Abstract
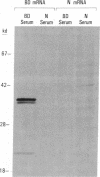
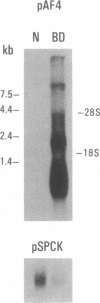
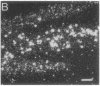
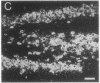
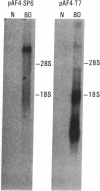
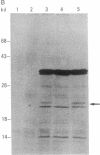
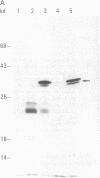
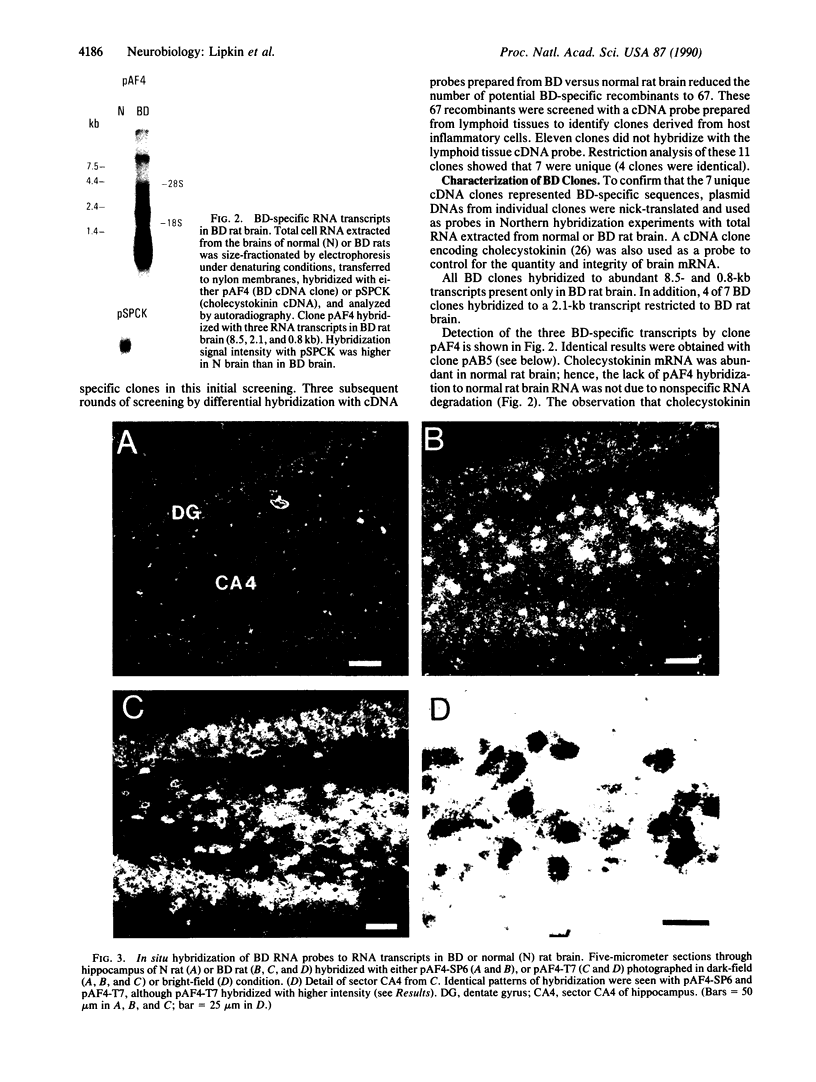
Borna disease (BD) is a neurologic syndrome characterized by behavioral disturbances and the accumulation of specific proteins in limbic system neurons. A viral etiology has been proposed because BD can be induced in birds, rodents, and primates by inoculation with filtered brain homogenates from animals with BD. We report here the isolation and preliminary characterization of cDNA clones from a rat with BD. These clones hybridized to specific transcripts in BD rat brain and arrested in vitro translation of BD proteins. In situ hybridization experiments using RNA probes prepared from these clones showed an abundance of these transcripts in limbic system neurons. Northern (RNA) hybridizations using these RNA probes indicated that the BD agent is probably a virus with major transcripts of 8.5, 2.1, and 0.8 kilobases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amsterdam J. D., Winokur A., Dyson W., Herzog S., Gonzalez F., Rott R., Koprowski H. Borna disease virus. A possible etiologic factor in human affective disorders? Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1985 Nov;42(11):1093–1096. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1985.01790340077011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode L., Riegel S., Ludwig H., Amsterdam J. D., Lange W., Koprowski H. Borna disease virus-specific antibodies in patients with HIV infection and with mental disorders. Lancet. 1988 Sep 17;2(8612):689–689. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90505-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone K. M., Duchala C. S., Griffin J. W., Kincaid A. L., Narayan O. Pathogenesis of Borna disease in rats: evidence that intra-axonal spread is the major route for virus dissemination and the determinant for disease incubation. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3431–3440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3431-3440.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschenes R. J., Lorenz L. J., Haun R. S., Roos B. A., Collier K. J., Dixon J. E. Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA encoding rat preprocholecystokinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M. B., Dawid I. B. Use of a cloned library for the study of abundant poly(A)+RNA during Xenopus laevis development. Dev Biol. 1980 May;76(2):449–464. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas B., Becht H., Rott R. Purification and properties of an intranuclear virus-specific antigen from tissue infected with Borna disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Feb;67(Pt 2):235–241. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin W. I., Carbone K. M., Wilson M. C., Duchala C. S., Narayan O., Oldstone M. B. Neurotransmitter abnormalities in Borna disease. Brain Res. 1988 Dec 20;475(2):366–370. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90627-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig H., Bode L., Gosztonyi G. Borna disease: a persistent virus infection of the central nervous system. Prog Med Virol. 1988;35:107–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig H., Kraft W., Kao M., Gosztonyi G., Dahme E., Krey H. Borna-Virus-Infektion (Borna-Krankheit) bei natürlich und experimentell infizierten Tieren: ihre Bedeutung für Forschung und Praxis. Tierarztl Prax. 1985;13(4):421–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Herzog S., Frese K., Scheefers H., Rott R. Behavioral disease in rats caused by immunopathological responses to persistent borna virus in the brain. Science. 1983 Jun 24;220(4604):1401–1403. doi: 10.1126/science.6602380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Roberts B. E., Kuff E. L. Structural gene identification and mapping by DNA-mRNA hybrid-arrested cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4370–4374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Hennighausen L., Taub R., DeGrado W., Leder P. Antibodies to human c-myc oncogene product: evidence of an evolutionarily conserved protein induced during cell proliferation. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):687–693. doi: 10.1126/science.6431612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schädler R., Diringer H., Ludwig H. Isolation and characterization of a 14500 molecular weight protein from brains and tissue cultures persistently infected with borna disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Nov;66(Pt 11):2479–2484. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-11-2479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprankel H., Richarz K., Ludwig H., Rott R. Behavior alterations in tree shrews (Tupaia glis, Diard 1820) induced by Borna disease virus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1978 May 26;165(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF02121228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis G. H., Sutcliffe J. G. Phenol emulsion-enhanced DNA-driven subtractive cDNA cloning: isolation of low-abundance monkey cortex-specific mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1696–1700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]