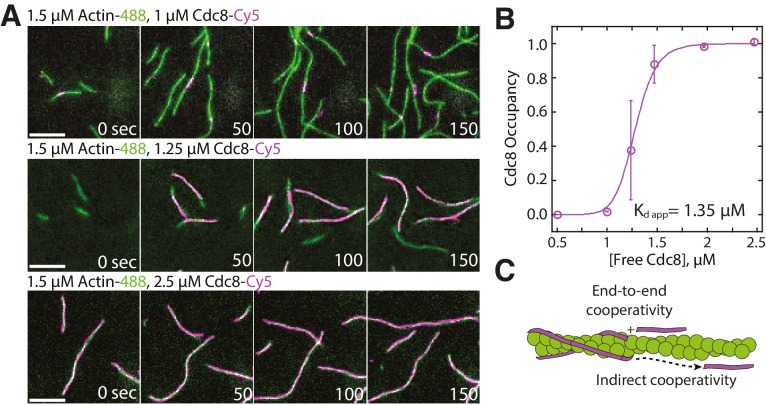
Figure 1. Tropomyosin Cdc8 loads cooperatively onto actin filaments.
(A) Two-color TIRFM of 1.5 μM Mg-ATP actin (15% Alexa 488 labeled) with a range of concentrations of tropomyosin Cdc8 (Cy5-labeled). Scale bar, 5 µm. (B) Plot of the fraction of actin filament bound by Cdc8 (‘Cdc8 occupancy’) over free Cdc8 dimer concentration. Data were fit to a Hill function, revealing a Hill coefficient >1 (Hill=14.6), that indicates cooperativity. Error bars represent standard error of the mean; n = 2 reactions. (C) Schematic of Cdc8 loading onto an actin filament. Observed cooperativity of Cdc8 could be the result of end-to-end binding of tropomyosin molecules (‘End-to-end cooperativity’) and/or indirect interactions between tropomyosin molecules via changes in the actin filament (‘Indirect cooperativity’).