Abstract
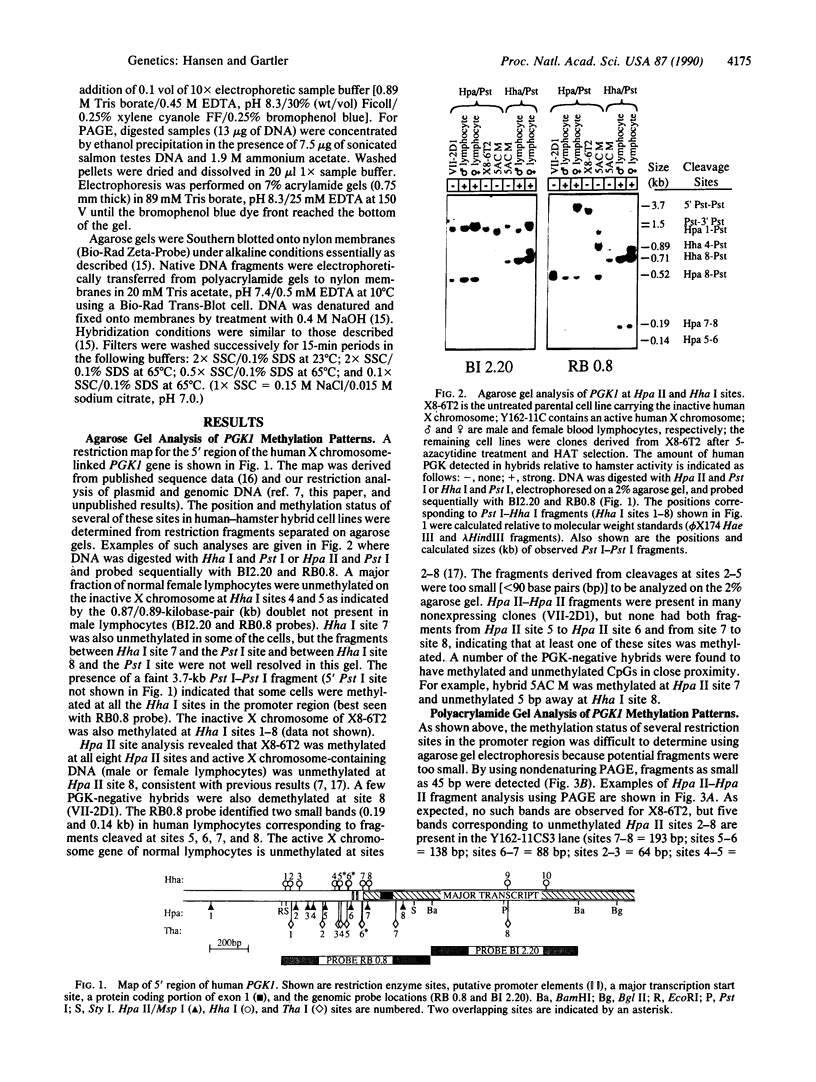
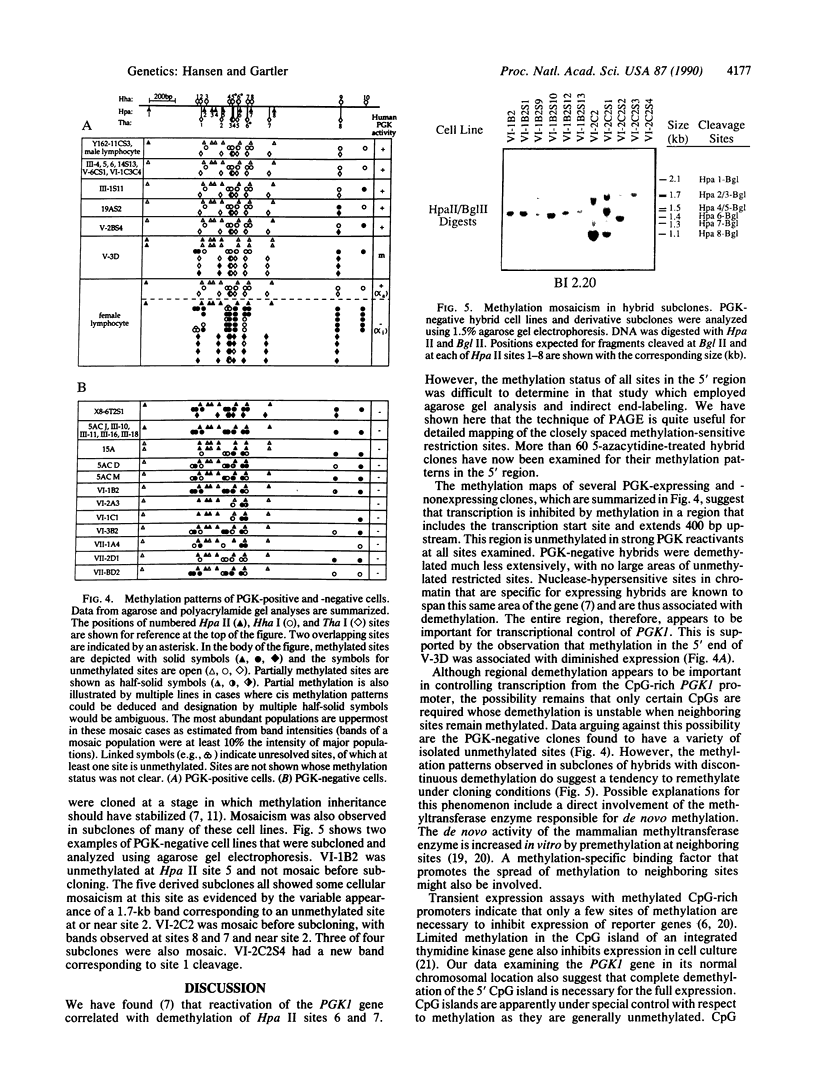
Hamster-human cell hybrids containing an inactive human X chromosome were treated with 5-azacytidine and derived clones were examined for phosphoglycerate kinase activity and cytosine methylation in the human PGK1 (X chromosome-linked phosphoglycerate kinase) gene. Comparisons between expressing and nonexpressing clones indicated that demethylation of several methylation-sensitive restriction sites outside of the 5' CpG island were unnecessary for expression. High-resolution polyacrylamide gel analysis of 25 Hpa II, Hha I, and Tha I sites revealed that all clones expressing PGK1 were unmethylated in a large region of the CpG island that includes the transcription start site and 400 base pairs upstream. Many nonexpressing clones had discontinuous patterns of demethylation. Remethylation was often observed in subclones of nonexpressing hybrids. These data suggest that a specific zone of methylation-free DNA within the PGK1 promoter is required for transcription. In addition, the presence of neighboring methylcytosines appears to decrease the heritable stability of unmethylated CpGs in this region.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P., Taggart M. H., Nicholls R. D., Higgs D. R. Non-methylated CpG-rich islands at the human alpha-globin locus: implications for evolution of the alpha-globin pseudogene. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):999–1004. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04851.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broad P. M., Symes A. J., Thakker R. V., Craig R. K. Structure and methylation of the human calcitonin/alpha-CGRP gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 12;17(17):6999–7011. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.17.6999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevers H., Lonberg N., Dunlap S., Lacy E., Terhorst C. An enhancer located in a CpG-island 3' to the TCR/CD3-epsilon gene confers T lymphocyte-specificity to its promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2527–2535. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrovic A., Gareau J. L., Ouellette G., Bradley W. E. DNA methylation and genetic inactivation at thymidine kinase locus: two different mechanisms for silencing autosomal genes. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Jan;14(1):55–68. doi: 10.1007/BF01535049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dracopoli N. C., Rettig W. J., Albino A. P., Esposito D., Archidiacono N., Rocchi M., Siniscalco M., Old L. J. Genes controlling gp25/30 cell-surface molecules map to chromosomes X and Y and escape X-inactivation. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jan;37(1):199–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorák M., Urbánek P., Bartůnek P., Paces V., Vlach J., Pecenka V., Arnold L., Trávnicek M., Ríman J. Transcription of the chicken myb proto-oncogene starts within a CpG island. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5651–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards Y. H., Charlton J., Brownson C. A non-methylated CpG-rich island associated with the human muscle-specific carbonic anhydrase III gene. Gene. 1988 Nov 30;71(2):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis N., Keitges E., Gartler S. M., Rocchi M. High-frequency reactivation of X-linked genes in Chinese hamster X human hybrid cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 May;13(3):191–204. doi: 10.1007/BF01535202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner-Garden M., Frommer M. CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):261–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. J., Mondello C., Darling S. M., Pym B., Little P., Goodfellow P. N. Absence of methylation of a CpG-rich region at the 5' end of the MIC2 gene on the active X, the inactive X, and the Y chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5605–5609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant S. G., Chapman V. M. Mechanisms of X-chromosome regulation. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:199–233. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen R. S., Ellis N. A., Gartler S. M. Demethylation of specific sites in the 5' region of the inactive X-linked human phosphoglycerate kinase gene correlates with the appearance of nuclease sensitivity and gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4692–4699. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R. The inheritance of epigenetic defects. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):163–170. doi: 10.1126/science.3310230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith D. H., Singer-Sam J., Riggs A. D. Active X chromosome DNA is unmethylated at eight CCGG sites clustered in a guanine-plus-cytosine-rich island at the 5' end of the gene for phosphoglycerate kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4122–4125. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolsto A. B., Kollias G., Giguere V., Isobe K. I., Prydz H., Grosveld F. The maintenance of methylation-free islands in transgenic mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9667–9678. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton J. P., Yen J. Y., Selby E., Chen Z., Chinsky J. M., Liu K., Kellems R. E., Crouse G. F. Dual bidirectional promoters at the mouse dhfr locus: cloning and characterization of two mRNA classes of the divergently transcribed Rep-1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3058–3072. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mays-Hoopes L. L. Age-related changes in DNA methylation: do they represent continued developmental changes? Int Rev Cytol. 1989;114:181–220. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60861-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Wold B. In vivo footprinting of a muscle specific enhancer by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):780–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2814500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray E. J., Grosveld F. Site specific demethylation in the promoter of human gamma-globin gene does not alleviate methylation mediated suppression. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2329–2335. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nur I., Pascale E., Furano A. V. The left end of rat L1 (L1Rn, long interspersed repeated) DNA which is a CpG island can function as a promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9233–9251. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Steigerwald S. D., Mueller P. R., Wold B., Riggs A. D. Genomic sequencing and methylation analysis by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):810–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2814502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Solowiejczyk D., Harpel B., Mory Y., Schwartz E., Surrey S. Construction of human gene libraries from small amounts of peripheral blood: analysis of beta-like globin genes. Hemoglobin. 1982;6(1):27–36. doi: 10.3109/03630268208996930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachal M. J., Yoo H., Becker F. F., Lapeyre J. N. In vitro DNA cytosine methylation of cis-regulatory elements modulates c-Ha-ras promoter activity in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5135–5147. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley D. E., Canfield T. K., Gartler S. M. Chromatin structure of active and inactive human X chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):1829–1845. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto S., Ortaldo J. R., Young H. A. Analysis of the methylation state of the T cell receptor beta chain gene in T cells and large granular lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmookler Reis R. J., Goldstein S. Interclonal variation in methylation patterns for expressed and non-expressed genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 24;10(14):4293–4304. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.14.4293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer-Sam J., Keith D. H., Tani K., Simmer R. L., Shively L., Lindsay S., Yoshida A., Riggs A. D. Sequence of the promoter region of the gene for human X-linked 3-phosphoglycerate kinase. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):409–417. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasseron-de Jong J., Aker J., den Dulk H., van de Putte P., Giphart-Gassler M. Cytosine methylation in the EcoRI site of active and inactive herpesvirus thymidine kinase promoters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jun 1;1008(1):62–70. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach A., Nalin C. M., Ward C. A., Bolden A. H. The effect of flanking sequences on the de novo methylation of C-G pairs by the human DNA methylase. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;198:79–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Migeon B. R. Studies of X chromosome DNA methylation in normal human cells. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):667–671. doi: 10.1038/295667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock D. M., Crowther P. J., Diver W. P., Graham M., Bateman C., Baker D. J., Smith S. S. RglB facilitated cloning of highly methylated eukaryotic DNA: the human L1 transposon, plant DNA, and DNA methylated in vitro with human DNA methyltransferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4465–4482. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang T. P., Singer-Sam J., Flores J. C., Riggs A. D. DNA binding factors for the CpG-rich island containing the promoter of the human X-linked PGK gene. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Sep;14(5):461–472. doi: 10.1007/BF01534712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]