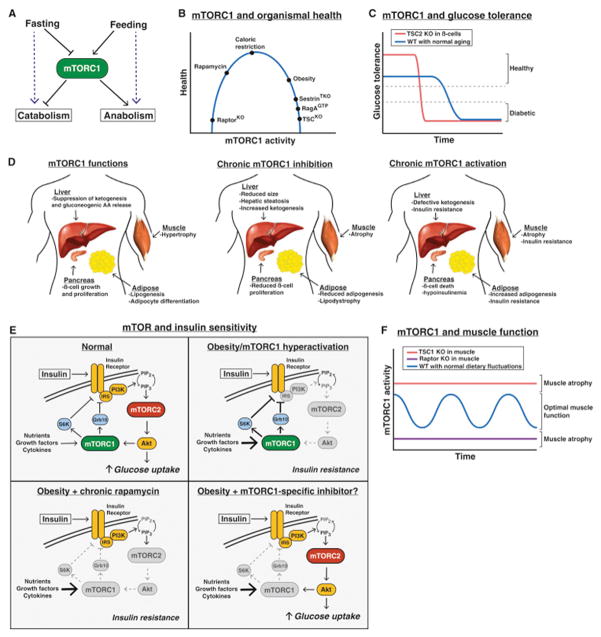
Figure 4. Physiological Roles of mTOR.
(A) mTORC1 controls the balance between anabolism and catabolism in response to fasting and feeding.
(B) The effect of cumulative mTORC1 activity on overall health.
(C) The effect of mTORC1 hyperactivation in pancreatic β-cells on glucose tolerance over time.
(D) The normal functions of mTORC1 in the liver, muscle, pancreas, and adipose tissue (left), and the consequences of chronic mTORC1 inhibition (middle) or activation (right).
(E) Deregulation of mTORC1 signaling in insulin resistance/diabetes, and the effect of rapamycin or a theoretical mTORC1 specific inhibitor.