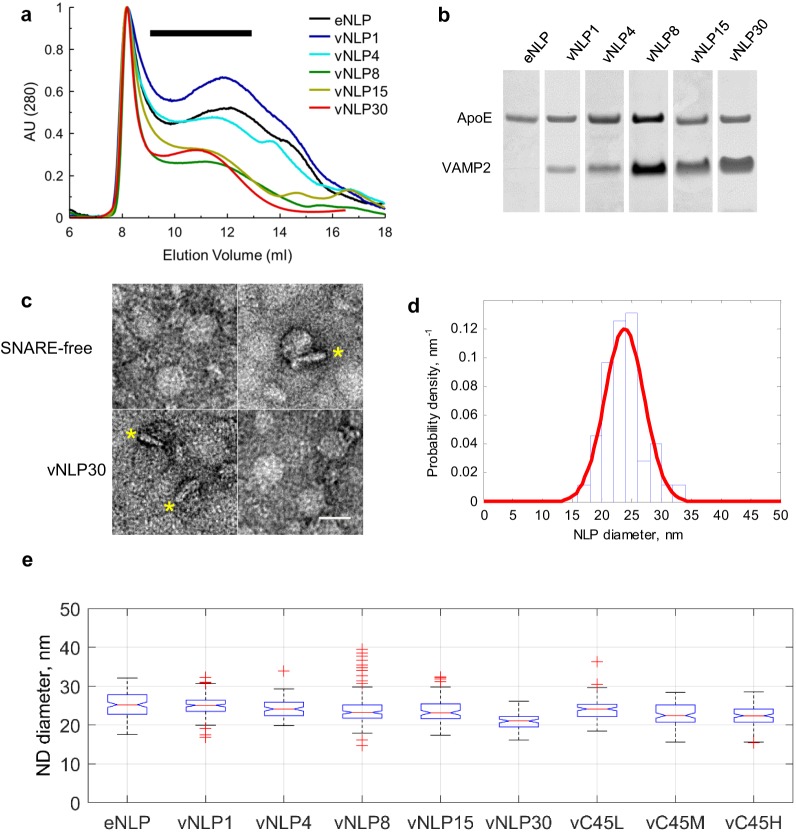
Figure 1. Size separation and characterization of NLPs.
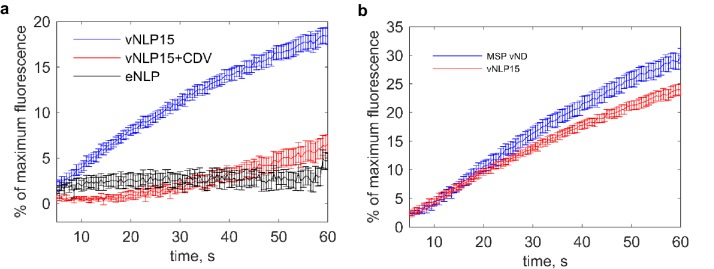
(a) Representative size exclusion chromatograms for various NLP preparations as indicated. NLPs were detected by absorption at 280 nm. Typically, fractions comprising 9–13 ml were collected (black horizontal bar). (b) Coomassie-stained SDS PAGE of NLPs. For each preparation, the amount of VAMP2 relative to ApoE was determined using densitometry. (c) Representative negative-stain EM micrographs of NLPs. The top row are SNARE-free NLPs. The bottom row are NLPs loaded with 30 v-SNARE copies. NLPs marked with * are oriented perpendicular to the imaging plane and show the flat disc structure. Scale bar = 25 nm. (d) Distribution of NLP diameters for a representative vNLP15 sample, determined from analysis of micrographs as in (c). A normal distribution fit is shown (red line). (e) Boxplot of representative NLP sizes under various conditions. NLPs containing lipid-anchored VAMP2 (vC45L, vC45M, vC45H for low, medium, and high copy numbers of C45 lipid-anchored VAMP2, bearing ~1, 4, and 15 copies) had sizes comparable to NLPs bearing similar loads of wild-type VAMP2 (vNLP1, vNLP4, and vNLP15). The activity of these NLPs was tested in an established bulk fusion assay with t-SNARE-reconstituted liposomes (Figure 1—figure supplement 1).