Figure 1.
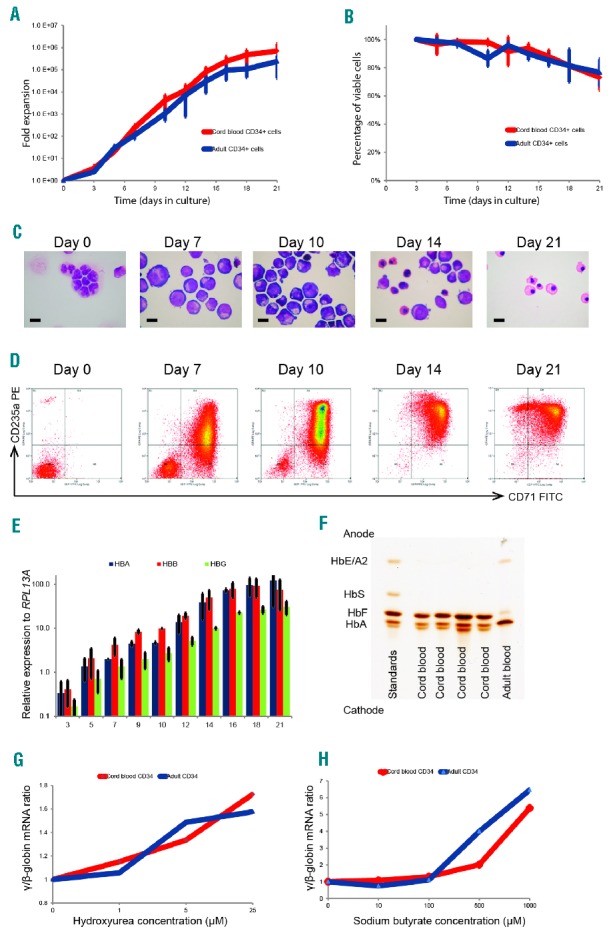
Characterization and validation of the small scale erythroid differentiation system used for small molecule screen. Human CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells purified from umbilical cord or adult peripheral blood were cultured in a two-phase liquid culture system in a serum-free medium for 21 days. (A) Mean fold expansion during erythroid differentiation; error bars represent SD (n=3). (B) Mean percentage cell viability during erythroid differentiation; error bars represent SD (n=3). (C) Morphology of cells by cytospins stained using modified Wright’s stain at different time points (day 0–21), in culture representing different stages of erythroid differentiation, demonstrating progression through stages of pro-, basophilic and polychromatic to orthochromatic erythroblasts; scale bar – 10μm. (D) Representative flow cytometry plots of cells stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated anti-CD71 and phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated anti-CD235a antibodies, demonstrating sequential expression of CD71 followed by CD235a and subsequent loss of CD71. (E) Relative expression of α (HBA)-, β (HBB)- and γ (HBG)-globin mRNA levels quantified by qPCR and normalized to the housekeeping gene RPL13A at different time points in culture (adult blood CD34+ cells); error bars represent SD (n=3). (F) Hemoglobin subtypes of the erythroid cells differentiated from umbilical cord and adult CD34+ cells analyzed by isoelectric focusing. The samples were run against a commercial set of standards. (G and H) γ/β mRNA ratio after incubation of erythroid cells in a dose range of hydroxyurea and sodium butyrate. Compounds were added to the liquid culture medium on day 7 of erythroid cell differentiation (corresponding to the proerythroblast stage), and the cells were then incubated in a 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37°C for 72 hours. Data on erythroid cells differentiated from umbilical cord and adult CD34+ cells are presented in red and blue, respectively. mRNA: messenger ribonucleic acid; HbF: hemoglobin F; HbA: hemoglobin A; HbS: hemoglobin S; HbE; hemoglobin E; HBA: α-globin; HBB: β-globin; HBG: γ-globin; HbA2: hemoglobin A2.
