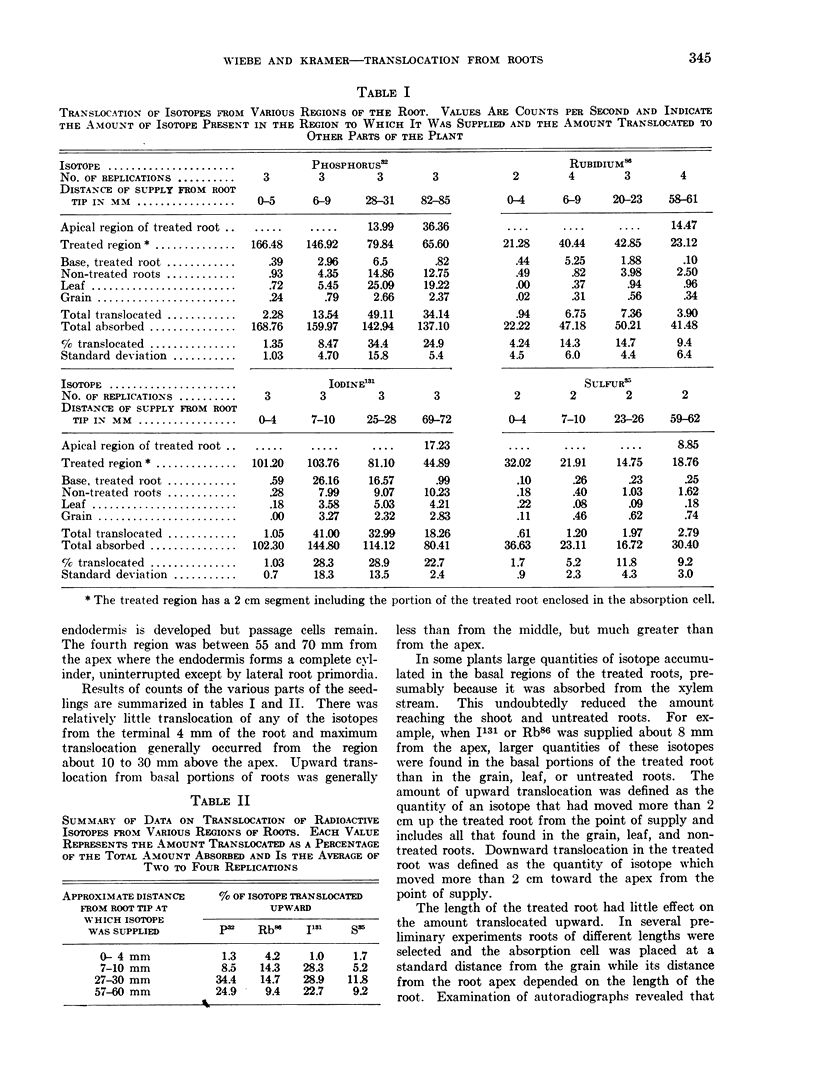
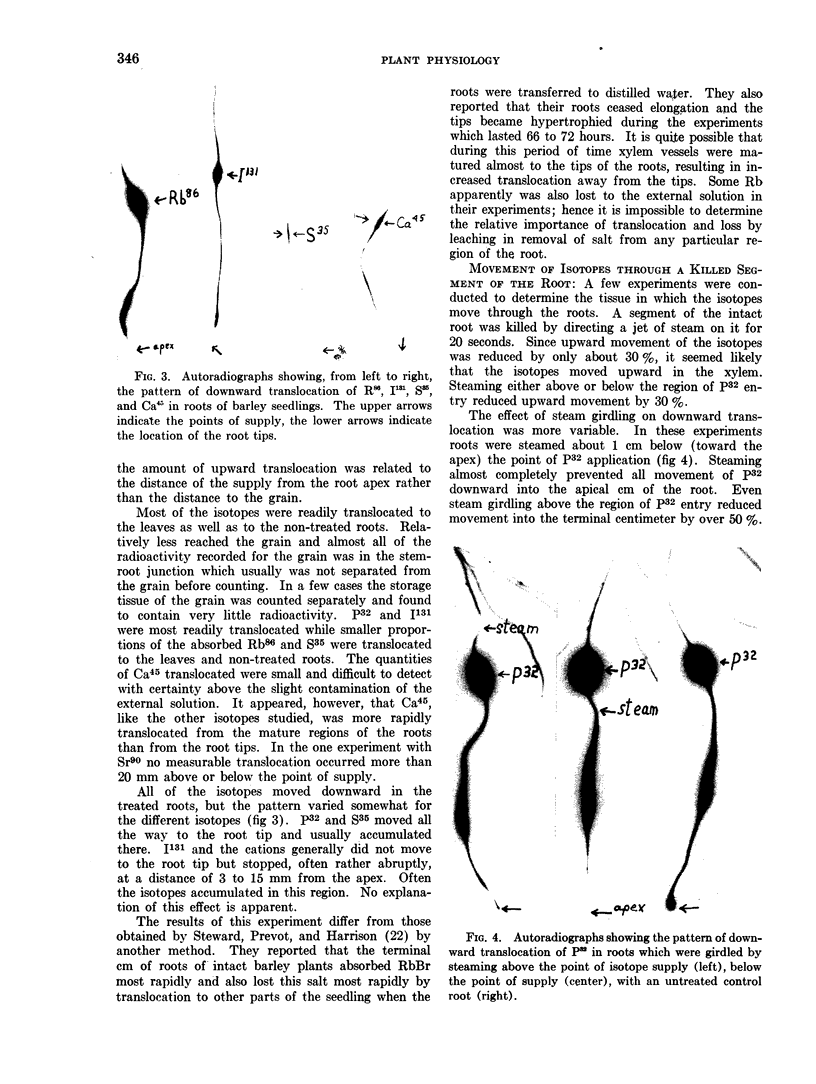
Full text
PDF
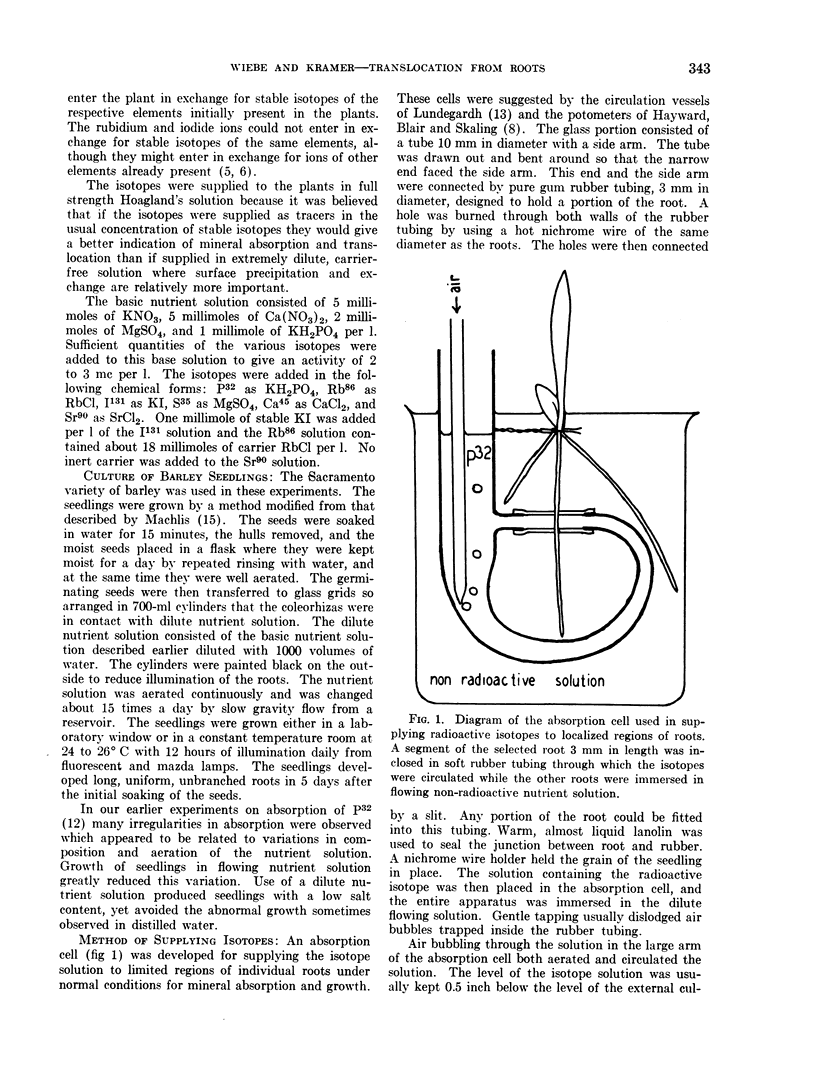



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYD G. A., BOARD F. A. A preliminary report on histochemography. Science. 1949 Dec 2;110(2866):586–588. doi: 10.1126/science.110.2866.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhning R. H., Swanson C. A., Linck A. J. The Effect of Hypocotyl Temperature on Translocation of Carbohydrates from Bean Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1952 Apr;27(2):417–421. doi: 10.1104/pp.27.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Hagen C. E. A KINETIC STUDY OF THE ABSORPTION OF ALKALI CATIONS BY BARLEY ROOTS. Plant Physiol. 1952 Jul;27(3):457–474. doi: 10.1104/pp.27.3.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer P. J., Wiebe H. H. LONGITUDINAL GRADIENTS OF P ABSORPTION IN ROOTS. Plant Physiol. 1952 Oct;27(4):661–674. doi: 10.1104/pp.27.4.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevot P., Steward F. C. SALIENT FEATURES OF THE ROOT SYSTEM RELATIVE TO THE PROBLEM OF SALT ABSORPTION. Plant Physiol. 1936 Jul;11(3):509–534. doi: 10.1104/pp.11.3.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosene H. F. DISTRIBUTION OF THE VELOCITIES OF ABSORPTION OF WATER IN THE ONION ROOT. Plant Physiol. 1937 Jan;12(1):1–19. doi: 10.1104/pp.12.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward F. C., Prevot P., Harrison J. A. ABSORPTION AND ACCUMULATION OF RUBIDIUM BROMIDE BY BARLEY PLANTS. LOCALIZATION IN THE ROOT OF CATION ACCUMULATION AND OF TRANSFER TO THE SHOOT. Plant Physiol. 1942 Jul;17(3):411–421. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]