Abstract
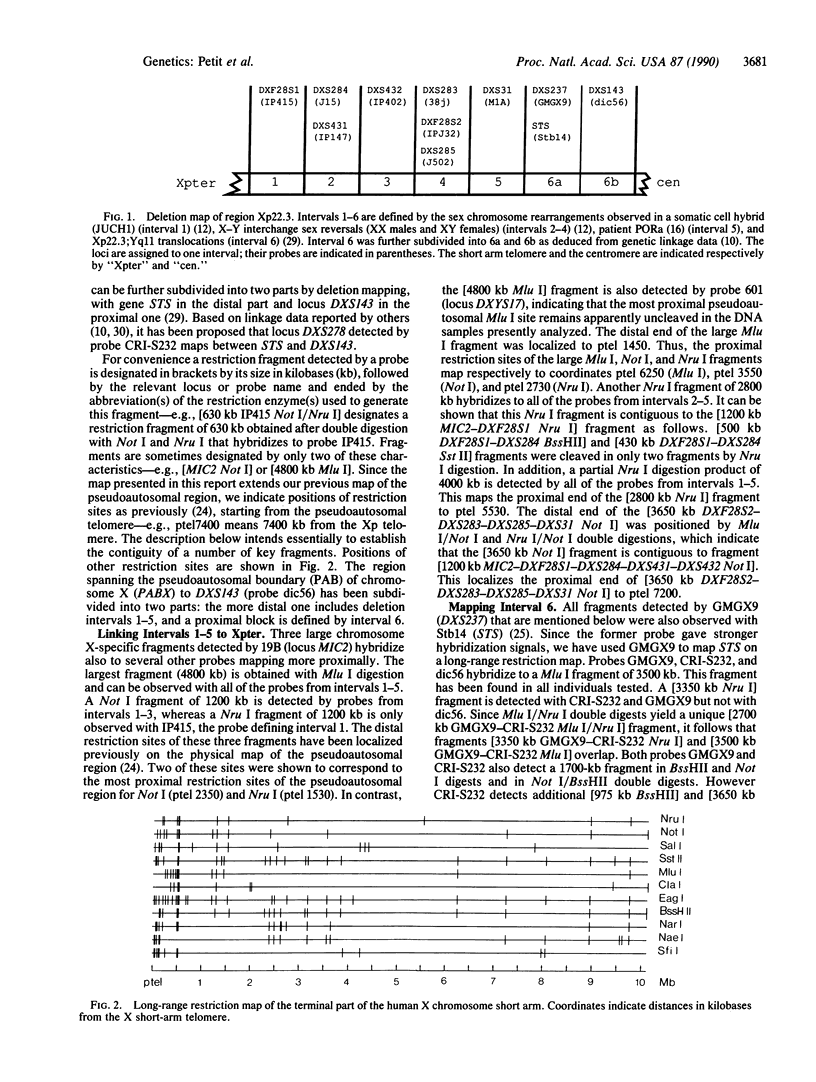
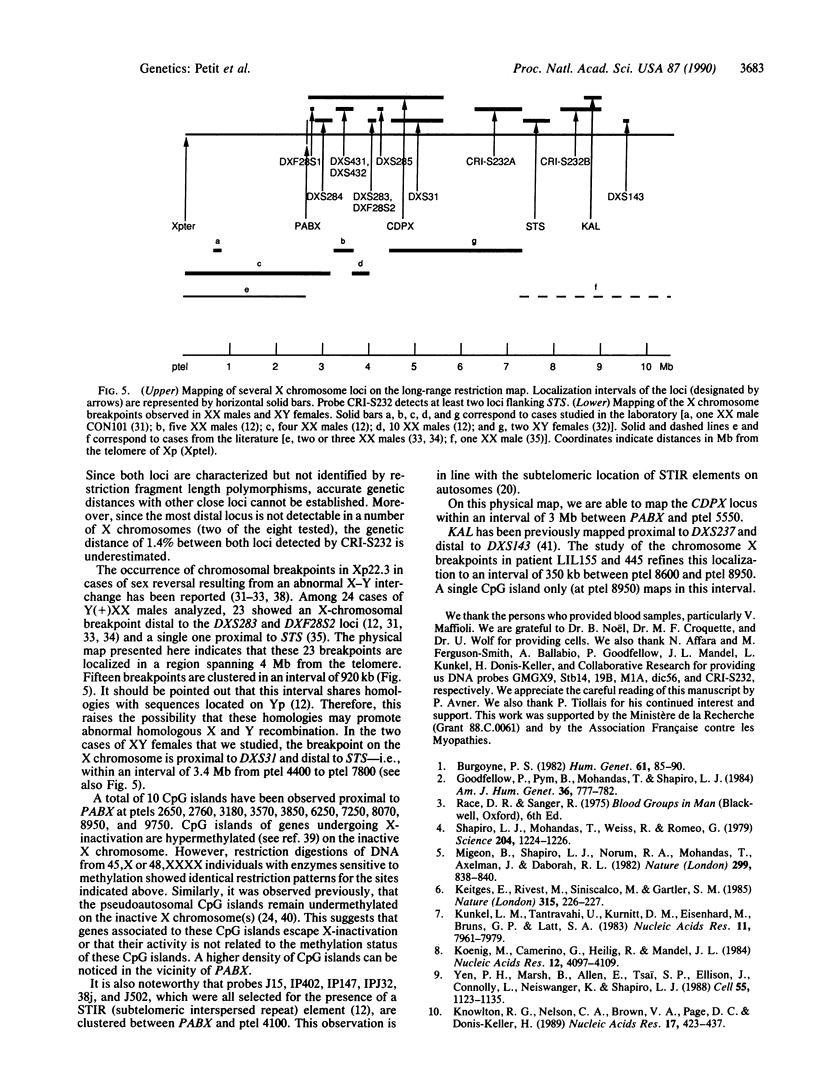
The terminal part of the short arm of the human X chromosome has been mapped by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). The map, representing the distal two-thirds of Xp22.3 spans a total of 10,000 kilobases (kb) from Xpter to the DXS143 locus. A comparison with linkage data indicates that 1 centimorgan (cM) in this region corresponds to about 600 kb. CpG islands were essentially concentrated in the 1500 kb immediately proximal to the pseudoautosomal boundary. Several loci, including the gene encoding steroid sulfatase (STS) and the loci for the X-linked recessive form of chondrodysplasia punctata (CDPX) and for Kallmann syndrome (KAL) have been placed relative to the Xp telomere. CDPX is located between 2650 and 5550 kb from Xpter, and STS is located between 7250 and 7830 kb from Xpter. KAL maps to an interval of 350 kb between 8600 and 8950 kb from the telomere. The X-chromosomal breakpoints of a high proportion of XX males resulting from X-Y interchange cluster to a 920-kb region proximal and close to the pseudoautosomal boundary.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agematsu K., Koike K., Morosawa H., Nakahori Y., Nakagome Y., Akabane T. Chondrodysplasia punctata with X;Y translocation. Hum Genet. 1988 Sep;80(1):105–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00451470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A., Bardoni B., Carrozzo R., Andria G., Bick D., Campbell L., Hamel B., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Gimelli G., Fraccaro M. Contiguous gene syndromes due to deletions in the distal short arm of the human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10001–10005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A., Parenti G., Carrozzo R., Coppa G., Felici L., Migliori V., Silengo M., Franceschini P., Andria G. X/Y translocation in a family with X-linked ichthyosis, chondrodysplasia punctata, and mental retardation: DNA analysis reveals deletion of the steroid sulphatase gene and translocation of its Y pseudogene. Clin Genet. 1988 Jul;34(1):31–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1988.tb02612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A., Parenti G., Carrozzo R., Sebastio G., Andria G., Buckle V., Fraser N., Craig I., Rocchi M., Romeo G. Isolation and characterization of a steroid sulfatase cDNA clone: genomic deletions in patients with X-chromosome-linked ichthyosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4519–4523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A., Parenti G., Tippett P., Mondello C., Di Maio S., Tenore A., Andria G. X-linked ichthyosis, due to steroid sulphatase deficiency, associated with Kallmann syndrome (hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and anosmia): linkage relationships with Xg and cloned DNA sequences from the distal short arm of the X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1986 Mar;72(3):237–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00291885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R. Molecular cloning of human telomeres in yeast. Nature. 1989 Apr 27;338(6218):774–776. doi: 10.1038/338774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne P. S. Genetic homology and crossing over in the X and Y chromosomes of Mammals. Hum Genet. 1982;61(2):85–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00274192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Brown W. R., Rappold G. A. Hypervariable telomeric sequences from the human sex chromosomes are pseudoautosomal. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):687–692. doi: 10.1038/317687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry C. J., Magenis R. E., Brown M., Lanman J. T., Jr, Tsai J., O'Lague P., Goodfellow P., Mohandas T., Bergner E. A., Shapiro L. J. Inherited chondrodysplasia punctata due to a deletion of the terminal short arm of an X chromosome. N Engl J Med. 1984 Oct 18;311(16):1010–1015. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198410183111603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard E. F., Affara N. A., Yates J. R., Goudie D. R., Lambert J., Aitken D. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Deletion of a DNA sequence in eight of nine families with X-linked ichthyosis (steroid sulphatase deficiency). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):3977–3985. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.3977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. J., Darling S. M., Thomas N. S., Goodfellow P. N. A pseudoautosomal gene in man. Science. 1986 Nov 7;234(4777):740–743. doi: 10.1126/science.2877492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. J., Mondello C., Darling S. M., Pym B., Little P., Goodfellow P. N. Absence of methylation of a CpG-rich region at the 5' end of the MIC2 gene on the active X, the inactive X, and the Y chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5605–5609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P., Pym B., Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J. The cell surface antigen locus, MIC2X, escapes X-inactivation. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jul;36(4):777–782. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant S. G., Chapman V. M. Mechanisms of X-chromosome regulation. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:199–233. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keitges E., Rivest M., Siniscalco M., Gartler S. M. X-linkage of steroid sulphatase in the mouse is evidence for a functional Y-linked allele. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):226–227. doi: 10.1038/315226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton R. G., Nelson C. A., Brown V. A., Page D. C., Donis-Keller H. An extremely polymorphic locus on the short arm of the human X chromosome with homology to the long arm of the Y chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):423–437. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Camerino G., Heilig R., Mandel J. L. A DNA fragment from the human X chromosome short arm which detects a partially homologous sequence on the Y chromosomes long arm. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4097–4109. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Tantravahi U., Kurnit D. M., Eisenhard M., Bruns G. P., Latt S. A. Identification and isolation of transcribed human X chromosome DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7961–7979. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau E. C., Mohandas T. K., Shapiro L. J., Slavkin H. C., Snead M. L. Human and mouse amelogenin gene loci are on the sex chromosomes. Genomics. 1989 Feb;4(2):162–168. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90295-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levilliers J., Quack B., Weissenbach J., Petit C. Exchange of terminal portions of X- and Y-chromosomal short arms in human XY females. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2296–2300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlesworth W., Bertelson C., Kunkel L. M. An RFLP detecting single copy X-chromosome fragment, dic56, from Xp22-Xpter [HGM8 assignment no. DXS 143]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5723–5723. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Shapiro L. J., Norum R. A., Mohandas T., Axelman J., Dabora R. L. Differential expression of steroid sulphatase locus on active and inactive human X chromosome. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):838–840. doi: 10.1038/299838a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondello C., Ropers H. H., Craig I. W., Tolley E., Goodfellow P. N. Physical mapping of genes and sequences at the end of the human X chromosome short arm. Ann Hum Genet. 1987 May;51(Pt 2):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1987.tb01055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Lathrop M., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Kamboh M. I., Lalouel J. M., White R. Frequent recombination is observed in the distal end of the long arm of chromosome 14. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):76–81. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90317-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. C., Bieker K., Brown L. G., Hinton S., Leppert M., Lalouel J. M., Lathrop M., Nystrom-Lahti M., de la Chapelle A., White R. Linkage, physical mapping, and DNA sequence analysis of pseudoautosomal loci on the human X and Y chromosomes. Genomics. 1987 Nov;1(3):243–256. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. C., Brown L. G., de la Chapelle A. Exchange of terminal portions of X- and Y-chromosomal short arms in human XX males. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):437–440. doi: 10.1038/328437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit C., Levilliers J., Weissenbach J. Physical mapping of the human pseudo-autosomal region; comparison with genetic linkage map. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2369–2376. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03081.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit C., de la Chapelle A., Levilliers J., Castillo S., Noël B., Weissenbach J. An abnormal terminal X-Y interchange accounts for most but not all cases of human XX maleness. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90535-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouyer F., Simmler M. C., Johnsson C., Vergnaud G., Cooke H. J., Weissenbach J. A gradient of sex linkage in the pseudoautosomal region of the human sex chromosomes. Nature. 1986 Jan 23;319(6051):291–295. doi: 10.1038/319291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouyer F., Simmler M. C., Page D. C., Weissenbach J. A sex chromosome rearrangement in a human XX male caused by Alu-Alu recombination. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90637-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouyer F., de la Chapelle A., Andersson M., Weissenbach J. An interspersed repeated sequence specific for human subtelomeric regions. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):505–514. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schempp W., Müller G., Scherer G., Bohlander S. K., Rommerskirch W., Fraccaro M., Wolf U. Localization of Y chromosome sequences and X chromosomal replication studies in XX males. Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;81(2):144–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00293890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L. J., Mohandas T., Weiss R., Romeo G. Non-inactivation of an x-chromosome locus in man. Science. 1979 Jun 15;204(4398):1224–1226. doi: 10.1126/science.156396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalvey J. R., Durbin E. J., Erickson R. P. Sex vesicle "entrapment": translocation or nonhomologous recombination of misaligned Yp and Xp as alternative mechanisms for abnormal inheritance of the sex-determining region. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Apr;32(4):564–572. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320320436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Haines J. L., Watkins P. C., Stewart G. D., Wallace M. R., Hallewell R., Wong C., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. Genetic linkage map of human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiepolo L., Zuffardi O., Fraccaro M., di Natale D., Gargantini L., Müller C. R., Ropers H. H. Assignment by deletion mapping of the steroid sulfatase X-linked ichthyosis locus to Xp223. Hum Genet. 1980;54(2):205–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00278973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. R., Goudie D. R., Gillard E. F., Aitken D. A., Affara N. A., Clayton J. F., Tippett P. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Multipoint linkage analysis of steroid sulfatase (X-linked ichthyosis) and distal Xp markers. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):52–59. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90104-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Marsh B., Allen E., Tsai S. P., Ellison J., Connolly L., Neiswanger K., Shapiro L. J. The human X-linked steroid sulfatase gene and a Y-encoded pseudogene: evidence for an inversion of the Y chromosome during primate evolution. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1123–1135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90257-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]