Abstract
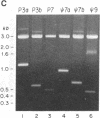
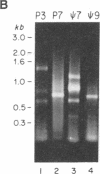
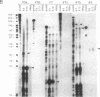
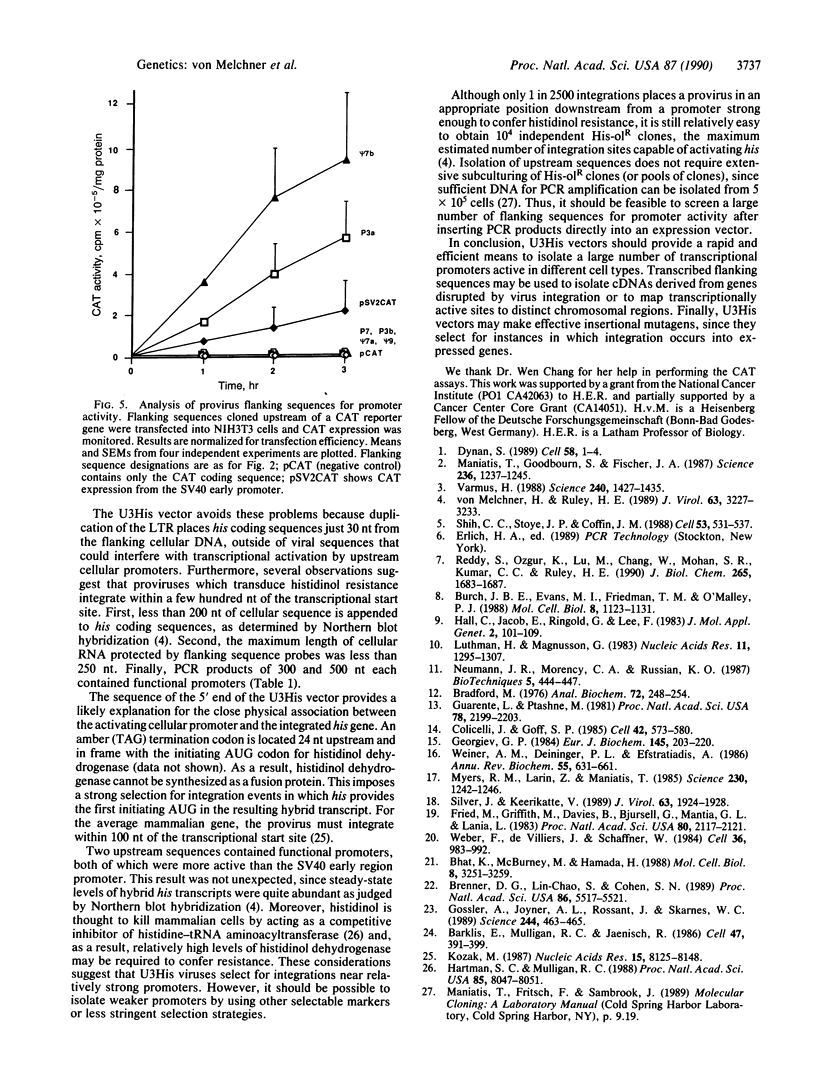
A retrovirus vector has been used to isolate transcriptional promoters from mammalian cells. The virus contains a selectable gene encoding histidinol dehydrogenase (his) in the U3 region of the 3' long terminal repeat (LTR). When the virus is passaged, duplication of LTRs places his sequences just 30 nucleotides from the adjacent cellular DNA. As a result, selection for histidinol resistance generates cell clones in which his is expressed on transcripts initiating in the flanking cellular DNA. Upstream cellular sequences, cloned after amplification by polymerase chain reaction, hybridized to RNA from uninfected cells, indicating that the adjacent promoters were transcriptionally active prior to virus integration. Two cloned transcribed flanking sequences also contained highly active transcriptional promoters, as estimated by their ability to activate expression of a linked reporter gene. Thus, U3His vectors provide a rapid and efficient means to isolate promoters active in different cell types. Moreover, by selecting for cell clones containing proviruses integrated in expressed genes, the virus may make an effective insertional mutagen.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barklis E., Mulligan R. C., Jaenisch R. Chromosomal position or virus mutation permits retrovirus expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90596-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat K., McBurney M. W., Hamada H. Functional cloning of mouse chromosomal loci specifically active in embryonal carcinoma stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3251–3259. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. G., Lin-Chao S., Cohen S. N. Analysis of mammalian cell genetic regulation in situ by using retrovirus-derived "portable exons" carrying the Escherichia coli lacZ gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5517–5521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Evans M. I., Friedman T. M., O'Malley P. J. Two functional estrogen response elements are located upstream of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1123–1131. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Mutants and pseudorevertants of Moloney murine leukemia virus with alterations at the integration site. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):573–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90114-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S. Modularity in promoters and enhancers. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Griffiths M., Davies B., Bjursell G., La Mantia G., Lania L. Isolation of cellular DNA sequences that allow expression of adjacent genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2117–2121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev G. P. Mobile genetic elements in animal cells and their biological significance. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 3;145(2):203–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossler A., Joyner A. L., Rossant J., Skarnes W. C. Mouse embryonic stem cells and reporter constructs to detect developmentally regulated genes. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):463–465. doi: 10.1126/science.2497519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Ptashne M. Fusion of Escherichia coli lacZ to the cytochrome c gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman S. C., Mulligan R. C. Two dominant-acting selectable markers for gene transfer studies in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8047–8051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Larin Z., Maniatis T. Detection of single base substitutions by ribonuclease cleavage at mismatches in RNA:DNA duplexes. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1242–1246. doi: 10.1126/science.4071043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy S., Ozgur K., Lu M., Chang W., Mohan S. R., Kumar C. C., Ruley H. E. Structure of the human smooth muscle alpha-actin gene. Analysis of a cDNA and 5' upstream region. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1683–1687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C. C., Stoye J. P., Coffin J. M. Highly preferred targets for retrovirus integration. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):531–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90569-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Keerikatte V. Novel use of polymerase chain reaction to amplify cellular DNA adjacent to an integrated provirus. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1924–1928. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1924-1928.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. Retroviruses. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1427–1435. doi: 10.1126/science.3287617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., de Villiers J., Schaffner W. An SV40 "enhancer trap" incorporates exogenous enhancers or generates enhancers from its own sequences. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Melchner H., Ruley H. E. Identification of cellular promoters by using a retrovirus promoter trap. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3227–3233. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3227-3233.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]