Abstract
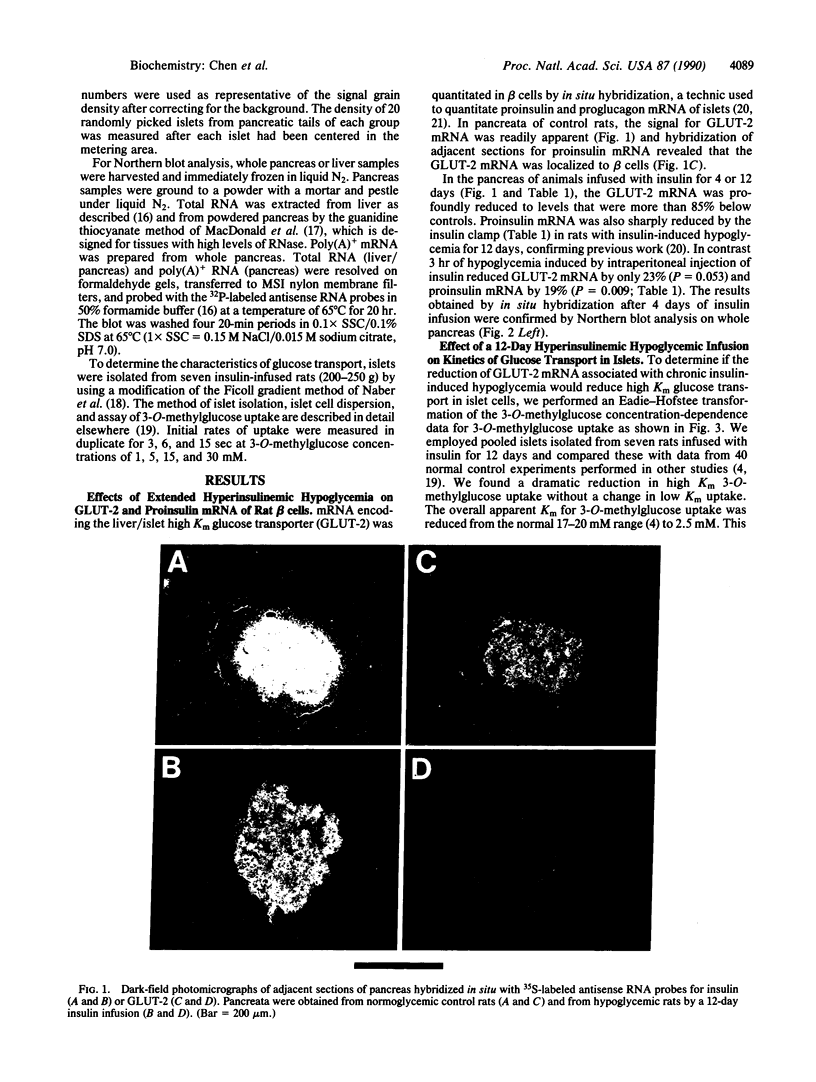
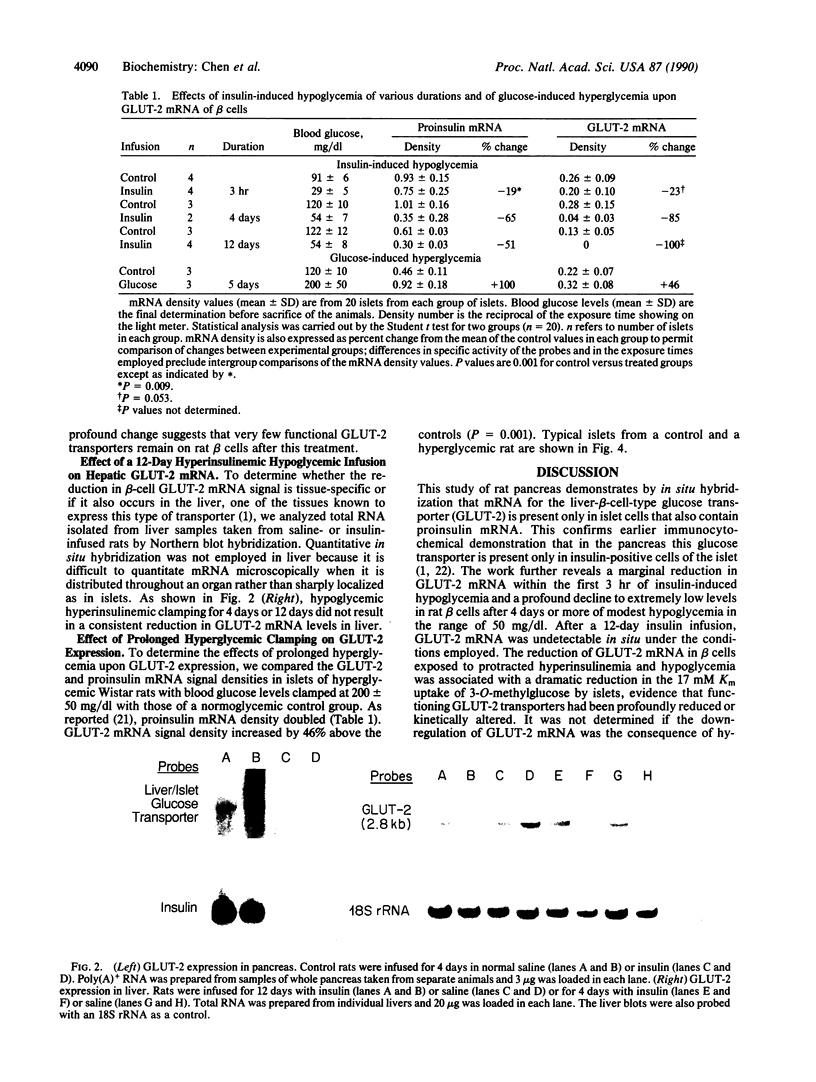
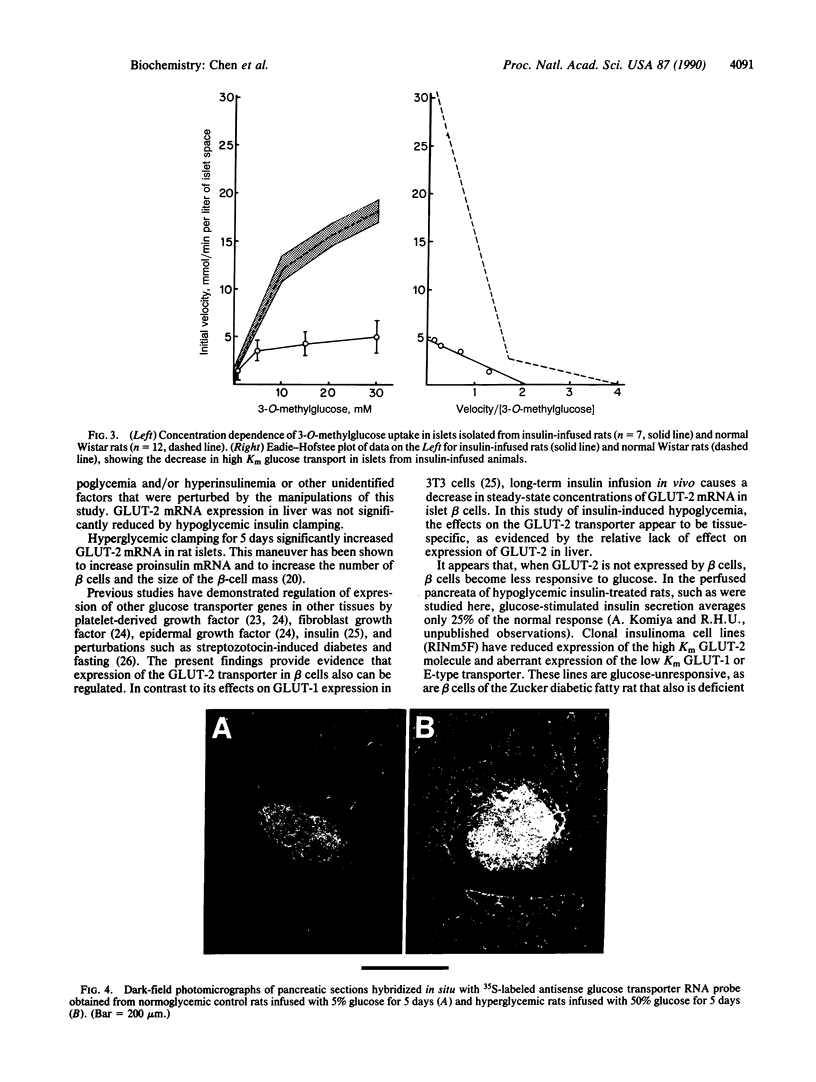
It has been postulated that a glucose transporter of beta cells (GLUT-2) may be important in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. To determine whether this transporter is constitutively expressed or regulated, we subjected conscious unrestrained Wistar rats to perturbations in glucose homeostasis and quantitated beta-cell GLUT-2 mRNA by in situ hybridization. After 3 hr of hypoglycemia (glucose at 29 +/- 5 mg/dl), GLUT-2 and proinsulin mRNA signal densities were reduced by 25% of the level in control rats. After 4 days (blood glucose at 57 +/- 7 mg/dl vs. 120 +/- 10 mg/dl in saline-infused control rats), GLUT-2 and proinsulin mRNA densities were reduced by 85% and 65%, respectively (P = 0.001). After 12 days (glucose at 54 +/- 8 mg/dl), GLUT-2 mRNA signal density was undetectable whereas proinsulin mRNA was reduced by 51%. After 12 days of hypoglycemia, the Km for 3-O-methyl-D-glucose transport in isolated rat islets, normally 18-20 mM, was 2.5 mM. This provides functional evidence of a profound reduction of high Km glucose transporter in beta cells. In contrast, GLUT-2 was only slightly reduced by hypoglycemia in liver. To determine the effect of prolonged hyperglycemia, we also infused animals with 50% (wt/vol) glucose for 5 days (glucose at 200 +/- 50 mg/dl). Hyperglycemic clamping increased GLUT-2 mRNA by 46% (P = 0.001) whereas proinsulin mRNA doubled (P = 0.001). We conclude that GLUT-2 expression in beta cells, but not liver, is subject to regulation by certain perturbations in blood glucose homeostasis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod J. D., Pilch P. F. Unique cytochalasin B binding characteristics of the hepatic glucose carrier. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2222–2227. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Biswas C., Vicario P. P., Strout H. V., Saperstein R., Pilch P. F. Decreased expression of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter in diabetes and fasting. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):70–72. doi: 10.1038/340070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Noyes B. E., Agarwal K. L., Steiner D. F. Construction and selection of recombinant plasmids containing full-length complementary DNAs corresponding to rat insulins I and II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5036–5040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Komiya I., Inman L., McCorkle K., Alam T., Unger R. H. Molecular and cellular responses of islets during perturbations of glucose homeostasis determined by in situ hybridization histochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1367–1371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Komiya I., Inman L., O'Neil J., Appel M., Alam T., Unger R. H. Effects of hypoglycemia and prolonged fasting on insulin and glucagon gene expression. Studies with in situ hybridization. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):711–714. doi: 10.1172/JCI114219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Seino S., Imura H., Seino Y., Eddy R. L., Fukushima Y., Byers M. G., Shows T. B., Bell G. I. Sequence, tissue distribution, and chromosomal localization of mRNA encoding a human glucose transporter-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5434–5438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia de Herreros A., Birnbaum M. J. The regulation by insulin of glucose transporter gene expression in 3T3 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9885–9890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Bell G. I. Facilitative glucose transporters: an expanding family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jan;15(1):18–23. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90125-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraki Y., Rosen O. M., Birnbaum M. J. Growth factors rapidly induce expression of the glucose transporter gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13655–13662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. H., Crider B. P., McCorkle K., Alford M., Unger R. H. Inhibition of glucose transport into rat islet cells by immunoglobulins from patients with new-onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 8;322(10):653–659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003083221003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Swift G. H., Przybyla A. E., Chirgwin J. M. Isolation of RNA using guanidinium salts. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:219–227. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meglasson M. D., Manning C. D., Najafi H., Matschinsky F. M. Glucose transport by radiation-induced insulinoma and clonal pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes. 1986 Dec;35(12):1340–1344. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.12.1340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naber S. P., McDonald J. M., Jarett L., McDaniel M. L., Ludvigsen C. W., Lacy P. E. Preliminary characterization of calcium binding in islet-cell plasma membranes. Diabetologia. 1980 Nov;19(5):439–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00281823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgard C. B., Nakano K., Hwang P. K., Fletterick R. J. Sequence analysis of the cDNA encoding human liver glycogen phosphorylase reveals tissue-specific codon usage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8132–8136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Thorens B., Ravazzola M., Lodish H. F. Localization of the pancreatic beta cell glucose transporter to specific plasma membrane domains. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):295–297. doi: 10.1126/science.2665080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Permutt M. A., Koranyi L., Keller K., Lacy P. E., Scharp D. W., Mueckler M. Cloning and functional expression of a human pancreatic islet glucose-transporter cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8688–8692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer M. A., Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr Insulin secretion in diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1981 Mar;70(3):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90579-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F. Glucose transporters: what's in a name? Endocrinology. 1990 Jan;126(1):3–5. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-1-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins B. J., Morrison E. D., Usher P., Flier J. S. Platelet-derived growth factor regulates glucose transporter expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16523–16526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikanta S., Ganda O. P., Eisenbarth G. S., Soeldner J. S. Islet-cell antibodies and beta-cell function in monozygotic triplets and twins initially discordant for Type I diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 10;308(6):322–325. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302103080607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R., Lodish H. F. Cloning and functional expression in bacteria of a novel glucose transporter present in liver, intestine, kidney, and beta-pancreatic islet cells. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga M., Komiya I., Johnson J. H., Inman L., Alam T., Moltz J., Crider B., Stefan Y., Baetens D., McCorkle K. Loss of insulin response to glucose but not arginine during the development of autoimmune diabetes in BB/W rats: relationships to islet volume and glucose transport rate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9749–9753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. J., Hinkle P. C. Kinetic properties of the reconstituted glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8907–8914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]