Abstract
Tripartite motif containing 28 (TRIM28) is a transcriptional regulator acting as an essential corepressor for Krüppel-associated box zinc finger domain-containing proteins in multiple tissue and cell types. An increasing number of studies have investigated the function of TRIM28; however, its prognostic value in breast cancer (BC) remains unclear. In the present study, the expression of TRIM28 was identified to be significantly higher in cancerous compared with healthy tissue samples. Furthermore, it was demonstrated that TRIM28 expression was significantly correlated with several clinicopathological characteristics of patients with BC, such as p53 mutation, tumor recurrence and Elston grade of the tumor. In addition, a protein-protein interaction network was created to illustrate the interactions of TRIM28 with other proteins. The prognostic value of TRIM28 in patients with BC was investigated using the Kaplan-Meier Plotter database, which revealed that high expression of TRIM28 is a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with BC. In conclusion, the results of the present study indicate that TRIM28 provides a survival advantage to patients with BC and is a novel prognostic biomarker, in addition to being a therapeutic target for the treatment of BC.
Keywords: tripartite motif 28, prognostic value, breast cancer, tumor protein p53, therapeutic target, prognostic marker
Introduction
Breast cancer (BC) is one of the most prevalent types of cancer in women, with ~231,840 new cases and an expected mortality rate of 6.8% in 2015 reported by the National Institutes of Health (1). Although there have been numerous advancements in early diagnostic tools, surgical treatments, chemoradiotherapy, hormone therapy and targeted therapy, the prognosis of certain patients with BC remains poor. This may be due to the fact that the probability of BC recurrence following treatment is high (2,3). Therefore, studies investigating the underlying mechanisms of carcinogenesis, progression, and the identification of prognostic markers and potential therapeutic targets for BC are warranted.
Tripartite motif (TRIM) family proteins, which contain a Really Interesting New Gene finger domain, B-box zinc finger domain and a coiled coil region, are considered important regulators of carcinogenesis (4). Previously, TRIM family proteins, such as TRIM3, TRIM16, TRIM26 and TRIM31 have been demonstrated to serve a significant role in the tumorigenesis and progression of numerous cancer types (5–8). TRIM28 (also known as KRAB-associated protein-1 or transcriptional intermediary factor 1β) belongs to the group of TRIM proteins that function as E3 ubiquitin ligases (9) and is an essential component of several multiprotein complexes (10–12). TRIM28 is involved in a wide range of biological processes (13–15). Several studies have investigated the prognostic value of TRIM28 in different cancer tissues. These studies revealed that upregulation of TRIM28 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer (16) and aggressive clinicopathological characteristics in patients with ovarian cancer (17), in addition to being a metastatic and prognostic biomarker in early stage non-small cell lung cancer (18). Furthermore, a high TRIM28 expression ratio between the stromal and epithelial compartments of colorectal cancer tissue has been demonstrated to be an independent predictor of poor patient prognosis (19).
The role of TRIM28 in tumorigenesis is complex and associated with numerous biological processes, including cellular proliferation, invasion, differentiation and senescence (13–15). Furthermore, a recent study investigating the role of TRIM28 in BC demonstrated that TRIM28 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis through the stimulation of multiple Krüppel-associated box (KRAB) zinc finger domain-containing proteins (12).
A growing number of studies have investigated the function of TRIM28; however, the association between TRIM28 expression and the prognosis of patients with BC remains unclear. In the current study, the clinical relevance and prognostic value of TRIM28 in BC was evaluated through bioinformatical analyses.
Materials and methods
Utilization of the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database
The GEO database from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) is a public data repository generated predominantly from microarray studies. A total of 16 different GEO datasets were downloaded and 15 of which contained cancerous and healthy tissue sample data were used to analyze the expression of TRIM28 mRNA [measured as log2 (probe intensities)] in cancer. The basic features of the 15 GEO datasets are illustrated in Table I.
Table I.
Basic features of the 15 Gene Expression Omnibus datasets.
| Cancer type | Accession number | Number of samples (tumor/control) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breast | GSE42568 | 104/17 | <0.0001 |
| Ovarian | GSE14407 | 12/12 | 0.0407 |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | GSE14520 | 214/214 | <0.0001 |
| Colorectal | GSE32323 | 17/17 | 0.0008 |
| Renal clear cell carcinoma | GSE36895 | 23/23 | 0.4799 |
| Prostate | GSE6919 | 56/56 | 0.1584 |
| Lung | GSE30219 | 293/14 | <0.0001 |
| Esophageal carcinoma | GSE20347 | 17/17 | 0.0001 |
| Pancreatic | GSE28735 | 45/45 | 0.8424 |
| Melanoma | GSE3189 | 45/25 | <0.0001 |
| Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | GSE12452 | 31/10 | 0.0043 |
| Gastric | GSE13911 | 31/31 | <0.0001 |
| Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | GSE26713 | 117/7 | <0.0001 |
| Papillary thyroid carcinoma | GSE3467 | 9/9 | 0.5215 |
| Myeloma | GSE27838 | 16/16 | 0.3133 |
P-values were obtained through the Mann-Whitney U test for the comparison of TRIM28 expression between tumor and control.
To analyze the association between the expression of TRIM28 and the clinicopathological characteristics of patients with BC, a large cohort of patients with BC (>100), and their corresponding clinical information and follow-up records were included in the present study. Datasets GSE42568 (n=121) (20) and GSE3494 (n=251) (21) were chosen for further analysis in the present study. Their clinical information was extracted and analyzed statistically. The tumor sample data from these two datasets was pooled and categorized into two groups according to their expression level of TRIM28 mRNA (top 1/3, high; bottom 2/3, low).
Construction of the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network
The corresponding TRIM28-associated PPI network was constructed using a web-based bioinformatics tool, Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins (STRING; version 10.0; http://string-db.org/) (22). STRING is a database containing known and predicted interactions for proteins, including physical and functional associations obtained from genomic analyses, high-throughput experiments, and co-expression studies. The phrase ‘TRIM28’ was entered into the STRING database for analysis and PPIs associated with proteins from Homo sapiens were selected. The PPI network was subsequently grown to obtain ≥100 protein interactions and further refined to include only those interactions with a confidence score >0.9.
Relapse-free survival analysis
The online database Kaplan-Meier Plotter (www.kmplot.com) was used to determine the association between TRIM28 mRNA expression and relapse-free survival (RFS) (23). This database includes data from studies on breast (23), lung (24), ovarian (25) and gastric cancer (26). Using Kaplan Meier-Plotter, it is currently possible to assess the effect of 54,675 genes on patient survival from the data of 10,188 tumor samples. The BC data on Kaplan Meier-Plotter was obtained from 4,142 patients, with a mean follow-up of 69 months. Briefly, ‘TRIM28’ or ‘200990_at’ (TRIM28 probe number) were entered into the breast cancer-specific area of the database (http://kmplot.com/analysis/index.php?p=service&cancer=breast) to obtain Kaplan-Meier survival curves, in which the number of patients at risk of mortality was reported below the main plot. Hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI), and P-values (from the log-rank test) were calculated and displayed on the webpage.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis of significant differences was acquired using the GraphPad Prism 5.0 software (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA). The differences of TRIM28 expression between tumor and non-tumor in 15 datasets were assessed by the Mann-Whitney U test. Pearson's χ2 test was used to analyze the association between the expression of TRIM28 and the clinicopathological characteristics of patients with BC. A statistically significant difference was considered as P<0.05.
Results
TRIM28 is upregulated in multiple tumors
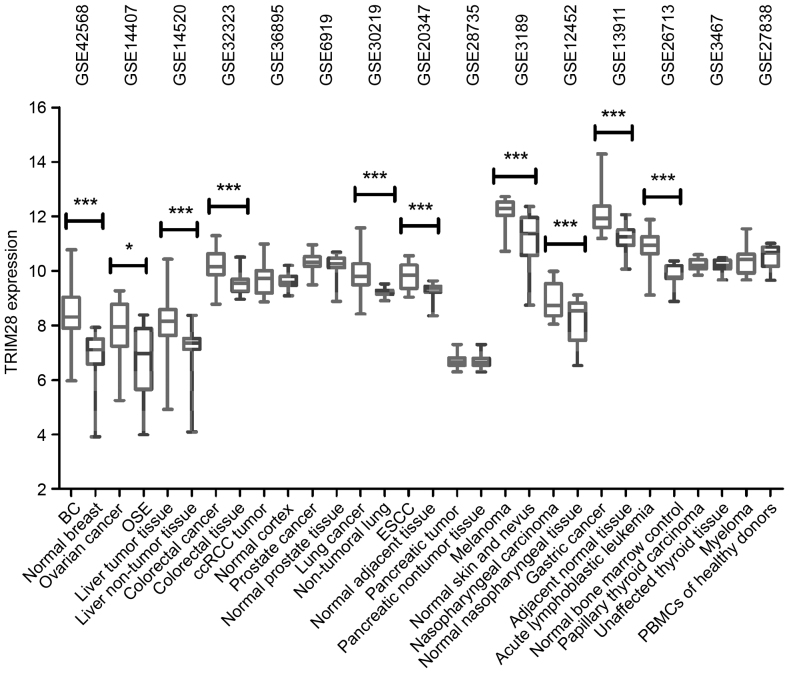
Differences in the expression of TRIM28 mRNA between cancerous and healthy tissue samples from multiple tumor types (GEO datasets) were assessed. As illustrated in Fig. 1, the expression of TRIM28 was significantly upregulated in BC (P<0.0001), ovarian cancer (P=0.0407), hepatocellular carcinoma (P<0.0001), colorectal cancer (P=0.0008), lung cancer (P<0.0001), esophageal carcinoma (P=0.0001), melanoma (P<0.0001), nasopharyngeal carcinoma (P=0.0043), gastric cancer (P<0.0001) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (P<0.0001). These results demonstrate that TRIM28 is significantly upregulated in multiple tumor types, indicating that it is involved in the tumorigenesis of these cancers.
Figure 1.
TRIM28 expression in cancer. TRIM28 expression was significantly elevated in the majority of tumor tissues compared with healthy tissue samples, from 15 publicly available Gene Expression Omnibus datasets. TRIM28 expression was measured as log2 (probe intensities), and presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. *P<0.05; ***P<0.001. TRIM28, tripartite motif containing 28; BC, breast cancer; OSE, ovarian surface epithelia samples; ccRCC, clear-cell Renal cell carcinoma; ESCC, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
TRIM28 is associated with the clinicopathological characteristics of patients with BC
In order to determine the association between TRIM28 expression and the clinicopathological characteristics of patients with BC, the datasets GSE42568 and GSE3494 were statistically analyzed. As illustrated in Tables II and III, TRIM28 expression was significantly correlated with patient age (P=0.016), tumor recurrence (P=0.004), p53 mutation status (P=0.002), progesterone receptor (PR) expression status (P=0.014) and Elston grade of the tumor (Nottingham histological score; P=0.001) in BC. These results indicate that TRIM28 effects BC development and recurrence, and the prognosis of patients with BC.
Table II.
Correlation between TRIM28 expression and the clinicopathological characteristics of patients with breast cancer in GSE42568.
| TRIM28 expression | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinicopathological characteristic | Number of patients | High | Low | Pearson's χ2 value | P-value |
| Age (years old) | 5.797 | 0.016 | |||
| ≤50 | 27 | 4 | 23 | ||
| >50 | 77 | 31 | 46 | ||
| ER expression status | 1.187 | 0.276 | |||
| Positive | 67 | 25 | 42 | ||
| Negative | 34 | 9 | 25 | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | 2.813 | 0.093 | |||
| <2 | 18 | 3 | 15 | ||
| ≥2 | 86 | 32 | 54 | ||
| Elston grade | 3.454 | 0.178 | |||
| I | 11 | 3 | 8 | ||
| II | 40 | 8 | 32 | ||
| III | 53 | 24 | 29 | ||
| Lymph node metastasis | 1.734 | 0.188 | |||
| Yes | 59 | 23 | 36 | ||
| No | 45 | 12 | 33 | ||
| Tumor recurrence | 8.122 | 0.004 | |||
| Yes | 48 | 23 | 25 | ||
| No | 56 | 12 | 44 | ||
The top 1/3 of patients with the highest TRIM28 expression were defined as the high-expression group and the bottom 2/3 were defined as the low-expression group. P-values were obtained through the Pearson χ2 test for the comparison of the two groups (high vs. low) in different clinicopathological characteristics of patients with BC. ER, estrogen receptor; TRIM28, tripartite motif containing 28.
Table III.
Correlation between TRIM28 expression and the clinicopathological characteristics of patients with breast cancer in GSE3494.
| TRIM28 expression | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinicopathological characteristic | Number of patients | High | Low | Pearson's χ2 value | P-value |
| Age (years old) | 0.346 | 0.557 | |||
| ≤50 | 55 | 20 | 35 | ||
| >50 | 196 | 63 | 133 | ||
| TP53 mutation status | 9.771 | 0.002 | |||
| Positive | 58 | 29 | 29 | ||
| Negative | 193 | 54 | 139 | ||
| ER expression status | 1.954 | 0.162 | |||
| Positive | 213 | 68 | 145 | ||
| Negative | 34 | 15 | 19 | ||
| PR expression status | 5.997 | 0.014 | |||
| Positive | 190 | 55 | 135 | ||
| Negative | 61 | 28 | 33 | ||
| Elston grade | 14.200 | 0.001 | |||
| I | 67 | 13 | 54 | ||
| II | 128 | 42 | 86 | ||
| III | 54 | 28 | 26 | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | 2.654 | 0.103 | |||
| <2 | 112 | 31 | 81 | ||
| ≥2 | 139 | 52 | 87 | ||
| Lymph node metastasis | 0.410 | 0.522 | |||
| Yes | 84 | 30 | 54 | ||
| No | 158 | 50 | 108 | ||
The top 1/3 of patients with the highest TRIM28 expression were defined as the high-expression group and the bottom 2/3 were defined as the low-expression group. P-values were obtained through the Pearson chi-square test for the comparison of the two groups (high vs. low) in different clinicopathological characteristics of patients with BC. ER, estrogen receptor; PR, progesterone receptor; TRIM28, tripartite motif containing 28; TP53, tumor protein p53.
PPI network of TRIM28
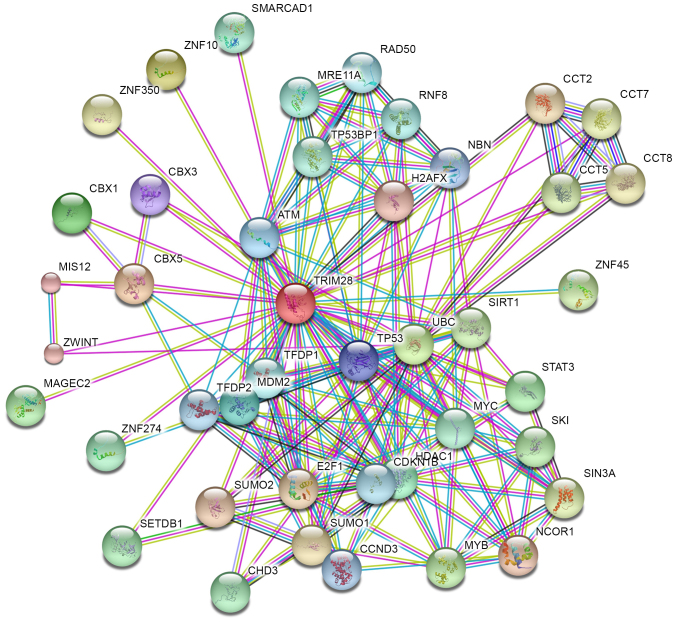
In order to better understand the function, regulatory mechanisms and interactions of TRIM28, the STRING database was used to build a PPI network for TRIM28 (Fig. 2). A total of 42 predicted functional partners were reported to interact with TRIM28 and each other within the network (all confidence score >0.9). The greater the number of connections between proteins the stronger the reported association is. Among the 42 predicted PPI network proteins for TRIM28 identified by STRING, several tumor-associated proteins were identified, indicating the tumor-promoting functions of TRIM28. These proteins included the following: Ubiquitin C (UBC); MDM2 proto-oncogene (MDM2); tumor protein p53 (TP53); E2F transcription factor 1 (E2F1); melanoma antigen family (MAGE) C2; and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3).
Figure 2.
Protein-protein interaction network for tripartite motif containing 28 protein. Different colored lines represent the types of evidence for the association. The purple, light blue and light green colored lines represent evidence from databases, experiments and text mining, respectively.
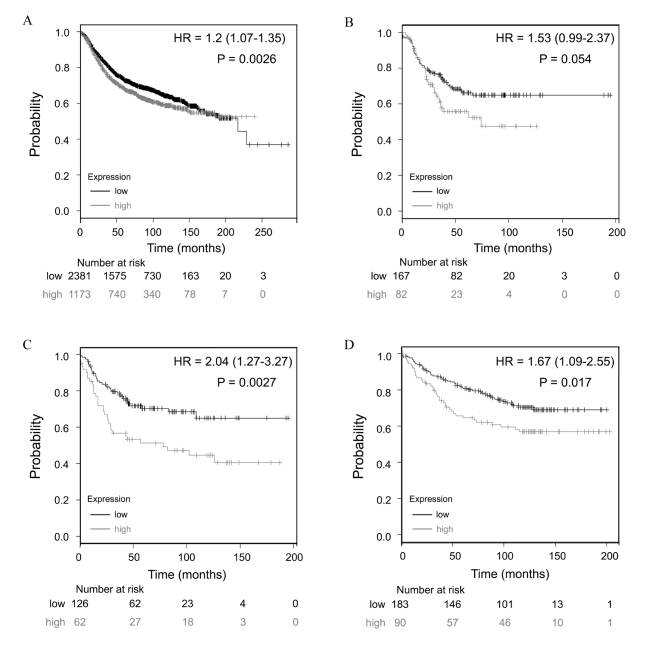
Increased TRIM28 expression is associated with poor patient prognosis in BC
The prognostic value of TRIM28 expression was examined using the Kaplan Meier-Plotter database. The same cut-off value was used to categorize patients into low and high expression groups prior to being subjected to survival comparison. Survival curves were plotted for all patients (n=3,554; Fig. 3A). In addition, further curves were plotted for the following subgroups: Estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative (triple-negative BC; n=249; Fig. 3B); TP53 mutation (n=188; Fig. 3C); and wild-type TP53 (n=273; Fig. 3D). Low expression of TRIM28 mRNA was significantly correlated with improved RFS in all patients over 20 years (HR, 1.2; 95% CI, 1.07–1.35; P=0.0026; Fig. 3A). This was not true in patients who had triple-negative BC, which is possibly due to the relatively low number of patients sampled (HR, 1.53; 95% CI, 0.99–2.37; P=0.0539; Fig. 3B).
Figure 3.
Prognostic value of TRIM28 expression in patients with BC. TRIM28 probe number is 200990_at. Survival curves for (A) all patients with BC combined (n=3554), (B) triple-negative BC patients (n=249), (C) TP53 mutated BC cases (n=188) and (D) wild-type TP53 BC cases (n=273). Results were analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier Plotter database. ‘Probability’ on the y-axes is referring to the relapse free survival rates. ‘Number at risk’ under the x-axes is referring to the number of BC survivors who were in the risk of a recurrence at a certain point in time. HR values were presented as HR=mean (95% CI). The generated P-value does not include correction for multiple hypothesis testing by default. TRIM28, tripartite motif containing 28; TP53, tumor protein p53; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence intervals; BC, breast cancer.
TP53 mutation has previously been associated with poor prognosis in patients with BC (27). Low expression of TRIM28 mRNA was significantly correlated with improved RFS in the TP53 mutated (HR, 2.04; 95% CI, 1.27–3.27; P=0.0027; Fig. 3C) and TP53 wild-type (HR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.09–2.55; P=0.0174; Fig. 3D) groups, which indicates that TRIM28 is an independent predictor of poor prognosis in patients with BC.
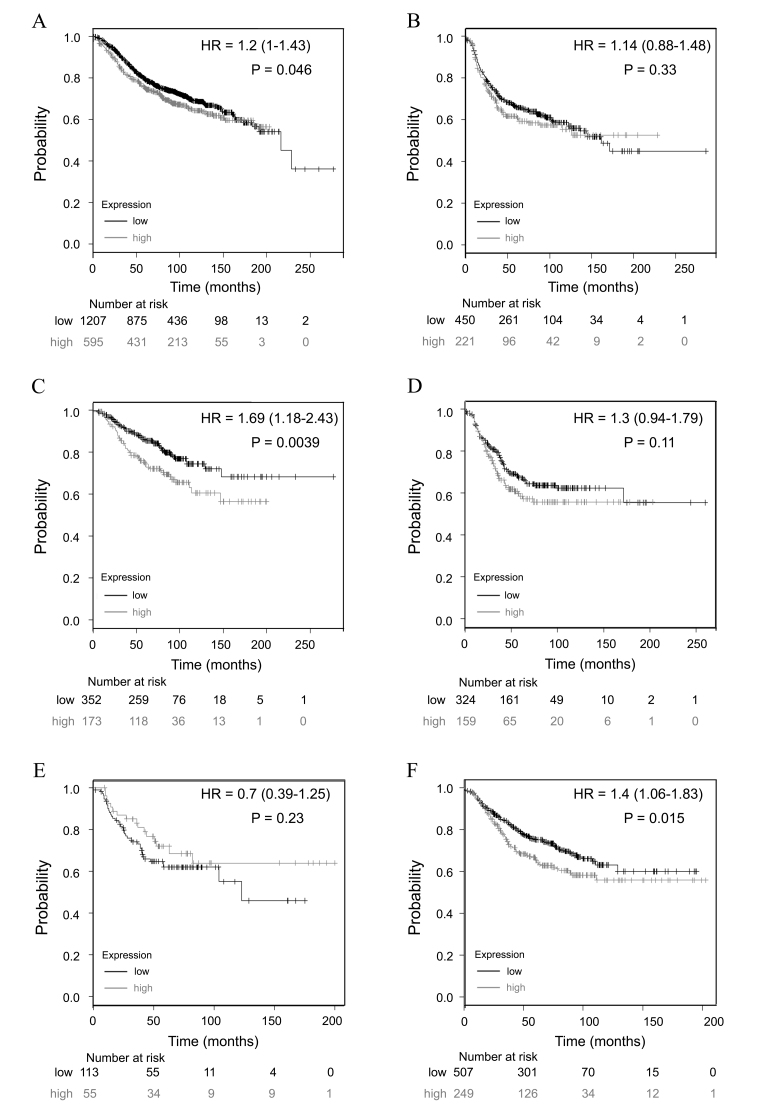
Tumor genotypes make a significant contribution to selection and response to adjuvant therapies (28). In the present study, low expression of TRIM28 was significantly correlated with improved RFS in patients with tumors that were ER-positive (HR, 1.2; 95% CI, 1–1.43; P=0.0462; Fig. 4A), PR-positive (HR, 1.69; 95% CI, 1.18–2.43; P=0.0039; Fig. 4C) or HER2-negative (HR, 1.4; 95% CI, 1.06–1.83; P=0.0154; Fig. 4F), which suggests that TRIM28 is a prognostic marker in patients with different phenotypes of BC.
Figure 4.
Prognostic value of TRIM28 expression in different BC genotypes. TRIM28 probe number is 200990_at. Survival curves for (A) ER-positive (n=1802), (B) ER-negative (n=671), (C) PR-positive (n=525), (D) PR-negative (n=483), (E) HER2-positive (n=168) and (F) HER2-negative (n=756) BC cases. Results were analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier Plotter database. ‘Probability’ on the y-axes is referring to the relapse free survival rates. ‘Number at risk’ under the x-axes is referring to the number of BC survivors who were in the risk of a recurrence at a certain point in time. HR values were presented as HR=mean (95% CI). The generated P-value does not include correction for multiple hypothesis testing by default. TRIM28, tripartite motif containing 28; ER, estrogen receptor; PR, progesterone receptor; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence intervals; BC, breast cancer.
To determine the association between TRIM28 expression and prognostic features, the association between TRIM28 and Elston grade, lymph node status, endocrine therapy use and chemotherapy use in patients with BC was investigated (Table IV). High expression of TRIM28 was significantly correlated with Elston grade I (HR, 1.98; 95% CI, 1.14–3.41; P=0.0127) and III (HR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.06–1.76; P=0.0142) tumors, but not Elston grade II tumors (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.86–1.48; P=0.3734). In addition, high expression of TRIM28 was significantly correlated with patients who had received endocrine therapy (HR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.19–1.98; P=0.0008), chemotherapy (HR, 2.14; 95% CI, 1.51–3.02; P=1×10−5), and the patients who had not received chemotherapy (HR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.02–1.43; P=0.0253).
Table IV.
Correlation between TRIM28 expression and prognostic factors in patients with breast cancer.
| Prognostic factor | Number of cases | HR | 95% CI | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elston grade | ||||
| I | 308 | 1.98 | 1.14–3.41 | 0.0127 |
| II | 724 | 1.13 | 0.86–1.48 | 0.3734 |
| III | 723 | 1.37 | 1.06–1.76 | 0.0142 |
| Lymph node metastasis | ||||
| Yes | 945 | 1.25 | 1-1.57 | 0.0514 |
| No | 1813 | 1.11 | 0.93–1.33 | 0.2542 |
| Endocrine therapy received | ||||
| Yes | 999 | 1.54 | 1.19–1.98 | 0.0008 |
| No | 1401 | 1.16 | 0.96–1.4 | 0.1341 |
| Chemotherapy received | ||||
| Yes | 425 | 2.14 | 1.51–3.02 | 1×10−05 |
| No | 1974 | 1.21 | 1.02–1.43 | 0.0253 |
Results were analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier Plotter database. P-values were obtained through the log-rank test from the website to compare the relapse free survival rates related to TRIM28 expression. The generated P-value does not include correction for multiple hypotheses testing by default. HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; TRIM28, tripartite motif containing 28.
Discussion
Proteins in the TRIM family serves a role in various physiological functions through activating or suppressing their corresponding molecules, including cell cycle regulators, checkpoint molecules, apoptosis-associated factors and tumor-promoting or inhibiting factors (9,29). Several previous studies have demonstrated that TRIM family proteins function in BC development and progression, including the following: TRIM22, which is underexpressed in BC due to p53 dysfunction (30); TRIM24, which is a viable therapeutic target for the treatment of patients with BC through reprogramming of glucose metabolism (31); and TRIM29, which functions as a tumor suppressor, as loss of TRIM29 expression in breast luminal cells can lead to the progression of ER-positive BC in premenopausal women (32). In addition, a recent study investigating the role of TRIM28 in BC demonstrated that TRIM28 promotes BC cell proliferation and metastasis by stimulating multiple KRAB family zinc finger domain-containing proteins (12). TRIM28 expression has been correlated with poor patient prognosis in various cancers, including gastric, ovarian, colorectal and lung (16–19). However, to the best of our knowledge, the prognostic value of TRIM28 expression in BC has not been investigated.
In the present study, the clinical relevance and prognostic value of TRIM28 in BC was investigated. The results of the present study revealed that TRIM28 expression was associated with the survival of patient with BC. In addition, expression of TRIM28 was significantly elevated in multiple tumor types, including BC, when compared with matched healthy tissue samples, suggesting that TRIM28 serves a role in tumorigenesis. Furthermore, it was demonstrated that TRIM28 mRNA expression was significantly associated with tumor recurrence, TP53 mutation status, PR expression status and Elston grade of the tumor in patients with BC. These results indicate that TRIM28 promotes BC progression, as TP53 mutation-correlated genes have been reported to predict the risk of tumor relapse (33).
The PPI network provides a better understanding of the functional associations between TRIM28 and other proteins. Among the 42 predicted functional partner proteins identified using the STRING database, several tumor-associated proteins, such as UBC, MDM2, TP53, E2F1, MAGEC2 and STAT3 were identified. Ubiquitination has been associated with protein degradation, DNA repair and cell cycle regulation (34–36). A previous study demonstrated that the downregulation of UBC inhibits the proliferation and radioresistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells (37). In addition, another study identified that MAGEA-TRIM28 functions as an oncogene (38). MDM2 is a non-redundant inhibitor of p53 (39,40) and has been demonstrated to promote cell proliferation in BC through a p53-independent mechanism (41). p53, a tumor suppressor, regulates the cell cycle, apoptosis, senescence and autophagy, and contributes to mammary gland development and BC progression (42). TRIM28 inhibits p53 acetylation and promotes the ubiquitination of p53 (43,44). E2F1 mediates cell proliferation and p53-dependent cell apoptosis, and its negative regulation by TRIM28 may serve as a backup mechanism to prevent E2F1-mediated cell apoptosis (45). MAGEC2 promotes the phosphorylation of TRIM28 (46). MAGEC proteins form a complex with TRIM28 and suppress p53-dependent apoptosis in MAGE-positive cell lines (47). STAT3 mediates the cellular response to interleukins and other growth factors. Deregulation of STAT3 activity is associated with a range of cancer types and TRIM28 has been demonstrated to inactivate STAT3 (48).
Patients with triple-negative BC typically have high-grade tumors and a poor prognosis (49,50). Thus, the association between TRIM28 expression and RFS in patients with triple-negative BC was evaluated in the present study. Although no significant association between these factors was detected, the low TRIM28 expression group demonstrated a markedly increased RFS compared with the high expression group. TP53 mutations in BC have been associated with poor patient prognosis (27). The results of the present study suggest that TRIM28 is an independent prognostic factor in patients with mutated and wild-type TP53 BC.
The identification of therapeutic targets in cancer tissue is essential in order to select the most appropriate anti-cancer drugs. In the case of BC, ER, PR and HER2 expression analysis has been a routine clinical practice for years, and has made a significant contribution to the drug selection process and tumor response to adjuvant therapies (28). ER/PR expression status guides the selection of hormone therapies for BC (51) and HER2 expression status is a predictive marker for the response of patients with BC to trastuzumab (52). In the present study, low expression of TRIM28 was significantly correlated with improved RFS in the ER-positive, HER2-negative and PR-positive expression groups. Therefore, therapeutic targeting of TRIM28 may improve patient outcome. In addition, the findings of the current study demonstrated that TRIM28 expression was significantly associated with Elston grade of the tumor. Furthermore, the results of the present study indicate that high expression of TRIM28 is a risk factor for BC recurrence in patients who have received endocrine therapy, and patients who have or have not received chemotherapy.
In conclusion, the present study demonstrated the clinical relevance and prognostic value of TRIM28 in patients with BC. TRIM28 is frequently elevated in multiple tumor types and is associated with aggressive clinical features of BC. The PPI network created revealed that TRIM28 may interact with other oncogenes to serve a role in BC progression. Furthermore, the overexpression of TRIM28 was significantly correlated with poor prognosis in patients with BC, suggesting that TRIM28 is a prognostic marker and potential therapeutic target in patients with BC.
References
- 1.National Institutes of Health, corp-author. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html. Surveillance epidemiology and end results SEER stat fact sheets: Breast Cancer. 2015 2015 Nov 8; [Google Scholar]
- 2.Coleman RE. Metastatic bone disease: Clinical features, pathophysiology and treatment strategies. Cancer Treat Rev. 2001;27:165–176. doi: 10.1053/ctrv.2000.0210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Redig AJ, McAllister SS. Breast cancer as a systemic disease: A view of metastasis. J Intern Med. 2013;274:113–126. doi: 10.1111/joim.12084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ikeda K, Inoue S. TRIM proteins as RING finger E3 ubiquitin ligases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;770:27–37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5398-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Liu Y, Raheja R, Yeh N, Ciznadija D, Pedraza AM, Ozawa T, Hukkelhoven E, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Gauthier NP, et al. TRIM3, a tumor suppressor linked to regulation of p21(Waf1/Cip1) Oncogene. 2014;33:308–315. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bell JL, Malyukova A, Kavallaris M, Marshall GM, Cheung BB. TRIM16 inhibits neuroblastoma cell proliferation through cell cycle regulation and dynamic nuclear localization. Cell Cycle. 2013;12:889–898. doi: 10.4161/cc.23825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wang Y, He D, Yang L, Wen B, Dai J, Zhang Q, Kang J, He W, Ding Q, He D. TRIM26 functions as a novel tumor suppressor of hepatocellular carcinoma and its downregulation contributes to worse prognosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;463:458–465. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.05.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sugiura T. The cellular level of TRIM31, an RBCC protein overexpressed in gastric cancer, is regulated by multiple mechanisms including the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Cell Biol Int. 2011;35:657–661. doi: 10.1042/CBI20100772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hatakeyama S. TRIM proteins and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:792–804. doi: 10.1038/nrc3139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Herquel B, Ouararhni K, Khetchoumian K, Ignat M, Teletin M, Mark M, Béchade G, Van Dorsselaer A, Sanglier-Cianférani S, Hamiche A, et al. Transcription cofactors TRIM24, TRIM28, and TRIM33 associate to form regulatory complexes that suppress murine hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:8212–8217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1101544108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cheng B, Ren X, Kerppola TK. KAP1 represses differentiation-inducible genes in embryonic stem cells through cooperative binding with PRC1 and derepresses pluripotency-associated genes. Mol Cell Biol. 2014;34:2075–2091. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01729-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Addison JB, Koontz C, Fugett JH, Creighton CJ, Chen D, Farrugia MK, Padon RR, Voronkova MA, McLaughlin SL, Livengood RH, et al. KAP1 promotes proliferation and metastatic progression of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2015;75:344–355. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen L, Chen DT, Kurtyka C, Rawal B, Fulp WJ, Haura EB, Cress WD. Tripartite motif containing 28 (Trim28) can regulate cell proliferation by bridging HDAC1/E2F interactions. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:40106–40118. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.380865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lin LF, Li CF, Wang WJ, Yang WM, Wang DD, Chang WC, Lee WH, Wang JM. Loss of ZBRK1 contributes to the increase of KAP1 and promotes KAP1-mediated metastasis and invasion in cervical cancer. PLoS One. 2013;8:e73033. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Iyengar S, Farnham PJ. KAP1 protein: An enigmatic master regulator of the genome. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:26267–26276. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R111.252569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yokoe T, Toiyama Y, Okugawa Y, Tanaka K, Ohi M, Inoue Y, Mohri Y, Miki C, Kusunoki M. KAP1 is associated with peritoneal carcinomatosis in gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:821–828. doi: 10.1245/s10434-009-0795-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cui Y, Yang S, Fu X, Feng J, Xu S, Ying G. High levels of KAP1 expression are associated with aggressive clinical features in ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;16:363–377. doi: 10.3390/ijms16010363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Liu L, Zhao E, Li C, Huang L, Xiao L, Cheng L, Huang X, Song Y, Xu D. TRIM28, a new molecular marker predicting metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013;37:71–78. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2012.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fitzgerald S, Sheehan KM, O'Grady A, Kenny D, O'Kennedy R, Kay EW, Kijanka GS. Relationship between epithelial and stromal TRIM28 expression predicts survival in colorectal cancer patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28:967–974. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Clarke C, Madden SF, Doolan P, Aherne ST, Joyce H, O'Driscoll L, Gallagher WM, Hennessy BT, Moriarty M, Crown J, et al. Correlating transcriptional networks to breast cancer survival: A large-scale coexpression analysis. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34:2300–2308. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Miller LD, Smeds J, George J, Vega VB, Vergara L, Ploner A, Pawitan Y, Hall P, Klaar S, Liu ET, Bergh J. An expression signature for p53 in breast cancer predicts mutation status, transcriptional effects, and patient survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:13550–13555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506230102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, Schmidt S, Bork P, Snel B. STRING: A database of predicted functional associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:258–261. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Györffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert C, Budczies J, Li Q, Szallasi Z. An online survival analysis tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer prognosis using microarray data of 1,809 patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;123:725–731. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0674-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Győrffy B, Surowiak P, Budczies J, Lánczky A. Online survival analysis software to assess the prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 2013;8:e82241. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gyorffy B, Lánczky A, Szállási Z. Implementing an online tool for genome-wide validation of survival-associated biomarkers in ovarian-cancer using microarray data from 1,287 patients. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2012;19:197–208. doi: 10.1530/ERC-11-0329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Szász AM, Lánczky A, Nagy Á, Förster S, Hark K, Green JE, Boussioutas A, Busuttil R, Szabó A, Győrffy B. Cross-validation of survival associated biomarkers in gastric cancer using transcriptomic data of 1,065 patients. Oncotarget. 2016;7:49322–49333. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Olivier M, Langerød A, Carrieri P, Bergh J, Klaar S, Eyfjord J, Theillet C, Rodriguez C, Lidereau R, Bièche I, et al. The clinical value of somatic TP53 gene mutations in 1,794 patients with breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:1157–1167. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ludwig JA, Weinstein JN. Biomarkers in cancer staging, prognosis and treatment selection. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:845–856. doi: 10.1038/nrc1739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Petrera F, Meroni G. TRIM proteins in development. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;770:131–141. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5398-7_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sun Y, Ho GH, Koong HN, Sivaramakrishnan G, Ang WT, Koh QM, Lin VC. Down-regulation of tripartite-motif containing 22 expressions in breast cancer is associated with a lack of p53-mediated induction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;441:600–606. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.10.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pathiraja TN, Thakkar KN, Jiang S, Stratton S, Liu Z, Gagea M, Shi X, Shah PK, Phan L, Lee MH, et al. TRIM24 links glucose metabolism with transformation of human mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene. 2015;34:2836–2845. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Liu J, Welm B, Boucher KM, Ebbert MT, Bernard PS. TRIM29 functions as a tumor suppressor in nontumorigenic breast cells and invasive ER+ breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 2012;180:839–847. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.10.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Győrffy B, Bottai G, Lehmann-Che J, Kéri G, Orfi L, Iwamoto T, Desmedt C, Bianchini G, Turner NC, de Thè H, et al. TP53 mutation-correlated genes predict the risk of tumor relapse and identify MPS1 as a potential therapeutic kinase in TP53-mutated breast cancers. Mol Oncol. 2014;8:508–519. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2013.12.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lan Q, Gao Y, Li Y, Hong X, Xu P. Progress in ubiquitin, ubiquitin chain and protein ubiquitination. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2016;32:14–30. (In Chinese) [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ordureau A, Münch C, Harper JW. Quantifying ubiquitin signaling. Mol Cell. 2015;58:660–676. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.02.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kessler BM. Ubiquitin-omics reveals novel networks and associations with human disease. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013;17:59–65. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.12.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tang Y, Geng Y, Luo J, Shen W, Zhu W, Meng C, Li M, Zhou X, Zhang S, Cao J. Downregulation of ubiquitin inhibits the proliferation and radioresistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitroin vivo. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9476. doi: 10.1038/srep09476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Pineda CT, Potts PR. Oncogenic MAGEA-TRIM28 ubiquitin ligase downregulates autophagy by ubiquitinating and degrading AMPK in cancer. Autophagy. 2015;11:844–846. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1034420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wade M, Li YC, Wahl GM. MDM2, MDMX and p53 in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:83–96. doi: 10.1038/nrc3430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Marine JC. MDM2 and MDMX in cancer and development. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2011;94:45–75. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380916-2.00003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Brekman A, Singh KE, Polotskaia A, Kundu N, Bargonetti J. A p53-independent role of Mdm2 in estrogen-mediated activation of breast cancer cell proliferation. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13:R3. doi: 10.1186/bcr2804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zuckerman V, Wolyniec K, Sionov RV, Haupt S, Haupt Y. Tumor suppression by p53: The importance of apoptosis and cellular senescence. J Pathol. 2009;219:3–15. doi: 10.1002/path.2584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wang C, Ivanov A, Chen L, Fredericks WJ, Seto E, Rauscher FJ, III, Chen J. MDM2 interaction with nuclear corepressor KAP1 contributes to p53 inactivation. EMBO J. 2005;24:3279–3290. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Okamoto K, Kitabayashi I, Taya Y. KAP1 dictates p53 response induced by chemotherapeutic agents via Mdm2 interaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;351:216–222. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wang C, FJ III Rauscher, Cress WD, Chen J. Regulation of E2F1 function by the nuclear corepressor KAP1. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:29902–29909. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704757200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bhatia N, Xiao TZ, Rosenthal KA, Siddiqui IA, Thiyagarajan S, Smart B, Meng Q, Zuleger CL, Mukhtar H, Kenney SC, et al. MAGE-C2 promotes growth and tumorigenicity of melanoma cells, phosphorylation of KAP1, and DNA damage repair. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:759–767. doi: 10.1038/jid.2012.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Yang B, O'Herrin SM, Wu J, Reagan-Shaw S, Ma Y, Bhat KM, Gravekamp C, Setaluri V, Peters N, Hoffmann FM, et al. MAGE-A, mMage-b, and MAGE-C proteins form complexes with KAP1 and suppress p53-dependent apoptosis in MAGE-positive cell lines. Cancer Res. 2007;67:9954–9962. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.King CA. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus kaposin B induces unique monophosphorylation of STAT3 at serine 727 and MK2-mediated inactivation of the STAT3 transcriptional repressor TRIM28. J Virol. 2013;87:8779–8791. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02976-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bauer KR, Brown M, Cress RD, Parise CA, Caggiano V. Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: A population-based study from the California Cancer Registry. Cancer. 2007;109:1721–1728. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Tischkowitz M, Brunet JS, Bégin LR, Huntsman DG, Cheang MC, Akslen LA, Nielsen TO, Foulkes WD. Use of immunohistochemical markers can refine prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2007;7:134. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wick MJ, Vaught T, Gamez L, Meade J, Diaz A, Papadopoulos KP, Rasco DW, Patnaik A, Beeram M, Lang A, Tolcher AW. 96 Evaluation of hormone therapies in a panel of breast PDX models: Relevance of ER status on sensitivity to letrozole and tamoxifen. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(Suppl 6):S35. doi: 10.1016/S0959-8049(14)70222-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Dressler LG, Berry DA, Broadwater G, Cowan D, Cox K, Griffin S, Miller A, Tse J, Novotny D, Persons DL, et al. Comparison of HER2 status by fluorescence in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry to predict benefit from dose escalation of adjuvant doxorubicinbased therapy in node-positive breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:4287–4297. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]