Abstract
Background
Understanding which factors influence participation in physical activity is important to improve the public health. The aim of the present review of reviews was to summarize and present updated evidence on personal and environmental factors associated with physical activity.
Methods
MEDLINE and EMBASE were searched for reviews published up to 31 Jan. 2017 reporting on potential factors of physical activity in adults aged over 18 years. The quality of each review was appraised with the Assessing the Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews (AMSTAR) checklist. The corrected covered area (CCA) was calculated as a measure of overlap for the primary publications in each review.
Results
Twenty-five articles met the inclusion criteria which reviewed 90 personal and 27 environmental factors. The average quality of the studies was moderate, and the CCA ranged from 0 to 4.3%. For personal factors, self-efficacy was shown as the strongest factor for participation in physical activity (7 out of 9). Intention to exercise, outcome expectation, perceived behavioral control and perceived fitness were positively associated with physical activity in more than 3 reviews, while age and bad status of health or fitness were negatively associated with participation in physical activity in more than 3 reviews. For environmental factors, accessibility to facilities, presence of sidewalks, and aesthetics were positively associated with participation in physical activity.
Conclusions
The findings of this review of reviews suggest that some personal and environmental factors were related with participation in physical activity. However, an association of various factors with physical activity could not be established because of the lack of primary studies to build up the organized evidence. More studies with a prospective design should be conducted to understand the potential causes for physical activity.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12889-017-4255-2) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Physical activity, Epidemiologic factors, Review of reviews
Background
Participation in regular physical activity contributes to health promotion, improving physical fitness, and prevention of non-communicable diseases [1–4]. The international health guideline for physical activity recommends that adults should be doing at least 150 min of moderate-intensity physical activity throughout the week or doing at least 75 min of vigorous-intensity physical activity regardless of the domains of physical activity such as leisure, transportation, occupational, and household chores [5]. However, the level of inactivity is reported to be high globally [6, 7]. Thus, motivating the public to participate in physical activity by finding which factors influence participation in physical activity is important to improve the public health and to mitigate the global burden of chronic diseases.
There are several theories that describe behavioral models of physical activity, and it is common to incorporate ideas from these theories into ecological models. According to an ecological model, factors which influence health behavior consisted of intra-personal, inter-personal, and environmental factors as well as policy [8]. Personal factors include demographic and biological factors, psychological, cognitive and emotional factors, behavioral factors, and social and cultural factors [9]. Environment factors include the facility, neighborhood, safety, home environment, location of region, and climate [10].
Although there has been one meta-analysis of associations between environmental factors and physical activity [11], most factors related to physical activity have been summarized by systematic reviews rather than by meta-analysis because of an insufficient number of primary studies on each factor and distinct analytical methods. In a study by Bauman, the authors conducted a review of reviews which is a capable method of summarizing previous evidence from systematic reviews, with or without synthesis [12, 13]. They reviewed variables as determinants of physical activity in children or adolescent among adults to investigate those factors throughout their life span; however, the variables studied in adults, but not in children or adolescents, were not reviewed [14].
The primary purpose of this study was to summarize and present updated evidence for personal and environmental factors potentially associated with participation in physical activity overall or by the domains of physical activity.
Methods
Search strategy and eligibility criteria
To identify systematic reviews, MEDLINE and EMBASE were searched for quantitative, peer-reviewed studies published up to 31 Jan. 2017 reporting on potential correlates, predictors or determinants of any type of physical activity in adults aged over 18 years (Fig. 1). Search terms indicative of physical activity were used in combination with correlates or determinants. For the adaption of search strategies, specific filters were used from the databases including study design, publication year, language, and age. In MEDLINE, medical subject headings (MeSH) such as ‘motor activity’ and ‘epidemiologic factors’ were also used in the search strategy.
Fig. 1.
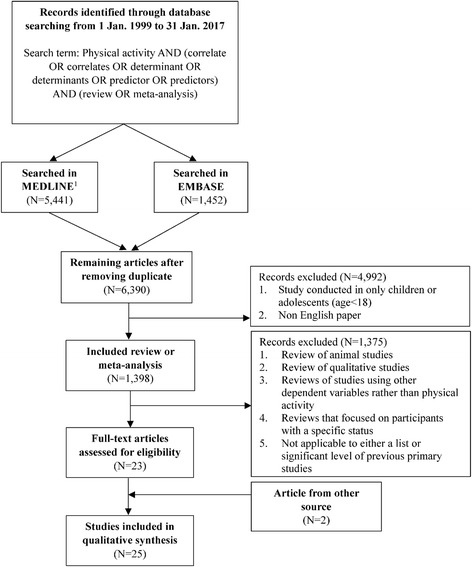
Flow chart of inclusion and exclusion criteria for previous reviews. 1Medical subject headings (MeSH) such as ‘Motor Activity’ and ‘Epidemiologic Factors’ were also used in the search strategy
After the removal of reviews that were duplicates in both literature databases or published in a non-English language or that targeted adolescents, the additional following reviews were excluded: 1) reviews of animal studies, 2) reviews of qualitative studies, 3) reviews of studies using other dependent variables rather than physical activity, 4) reviews that focused on participants with a specific status such as cancer, pregnancy, and alcohol use disorder, and 5) studies which did not provide either a list or significant level of previous primary studies because that information was used in the classification of the variables. Reference lists of the included reviews and primary studies in each review were checked to identify any unrevealed studies.
Rating the methodological quality
To assess the quality of each included review, the 11-item Assessment of Multiple Systematic Review (AMSTAR) checklist was used for the assessment [15]. The measure satisfies inter-observer agreement, reliability, construct validity and feasibility. The quality score ranges from 0 (lowest quality) to 11 (highest quality). In the current study, a review with a 0–2 AMSTAR score was considered as having a low quality, 3–6 as having a moderate quality and 7–11 as having a high quality. The checklist of the AMSTAR score is provided in Additional file 1: Table S1.
Data extraction
The following characteristics were extracted from the included reviews: report type (e.g., systematic review or meta-analysis), publication year, age of population, number of quantitative studies, outcomes, and proportion of longitudinal studies, and measurement method of physical activity and environmental factors. The domains of physical activity were collected as the outcome if the results of the primary studies included in each review were identifiable by the domains of physical activity.
Classification of variables
Variables from each review were classified according to the number of primary studies supporting the association or no association and the percentage of expected association among the total number of primary studies (Additional file 1: Table S2) [14]: not a correlate (NC) or not a determinant (ND), inconclusive (IC), a correlate (Cor) or determinant (Det). When more than 50% of the primary studies supporting an association or no association were derived from a longitudinal design, the variables were coded as a determinant rather than a correlate. If the factors were classified as a ‘correlate’ or a ‘determinant’, it was regarded as a definitely associated factor (DAF).
Corrected Covered Area (CCA)
Because some primary studies were included in more than one review, the summarized results from each review can be biased by those overlaps. To assess this bias, the degree of overlap between reviews was calculated with the Corrected Covered Area (CCA) method. The details of the CCA calculation have been described elsewhere [16]. Briefly, the CCA was calculated with the following equation showing how the primary studies in each review are duplicated:
where N is the sum of the number of primary studies in each review, r is the total number of primary studies, and c is the number of reviews. This measure has been validated in which the number of overlapped primary publications has a strong correlation with the CCA. A CCA score of less than 5% is regarded as a slight overlap, 5–9.9% as moderate overlap, 10–14.9% as high overlap and over 15% as a very high level of overlap [16]. The CCA was estimated for overall personal and environmental factors as well as for the factors classified as DAFs in more than 3 reviews. A study by Duncan et al. [11] was excluded in the CCA calculation because the list of included primary studies was not available.
Results
A total of 25 reviews with 980 primary studies met the inclusion criteria [9–11, 17–38]. Among those reviews, there were 13 reviews with personal factors [9, 10, 17, 19, 22, 23, 26, 28, 32–34, 36, 38] and 19 reviews with environmental factors [9–11, 18–21, 24, 25, 27–31, 33, 35–38], respectively (Table 1). The number of primary studies for personal factors included in each review ranged from 11 to 91, and the number of primary studies for environmental factors ranged from 3 to 70. Four reviews included only primary studies conducted with a longitudinal design [28, 33, 36, 38]. Thus, the results derived from those reviews were regarded as a determinant rather than as a correlate. Reviews published before 1999 were not considered in the present study because a study by Trost et al. [9] had included and updated the results of those reviews [39–42].
Table 1.
Characteristics of previous reviews of personal and environmental factors on participation in physical activity
| Author | Year | Population age | Publication period of studies | No. of quantitative studies | Outcomes | Proportion of longitudinal studies | No. of assessed factors | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reviews of personal factors | ||||||||
| Rhodes | 1999 | ≥65 | ~1999 | 41 | Leisure | 14 (34%) | 23 | [17] |
| Eyler | 2002 | ≥18 women | 1980–2000 | 81 | Overall, leisure, household, transport | 0 | 32 | [10] |
| Trost | 2002 | ≥18 | 1998–2000 | 36 | Overall | 7 (18%) | 48 | [9] |
| Plonczynski | 2003 | ≥65 women | 1994–2001 | 15 | Overall | 1 (6%) | 16 | [19] |
| Rhodes | 2006 | ≥18 | 1969–2006 | 33 | Overall | 16 (50%) | 6 | [23] |
| Kaewthummanukul | 2006 | NA | 1990–2002 | 11 | Overall | 0 | 22 | [22] |
| Allender | 2008 | NA | 1977–2007 | 19 | Overall | 9 (47%) | 5 | [26] |
| VanStralen | 2009 | ≥40 | 1900–2008 | 54 | Overall | 54 (100%) | 36 | [28] |
| Kirk | 2011 | 18–64 | 1974–2010 | 62 | Leisure | 11 (18%) | 6 | [32] |
| Koeneman | 2011 | ≥55 | 1990–2010 | 34 | Overall, leisure | 34 (100%) | 31 | [33] |
| Engberg | 2012 | 17–70 | 1992–2012 | 34 | Leisure | 27 (79%) | 5 | [34] |
| Rhodes | 2015 | 18–64 | 2012–2014 | 78 | Overall | 75 (100%) | 20 | [36] |
| Prince | 2016 | 18–65 women | ~2014 | 91 | Overall | 91 (100%) | 29 | [38] |
| Reviews of environmental factors | ||||||||
| Eyler | 2002 | ≥18 | 1980–2000 | 15 | Overall, leisure, household | 0 | 13 | [10] |
| Trost | 2002 | ≥18 | 1998–2000 | 8 | Overall | 0 | 14 | [9] |
| Humpel | 2002 | Adults | NR | 19 | Overall | 1 (5%) | 14 | [18] |
| Plonczynski | 2003 | ≥65 women | 1994–2001 | 5 | Overall | 0 | 6 | [19] |
| Cunningham | 2004 | Adults | 1966–2002 | 27 | Overall, leisure, walking, | 0 | 13 | [20] |
| Owen | 2004 | Adults | ~2004 | 18 | Walking | 2 (11%) | 14 | [21] |
| Duncana | 2005 | NA | 1989-2005 | 16 | Overall | 0 (0%) | 6 | [11] |
| Tucker | 2007 | NA | 1980–2006 | 6 | Overall | 0 | 2 | [24] |
| Wendel-Vos | 2007 | ≥18 | 1980–2004 | 47 | Overall | 3 (6%) | 20 | [25] |
| Saelens | 2008 | Adults | 2005–2006 | 29 | Walking | 0 | 8 | [27] |
| Van Stralen | 2009 | ≥40 | 1900–2008 | 13 | Overall | 13 (100%) | 12 | [28] |
| Panter | 2010 | 18–65 | 1990–2009 | 43 | Transport | 0 | 4 | [29] |
| Koeneman | 2011 | ≥55 | 1990–2010 | 3 | Leisure, overall | 3 (100%) | 4 | [33] |
| McCormack | 2011 | ≥18 | 1996–2010 | 31 | Overall, leisure, walking/cycling, transport | 2 (6%) | 10 | [30] |
| Van Cauwenberg | 2011 | Mean > 65 | 2000–2010 | 31 | Overall, leisure, walking/cycling, transport | 3 (10%) | 10 | [31] |
| Van Holle | 2012 | 18–65 | 2000–2011 | 70 | Overall, leisure, walking/cycling, transport | 1 (0%) | 11 | [35] |
| Rhodes | 2015 | 18–64 | 2012–2014 | 12 | Overall | 12 (100%) | 2 | [36] |
| Day | 2016 | NA | ~2014 | 42 | Overall, leisure, transport, occupation | 0 | 12 | [37] |
| Prince | 2016 | 18–65 women | ~2014 | 9 | Overall | 9 (100%) | 6 | [38] |
aMeta-analysis
The quality assessment scores are presented in Additional file 1: Table S1. The AMSTAR score for each review ranged from 2 to 8. Most of the reviews (21 out of 25) were rated as having a moderate quality. Information on study design (checklist 1), literature search strategy (checklist 3) and list of included studies (checklist 5) were provided in most studies. However, information on the status of the publication as an inclusion criterion (checklist 4), the combining methods (checklist 9), publication bias assessment (checklist 10) and conflict of interest of the included studies (checklist 11) were rarely provided.
Correlates of physical activity overall
A total of 117 factors were reported in the previous reviews. The definitions of each factor are shown in Additional file 1: Table S3 in alphabetical order.
Table 2 lists the relationships between personal factors and physical activity overall. There were 90 personal factors consisting of 24 demographic/biological factors, 40 psychological factors, 13 behavioral factors, and 13 social factors. Among the 90 personal factors, 53 factors were considered as DAFs in more than one of the reviews. For demographic and biological factors, age, gender, ethnicity, marital status, education, income, and employment were assessed in more than half of the reviews (7 out of 13). Among those, age was regarded as a negative DAF in 3 reviews. Bad health or fitness status was assessed in 5 reviews and classified as a negative DAF in 3 reviews. For psychological factors, cognitive and emotional factors, attitude, intention to exercise, outcome expectations, self-efficacy, and stress were assessed in more than half of the reviews. Intention to exercise, outcome expectations, perceived behavioral control, self-efficacy and perceived good fitness were assessed as positive DAFs in more than 3 reviews. Self-efficacy classified as a DAF in 7 reviews had the strongest association with participation in physical activity in this review of reviews. For behavioral factors, smoking was assessed in 7 reviews, which was not determined as a DAF in any of the reviews. For social and cultural factors, there were no variables evaluated in more than half of the reviews.
Table 2.
Relationships between personal factors and physical activity
| Rhodes (1999) [17] | Eyler (2002) [10] | Trost (2002)a [9] | Plonczynski (2003) [19] | Rhodes (2006) [23] | Kaewthummanukul (2006) [22] | Allender (2008) [26] | Van Stralen (2009) [28] | Kirk (2011) [32] | Koeneman (2011) [33] | Engberg (2012) [34] | Rhodes (2015) [36] | Prince (2016) [38] | No. of DAF/total No.b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic and biological factors | ||||||||||||||
| Age | Cor (−) | IC | Cor (−) | IC | - | Cor (−) | - | ND | - | ND | - | ND | - | 3/8 |
| Gender, men | Cor (+) | - | Cor (+) | - | - | IC | - | ND | IC | IC | - | ND | - | 2/7 |
| Ethnicity, white | - | Cor (+) | Cor (+) | IC | - | IC | - | ND | - | ND | - | IC | - | 2/7 |
| Marital status, married | - | IC | IC | IC | - | IC | IC | ND | - | - | Det (−) | ND | ND | 1/9 |
| Education, higher | IC | Cor (+) | Cor (+) | - | - | IC | - | ND | - | - | - | ND | IC | 2/7 |
| Income, higher | IC | NC | Cor (+) | Cor (+) | - | IC | - | ND | - | - | - | IC | IC | 2/8 |
| Occupation, blue color | - | IC | IC | - | - | Cor (−) | - | - | Cor (−) | - | - | - | - | 2/4 |
| Employment | - | IC | - | - | - | - | Cor (−) | IC | - | IC | IC | ND | IC | 1/7 |
| Total work hours | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | Cor (−) | - | - | - | IC | 1/3 |
| Overtime work hours | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Cor (−) | - | - | - | - | 1/1 |
| Fixed day time work | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | 0/1 |
| Shift work | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | 0/1 |
| Multiple job | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | 0/1 |
| Full time employment | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Retirement | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | Det (−) | - | - | 1/2 |
| Trajectory of employment, downward | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | 0/1 |
| Transition to university | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Cor (−) | - | - | 1/1 |
| Pregnancy | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | Det (−) | - | - | 1/2 |
| Health or fitness status, bad | Cor (−) | Cor (−) | - | - | - | IC | - | Det (−) | - | IC | - | - | - | 3/5 |
| Chronic diseases, hypertension, CVD, cancer, and diabetes | - | IC | IC | - | - | - | IC | - | - | IC | - | - | - | 0/4 |
| Injury history | - | IC | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/2 |
| Childhood illness/disability | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Functional limitation, disability | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | 0/2 |
| Genetic factor | - | - | Cor (+) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1/1 |
| Psychological, cognitive and emotional factors | ||||||||||||||
| Attitude | Cor (+) | - | ND | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | IC | - | IC | IC | 1/7 |
| Control over exercise | Cor (+) | - | IC | - | - | Cor (+) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2/3 |
| Intention to exercise | Cor (+) | - | Cor (+) | - | - | IC | - | Det (+) | - | IC | - | IC | Det (+) | 4/7 |
| Outcome expectations (expect benefit) | Cor (+) | Cor (+) | Cor (+) | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | IC | - | IC | - | 3/7 |
| Value of exercise outcomes | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Physical outcome realization | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Det (+) | - | IC | - | - | - | 1/2 |
| Psychological outcome realization | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Det (+) | - | - | - | - | - | 1/1 |
| Health locus of control | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | - | - | 0/3 |
| Action planning | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Det (+) | - | - | - | - | - | 1/1 |
| Perceived behavioral control | Cor (+) | - | IC | - | - | Cor (+) | - | - | - | IC | - | IC | Det (+) | 3/6 |
| Self-efficacy | Cor (+) | Cor (+) | Cor (+) | Cor (+) | - | Cor (+) | - | Det (+) | - | IC | - | IC | Det (+) | 7/9 |
| Self-motivation | - | Cor (−) | Cor (+) | - | - | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | - | IC | 2/5 |
| Self-schemata for exercise | - | - | Cor (+) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1/1 |
| Enjoyment of exercise | IC | IC | Cor (+) | IC | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | 1/5 |
| Stage of change | IC | - | Cor (+) | - | - | IC | - | Det (+) | - | IC | - | - | - | 2/5 |
| Process of psychological change | - | - | Cor (+) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | 1/2 |
| Knowledge of health and exercise | Cor (+) | Cor (+) | NC | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | IC | IC | 2/6 |
| Normative beliefs | - | - | NC | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | ND | 0/3 |
| Body image | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Psychological health | IC | - | IC | Cor (+) | - | - | - | ND | - | - | - | - | - | 1/4 |
| Stress | - | Cor (−) | IC | IC | - | IC | - | Det (−) | - | IC | - | - | ND | 2/7 |
| High job strain | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Cor (−) | - | - | - | - | 1/1 |
| Barrier to exercise | Cor (−) | - | Cor (−) | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | IC | - | - | IC | 2/6 |
| Perceived fitness, good | - | Cor (+) | Cor (+) | Cor (+) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Det (+) | 4/4 |
| Quality of life, good | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | 0/1 |
| Lack of time | - | Cor (−) | Cor (−) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2/2 |
| Susceptibility to illness/seriousness of illness | - | - | NC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Fear of symptoms | - | Cor (−) | - | Cor (−) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2/2 |
| Mood disturbance | - | - | Cor (−) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1/1 |
| Depression | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | - | IC | 0/3 |
| Fatigue | - | Cor (−) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | 1/2 |
| Anxiety | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | 0/1 |
| John Henryism | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Personality variables | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Extraversion | - | - | - | - | Cor (+) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1/1 |
| Openness to experience | - | - | - | - | NC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Agreeableness | - | - | - | - | NC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Neuroticism | - | - | - | - | Cor (−) | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | 1/2 |
| Conscientiousness | - | - | - | - | Cor (+) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1/1 |
| Psychoticism | - | - | - | - | NC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Behavioral factors | ||||||||||||||
| Dietary habits | - | IC | Cor (+) | IC | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1/4 |
| Overweight/obesity | - | IC | Cor (−) | - | - | IC | - | ND | - | IC | - | - | - | 1/5 |
| Alcohol | - | IC | IC | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | ND | - | 0/4 |
| Smoking | - | NC | IC | IC | - | IC | - | IC | - | IC | - | ND | - | 0/7 |
| Activity during adulthood | IC | - | Cor (+) | - | - | - | - | Det (+) | - | IC | - | - | - | 2/4 |
| Activity during childhood | IC | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | 0/3 |
| Past exercise program | - | IC | Cor (+) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1/2 |
| Processes of behavioral change | - | - | Cor (+) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | 1/2 |
| School sports | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Type A behavior pattern | - | IC | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/2 |
| Decisional balance sheet | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Screening | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Physical activity intensity | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | 0/2 |
| Social and cultural factors | ||||||||||||||
| Social support for exercise | - | - | - | Cor (+) | - | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | IC | - | 1/4 |
| Social support for exercise from friends/peers | Cor (+) | - | Cor (+) | IC | - | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | - | - | 2/5 |
| Social support for exercise from spouse/family | IC | - | Cor (+) | IC | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | 1/4 |
| Social support from staff/instructor | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | - | - | 0/2 |
| Physician influence | IC | Cor (+) | Cor (+) | IC | - | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | - | - | 2/6 |
| Spousal physical activity habits | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | 0/1 |
| Work-family conflict | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | 0/1 |
| Social support | NC | Cor (+) | - | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | 1/4 |
| Group cohesion | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | - | IC | 0/3 |
| Social isolation | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | 0/2 |
| Neighborhood deprivation | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | 0/1 |
| Caregiver to ill family member | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | 0/1 |
| Change in family structure: having child | - | Cor (−) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Det (−) | 2/2 |
Abbreviations: NC not a correlate, ND not a determinant, Cor a correlate, Det a determinant, IC inconclusive, DAF definitely associated factor
aIncluding results of following reviews: “Dishman et al. [39]”, “Dishman et al. [40]”,"Dishman et al. [41]” “Sallis and Owen. 1999”
bNumber of reviews regarding the factor as definitely associated factor / total number of reviews assessing the factor
Table 3 lists the relationships between environmental factors and physical activity overall. There were 27 environment factors consisting of 4 facility factors, 8 neighborhood factors, 6 safety factors, 3 home environment factors, 3 location of region factors, and 3 climate factors. Among the 27 environmental factors, ten factors were considered as DAFs in more than one of the reviews. For facility factors, accessibility was assessed in more than half of the reviews (10 out of 19) and classified as a positive DAF in 5 reviews. For neighborhood factors, the presence of sidewalks and aesthetics were evaluated in 14 reviews and regarded as positive DAFs in more than three reviews. For safety factors, high crime rates in the region and heavy traffic were only determined as DAFs in less than three reviews although they were summarized in more than half of the reviews. There were no factors which were assessed in more than half of the reviews (10 out of 19) for home environment, location of region, and climate factors.
Table 3.
Relationships between environmental factors and physical activity
| Eyler (2002) [10] | Trost (2002) a[9] | Humpel (2002) [18] | Plonczynski (2003) [19] | Cunningham (2004) [20] | Owen (2004) [21] | Duncan (2005) [11] | Tucker (2007) [24] | Wendel-vos (2007) [25] | Saelens (2008) [27] | Van Stralen (2009) [28] | Panter (2010) [29] | Koeneman (2011) [33] | McCormack (2011) [30] | Van Cauwenberg (2011) [31] | Van Holle (2012) [35] | Rhode (2015) [36] | Day (2016) [37] | Prince (2016) [38] | No. of DAF/ total No.b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Facility | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Accessibility | - | IC | Cor (+) | - | IC | Cor (+) | Cor (+) | - | Cor (+) | IC | IC | - | IC | IC | IC | IC | ND | Cor (+) | IC | 5/15 |
| Convenience of facilities | IC | - | IC | - | IC | Cor (+) | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ND | 1/6 |
| Satisfaction with facilities | - | IC | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/3 |
| Cost of programs | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/2 |
| Neighborhood | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Presence of sidewalks | IC | IC | Cor (+) | IC | IC | IC | Cor (+) | - | NC | IC | IC | IC | - | IC | IC | - | - | Cor (+) | - | 3/14 |
| Aesthetics | IC | IC | Cor (+) | - | Cor (+) | Cor (+) | - | - | IC | IC | IC | IC | - | IC | NC | Cor (+) | ND | IC | - | 4/14 |
| Transportation | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | 0/3 |
| Sprawl | - | - | IC | - | IC | IC | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | 0/5 |
| Population density | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | IC | IC | IC | - | IC | - | 0/5 |
| Network connectivity | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | IC | - | - | IC | IC | IC | - | IC | IC | 0/7 |
| Land-use mix | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | Cor (+) | IC | - | - | NC | IC | IC | - | Cor (+) | - | 2/7 |
| Quality of environment | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Safety | ||||||||||||||||||||
| High crime rates in the region | IC | IC | IC | - | NC | IC | Cor (+) | - | IC | IC | IC | - | - | - | IC | IC | - | IC | IC | 1/13 |
| Heavy traffic | IC | IC | IC | - | NC | IC | Cor (+) | - | IC | IC | IC | IC | - | IC | IC | IC | - | IC | - | 1/14 |
| Frequently observe others exercising | IC | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/3 |
| Neighborhood safety | Cor (−) | IC | IC | IC | IC | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | IC | IC | - | - | - | 1/9 |
| Adequate lighting | IC | IC | IC | - | IC | IC | IC | - | IC | - | IC | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | 0/9 |
| Unattended dogs | IC | IC | IC | - | IC | IC | IC | - | IC | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | 0/9 |
| Home environment | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Home equipment | - | IC | IC | - | - | IC | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/5 |
| Home age | - | - | - | IC | IC | IC | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/4 |
| Stair in the home | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/1 |
| Location of region | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Hilly terrain | IC | IC | IC | - | IC | IC | - | - | IC | - | IC | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | 0/8 |
| Coastal location | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | IC | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/3 |
| Urban location | IC | IC | - | IC | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | IC | IC | - | Cor (−) | IC | 1/8 |
| Climate | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Bad weather | IC | - | IC | IC | - | IC | - | IC | NC | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | IC | - | 0/8 |
| Pollution | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | - | 0/2 |
| Season, summer | IC | - | - | - | - | - | - | Cor (+) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | IC | 1/3 |
Abbreviations: NC not a correlate, ND not a determinant, Cor a correlate, Det a determinant, IC inconclusive, DAF definitely associated factor
aIncluding results of following reviews: “Dishman et al. [39]”, “Dishman et al. [40]”,"Dishman et al. [41]” “Sallis and Owen. 1999”
bNumber of reviews regarding the factor as definitely associated factor / total number of reviews assessing the factor
Correlates of physical activity by the domains of the physical activity
The results by the domains of physical activity are summarized in Additional file 1: Tables S4 ~ S7. For personal factors, the factors for leisure-time physical activity were summarized (Additional file 1: Table S4). Of the 46 personal factors, twenty-two factors were considered as DAFs in one of the reviews. There were no personal factors considered more than twice as a DAF. For environmental factors, factors were summarized in leisure time physical activity, walking/cycling, and transportation, respectively (Additional file 1: Table S5 ~ S7). There were 6 factors regarded as DAFs in more than one of the reviews. Accessibility was considered as a DAF in all three domains. Population density and high crime rate in the region were considered as DAFs only in the leisure-time physical activity domain (Additional file 1: Table S5). Land-use mix and urban location were classified as DAFs in transportation (Additional file 1: Table S6) and walking/cycling (Additional file 1: Table S7). Aesthetics was considered once as a DAF only in the walking/cycling domain (Additional file 1: Table S7). The results for the occupation and household domain could be not summarized for both personal and environmental factors because there was only one or no reviews for those domains.
Other issues for correlates of physical activity
When summarizing the review of studies conducted in older subjects, no differences were found when compared with the results for all adults. There were 13 personal factors which were classified as DAFs in at least one of two reviews that only focused on factors of older adults (> 65 years) (See the results of Rhode et al. [17] and Plonczynski et al. [19] in Table 2). There were no environmental factors considered as DAFs for older adults.
The results of objectively measured physical activity could be not summarized in this review of reviews because most of the reviews included less than four primary studies using objectively measured physical activity or did not provide information on the measurement of physical activity in the primary studies. In the results of objectively measured environmental factors, the following 5 factors were considered as DAFs in more than one of the reviews from among 17 factors: accessibility, population density, land-use mix, urban location, and high crime rate in the region (Additional file 1: Table S8).
Corrected Covered Area (CCA)
Additional file 1: Table S9 presents the CCA for each factor. The primary studies had a slight overlap across 13 (CCA: 2.0%) and 18 reviews (CCA: 1.6%) for personal and environmental factors, respectively. In addition, all the CCAs for the factors classified as DAFs in more than 3 reviews were less than 5%.
Discussion
This review of reviews summarized the results of 25 previous reviews that reported on the potential factors of participation in physical activity all of which showed mostly a moderate methodological quality. Several personal factors including age, health or fitness status, intention to exercise, outcome expectations, perceived behavioral control, self-efficacy, and perceived fitness and several environmental factors including accessibility, presence of sidewalks, and aesthetics were assessed as DAFs in more than three studies.
This study is the first updated review of reviews on factors for physical activity after the study by Bauman in 2012 [13]. Four reviews for personal factors [10, 34, 36, 38] and ten reviews for environmental factors [9, 10, 19, 24, 30, 33, 35–38] were added in the present study after the previous review of reviews [13]. Most factors presented as correlates in the study by Bauman were considered as DAFs in the present study including personal history of physical activity during adulthood which was classified as a DAF in two reviews. Fifty-four factors were additionally summarized which were not evaluated in the review by Bauman. Among them, transition to university, pregnancy, past exercise program, processes of behavioral change, change in family structure, presence of sidewalks, and season were classified as DAFs at least once. A summary of previous reviews by the domains of physical activity and by measures of environmental factors was added.
For personal factors, self-efficacy was consistently evaluated as the clearest correlate in the present study consistent with the previous review of reviews [13]. According to Bandura’s Social Cognitive Theory, self-efficacy functions both directly and indirectly with outcome expectations and other constructs [43] and has a role as a mediating factor of social support in health behavior [44, 45].
For environmental factors, this study summarized the factors by the domains of physical activity, and the results of some factors such as accessibility were consistent overall and by the domains of physical activity. However, it can be concluded that it is too early to summarize the results of the review because there were a limited number of primary studies for each factor.
Although there were a number of factors whose effects on physical activity were assessed, we could not perform a meta-analysis because of the lack of primary studies for each factor, different analytical measures, and the presence of unclearly distinguished factors when compared with each other. For example, some psychological factors had similar definitions such as attitude and outcome expectation. There were many factors classified as a group such as employment-related factors including occupation type, employment status, total work hours, overtime work hour, fixed day time work, shift work, multiple job, and full time employment and social support-related factors including social support for exercise overall and from friends/peers, spouse/family, and staff/instructor and those factors were listed in their originally written form from each review to convey the most accurate meaning of each factor rather than conducting a meta-analysis.
Instead of a meta-analysis, the present study conducted a review of reviews. Although a review of reviews can only show the tendency or direction of an association rather than providing the magnitude or significance level of an association [46], the current evidence on participation in physical activity was comprehensively summarized. When using the review of reviews, there were some challenges. First, the quality of the review of reviews was greatly affected by the quality of the original reviews [47]. In this study, we confirmed that the quality of the original reviews were mostly moderate or higher by assessing the AMSTAR score. Second, if the primary studies were included in several reviews, they may produce bias related to overlapping effects [47]. By calculating the CCA, we showed that the primary studies included in each review were only slightly overlapped and proved that the results from each review were relatively independent.
The present study has limitations. First, a study by Duncan [11] was not included in the calculation of the CCA because it did not provide a list of the included primary studies. However, the effect of not including these primary studies is expected to be slight because there were only 16 primary studies in the study by Duncan. Second, the results of intervention and observational studies could not be separately summarized because the results were not presented separately for each design in most reviews. Further studies should summarize the effects of potential factors on physical activity by the design of the study. Third, policy-related variables were not considered in the present study because policies were rarely considered in previous reviews. Although the effects of policy-related factors were overlapped with the effects of environmental factors such as the presence of sidewalks, the effects of policies on participation in physical activity should be investigated in a future study. Fourth, the interaction effect between different types of factors such as age and presence of sidewalks could not be assessed because the previous reviews were only focused on the individual effect of each factor. Like the interaction effect, the moderating effect of individual factors such as gender and age could not be evaluated also because there were no reviews on this issue. Future research should be conducted to identify the interaction or moderating effect of each factor.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the present study summarized the associations of potential factors with physical activity which could provide directions for improving participation in physical activity. More studies with a longitudinal design are needed to validate the associations of many factors. If more correlates are established with an accurate method, those factors can be used to form public policies and programs that will encourage the public to participate in physical activity and ultimately improve the public health.
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by a grant from Seoul National University Hospital (2016) and Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2004-E71004-00, 2005-E71011-00, 2005-E71009-00, 2006-E71001-00, 2006-E71004-00, 2006-E71010-00, 2006-E71003-00, 2007-E71004-00, 2007-E71006-00, 2008-E71006-00, 2008-E71008-00, 2009-E71009-00, 2010-E71006-00, 2011-E71006-00, 2012-E71001-00, and 2013-E71009-00).
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from Seoul National University Hospital (2016) and Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2004-E71004–00, 2005-E71011–00, 2005-E71009–00, 2006-E71001–00, 2006-E71004–00, 2006-E71010–00, 2006-E71003–00, 2007-E71004–00, 2007-E71006–00, 2008-E71006–00, 2008-E71008–00, 2009-E71009–00, 2010-E71006–00, 2011-E71006–00, 2012-E71001–00, and 2013-E71009–00).
Authors’ contributions
JC conducted the literature searches, the selection of reviews, the data extraction, the quality rating and the data analysis, and drafted the manuscript. ML, JKL and DK were involved in the study as advisors and were also involved in commenting on the manuscript. JYC conducted the literature searches, the selection of reviews, the data extraction, the quality rating and the data analysis, and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final draft.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- AMSTAR
assessing the methodological quality of systematic reviews
- CCA
corrected covered area
- Cor
correlate
- DAF
definitely associated factor
- Det
determinant
- IC
inconclusive
- MeSH
medical subject heading
- NC
not correlate
- ND
not determinant
Additional file
AMSTAR score for each review. Table S2. Modified classification of the variables from each review based the evidence from the primary studies. Table S3. Definition of each factor. Table S4. Relationships between personal factors and leisure-time physical activity. Table S5. Relationships between environmental factors and leisure-time physical activity. Table S6. Relationships between environmental factors and transportation. Table S7. Relationships between environmental factors and walking/cycling. Table S8. Relationships between objectively measured environmental factors and physical activity. Table S9. CCA for each factor. (DOCX 85 kb)
Contributor Information
Jaesung Choi, Email: cksjwjsja@snu.ac.kr.
Miyoung Lee, Email: mylee@kookmin.ac.kr.
Jong-koo Lee, Email: docmohw@snu.ac.kr.
Daehee Kang, Email: dhkang@snu.ac.kr.
Ji-Yeob Choi, Phone: +82-2-740-8922, Email: jiyeob.choi@gmail.com.
References
- 1.Berlin JA, Colditz GA. A meta-analysis of physical activity in the prevention of coronary heart disease. Am J Epidemiol. 1990;132(4):612–628. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Thune I, Brenn T, Lund E, Gaard M. Physical activity and the risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1997;336(18):1269–1275. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199705013361801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Michaud DS, Giovannucci E, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Fuchs CS. Physical activity, obesity, height, and the risk of pancreatic cancer. JAMA. 2001;286(8):921–929. doi: 10.1001/jama.286.8.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Warburton DE, Nicol CW, Bredin SS. Health benefits of physical activity: the evidence. CMAJ. 2006, 174(6):801–809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.Organization WH . Global recommendations on physical activity for health. 2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lee IM, Shiroma EJ, Lobelo F, Puska P, Blair SN, Katzmarzyk PT. Effect of physical inactivity on major non-communicable diseases worldwide: an analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy. Lancet (London, England). 2012, 380(9838):219–229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.Hallal PC, Andersen LB, Bull FC, Guthold R, Haskell W, Ekelund U. Global physical activity levels: surveillance progress, pitfalls, and prospects. Lancet (London, England). 2012, 380(9838):247–257. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 8.Sallis JF, Owen N. Ecological models of health behavior. Health Behav: Theory Res practice. 2015;5:43–64. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Trost SG, Owen N, Bauman AE, Sallis JF, Brown W. Correlates of adults' participation in physical activity: review and update. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002;34(12):1996–2001. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200212000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Eyler AE, Wilcox S, Matson-Koffman D, Evenson KR, Sanderson B, Thompson J, Wilbur J, Rohm-Young D. Correlates of physical activity among women from diverse racial/ethnic groups. J Women's Health Gender-Based Med. 2002;11(3):239–253. doi: 10.1089/152460902753668448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Duncan MJ, Spence JC, Mummery WK. Perceived environment and physical activity: a meta-analysis of selected environmental characteristics. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2005;2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 12.Baker PR, Costello JT, Dobbins M, Waters EB. The benefits and challenges of conducting an overview of systematic reviews in public health: a focus on physical activity. J Public Health. 2014;36(3):517–21. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 13.Bauman AE, Reis RS, Sallis JF, Wells JC, Loos RJ, Martin BW. Correlates of physical activity: why are some people physically active and others not? Lancet (London, England). 2012, 380(9838):258–271. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 14.Sallis JF, Prochaska JJ, Taylor WC. A review of correlates of physical activity of children and adolescents. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000;32(5):963–975. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200005000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shea BJ, Grimshaw JM, Wells GA, Boers M, Andersson N, Hamel C, Porter AC, Tugwell P, Moher D, Bouter LM. Development of AMSTAR: a measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2007;7:10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-7-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pieper D, Antoine SL, Mathes T, Neugebauer EA, Eikermann M. Systematic review finds overlapping reviews were not mentioned in every other overview. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67(4):368–375. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rhodes RE, Martin AD, Taunton JE, Rhodes EC, Donnelly M, Elliot J. Factors associated with exercise adherence among older adults. An individual perspective. Sports Med. 1999;28(6):397–411. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199928060-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Humpel N, Owen N, Leslie E. Environmental factors associated with adults' participation in physical activity: a review. Am J Prev Med. 2002;22(3):188–199. doi: 10.1016/S0749-3797(01)00426-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Plonczynski DJ. Physical activity determinants of older women: what influences activity? Medsurg Nurs. 2003;12(4):213–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cunningham GO, Michael YL. Concepts guiding the study of the impact of the built environment on physical activity for older adults: a review of the literature. Am J Health Promot. 2004;18(6):435–443. doi: 10.4278/0890-1171-18.6.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Owen N, Humpel N, Leslie E, Bauman A, Sallis JF. Understanding environmental influences on walking: review and research agenda. Am J Prev Med. 2004;27(1):67–76. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2004.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kaewthummanukul T, Brown KC. Determinants of employee participation in physical activity: critical review of the literature. AAOHN J. 2006;54(6):249–261. doi: 10.1177/216507990605400602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rhodes RE, Smith NEI. Personality correlates of physical activity: a review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2006;40(12):958–965. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2006.028860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tucker P, Gilliland J. The effect of season and weather on physical activity: a systematic review. Public Health. 2007;121(12):909–922. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2007.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wendel-Vos W, Droomers M, Kremers S, Brug J, van Lenthe F. Potential environmental determinants of physical activity in adults: a systematic review. Obes Rev. 2007;8(5):425–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2007.00370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Allender S, Hutchinson L, Foster C. Life-change events and participation in physical activity: a systematic review. Health Promot Int. 2008;23(2):160–172. doi: 10.1093/heapro/dan012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Saelens BE, Handy SL. Built environment correlates of walking: a review. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008;40(7 Suppl):S550–S566. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e31817c67a4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.van Stralen MM, De Vries H, Mudde AN, Bolman C, Lechner L. Determinants of initiation and maintenance of physical activity among older adults: a literature review. Health Psychol Rev. 2009;3(2):147–207. doi: 10.1080/17437190903229462. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Panter JR, Jones A. Attitudes and the environment as determinants of active travel in adults: what do and don't we know? J Phys Act Health. 2010;7(4):551–561. doi: 10.1123/jpah.7.4.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.McCormack GR, Shiell A. In search of causality: a systematic review of the relationship between the built environment and physical activity among adults. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2011;13(8):125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 31.Van Cauwenberg J, De Bourdeaudhuij I, De Meester F, Van Dyck D, Salmon J, Clarys P, Deforche B. Relationship between the physical environment and physical activity in older adults: a systematic review. Health Place. 2011;17(2):458–469. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2010.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kirk MA, Rhodes RE. Occupation correlates of adults' participation in leisure-time physical activity: a systematic review. Am J Prev Med. 2011;40(4):476–485. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2010.12.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Koeneman MA, Verheijden MW, Chinapaw MJM, Hopman-Rock M: Determinants of physical activity and exercise in healthy older adults: a systematic review. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2011;28(8):142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 34.Engberg E, Alen M, Kukkonen-Harjula K, Peltonen JE, Tikkanen HO, Pekkarinen H. Life events and change in leisure time physical activity: a systematic review. Sports Med. 2012, 42(5):433–447. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 35.Van Holle V, Deforche B, Van Cauwenberg J, Goubert L, Maes L, Van de Weghe N, De Bourdeaudhuij I. Relationship between the physical environment and different domains of physical activity in European adults: a systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2012;12(1):807. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rhodes RE, Quinlan A. Predictors of physical activity change among adults using observational designs. Sports Med. 2015, 45(3):423–441. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 37.Day K. Built environmental correlates of physical activity in China: a review. Prev Med Rep. 2016;3:303–316. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2016.03.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Prince SA, Reed JL, Martinello N, Adamo KB, Fodor JG, Hiremath S, Kristjansson EA, Mullen KA, Nerenberg KA, Tulloch HE, et al. Why are adult women physically active? A systematic review of prospective cohort studies to identify intrapersonal, social environmental and physical environmental determinants. Obes Rev. 2016;17(10):919–944. doi: 10.1111/obr.12432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dishman RK, Sallis JF, Orenstein DR. The determinants of physical activity and exercise. Public Health Rep. 1985;100(2):158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dishman RK, Chubb M, Bouchard C, Shephard R, Stephens T, Sutton J, McPherson B. Determinants of participation in physical activity. In: Exercise, fitness, and health: a consensus of current knowledge: proceedings of the International Conference on Exercise, fitness and health, May 29–June 3, 1988. Toronto, Canada: Human Kinetics Publishers; 1990: 75–108.
- 41.Dishman RK. Advances in exercise adherence: human kinetics publishers. 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sallis JF, Owen N. Physical activity and behavioral medicine, vol. 3. Thousand Oaks: SAGE publications; 1998.
- 43.Bandura A. Social foundations of thought and action: a social cognitive theory: prentice-hall, inc. 1986. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Duncan TE, McAuley E. Social support and efficacy cognitions in exercise adherence: a latent growth curve analysis. J Behav Med. 1993;16(2):199–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00844893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.McNeill LH, Wyrwich KW, Brownson RC, Clark EM, Kreuter MW. Individual, social environmental, and physical environmental influences on physical activity among black and white adults: a structural equation analysis. Ann Behav Med. 2006;31(1):36–44. doi: 10.1207/s15324796abm3101_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Smith V, Devane D, Begley CM, Clarke M. Methodology in conducting a systematic review of systematic reviews of healthcare interventions. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2011;11(1):15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-11-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hartling L, Vandermeer B, Fernandes RM. Systematic reviews, overviews of reviews and comparative effectiveness reviews: a discussion of approaches to knowledge synthesis. Evid Based Child Health. 2014;9(2):486–494. doi: 10.1002/ebch.1968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


