorylation during infection of control and MYO6-depleted cells. Salmonella invasion stimulated Akt phosphorylation in control cells but not in MYO6-depleted cells (Fig. 4C). Together, these data demonstrate that SopB requires MYO6 to concentrate PI(3)P, PI(3,4)P2, and PI(3,4,5)P3 at invasion foci, leading to phosphorylation of Akt.
Fig. S4.
(A) Localization of PI(3,4,5)P3 at actin-rich Salmonella membrane ruffles during invasion. Cells were transfected with the PI(3,4,5)P3 probe YFP-Btk-PH and then were infected with Alexa-Fluor 594-labeled wild-type Salmonella (red) and actin stained with Alexa-Fluor 350-conjugated phalloidin (blue). (Scale bars: 5 μm.) Insets 3× magnify membrane ruffles and invading Salmonella. (B) Localization of PI(3,4)P2 at actin-rich Salmonella membrane ruffles during invasion. Cells were transfected with the PI(3,4)P3 probe GFP-TAPP1-PH and then were infected with Alexa-Fluor 594-labeled wild-type Salmonella (red) and actin stained with Alexa-Fluor 350-conjugated phalloidin (blue). (Scale bars: 5 μm.) Insets 2× magnify membrane ruffles and invading Salmonella. (C) Localization of PI(3)P and Frabin during Salmonella invasion. Cells were transfected with RFP-p40-PX [PI(3)P] and GFP-Frabin and then were infected with Alexa-Fluor 350-labeled wild-type Salmonella (blue). Insets 2× magnify invading Salmonella. The purple arrows indicate an invading bacterium colocalized with PI(3)P and Frabin. (Scale bar: 5 μm.) (D) Knockdown efficiency of Frabin. Cells were transfected with nontargeting (−) or Frabin (+) siRNA before immunoblotting with antibodies against Frabin and tubulin as a control.
MYO6-Mediated PI(3)P Formation Recruits Frabin to Promote Invasion.
We next examined the significance of PI(3)P at the macropinocytic cup. Previously, EPEC manipulation of phosphoinositides was shown to control the recruitment of PIP-binding proteins to the site of actin pedestals (29). Thus, we hypothesized that Salmonella targets MYO6 to generate PI(3)P-rich platforms to recruit specific PI(3)P-binding proteins that promote invasion. Upon closer inspection of the SopE-recruited cytoskeleton network, we noticed a PI(3)P-binding FYVE domain containing a protein called “Frabin” (FGD4; FYVE, RhoGEF, and PH domain-containing protein 4) (Tables S1 and S2). Indeed, we found that GFP-tagged Frabin colocalized with PI(3)P at the Salmonella entry site (Fig. S4C, pink arrow). Because MYO6 mediates PI(3)P localization at the macropinocytic cup (Fig. 3), we examined Frabin localization in infected MYO6-depleted cells (Fig. 4E). Frabin was enriched at the macropinocytic cup in Salmonella-infected control cells, but this recruitment was lost in MYO6-depleted cells, where Frabin was diffusely localized (Fig. 4E, Insets). Importantly, when we depleted host cells of Frabin by siRNA transfection, Salmonella invasion was reduced by ∼40% (Fig. 4D and Fig. S4D). Together, the data indicate that SopB and MYO6 work in the same pathway to potentiate the recruitment of PI(3)P-binding proteins at the macropinocytic cup and thereby promote pathogen uptake.
SI Experimental Procedures
In Vitro Actin-Based Motility and Pulldowns.
Preparation of porcine brain extract, actin-based motility assays, and pulldowns have been described in detail (14, 40). To focus on genuine interactions driven by Rho GTPases following activation by SopE, we used PC and PI as a negative control (e.g., in the absence of phosphoinositides) in studies that reconstituted Rho GTPase-dependent actin-based motility (13, 14). When appropriate, the extract was incubated with 1 μM recombinant SopE, PBD, GDI, or cytochalasin D (5 μM) or IPA-3 (40 μM) just before the addition of phospholipid-coated beads. To identify recruited proteins, beads were washed with 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate (pH 8.5) supplemented with 0.5 mM DTT and then were incubated with trypsin. The digested proteins were identified by electrospray ionization liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (Mass Spectrometry Service, Cambridge Centre for Proteomics, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK). The MS fragmentation data were used to search the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database using the MASCOT search engine (www.matrixscience.com).
Infection of HeLa Cells by S. flexneri and EPEC.
EPEC E2348/69 infections were performed as previously described (29). S. flexneri M90T infections were performed by culturing bacteria in 2TY medium (Formedium) to an OD600 of 2.0. Bacteria at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 100 were centrifuged onto HeLa cells [1,000 × g] for 10 min and then were incubated for 5 min at 37 °C before fixation.
Plasmids and Recombinant Proteins.
All peGFP-tagged MYO6 plasmids encoding full-length MYO6 (amino acids 1–1252), head domain (amino acids 1–835), tail domain (amino acids 840–1252), T405A, and T405E were constructed as described in refs. 41, 42, and 18. Full-length human Frabin was cloned into peCFP-DEST using Gateway Cloning (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with pTrc:sopB-FLAG (43) and peGFP-p40-PX. peYFP-Btk and peGFP-TAPP1 were gifts from Phil Hawkins, Babraham Institute, Cambridge, UK, and were used as previously described (29); pM975 was a gift from Wolf-Dietrich Hardt, ETH Zurich, Zurich. GST-tagged (SopE, PBD), and His-tagged (GDI) proteins were expressed in E. coli Rosetta (Novagen) at 16 °C before affinity purification (43).
Antibodies.
Antibodies were purchased from Abcam (Rac1, ab33186; Cdc42, ab64533; Frabin, ab97785; N-WASP, ab56454; PAK1, ab154284; Salmonella, ab35156; tubulin; 7291), Sigma (Actin, A2066; Nap1, N3788; His, H1029), GE Healthcare (GST, 27-4577-01), Cell Signaling (AKT, 2967; pAKT, 4050) and/or were raised against recombinant peptides in rabbits (MYO6).
Mammalian Cell Culture and RNAi.
Mammalian HeLa cells (ATCC-CCL-2) were routinely cultured in complete growth medium consisting of DMEM supplemented with 10% (vol/vol) FCS, 2 mM l-glutamine, 200 mg/mL streptomycin, and 100 U/mL penicillin (37 °C, 5% CO2). Plasmid DNA was transfected into HeLa cells by microporation using a Neon transfection system according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Life Technologies). For RNAi, siRNA against MYO6 from Dharmacon (SMARTpool: ON-TARGETplus MYO6 siRNA; catalog no. 006355-00-0005; sequence: CCACACUGCUCCAUAAUAU, UAUGAAAGAUCCUCUGCUA, CAUUGUAUCUGGAGAAUCA and GAAUCCAUACUUUGACAUA) and against ArpC3 from QIAGEN (CTGATAGGACCTTGATATATA, CAGCATTAAAGCTGGCGCTTA, TACGCTGGGAATCACTAATTT, TTCGACCCTCAGAATGATAAA) or nontargeting siControl siRNA (Table S3) was transfected into HeLa cells using Oligofectamine Transfection Reagent (Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The transfection mixture was replaced after 24 h with complete growth medium, and cells were cultured for a further 48 h. RNAi efficiency was determined either by quantitative RT-PCR using the Express One-Step SYBR GreenER kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Invitrogen) with VCP used as a standard or by immunoblotting.
CRISPR/Cas9 MYO6-Knockout Cells.
CRISPR/Cas9 MYO6-knockout HeLa cells were prepared by a modification of the technique described by Ran et al. (44). A 20-bp target to the N terminus of MYO6 (GGAGGATGGAAAGCCCGTTT) was selected using the CRISPR design tool crispr.mit.edu (Zhang laboratory). Single-guide RNA oligos were annealed and ligated to the pSpCas9(BB)-2A-Puro (PX459) vector (Addgene). HeLa cells were seeded at 50–80% confluency in a six-well plate, and the CRISPR plasmid was transfected using FuGENE 6 (Promega). After 24 h cells were incubated with 1.5 µg/mL puromycin for 72 h and were expanded. Colonies were isolated from a 15-cm plate, expanded, and tested by immunoblotting using an antibody to MYO6. Cas9 cleavage of clones lacking MYO6 was assessed for indels by Sanger sequencing.
Myosin siRNA Invasion Screen.
HeLa cells (5 × 10e3) were seeded into 96-well plates and transfected according to the manufacturer’s instructions with 100 nM siRNAs (Dharmacon) targeting the myosin motor proteins outlined in Table S3. Cells were incubated at 37 °C with 5% (vol/vol) CO2 for 48 h. The cells were transfected with the corresponding siRNAs a second time and were incubated for a further 48 h. Cells then were infected with S. enterica Typhimurium pM975 at an MOI of 100 for 30 min, washed three times with PBS, and incubated for a further 90 min with growth medium supplemented with 50 μg/mL gentamicin to kill extracellular bacteria. Infected cells were fixed with Hepes-buffered 4% paraformaldehyde, and invasion was quantified microscopically by counting the number of GFP bacteria per cell that were labeled with Alexa Fluor 594-phalloidin and DAPI.
Akt Activation Assay.
HeLa cells were serum starved overnight and then were infected with Salmonella (MOI 100, 20 min). Cells were washed with PBS and then were lysed in radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer (Sigma) supplemented with 15 mM NaF, 2 mM Na-Orthovanadate (Sigma), 1 mM potassium bisperoxo (1,10-phenanthroline) [bpV(phen)] (Sigma), 10 μg/mL pepstatin (Fluka), and 10 μg/mL Chymostatin (Sigma). Lysates were clarified by centrifugation (13,000 relative centrifugal field, 5 min); 5× SDS-PAGE loading buffer was added to the supernatant before analysis by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting.
Fluorescence Microscopy.
Fluorescence microscopy was performed on an Olympus IX81 inverted microscope. Digital images were captured on a CCD camera (Hamamatsu) and analyzed (Volocity, Improvision); then figures were assembled using Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator.
Statistics.
All experiments were performed at least three times. Geometric means were calculated, and significance was determined by Student’s t test, or one-way ANOVA followed by a post hoc Dunnett’s comparison. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 were considered significant.
Discussion
This study investigated how Salmonella hijacks the Rho GTPase networks to mediate uptake and establish intracellular infections. By reconstituting SopE-mediated Rho GTPase-driven actin polymerization, we identified a network of cytoskeleton proteins exploited by SopE that included members of the myosin motor protein family. Previous studies have shown that MYO1C and MYO2 are able to promote Salmonella invasion through lipid raft recycling (17) and through Arp2/3-independent actomyosin-mediated contractility (30), respectively. MYO2 also was found on actin filaments surrounding intracellular Salmonella within SCVs (31). It is becoming increasingly clear that MYO6 plays diverse roles in host–pathogen interactions. MYO6 was shown to defend host cells against intracellular Salmonella residing in the cytosol, revealing a role in xenophagy (32, 33). Moreover, MYO6 was found to promote the clathrin-dependent endocytosis of the intracellular pathogen Listeria monocytogenes, referred to as the “zipper mechanism” (19, 22). Our study shows that in host–pathogen interactions MYO6 facilitates Salmonella invasion by macropinocytosis through the trigger mechanism.
What is the molecular role of MYO6 during pathogen invasion? A long-standing mystery in Salmonella invasion is the mechanism by which SopB activates PI3Ks to generate the phosphoinositide PI(3,4,5)P3. Investigations are partly hampered by SopB’s insensitivity to classical PI3K inhibitors such as wortmannin, which targets class I PI3K, and also by kinase redundancy, e.g., Salmonella exploits class II PI3K and inositol polyphosphate multikinase (27, 28). We found that MYO6 was critical to SopB-mediated activation of PI3K; however, the molecular role of MYO6 in this process remains to be established. MYO1D, MYO1E, and MYO1F are known to bind PI(3,4,5)P3 (34), but to our knowledge a myosin has not previously been implicated in PI3K activity. This study places MYO6 at the center of the mechanism by which SopB activates PI3K and generates phosphoinositides at the plasma membrane. Unraveling the PI3K–MYO6 mechanism will be a substantial focus of future studies for researchers studying a spectrum of MYO6-dependent functions in health and disease.
SopB is known to dephosphorylate PI(3,4,5)P3 to generate PI(3,4)P2 and PI(3)P (35). PI(3,4,5)P3 and PI(3,4)P2 are enriched throughout the ruffle (25), and PI(3,4)P2 was recently shown to recruit SNX9 to enhance invasion (36). In contrast, we found that PI(3)P was coincident with SopB localization at the macropinocytic cup and was enriched in a MYO6-dependent manner. We found that PI(3)P facilitated the recruitment of Frabin to promote pathogen invasion. Frabin comprises a PI(3)P-binding FYVE domain, a Cdc42 GEF, and an F-actin–binding domain. Frabin has been implicated in the invasion of the intracellular parasite Cryptosporidium parvum in a PI3K-dependent manner (37) and in the generation of filopodium-like microspikes (38). Even so, Frabin’s role in the cell remains unclear, and no previous interaction with a bacterial pathogen has been reported. Understanding Frabin’s involvement in Salmonella invasion will likely shed light on its role in the cell and in disease.
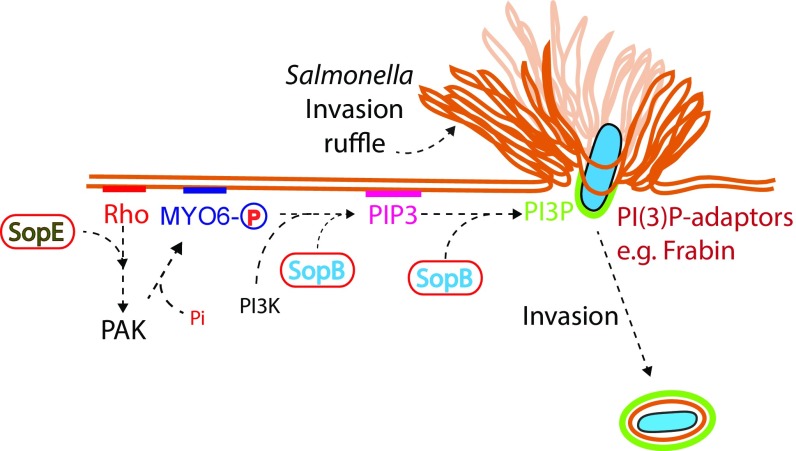
In summary, we reveal a mechanism by which SopE mediates MYO6 recruitment to the membrane via Rho GTPase activation of PAK. We identify MYO6 as a participant in phosphoinositide distribution that acts with the Salmonella effector SopB to regulate lipid and protein composition of the macropinocytic cup during pathogen uptake. In doing so, we uncover a mechanism by which Salmonella effectors work in synergy to manipulate MYO6 and facilitate pathogen invasion (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
Proposed model for Salmonella manipulation of MYO6 during invasion. Salmonella SopE activates Rho GTPases, which induce actin cytoskeleton reorganization and the recruitment of MYO6 to the membrane via PAK. SopB and MYO6 trigger PI3K signaling to generate PIP3. PIP3 acts as a substrate for SopB, which dephosphorylates PIP3 to generate PI(3)P at the macropinocytic cup of invading bacteria. PI(3)P recruits PI(3)P-binding proteins, such as Frabin, that promote Salmonella uptake.
Experimental Procedures
Salmonella Strains and Invasion of HeLa Cells.
Wild-type, S. enterica serovar Typhimurium SL1344 (gift from Jean Guard-Petter, University of Georgia College of Veterinary Medicine, Athens, GA) and isogenic ΔsopE, ΔsopE2, ΔsopE/ΔsopE2, and ΔsopB strains were used as previously described (10, 39). To quantify invasion, Salmonella encoding pM975, which expresses GFP when bacteria are intracellular (12), were used to invade HeLa cells (15 min). Infected cells then were incubated for 90 min in fresh growth medium containing 50 μg/mL gentamicin to kill extracellular bacteria. Intracellular GFP+ Salmonella were quantified microscopically. For fluorescence microscopy bacteria were visualized by labeling with Alexa Fluor 350 carboxylic acid succinimidyl ester (Life Technologies) or anti-Salmonella antibodies. When appropriate, cells were preincubated for 30 min and then for 15 min during Salmonella invasion with 40 μM MYO6 inhibitor Triiodolphenol (TIP; Sigma), 40 μM inhibitor of PAK activation-3 (IPA-3; Merck), 40 μM inhibitor of Rac1 (EHT1864; Merck), Cdc42 (ML141; Merck), or Rac1 and Cdc42 (AZA1; Merck).
Quantification of Macropinocytic Cups.
HeLa cells were infected for 5 min with Alexa-Fluor 350-labeled Salmonella to mark total bacteria. Macropinocytic cups protected the penetrating tip of invading Salmonella from labeling with anti-Salmonella antibodies on nonpermeabilized cells. Macropinocytic cups thus were identified by anti-Salmonella antibody labeling of exposed extracellular portions of bacteria (e.g., the bacterial pole and/or flagella). When possible, PI(3)P accumulating at the base of invasion sites via peGFP-p40-PX expression also marked macropinocytic cups. The proportion of macropinocytic cups relative to the total number of colonizing Salmonella (i.e., surface-adherent and intracellular bacteria) was quantified.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Peter Hume and Dr. Tomas Masters for technical help and reading of the manuscript and Dr. John Kendrick-Jones for advice and critical reading of the manuscript. This work was funded by Wellcome Trust Grant 101828/Z/13/Z (to V.K.), by Medical Research Council Grants MR/K000888/1 and MR/N000048/1 (to F.B.), MR/L008122/1 (to V.K.), and MR/M011771/1 (to D.H.), and by the Cambridge Isaac Newton Trust.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1616418114/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Sit S-T, Manser E. Rho GTPases and their role in organizing the actin cytoskeleton. J Cell Sci. 2011;124:679–683. doi: 10.1242/jcs.064964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Edwards DC, Sanders LC, Bokoch GM, Gill GN. Activation of LIM-kinase by Pak1 couples Rac/Cdc42 GTPase signalling to actin cytoskeletal dynamics. Nat Cell Biol. 1999;1:253–259. doi: 10.1038/12963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wells AL, Lin AW, Chen L, Safer D. Myosin VI is an actin-based motor that moves backwards. Nature. 1999;401:505–508. doi: 10.1038/46835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Buss F, et al. The localization of myosin VI at the Golgi complex and leading edge of fibroblasts and its phosphorylation and recruitment into membrane ruffles of A431 cells after growth factor stimulation. J Cell Biol. 1998;143:1535–1545. doi: 10.1083/jcb.143.6.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chibalina MV, Poliakov A, Kendrick-Jones J, Buss F. Myosin VI and optineurin are required for polarized EGFR delivery and directed migration. Traffic. 2010;11:1290–1303. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01101.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tumbarello DA, Kendrick-Jones J, Buss F. Myosin VI and its cargo adaptors - linking endocytosis and autophagy. J Cell Sci. 2013;126:2561–2570. doi: 10.1242/jcs.095554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hardt W-D, Chen L-M, Schuebel KE, Bustelo XR, Galán JE. S. typhimurium encodes an activator of Rho GTPases that induces membrane ruffling and nuclear responses in host cells. Cell. 1998;93:815–826. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Patel JC, Galán JE. Differential activation and function of Rho GTPases during Salmonella-host cell interactions. J Cell Biol. 2006;175:453–463. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200605144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhou D, Chen LM, Hernandez L, Shears SB, Galán JE. A Salmonella inositol polyphosphatase acts in conjunction with other bacterial effectors to promote host cell actin cytoskeleton rearrangements and bacterial internalization. Mol Microbiol. 2001;39:248–259. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Humphreys D, Davidson A, Hume PJ, Koronakis V. Salmonella virulence effector SopE and Host GEF ARNO cooperate to recruit and activate WAVE to trigger bacterial invasion. Cell Host Microbe. 2012;11:129–139. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.01.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Friebel A, et al. SopE and SopE2 from Salmonella typhimurium activate different sets of RhoGTPases of the host cell. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:34035–34040. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100609200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Misselwitz B, et al. RNAi screen of Salmonella invasion shows role of COPI in membrane targeting of cholesterol and Cdc42. Mol Syst Biol. 2011;7:474. doi: 10.1038/msb.2011.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rohatgi R, et al. The interaction between N-WASP and the Arp2 / 3 complex links Cdc42-dependent signals to actin assembly. Cell. 1999;97:221–231. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80732-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Koronakis V, et al. WAVE regulatory complex activation by cooperating GTPases Arf and Rac1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:14449–14454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1107666108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hartman MA, Spudich JA. The myosin superfamily at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:1627–1632. doi: 10.1242/jcs.094300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Maliga Z, et al. A genomic toolkit to investigate kinesin and myosin motor function in cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15:325–334. doi: 10.1038/ncb2689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Brandstaetter H, Kendrick-Jones J, Buss F. Myo1c regulates lipid raft recycling to control cell spreading, migration and Salmonella invasion. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:1991–2003. doi: 10.1242/jcs.097212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Heissler SM, et al. Kinetic properties and small-molecule inhibition of human myosin-6. FEBS Lett. 2012;586:3208–3214. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.07.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cossart P, Sansonetti PJ. 2004. Bacterial invasion: the paradigms of enteroinvasive pathogens. 304:242–8.
- 20.Mounier J, et al. Rho family GTPases control entry of Shigella flexneri into epithelial cells but not intracellular motility. J Cell Sci. 1999;112:2069–2080. doi: 10.1242/jcs.112.13.2069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ben-Ami G, et al. Agents that inhibit Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 do not block formation of actin pedestals in HeLa cells infected with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1998;66:1755–1758. doi: 10.1128/iai.66.4.1755-1758.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bonazzi M, et al. Clathrin phosphorylation is required for actin recruitment at sites of bacterial adhesion and internalization. J Cell Biol. 2011;195:525–536. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201105152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chen LM, Bagrodia S, Cerione RA, Galán JE. Requirement of p21-activated kinase (PAK) for Salmonella typhimurium-induced nuclear responses. J Exp Med. 1999;189(9):1479–1488. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.9.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bement WM, Mooseker MS. Views and reviews. TEDS rule: A molecular rationale for differential regulation of myosins by phosphorylation of the heavy chain head. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1995;31:87–92. doi: 10.1002/cm.970310202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mallo GV, et al. SopB promotes phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate formation on Salmonella vacuoles by recruiting Rab5 and Vps34. J Cell Biol. 2008;182:741–752. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200804131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Norris FA, Wilson MP, Wallis TS, Galyov EE, Majerus PW. SopB, a protein required for virulence of Salmonella dublin, is an inositol phosphate phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:14057–14059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.24.14057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Roppenser B, et al. Multiple host kinases contribute to Akt activation during Salmonella infection. PLoS One. 2013;8:e71015. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cooper KG, et al. Activation of Akt by the bacterial inositol phosphatase, SopB, is wortmannin insensitive. PLoS One. 2011;6:e22260. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Smith K, Humphreys D, Hume PJ, Koronakis V. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli recruits the cellular inositol phosphatase SHIP2 to regulate actin-pedestal formation. Cell Host Microbe. 2010;7:13–24. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2009.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hänisch J, et al. Activation of a RhoA/myosin II-dependent but Arp2/3 complex-independent pathway facilitates Salmonella invasion. Cell Host Microbe. 2011;9:273–285. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Odendall C, et al. The Salmonella kinase SteC targets the MAP kinase MEK to regulate the host actin cytoskeleton. Cell Host Microbe. 2012;12:657–668. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.09.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tumbarello DA, Manna PT, Allen M, Bycroft M, Arden SD. The autophagy receptor TAX1BP1 and the molecular motor myosin VI are required for clearance of Salmonella typhimurium by autophagy. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:e1005174. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Verlhac P, et al. Autophagy receptor NDP52 regulates pathogen- containing autophagosome maturation. Cell Host Microbe. 2015;17:515–525. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chen CL, Iijima M. Myosin I: A new pip(3) effector in chemotaxis and phagocytosis. Commun Integr Biol. 2012;5:294–296. doi: 10.4161/cib.19892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Marcus SL, Wenk MR, Steele-Mortimer O, Finlay BB. A synaptojanin-homologous region of Salmonella typhimurium SigD is essential for inositol phosphatase activity and Akt activation. FEBS Lett. 2001;494:201–207. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02356-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Piscatelli HL, Li M, Zhou D. Dual 4- and 5-phosphatase activities regulate SopB-dependent phosphoinositide dynamics to promote bacterial entry. Cell Microbiol. 2016;18:705–719. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chen X-M, et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and frabin mediate Cryptosporidium parvum cellular invasion via activation of Cdc42. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:31671–31678. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401592200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ono Y, et al. Two actions of frabin: Direct activation of Cdc42 and indirect activation of Rac. Oncogene. 2000;19:3050–3058. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Humphreys D, Davidson AC, Hume PJ, Makin LE, Koronakis V. Arf6 coordinates actin assembly through the WAVE complex, a mechanism usurped by Salmonella to invade host cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:16880–16885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1311680110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hume PJ, Humphreys D, Koronakis V. WAVE regulatory complex activation. Methods Enzymol. 2014;540:363–379. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-397924-7.00020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Spudich G, et al. Myosin VI targeting to clathrin-coated structures and dimerization is mediated by binding to Disabled-2 and PtdIns(4,5)P2. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:176–183. doi: 10.1038/ncb1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chibalina MV, Seaman MNJ, Miller CC, Kendrick-Jones J, Buss F. Myosin VI and its interacting protein LMTK2 regulate tubule formation and transport to the endocytic recycling compartment. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:4278–4288. doi: 10.1242/jcs.014217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Cain RJ, Hayward RD, Koronakis V. The target cell plasma membrane is a critical interface for Salmonella cell entry effector-host interplay. Mol Microbiol. 2004;54:887–904. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04336.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ran FA, et al. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat Protoc. 2013;8:2281–2308. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.