Abstract
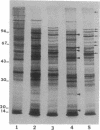
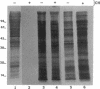
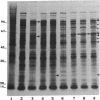
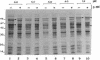
Shigellae were intrinsically radiolabeled with [35S]methionine either extracellularly or while multiplying within infected HeLa cell monolayers. A complex pattern of suppression and induction of proteins was observed. Proteins of approximately 97, 62, 58, 50, 25, and 18 kilodaltons (kDa) were induced in Shigella flexneri isolated from infected monolayers. Proteins of 100, 85, 70, 64, and 55 kDa were suppressed under the same conditions but were seen in cells labeled in the tissue culture medium alone. Protein expression during the stages of attachment, invasion, and intracellular multiplication was examined by pulse-labeling. The 58-kDa protein was induced only during invasion, and the 62- and 25-kDa proteins were induced only during intracellular multiplication. Shift into a minimal medium with ion concentrations and pH mimicking intracellular conditions and endosomal pH resulted in the induction of the 97- and 58-kDa proteins, and reduction of the intracellular-like medium with 2-mercaptoethanol resulted in the induction of the 97-, 50-, and 25-kDa proteins and suppression of the 55-kDa protein. Radioimmunoprecipitations of shigellae grown in vitro and in vivo revealed differential expression of immunogenic proteins. Proteins corresponding in size to IpaB (62 kDa), IpaC (42 kDa), and IpaD (38 kDa) were lost during intracellular multiplication, whereas another protein corresponding to IpaA (80 kDa) was found to increase under the same conditions.
Full text
PDF

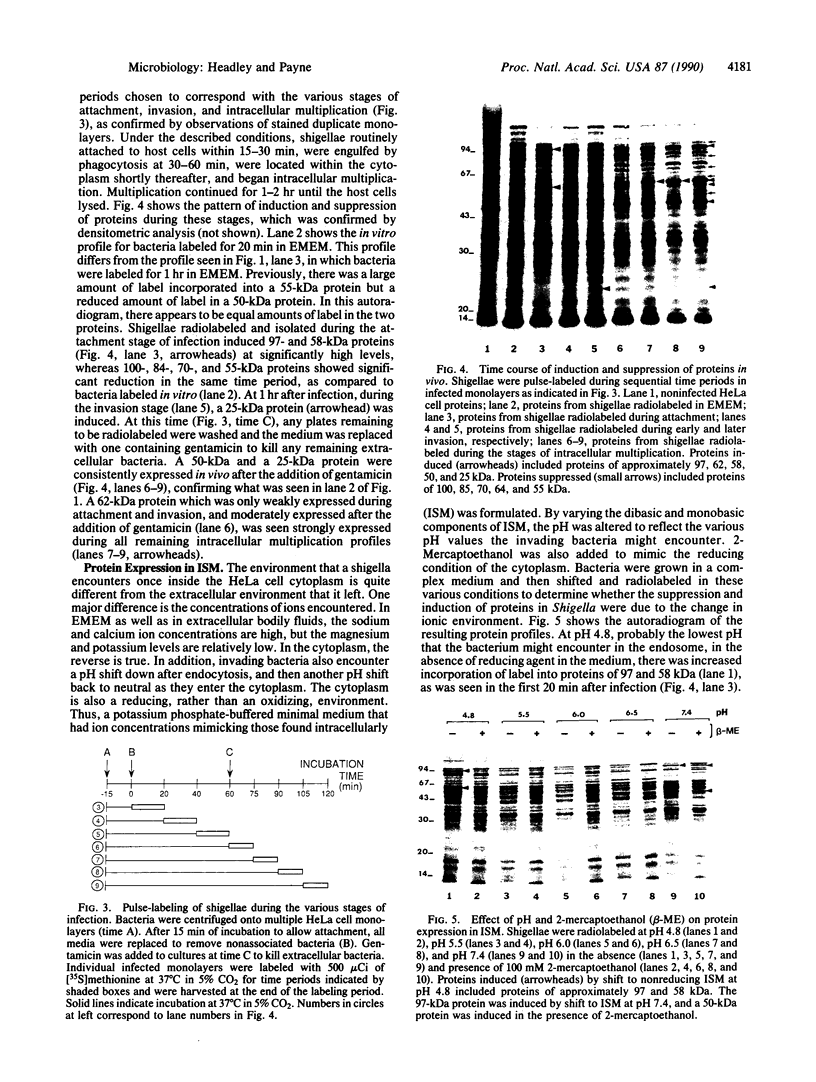


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baudry B., Maurelli A. T., Clerc P., Sadoff J. C., Sansonetti P. J. Localization of plasmid loci necessary for the entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells, and characterization of one locus encoding four immunogenic polypeptides. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Dec;133(12):3403–3413. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-12-3403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. Growth of Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis in simulated intracellular and extracellular environments. J Infect Dis. 1967 Dec;117(5):403–417. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.5.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P., Baudry B., Sansonetti P. J. Plasmid-mediated contact haemolytic activity in Shigella species: correlation with penetration into HeLa cells. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 May-Jun;137A(3):267–278. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P., Sansonetti P. J. Entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells: evidence for directed phagocytosis involving actin polymerization and myosin accumulation. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2681–2688. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2681-2688.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daskaleros P. A., Payne S. M. Congo red binding phenotype is associated with hemin binding and increased infectivity of Shigella flexneri in the HeLa cell model. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1393–1398. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1393-1398.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Heffron F., Falkow S. Epithelial cell surfaces induce Salmonella proteins required for bacterial adherence and invasion. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):940–943. doi: 10.1126/science.2919285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Gemski P., Baron L. S., Labrec E. H. Genetic Transfer of Shigella flexneri Antigens to Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):279–287. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.279-287.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T., Todd W. J., Caldwell H. D. Disulfide-mediated interactions of the chlamydial major outer membrane protein: role in the differentiation of chlamydiae? J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):25–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.25-31.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T., Williams J. C. Biochemical stratagem for obligate parasitism of eukaryotic cells by Coxiella burnetii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3240–3244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Formal S. B. Protein synthesis in HeLa or Henle 407 cells infected with Shigella dysenteriae 1, Shigella flexneri 2a, or Salmonella typhimurium W118. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.137-144.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Loss of pigmentation in Shigella flexneri 2a is correlated with loss of virulence and virulence-associated plasmid. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):397–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.397-401.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Temperature-dependent expression of virulence genes in Shigella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):195–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.195-201.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Taylor R. K., Mekalanos J. J. Cholera toxin transcriptional activator toxR is a transmembrane DNA binding protein. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. A., Buysse J. M., Oaks E. V. Shigella flexneri invasion plasmid antigens B and C: epitope location and characterization with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2933–2941. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2933-2941.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):298–337. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.298-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks E. V., Hale T. L., Formal S. B. Serum immune response to Shigella protein antigens in rhesus monkeys and humans infected with Shigella spp. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.57-63.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. Detection and differentiation of iron-responsive avirulent mutants on Congo red agar. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):94–98. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.94-98.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Niesel D. W., Peixotto S. S., Lawlor K. M. Expression of hydroxamate and phenolate siderophores by Shigella flexneri. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):949–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.949-955.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeling R. W., Peeling J., Brunham R. C. High-resolution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance study of Chlamydia trachomatis: induction of ATPase activity in elementary bodies. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3338–3344. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3338-3344.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pál T., Newland J. W., Tall B. D., Formal S. B., Hale T. L. Intracellular spread of Shigella flexneri associated with the kcpA locus and a 140-kilodalton protein. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):477–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.477-486.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Sakai T., Makino S., Yamada M., Okada N., Yoshikawa M. Virulence-associated genetic regions comprising 31 kilobases of the 230-kilobase plasmid in Shigella flexneri 2a. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2480–2484. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2480-2484.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. Mechanisms of receptor function and the molecular biology of information processing in bacteria. Bioessays. 1987 May;6(5):199–203. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Bowmer W. S. Virulence genes regulated at the transcriptional level by Ca2+ in Yersinia pestis include structural genes for outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):445–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.445-454.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Miller V. L., Furlong D. B., Mekalanos J. J. Use of phoA gene fusions to identify a pilus colonization factor coordinately regulated with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]