Fig 3.
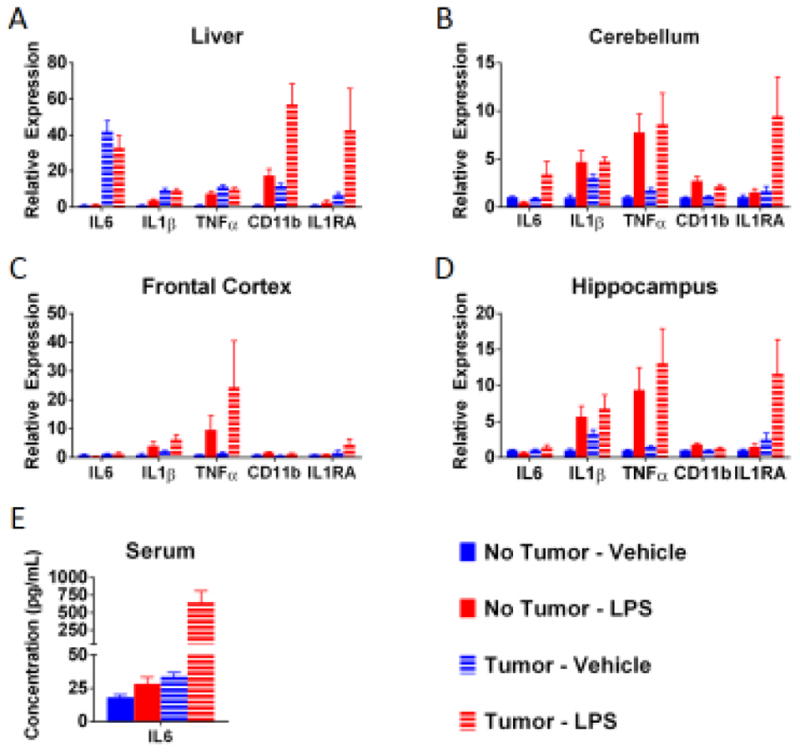
Tumor-bearing mice had increased expression of some inflammatory markers following administration of LPS. Within the liver (A), there was effect of the tumor on IL6, IL1β, TNFα, CD11b, and IL1RA; an effect of LPS for TNFα and CD11b, with a trend for IL1RA. Tumor-bearing mice treated with LPS has the highest levels of CD11b (and a trend toward higher IL1R1). Additionally, there was a significant effect of LPS in the non-tumor-bearing mice on TNFα, but this effect was not observed in the already elevated tumor-bearing mice. A similar non-significant trend was observed for IL-1β. Within the cerebellum (B), there was a trend toward an effect of tumor on IL6 and IL1RA as well as an effect of LPS for IL1β, TNFα, and CD11b (a trend for IL1RA). Further, there were higher levels of IL6 and a trend for IL1RA in tumor-bearing mice treated with LPS. Within the frontal cortex of the brain (C), there was an effect of LPS for IL1β and CD11b as well as a trend for TNFα. In tumor-bearing mice there is a trend toward an increase in IL1RA and a trend toward a suppression of CD11b. Within the hippocampus (D), tumor-bearing mice had increased IL1RA and suppressed CD11b, and LPS induced an increase in IL1β, TNFα, and CD11b mRNA expression (trend for IL1RA). There was also a trend toward a greater elevation in IL1RA following LPS in tumor-bearing mice. Within the serum (E), here was a significant effect of tumor on IL6 protein and an effect of LPS, however the LPS effect was more marked in the tumor-bearing mice. n=6 mice/group. Post hoc analyses were conducted when statistically significant main effects or interactions were noted. Lowercase letters in the figure indicate homogenous groups.
