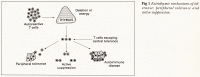
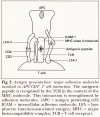
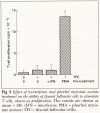
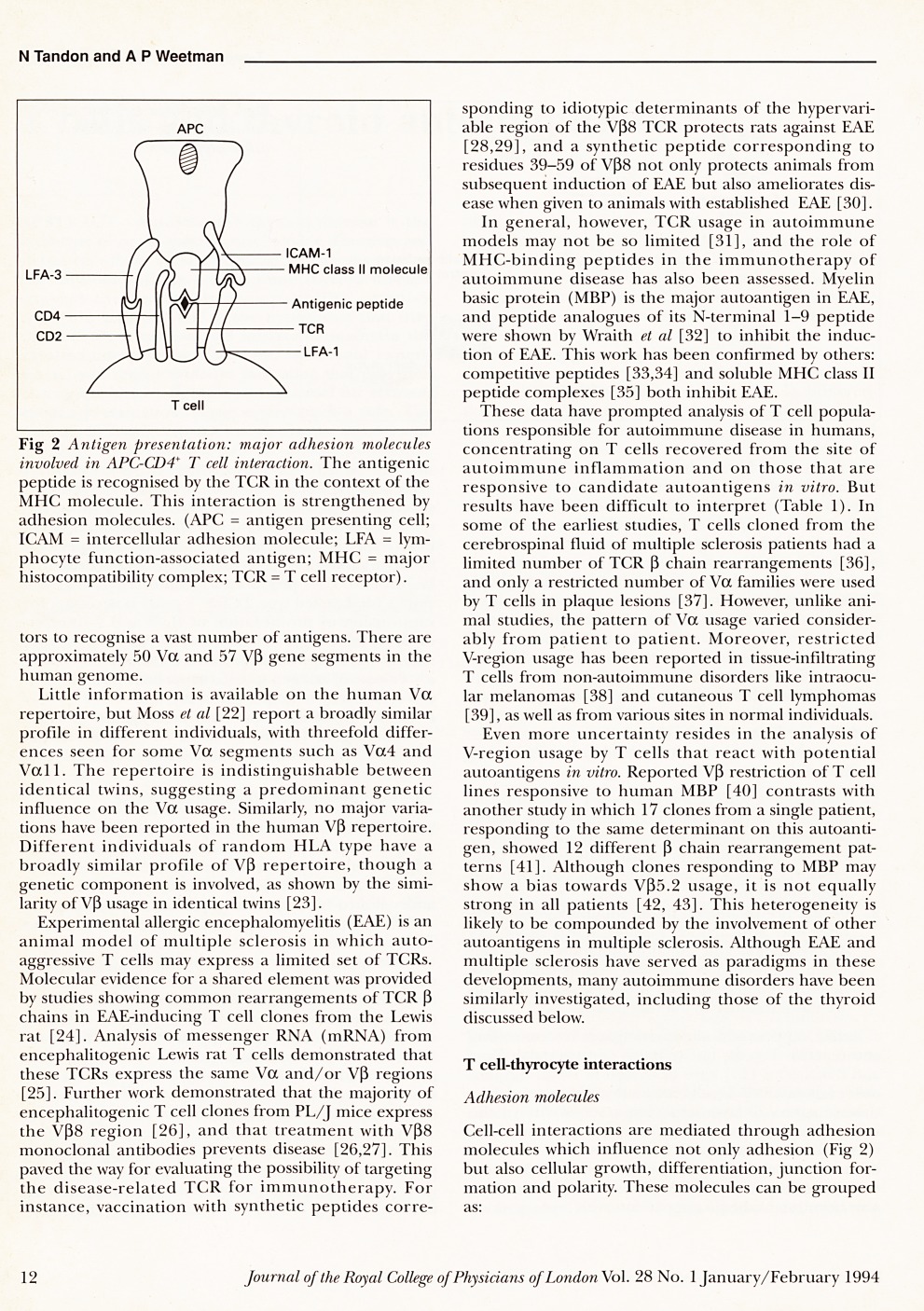
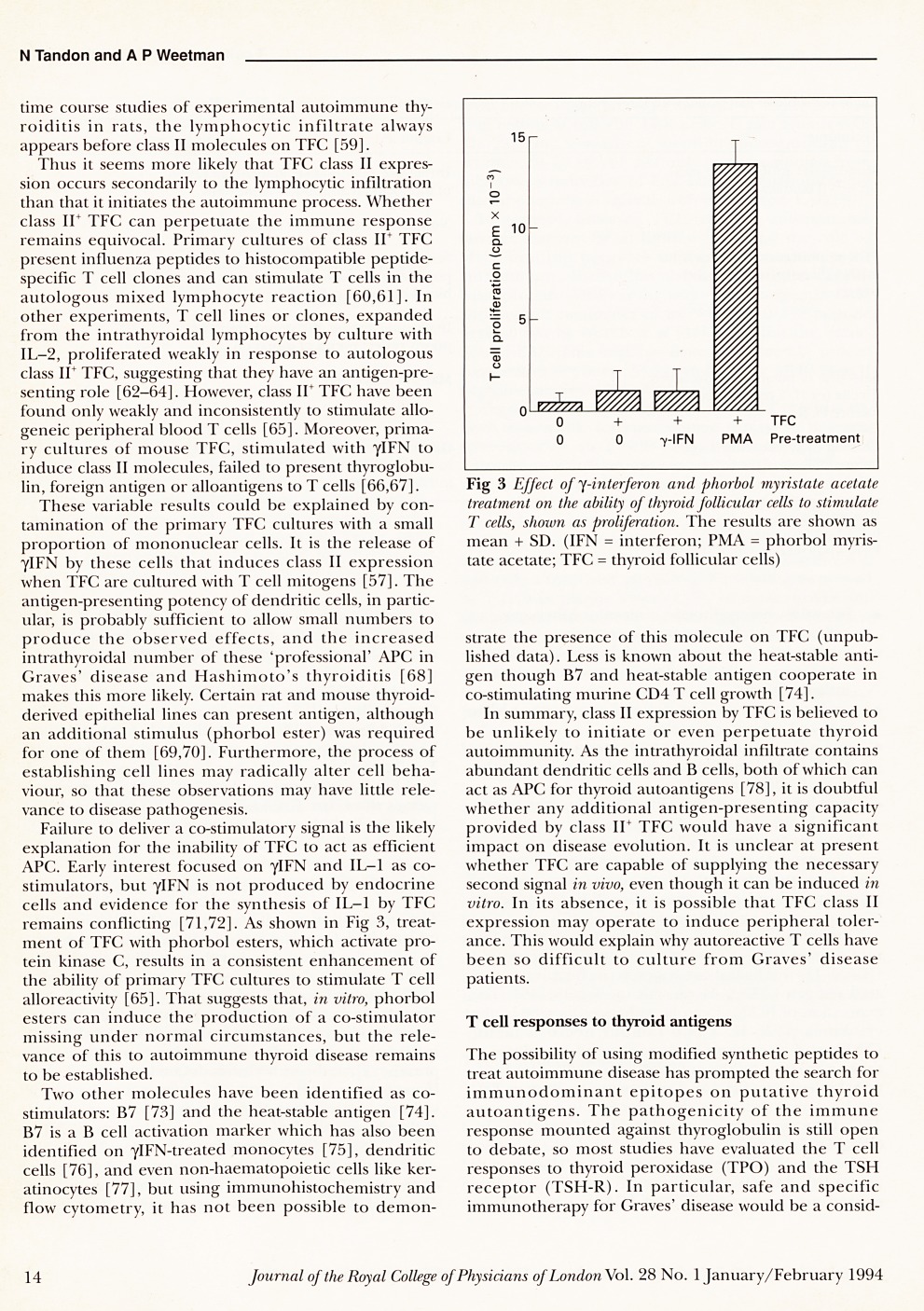
Abstract
Autoimmune thyroid disease is the archetype of organ-specific autoimmune disorders and shares with them T cell dependence. The observation that thyroid cells in autoimmune thyroid disease express the major histocompatibility complex molecule HLA-DR led to the hypothesis that they could present antigen and initiate or maintain the autoimmune process. However, functional experiments, and recent evidence indicating that provision of a co-stimulatory signal is also essential for efficient antigen presentation, argue against such a role. The analysis of T cell responses to two major thyroid antigens, thyroid peroxidase and the thyroid stimulating hormone receptor, reveals a heterogeneity both within and between patients, and intrathyroidal T cells show diverse usage of T cell receptor genes. Therefore, any strategy that uses modified peptides, monoclonal antibodies against specific T cell receptor molecules, or T cell vaccination for the purpose of treating thyroid autoimmunity is unlikely to succeed.
Full text
PDF





Contributor Information
N Tandon, Cambridge Nehru Scholar, Department of Medicine, University of Sheffield Clinical Sciences Centre.
A P Weetman, Professor of Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Sheffield Clinical Sciences Centre.