Abstract
Upon cardiac pathological conditions such as ischemia, microenvironmental changes instruct a series of cellular responses that trigger cardiac fibroblasts-mediated tissue adaptation and inflammation. A comprehensive model of how early environmental changes may induce cardiac fibroblasts (CF) pathological responses is far from being elucidated, partly due to the lack of approaches involving complex and simultaneous environmental stimulation. Here, we provide a first analysis of human primary CF behavior by means of a multi-stimulus microdevice for combined application of cyclic mechanical strain and controlled oxygen tension. Our findings elucidate differential human CFs responses to different combinations of the above stimuli. Individual stimuli cause proliferative effects (PHH3+ mitotic cells, YAP translocation, PDGF secretion) or increase collagen presence. Interestingly, only the combination of hypoxia and a simulated loss of contractility (2% strain) is able to additionally induce increased CF release of inflammatory and pro-fibrotic cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22847.001
Research Organism: Human
eLife digest
When the supply of oxygen to the heart is reduced, its cells start to die within hours, the heart muscle becomes less able to contract, and the area becomes inflamed. This inflammation is accompanied by an influx of immune cells. It also activates other cells known as cardiac fibroblasts that help to break down the framework of molecules that supported the damaged heart tissue and replace it with a scar. This response is part of the normal repair process, but it can lead to the formation of scar tissue in non-damaged areas of the heart. Excess scar tissue makes the heart muscle less able to contract and increases the affected individual’s chance of dying.
Understanding how this repair process works is an important step in developing strategies to minimise the damage caused by coronary artery disease or heart attacks. However, existing laboratory models are only partly able to recreate the conditions seen in real heart tissue. To properly understand the response at the level of living cells, a more complete model is needed.
Ugolini et al. now report improvements to a small device, referred to as a lab-on-chip, that can subject cells to mechanical strain. The improvements mean the device could also recreate other conditions seen early on in damaged heart tissue, specifically the reduced supply of oxygen. Replicating combinations of mechanical changes and oxygen supplies meant that the impact of these conditions on human cardiac fibroblasts could be directly observed in the laboratory for the first time. Ugolini et al. found that a lack of contraction and low oxygen levels triggered the cardiac fibroblasts to produce inflammatory molecules and molecules associated with the formation of scar tissue. This resembles the response seen in living hearts.
The next step is to improve the lab-on-chip device further by adding other cell types, including heart muscle cells and immune cells. A more complete model may aid future research into how our hearts operate in both health and disease.
Introduction
When supply of oxygen and nutrients to the myocardium is critically reduced (ischemia), a complex tissue response takes place: within hours tissue necrosis and death of contractile cardiac myocytes occurs in the infarcted area giving rise to an inflammatory phase that recruits immune cells and activates quiescent cardiac fibroblasts (CFs); within a few days a proliferative phase begins, where activated CFs invade the infarcted area and contribute to degrading and replacing the extra-cellular matrix with a collagen-based scar; within weeks the maturation of the fibrotic scar is completed (Frangogiannis, 2014; Heusch et al., 2014). Cellular and molecular events such as excessive proliferation of CFs, phenotypic switch of CFs, high levels of inflammatory cytokines and humoral factors, unbalanced synthesis of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins and matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-mediated degradation of ECM are generally regarded as hallmarks of early fibrotic tissue response (Fan et al., 2012; Krenning et al., 2010; Porter and Turner, 2009; Shinde and Frangogiannis, 2014). This essential process maintains tissue integrity, however, it often leads to excessive and adverse CFs remodeling of non-infarcted areas (Fan et al., 2012; Kania et al., 2009; Talman and Ruskoaho, 2016) associated with cardiac dysfunction and increased mortality (Okada et al., 2005). Controlled anti-fibrotic strategies still require deeper understanding and advanced models of cardiac fibrosis mechanisms (Leask, 2010; Roubille et al., 2014).
In general, the onset of pathological myocardial conditions causes alterations of specific environmental cues at the cellular scale: mechanical strain decreases (loss of contractility); oxygen and nutrient levels dramatically decrease (ischemia); levels of inflammatory cytokines increase (post-injury inflammatory response). In an attempt to provide in vitro models of cardiac disease, CFs have been widely studied under relevant physico-chemical stimulation such as mechanical stress (Schroer and Merryman, 2015; Tomasek et al., 2002), oxygen deprivation (Clancy et al., 2007; Tamamori et al., 1997) and biochemical stimulation with pro-fibrotic cytokines (Edgley et al., 2012; Lijnen et al., 2000; Petrov et al., 2002). The application of mechanical stress has been shown to have the following effects on CFs: increased ECM protein synthesis (Carver et al., 1991); controversial proliferative behavior (Atance et al., 2004; Butt and Bishop, 1997; Dalla Costa et al., 2010; Liao et al., 2004), with recent reports of strain intensity-dependent effects (Ugolini et al., 2016); increased production of pro-fibrotic and inflammatory cytokines such as TGF-β (transforming growth factor-beta) (Leask, 2007) and TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-alpha) (Yokoyama et al., 1999).
While previous mechanical stress experiments were performed in a normoxic environment (NX, approximately 20% O2, the standard oxygen level of ambient air), CFs were shown to be sensitive to O2 level variations from physoxia (PX), defined as the physiologic oxygen level in living tissues (about 5–6% O2 in the myocardium [Gonschior et al., 1992; Roy et al., 2003; Sen et al., 2006; Winegrad et al., 1999]). Both hypoxia (HX, 1–3% O2) and NX induce a pro-inflammatory and fibrogenic phenotype in cultured CFs (Roy et al., 2003; Sen and Roy, 2010). These findings imply that normoxic oxygen levels are perceived by CFs as a state of hyperoxia and that a significant bias exists when culturing CFs in non-physiological oxygen environments. The exposure of CFs to HX has been shown to induce collagen production and proliferation of CFs (Gao et al., 2014; Tamamori et al., 1997), while studies suggest that MMP-based remodeling may not be triggered by HX alone (Riches et al., 2009).
Given the complexity of in vivo pathological evolution, the elucidation of how environmental stimuli interplay and guide cellular responses is paramount. To date, no comprehensive model is able to recapitulate early cellular events taking place after acute myocardial injury and there is no report of cardiac cells subjected to simultaneous mechanical strain and controlled oxygen changes, two major environmental variables involved in cardiac injury and CF adaptive responses. This is mostly due to the lack of compact platforms enabling the controlled application of multiple stimuli.
To address this need, we here report the improvement of a previously described multi-chamber microdevice dedicated to the application of cyclic strain to cell monolayers (Ugolini et al., 2016). By adding a system for controlling oxygen changes, we significantly expanded the experimental complexity and mimicking capabilities of the device. We here finely controlled the applied mechanical strain and oxygen regimes sensed by CFs to model early environmental changes in cardiac injury and provide insights into individual or synergistic contributions of the environmental signals in the activation of early CF responses relevant to cardiac fibrotic disease. Shortly after an ischemic myocardial insult (e.g., acute coronary artery occlusion) tissue oxygen levels drop from approximately 5–6% O2 (Gonschior et al., 1992; Sen et al., 2006; Winegrad et al., 1999) to near-zero (Roy et al., 2003), rapidly inducing loss of cardiac myocytes contractility. In terms of in vitro model parameters, we thus selected 5% O2 (PX) as a physiological oxygen level and 1% O2 (HX) as an oxygen level characteristic of ischemic myocardial injury. Dramatic alterations of injured myocardial tissue also take place in early timeframes: tissue bulging and dilations are commonly observed together with loss of contractile function (Eek et al., 2010; Pfeffer and Braunwald, 1990; Picard et al., 1990; Tennant and Wiggers, 1935). Cardiac imaging studies agree in the interpretation that global strains are abruptly reduced shortly after myocardial insult (Flachskampf et al., 2011; Hoit, 2011; Mollema et al., 2010). Quantitatively, strain values recorded vary significantly throughout the heart. Although absolute values may depend on imaging algorithms, strains in ischemic/injured regions have been reported to be 2–4 fold lower than in healthy myocardial regions (e.g. less than 3% in ischemic regions versus approximately 10% in healthy regions [Dandel et al., 2009; Vartdal et al., 2007]). Within this range and in line with previous in vitro observations of CFs behavior (Ugolini et al., 2016), we selected 2% strain as indicative of reduced contractility and 8% strain as representative of full myocardial contractility. These environmental changes and the following initial cellular responses happen in a timeframe of hours, as shown in vitro (van Nieuwenhoven et al., 2013; Turner et al., 2007, 2009) as well as in vivo (Guillén et al., 1995; Morishita et al., 2015). We thus performed experiments lasting 24 hr and evaluated the main early aspects that govern fibrotic responses in the injured myocardium: ECM remodeling, with stainings for collagen I and quantifications of MMP expression; proliferation of CFs, with analyses of mitotic cells, Hippo pathway signaling and mitogenic PDGF (platelet-derived growth factor) expression; secretion of inflammatory and pro-fibrotic cytokines in CF supernatants; myofibroblast differentiation, through stainings for αSMA (α-smooth muscle actin). Results of our investigation provide insights into how the combination of environmental stimuli may act synergistically or independently to drive in vitro adaptive early CF responses.
Results
ECM remodeling
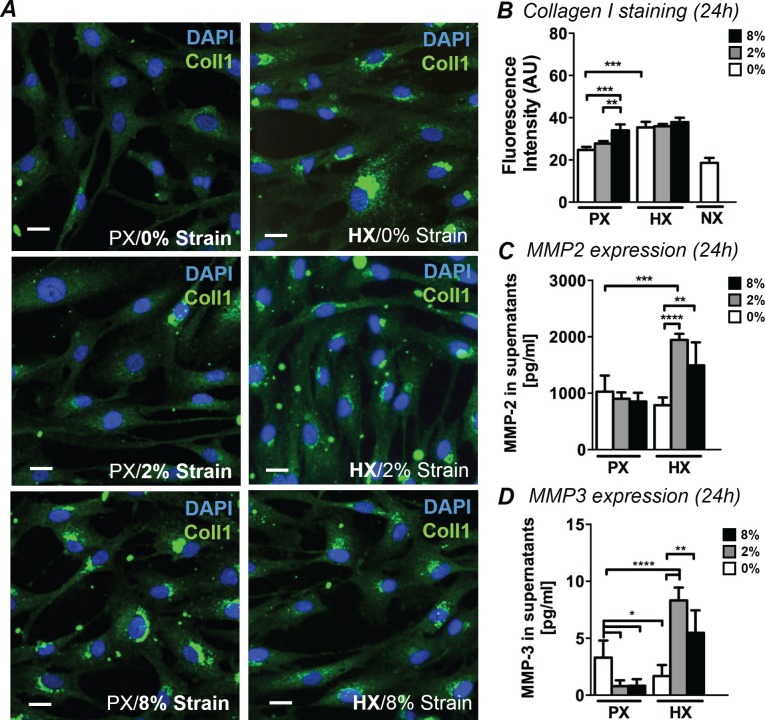
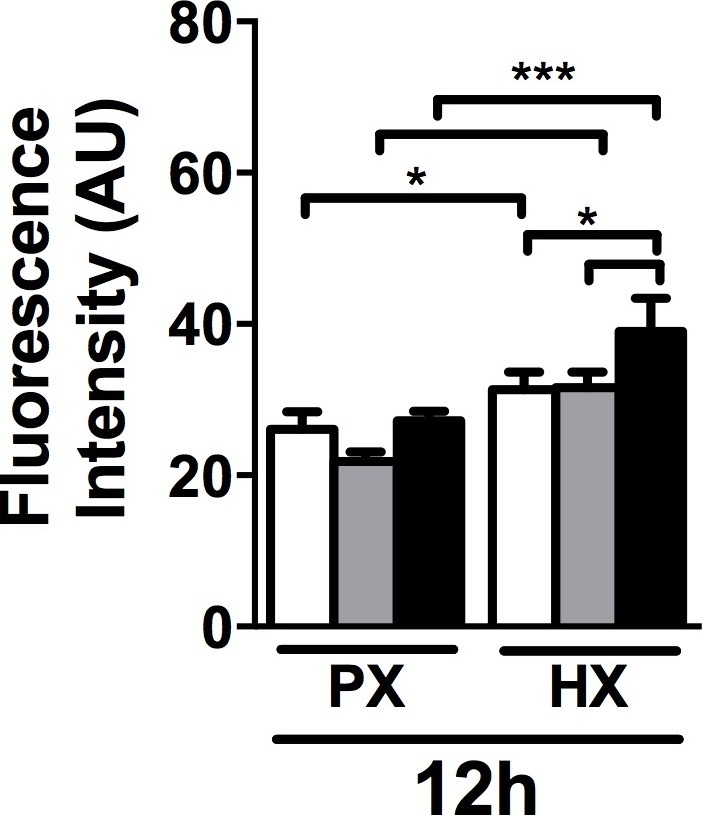
Myocardial pathological remodeling is largely based on unbalanced CF production of collagen I and MMP-mediated matrix remodeling. To analyze CF-mediated early remodeling events under combined stimulations, we analyzed immunofluorescence images of CFs stained for collagen I. In addition, we quantified the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-3 in cell culture supernatants, two enzymes specifically expressed by CFs during cardiac remodeling (Fan et al., 2012). While CFs normally exhibit diffuse cytoplasmic staining for collagen I, an intense staining localized to perinuclear regions of CFs was observed after 24 hr under specific stimulations (Figure 1A). Based on analysis of intracellular fluorescence intensity, we found that the increase in collagen I was similarly triggered by HX alone and 8% strain alone (Figure 1B). No significant synergy was found for the two stimulations: levels of collagen I are similarly elevated in all HX conditions regardless of strain applied. Correspondingly, collagen I staining exhibits similar intensity in all 8% strain conditions regardless of the oxygen stimulation employed. After only 12 hr of stimulation, collagen I fluorescence showed similar trends, with the exception of HX combined with 8% cyclic strain which provided a greater synergistic effect compared to the single stimulations (Figure 1—figure supplement 1). We also report that culturing CFs at NX levels does not induce significant changes in collagen I presence.
Figure 1. Analyses of early ECM adaptive responses by CFs subject to combined environmental stimulation.
(A) Representative images of CFs fixed after 24 hr stimulations and stained for collagen I (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 20 μm. An intense perinuclear staining is observed in CFs stimulated either by 8% mechanical strain or by HX. (B) Quantitative fluorescence intensity analyses on Collagen I staining plotted as graph. Collagen I staining is increased by HX, 8% strain or NX conditions. Data collected from one cell donor, two independent experiments, minimum number of experimental replicates n = 4, technical replicates (multiple images per replicate) n = 3. Detected amounts of MMP-2 (C) and MMP-3 (D) in supernatants of CFs. Both MMP-2 and MMP-3 expression is significantly increased in combined HX and mechanical strain stimulation. Protein secretion data collected from one cell donor, two independent experiments, minimum number of experimental replicates n = 4, technical replicates n = 2. White histograms correspond to 0% strain conditions, grey histograms to 2% strain conditions and black histograms to 8% strain conditions. Two-way ANOVA test was performed for all groups. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. One outlier measurement in MMP-3 expression was detected by performing Grubb’s test (α = 0.05; p<0.05) and removed from the analysis.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22847.003
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Quantitative fluorescence intensity analyses on collagen I staining performed on CFs fixed after 12 hr of combined stimulation.
The expression of MMP-2 and MMP-3 in CFs supernatants (Figure 1CD) was significantly influenced by combined mechanical strain and oxygen changes. MMP-2 was more prominently expressed than MMP-3 (>100X higher). Nevertheless, the expression of both enzymes was similarly regulated by the pattern of stimulations applied: a significant two-fold increase in MMP-2 and MMP-3 expression was induced by the combination of HX and mechanical strain, with a more pronounced increase observed in the HX/2% strain combined conditions. MMP-3 expression was negatively affected when CFs were subjected to mechanical strain at PX or HX stimulus alone.
Cell proliferation
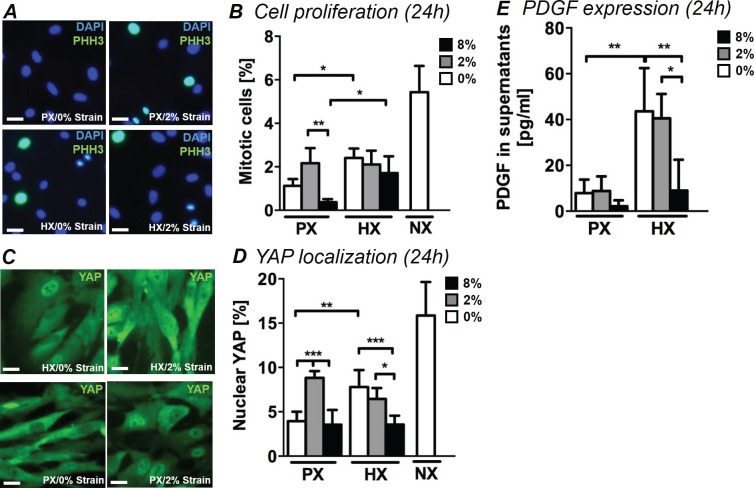
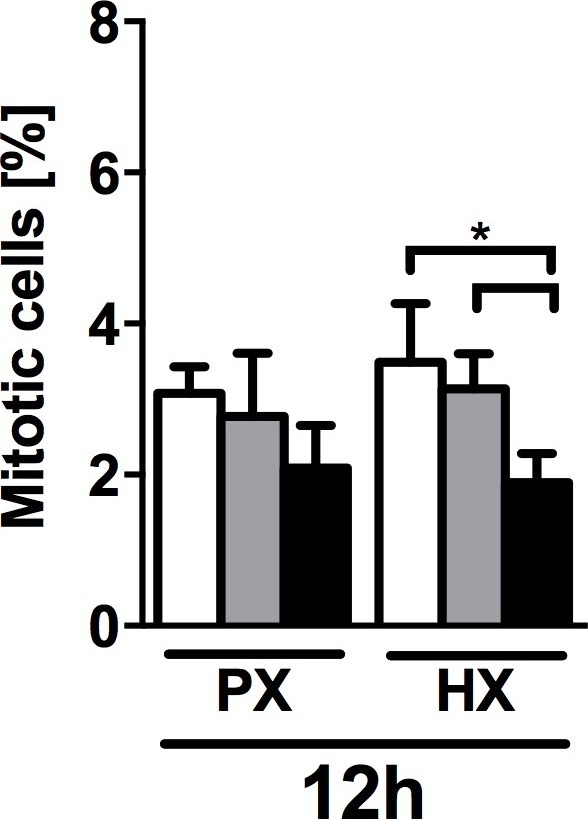
During the proliferative phase of myocardial healing, excessive CF proliferation is observed as well as a phenotypic switch giving rise to the fibrotic response. In order to understand how environmental stimuli modulate the proliferation of human CFs, we examined the fraction of mitotic cells (PHH3+/DAPI) under combined mechanical stimulation and changes in oxygen tension. Figure 2A shows representative images of CFs stained for PHH3 and DAPI. Without application of cyclic strain, we observed a two-fold significant increase in the number of mitotic cells (Figure 2B) when CFs were stimulated with HX compared to their PX counterparts. Mechanical strain significantly impacted cell proliferation within the PX culture condition: culturing CFs at PX and subjecting them to 2% strain induced a striking increase in mitotic cells compared to no strain control and 8% strain cultures. This strain intensity-dependent effect is in line with our previous investigations of CF proliferation under mechanical strain in NX conditions (Ugolini et al., 2016). After 12 hr of stimulation, the proliferative increase with HX is not statistically significant, while we report a significant synergistic decrease of mitotic cells induced by the combination of 8% strain and HX (Figure 2—figure supplement 1).
Figure 2. Analyses of CFs proliferation under combined environmental stimulation.
(A) Representative images of CFs fixed after 24 hr stimulations and stained for PHH3 (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 50 μm. (B) Quantitative analyses of mitotic cell fraction plotted as graph. Cell mitosis is increased by either HX alone and by 2% strain at PX. (C) Representative images of CFs fixed after 24 hr stimulations and stained for YAP (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 50 μm. (D) Quantitative analyses of cells presenting nuclear YAP plotted as graph. YAP translocation into nuclei is increased by either HX or by 2% strain at PX. Data in Panels B and D were collected from one cell donor, two independent experiments, minimum number of experimental replicates n = 4, technical replicates (multiple images per replicate) n = 3. (E) Detected amounts of PDGF in supernatants of CFs plotted as graph. PDGF expression is significantly increased in HX alone and HX combined with mechanical strain stimulation (2% strain). Protein secretion data collected from one cell donor, two independent experiments, minimum number of experimental replicates n = 4, technical replicates n = 2. White histograms correspond to 0% strain conditions, grey histograms to 2% strain conditions and black histograms to 8% strain conditions. Two-way ANOVA test was performed for mitotic cells and nuclear YAP, whereas Kruskal-Wallis test was performed on PDGF expression. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22847.006
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Quantification of mitotic cells (PHH3+/DAPI) performed on CFs fixed after 12 hr of combined stimulation (PX, HX and mechanical strain).
In addition, we performed mitotic cell counts on CFs cultured under NX conditions without mechanical strain in order to evaluate any influence of non-physiological oxygen environments on CF proliferation. Interestingly, CFs exhibited much greater mitosis under NX environments (approx. 5% mitotic cells) compared to PX environments (approx. 1% mitotic cells) denoting a strong proliferative effect of standard cell culture environments.
Further, we evaluated the effects of the environmental changes on YAP, a transcription factor mainly known as the principal effector of the Hippo proliferative pathway, a crucial pathway involved in cardiac regeneration and repair (Papizan and Olson, 2014; Xin et al., 2013). Recent literature has also described a parallel mechano-sensing associated role of YAP (Dupont et al., 2011; Mosqueira et al., 2014). YAP translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus leads to inactivation of Hippo pathway and a subsequent increase in cell proliferation. We therefore quantified nuclear localization of YAP by means of immunofluorescence, which revealed that the fraction of CFs displaying nuclear YAP is influenced by the combination of stimuli with trends similar to the fraction of mitotic cells (Figure 2C,D). In CFs cultured at PX, 2% strain induces higher YAP translocation into cell nuclei. CFs solely exposed to HX environment show a significant two-fold increase in nuclear YAP compared to a PX environment. Mechanical strain shows a negative interaction when combined with HX, with CFs subject to HX/8% strain condition showing lower fractions of nuclear YAP compared to CFs subject to HX alone. This effect can also be observed in the analysis of mitotic cells, although the result is not statistically significant. Interestingly, CFs cultured in an NX environment show a three-fold increase in nuclear YAP compared to PX conditions.
Finally, we detected the expression of PDGF in CF supernatants. PDGF has been described as a potent mitogen for CFs, is significantly over-expressed in in vivo models of heart injury (Zhao et al., 2011), and has recently been studied as a putative pharmacological target for attenuating adverse effects of cardiac fibrotic disease (Liu et al., 2014). Expression of PDGF in CF culture supernatant (Figure 2E) was significantly affected by HX stimulation: a four-fold increase in the detected amounts of PDGF was observed in HX compared to PX, without application of cyclic strain. Mechanical stimulation showed a negative interaction with the HX-induced secretion of PDGF: while levels of PDGF expression remain elevated under HX/2% strain, application of 8% cyclic strain shows a negative regulation of PDGF secretion back to PX levels of expression.
Cytokine secretion
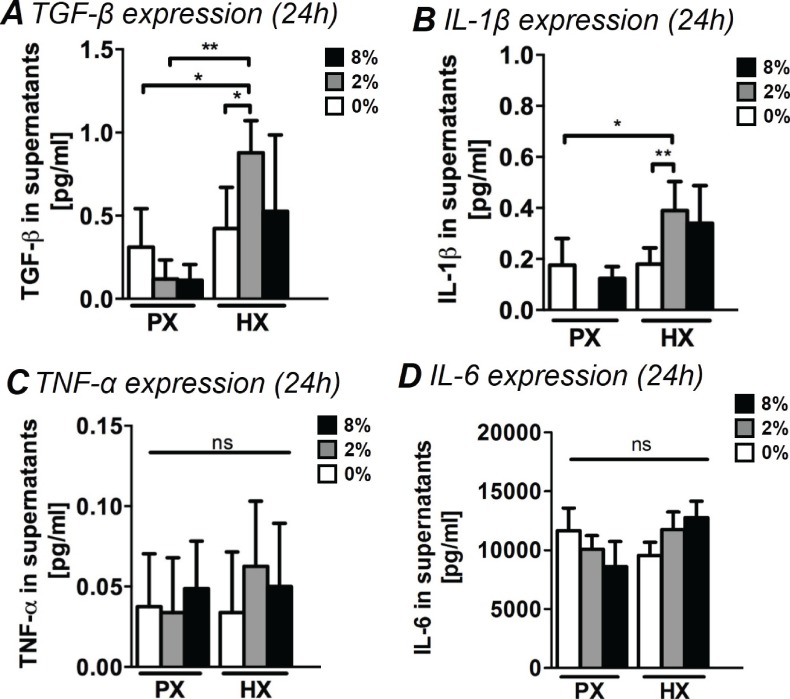
Acute inflammatory tissue responses after myocardial injuries are thought to be largely based on cellular signaling by means of secreted factors. The precise contribution of CFs in the regulation of the early inflammatory response in myocardial remodeling is still to be determined, however, recent reports suggest that CFs play a key role in modulating a functional inflammasome that includes inflammatory and pro-fibrotic cytokines (Kawaguchi et al., 2011; Lindner et al., 2014; Turner, 2016). We therefore studied the amount of inflammatory cytokines (namely interleukins IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α) and of pro-fibrotic TGF-β in CF culture supernatants after 24 hr of combined stimulations (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Analyses of pro-fibrotic and pro-inflammatory cytokines in supernatants of CFs.
(A) TGF-β expression in supernatants. TGF-β expression resulted significantly increased by the combination of HX and mechanical strain (2% strain). (B) Expression of IL-1β in CFs supernatants. IL-1β expression resulted significantly upregulated by the combination of HX and mechanical strain (2% strain). (C) TNF-α expression in supernatants. Extremely low amounts were detected and environmental stimulations do not induce significant differences in the expression. (D) IL-6 expression in supernatants. IL-6 resulted abundantly expressed by CFs with no statistically significant differences induced by environmental stimulations. Protein secretion data from each marker was collected from one cell donor, two independent experiments, minimum number of experimental replicates n = 4, technical replicates n = 2. White histograms correspond to 0% strain conditions, grey histograms to 2% strain conditions and black histograms to 8% strain conditions. Kruskal-Wallis tests were performed for all groups except for IL-6 analyzed with Two-way ANOVA tests. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ns = non-significant.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22847.009
TGF-β is a major contributor to fibrotic responses, widely studied across a variety of tissues and organs. During post-injury myocardial remodeling, TGF-β is known to stimulate a wide range of CF responses from phenotypic switch to collagen synthesis and ECM remodeling (Leask, 2007). CFs stimulated with a combination of HX and mechanical strain (specifically 2% strain) were found to increase secretion of TGF-β by approximately two-fold. CFs cultured at PX expressed lower amounts of TGF-β, regardless of the mechanical strain applied (Figure 3A).
IL1-β is one of the first cytokines detected in vivo after myocardial injury (Guillén et al., 1995) and is known to stimulate CF response including the production of MMPs (Brown et al., 2007; Guo et al., 2008; Siwik et al., 2000). Interestingly, we found that a significant two-fold increase in IL1-β expression occurred only when CFs were subjected to the combination of HX and mechanical strain, particularly with 2% strain (Figure 3B).
Conversely, we observed how the expression of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 was not influenced by the application of environmental stimuli. We detected extremely low amounts of TNF-α (Figure 3C), with non-significant variations across all stimulation conditions. IL-6 (Figure 3D) was abundantly expressed by CFs yet none of the differences in its expression were found to be statistically significant.
Myofibroblast differentiation
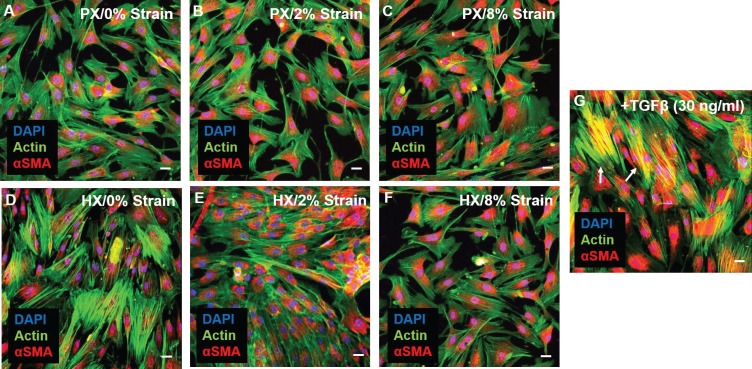
In the remodeling myocardium, CFs undergo a phenotypic modulation to myofibroblasts, a motile and contractile cell type that maintains tissue integrity and promotes scar formation and tissue fibrosis (Santiago et al., 2010). The hallmark of this phenotype switch is the expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin (αSMA) that, by being incorporated into actin stress fibers, confers increased mechanical and motile capabilities to differentiated myofibroblasts (Baum and Duffy, 2011). To analyze whether CFs differentiation into myofibroblasts took place under environmental changes we evaluated expression and localization of αSMA after 24 hr of combined stimulation. Immunostainings of CFs (Figure 4) reveal that a basal expression of cytoplasmic αSMA is present in all combined stimulation conditions. However, under no experimental condition did CFs exhibit co-localization of αSMA (red) and actin stress fibers (green), indicating that differentiation into myofibroblasts was not induced by our pattern of environmental stimuli. Conversely, stimulating CFs by supplementing TGF-β in the culture medium (a known inducer of CF differentiation to myofibroblasts) caused the appearance of cells exhibiting superimposed αSMA and actin signal (yellow).
Figure 4. Representative images of CFs fixed after 24 hr combined stimulations (A–F) and stained for actin (green) and αSMA (red), nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue).
Scale bars = 20 μm. αSMA is similarly expressed in all conditions and diffused in perinuclear and cytoplasmic localization. (G) Positive control for αSMA immunofluorescence through stimulation with 30 ng/ml TGF-β: CFs exhibit co-localization of αSMA staining with actin stress fibers (resulting in yellow signal) denoting differentiation into myofibroblasts (white arrows). Representative images were collected from a pool of images obtained from one cell donor, one independent experiment, minimum number of experimental replicates n = 4, technical replicates n = 3.
Discussion
Microenvironmental changes taking place in the injured myocardium trigger tissue responses that are orchestrated between multiple cell types (mainly cardiac myocytes, cardiac fibroblasts and immune cells) and involve multiple cell functions and signaling pathways. The outcome of this process is a substantial remodeling of the injured myocardial region by ECM-producing CFs that often results in excessive and dysfunctional alterations of the myocardial architecture and functionality. The elucidation of pathological cellular routes leading to tissue-level failure can clearly benefit from effective in vitro studies capable of dissecting and analyzing responses to multiple physiological and pathological conditions. Microfluidic technologies have recently enabled the development of advanced cardiac models by integrating key environmental cues in cardiac cell cultures (Agarwal et al., 2013; Marsano et al., 2016; Pavesi et al., 2015; Uzel et al., 2014). We here investigated CF behaviors in a compact multi-chamber in vitro platform designed to perform cell cultures under combined mechanical stimulation and changes in oxygen levels. This novel tool enabled us to perform for the first time a systematic evaluation of early CF responses to the combination of oxygen levels and mechanical strain regimes that facilitate a more realistic model of cardiac physiology and pathology.
Despite being overlooked in most previous studies, rigorous replication of in vivo oxygen tensions proved fundamental for interpreting physiological and pathological CF responses (Roy et al., 2003). Two oxygen conditions were tested: physiological oxygen levels experienced by CFs in the myocardium (5% O2, PX) and a rapid decrease of oxygen levels resembling an acute ischemic event (1% O2, HX). We also performed analyses on CFs cultured under non-physiological normoxic (NX) conditions and confirmed a substantial impact of NX compared to PX, especially on cell proliferation.
The mechanical microenvironment is known to change upon cardiac injury. It is known that injured myocardial regions are characterized by an early reduction of mechanical load due to loss of contractile cardiac myocytes (Eek et al., 2010; Pfeffer and Braunwald, 1990; Picard et al., 1990; Tennant and Wiggers, 1935). We therefore focused on evaluating how significant changes in mechanical strain affect cellular responses. To explore these effects we employed low cyclic strain mimicking reduced contractility (2% strain), physiological cyclic strain (8% strain) and a static control. These values were based on cardiac imaging studies performed shortly after myocardial injury (Dandel et al., 2009; Vartdal et al., 2007) and were previously reported to elicit strain-dependent effects in CFs (Ugolini et al., 2016).
Pathological remodeling of the myocardium involves activation of multiple CF cell functions. In a significant step forward compared to previous studies, our analyses encompassed most known pathological responses of CFs: production of ECM proteins and ECM-remodeling enzymes, cellular proliferation, secreted pro-fibrotic or inflammatory cytokines and myofibroblast differentiation. This in-depth assessment demonstrates how environmental factors participate in driving CF pathological responses and elucidates the existence of separate and synergistic roles of mechanical stimulation and oxygen levels in directing cellular functions relevant to early phases of cardiac fibrotic remodeling.
Our findings demonstrated that upon sensing of hypoxic environments CFs quickly (<24 hr) activate proliferative responses (Table 1). We propose that the increase in cell proliferation is mediated by the Hippo pathway given the correlation between nuclear YAP translocation and mitotic cells (PHH3+). YAP is widely recognized as a key factor in cardiac repair (Papizan and Olson, 2014; Xin et al., 2013). We found, however, that in contrast with other studies performed at NX (Codelia et al., 2014), YAP nuclear translocation is not related to increasing cyclic mechanical strain. In addition, an increased secretion of mitogenic PDGF by CFs at HX suggests a possible autocrine CF mechanism aimed at modulating proliferation upon pathological myocardial conditions.
Table 1.
Summary of the main cellular responses observed in experiments of combined environmental stimulation. Cellular responses were included in the corresponding stimulation condition if the measured parameter was significantly different from the parameter at reference condition PX(5% O2)/0% strain (single arrow ↑) and if more than two-fold significant difference was observed compared to PX(5% O2)/0% strain condition (double arrow ↑↑). Different background cell color are added as a function of the number of significant cellular responses observed (yellow: 2 or less changes; orange: up to 5 changes; red: more than 5 changes).
| 0% Strain | 2% Strain | 8% Strain | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
HX
(1% O2) |
↑↑ Mitosis
↑↑ Nuclear YAP ↑↑ PDGF ↑ Collagen ↓ MMP-3 |
↑ Mitosis
↑ Nuclear YAP ↑↑ PDGF ↑ Collagen ↑↑ MMP-2–3 ↑↑TGF-β ↑ IL-1β |
↑ Collagen
↑ MMP-2 |
|
PX
(5% O2) |
Reference
condition |
↑ Mitosis
↑↑ Nuclear YAP ↓ MMP-3 |
↑ Collagen
↓ MMP-3 |
We also showed that hypoxia alone causes an increased collagen presence in CFs cultures. This is consistent with data obtained in previous works focused on collagen production by CFs subject to HX (Tamamori et al., 1997). We therefore demonstrated how HX alone induces pro-fibrotic responses in CFs.
A significant novel insight observed in the present study is that the combination of HX and mechanical strain incrementally instructed further pathological cell responses. Indeed, the production of pro-fibrotic TGF-β, inflammatory cytokine IL1-β and matrix-degrading enzymes (MMP-2 and MMP-3) significantly increased only when cells were subject to combined HX and low levels of cyclic strain (HX/2% strain). TGF-β is markedly upregulated in vivo in regions of cardiac tissue injury and is known to act in vitro on CFs phenotypic switch, proliferation and collagen synthesis (Leask, 2007; Lijnen et al., 2000). IL1-β has been described in vivo as an early (<10 hr) post-injury inflammatory cytokine (Guillén et al., 1995) and CFs are thought to be one of the main cellular sources of IL1-β (Turner, 2014). MMPs are known to be primarily involved in the remodeling of the injured myocardium and it is worth noting that previous studies reported inhibitory effects of HX alone on MMP expression (Riches et al., 2009). In another study, mechanical stress did not alter MMP expression unless cells were cultured in serum deprivation (Tyagi et al., 1998). This context strengthens the hypothesis of a combined contribution of environmental conditions in driving MMP secretion by CFs, and the importance of reproducing complex environmental changes in vitro. In addition, literature suggests a direct effect of TGF-β and IL1-β on the expression of MMPs in CFs (Brown et al., 2007; Stawowy et al., 2004) and we observed how the expression levels of TGF-β and IL1-β under combined stimulation are in line with the altered expression of MMPs. Further studies may therefore be directed towards the elucidation of such possible autocrine mechanisms regulating CFs-mediated ECM remodeling. Notably, no experimental condition led to myofibroblast differentiation, with the exception of the positive control (additional biochemical stimulation with TGF-β), thus highlighting the importance of soluble pro-fibrotic factors for this aspect of CF pathological activation.
Intriguingly, we found that when cells were subject to physiological cyclic strain (8% strain) together with HX condition, most of the above pathological CF responses were not observed and we found only a modest increase in collagen presence. Similarly, when oxygen conditions resemble those of healthy tissue (PX), cyclic mechanical strain only results in increased collagen presence (at 8% strain) or in increased proliferation (at 2% strain). These results are in line with previous studies (performed in NX environments) on mechanically stimulated CFs (Carver et al., 1991; Husse et al., 2007; Ugolini et al., 2016).
Overall, these outcomes suggest that CFs respond differently to different regimes of cyclic strain, to different oxygen conditions and to combinations of these. In the context of an acute myocardial insult, loss of contractility and decrease in sensed oxygen levels are able to instruct a consistent response of CFs that involves matrix remodeling, inflammatory and proliferative behaviors. Our combined conditions allowed us to report that a mechanical environment resembling full contractility (8% strain) may hold a protective potential and resulted in attenuating CFs inflammatory, remodeling and pro-fibrotic responses taking place in HX.
These findings help to validate an on-chip model capable of exploring in vitro early fibrotic responses elicited in the injured myocardium. To estimate how this novel approach quantitatively correlates with standard readouts associated with cardiac fibrotic responses, we compared the fold changes of CF markers assessed in our model to those observed in standard in vitro models. Standard approaches typically involve the biochemical stimulation of CFs with known concentrations of pro-fibrotic (e.g., TGF-β) or inflammatory (e.g., interleukins) molecules. We collected literature studies where protein expression of relevant markers was measured at early stages of CFs culture under pro-fibrotic/inflammatory conditions. Table 2 shows quantitative comparisons between standard models and our on-chip model. Our model correlates well with quantitative readouts involving ECM, ECM-remodeling enzymes (collagen and MMPs expression) and proliferative effects, although contradictory studies also showed decreased CF proliferation under pro-fibrotic stimuli. Notably, MMP levels in serum were shown to increase by approximately two-fold in patients after 24 hr from acute myocardial injury diagnosis (Morishita et al., 2015). As for CF secretion of pro-fibrotic and inflammatory factors, our model was able to capture the triggering of PDGF expression by CFs, an aspect not yet described by standard in vitro approaches. Interestingly, this also correlated with in vivo increments in plasma levels of PDGF (approximately two-fold increment) at the early onset (12 hr) of myocardial injury in human patients (Koizumi et al., 2015). Additionally, our results correlated with secretion of TGF-β and IL-1β, while our environment-based model did not induce significant changes to the secreted levels of IL-6 and TNF-α as in standard models.
Table 2.
Summary of literature studies investigating early CFs responses under standard pro-fibrotic and inflammatory stimulation. Quantitative fold-changes of selected markers (fibrotic vs. control condition) are reported for studies that carried out protein expression assays or proliferation assays at early stimulation timepoints and compared to our on-chip model (grey background). The on-chip model well correlates to standard in vitro models in terms of ECM remodeling markers (Collagen 1, MMPs), cell proliferation and pro-fibrotic or inflammatory cytokynes (TGF-β and IL-1β). The on-chip model did not elicit production of IL-6 and TNF-α as compared to standard in vitro models. Assays: WB=Western Blot; ELISA= Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; HP= Hydroxyproline assay; CCK-8= Cell-counting kit eight proliferation assay; FACS= Fluorescence-activated cell sorting; Count= Standard cell counting; BrdU= Bromodeoxyuridine proliferation assay. Chemical stimuli: Ang II= Angiotensin II; TGF-β= Transforming Growth Factor-β; IL-1α/IL-1β= Interleukin-1α/1β; TNF-α= Tumor Necrosis Factor-α. Source data file linked to Table 2 shows this comparison data plotted in a chart.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22847.013
|
Collagen Expression | ||||||
| Ref. | Species | Assay | Stimulus | Culture Time | Change vs. control (standard model) |
Change vs. control (24 hr on-chip model) |
| (Xiao et al., 2016) | Mouse | WB | Ang II | 24 hr | ↑1.5-fold | ↑1.45-fold |
| (Guo et al., 2016) | Rat | WB | TGF-β | 48 hr | ↑2.2-fold | |
| (Pan et al., 2013) | Rat | WB | TGF-β | 24 hr | ↑1.5-fold | |
| (Peng et al., 2010) | Human | HP | TGF-β | 48 hr | ↑1.6-fold | |
| (Li et al., 2015) | Rat | WB | Ang II | 24 hr | ↑2.1-fold | |
|
MMP-2 Expression | ||||||
| Ref. | Species | Assay | Stimulus | Culture Time | Change vs. control (standard model) |
Change vs. control (24 hr on-chip model) |
| (Xiao et al., 2016) | Mouse | WB | Ang II | 24 hr | ↑1.8-fold | ↑2-fold |
| (Rhaleb et al., 2013) | Rat | WB | IL-1β | 72 hr | ↑2-fold | |
| (Brown et al., 2007) | Rat | WB | IL-1 | 48 hr | ↑2.2-fold | |
| (Li et al., 2015) | Rat | WB | Ang II | 24 hr | ↑2-fold | |
| MMP-3 Expression | ||||||
| Ref. | Species | Assay | Stimulus | Culture Time | Change vs. control (standard model) |
Change vs. control (24 hr on-chip model) |
| (van Nieuwenhoven et al., 2013 ) | Human | WB | IL-1α | 24 hr | ↑2-fold | ↑2.7-fold |
| (Brown et al., 2007) | Rat | WB | IL-1 | 48 hr | ↑2-fold | |
| Cell proliferation | ||||||
| Ref. | Species | Assay | Stimulus | Culture Time | Change vs. control (standard model) |
Change vs. control (24 hr on-chip model) |
| (Xiao et al., 2016) | Mouse | CCK-8 | Ang II | 24 hr | ↑2-fold | ↑1.9-fold |
| (Guo et al., 2016) | Rat | FACS | TGF-β | 48 hr | ↑2-fold | |
| (Porter et al., 2004) | Human | Count | TNF-α | 4 days | ↑1.5-fold | |
| (Dobaczewski et al., 2010) | Mouse | BrdU | TGF-β | 24 hr | ↓2-fold | |
| (Vivar et al., 2016) | Rat | FACS | TGF-β | 72 hr | ↓2-fold | |
| (Ai et al., 2015) | Rat | CCK-8 | Ang II | 48 hr | ↑1.8-fold | |
| (Li et al., 2015) | Rat | MTT | Ang II | 24 hr | ↑2-fold | |
| TGF- β Expression | ||||||
| Ref. | Species | Assay | Stimulus | Culture Time | Change vs. control (standard model) |
Change vs. control (24 hr on-chip model) |
| (Gu et al., 2012) | Mouse | WB | Ang II | 24 hr | ↑2-fold | ↑2.7-fold |
| (Xiao et al., 2016) | Mouse | WB | Ang II | 24 hr | ↑1.8-fold | |
| (Ai et al., 2015) | Rat | ELISA | Ang II | 48 hr | ↑2.5-fold | |
| (Li et al., 2015) | Rat | WB | Ang II | 24 hr | ↑1.9-fold | |
| IL-1β Expression | ||||||
| Ref. | Species | Assay | Stimulus | Culture Time | Change vs. control (standard model) |
Change vs. control (24 hr on-chip model) |
| (Turner et al., 2009) | Human | ELISA | IL-1α | 24 hr | ↑8-fold | ↑2.2-fold |
| (Turner et al., 2009) | Human | ELISA | TNF-α | 24 hr | ↑2-fold | |
| TNF-α Expression | ||||||
| Ref. | Species | Assay | Stimulus | Culture Time | Change vs. control (standard model) |
Change vs. control (24 hr on-chip model) |
| (Turner et al., 2009) | Human | ELISA | IL-1α | 24 hr | ↑4-fold | ns |
| (Humeres et al., 2016) | Rat | Luminex | TGF-β | 72 hr | ↓4-fold | |
| (Yokoyama et al., 1999) | Rat | ELISA | Ang II | 6h | ↑5-fold | |
| IL-6 Expression | ||||||
| Ref. | Species | Assay | Stimulus | Culture Time | Change vs. control (standard model) |
Change vs. control (24 hr on-chip model) |
| (Turner et al., 2009) | Human | ELISA | IL-1α | 24 hr | ↑19-fold | ns |
| (Turner et al., 2009) | Human | ELISA | TNF-α | 24 hr | ↑3.5-fold | |
| (Turner et al., 2007) | Human | ELISA | TNF-α | 24 hr | ↑2.8-fold | |
This last missing readout suggests that indirect paracrine action provided by other cellular actors involved in myocardial homeostasis and typically modeled in standard biochemical stimulation approaches is likely to play a role in driving the inflammatory responses that are not captured in our model. For instance, immune cells such as monocytes or macrophages are known to infiltrate the injured myocardium, supporting the inflammatory environment and providing additional paracrine cytokines to CFs (van Amerongen et al., 2007; Frantz et al., 2013; Nahrendorf et al., 2010). In addition, cross talk between cardiac myocytes and CFs has been widely described (Cartledge et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2012) and shown to drive CF behaviors such as myofibroblast differentiation(Tsoporis et al., 2012) and increased production of inflammatory molecules (Bowers et al., 2010). These indirect mechanisms could help evoke additional responses not captured in our model or could increase to an even greater magnitude the ones that we described as driven by environmental signals. Direct effects of cardiomyocyte contractility also mechanically influence CF behavior in vivo, however, this aspect is recreated in vitro by our system that exposes cultured CFs to uniform but tunable mechanical signals, thus proving advantageous for improving the clarity of readouts. Further improvements to the current model, such as the addition of paracrine signaling with other cell types, represents a promising future direction for this work, with the aim of developing a more accurate on-chip model combining fine control over the microenvironment with realistic biochemical signaling.
Conclusions
In summary, we propose an innovative model that recreates a pathological environment for understanding CF responses during cardiac injury. Replicating for the first time the combination of oxygen changes and mechanical cues, we revealed how these environmental stimulations combine to trigger CF pathological responses and highlighted emerging adaptive cellular mechanisms. We found that mimicking the combination of HX and reduced contractility proved crucial in eliciting inflammatory and fibrotic remodeling responses of CFs, while individual environmental stimuli only regulated proliferative and collagen-related responses. These insights have impact on future studies of pathological myocardial remodeling and the in vitro model here described provides a tool for better understanding pathological mechanisms and tailoring reparative strategies.
Materials and methods
Experimental design
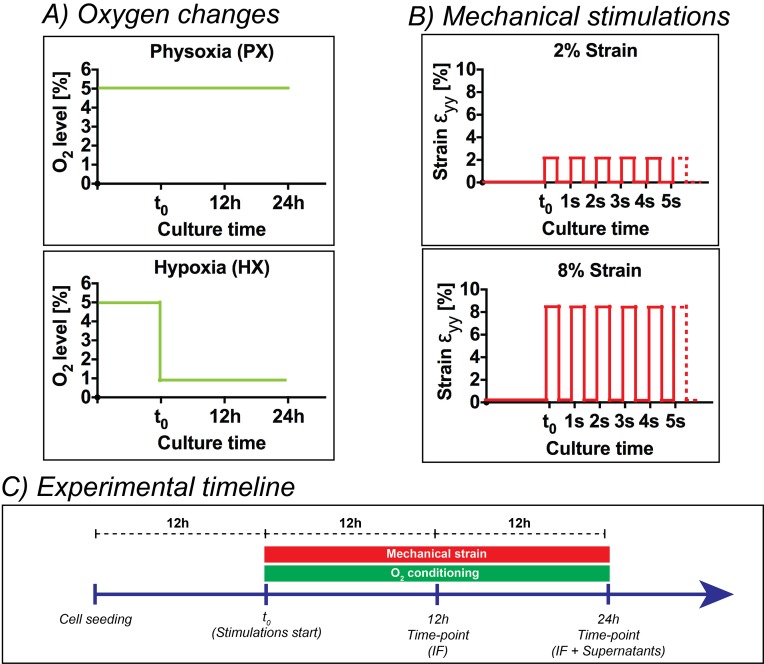
Figure 5 shows a detailed representation of oxygen dynamics and mechanical strain conditions employed (Figure 5A and B) together with a timeline of experiments (Figure 5C). After cells seeding, CFs were kept in static incubation for 12 hr in order to allow for cell adhesion. Subsequently – being this initial time-point referred to as t0 – CFs seeded in the inlet and outlet wells of the culture chambers were manually scraped, aspirated and stimulations were started. We employed two mechanical stimulation regimes (Figure 5B): 2% strain or 8% strain at 1 Hz. Concerning the oxygenation stimulus applied, the microdevices were employed at a base environmental oxygen level corresponding to physoxia (5% O2) in order to precisely model the oxygen levels in healthy myocardium until t0. Then, two oxygen concentration dynamics were imposed (Figure 5C): (i) a static incubation at 5% O2 (physoxia, PX) for 24 hr, (ii) an abrupt reduction of oxygen concentrations to 1% O2 that was maintained for 24 hr (hypoxia, HX). CFs were subject to all possible combinations of the above stimuli (six total conditions) for a total of 24 hr. Immunofluorescence analyses were performed after 12 hr and 24 hr of stimulation, while cell culture supernatants were collected and analyzed after 24 hr of stimulation. Immunofluorescence analyses were also performed on CFs cultured at NX levels under 0% strain condition to investigate responses induced by culturing CFs in non-physiological NX environments, a standard condition for most previous studies on CFs.
Figure 5. Overview of the experimental design of the present work.
(A) Oxygen changes reproduced in the present work: an incubation at PX; an abrupt reduction to HX environments (1% O2) maintained for 24 hr. (B) Mechanical stimulation regimes investigated in the present work: a static control at constant 0% strain; a cyclic mechanical strain stimulation at 2% strain and 1 Hz frequency; a cyclic mechanical strain stimulation at 8% strain and 1 Hz frequency. (C) Experimental timeline of the experiments performed: cells were seeded on microdevices and allowed to adhere to the culture membranes for 12 hr at PX and 0% strain before starting the combination of environmental stimuli. After 12 hr from the beginning of stimulations, we fixed samples for immunofluorescence analyses and after 24 hr we fixed samples for immunofluorescence analyses and collected supernatants for protein expression quantifications.
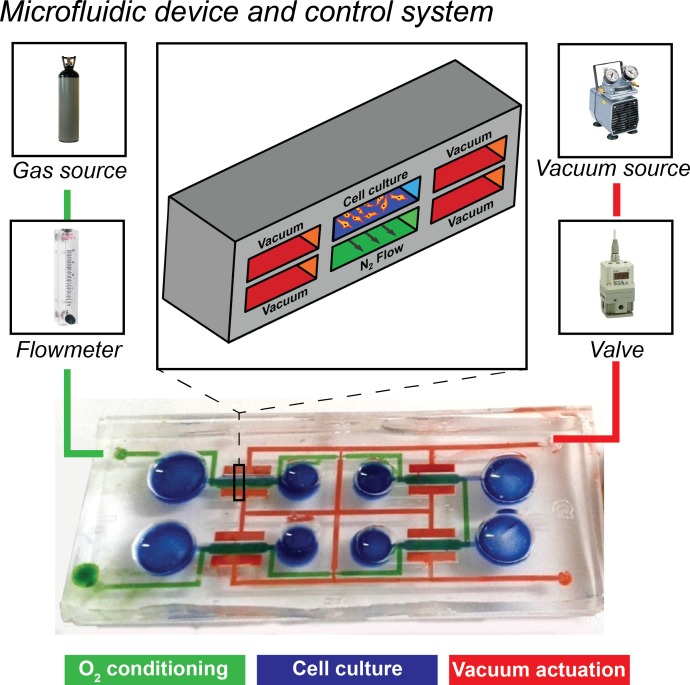
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Overview of the microfluidic platform employed in the present work together with control system.
Figure 5—figure supplement 2. Numerical modeling and experimental characterization of oxygen conditioning system included in the microdevices employed for the present work.
Microdevice outline
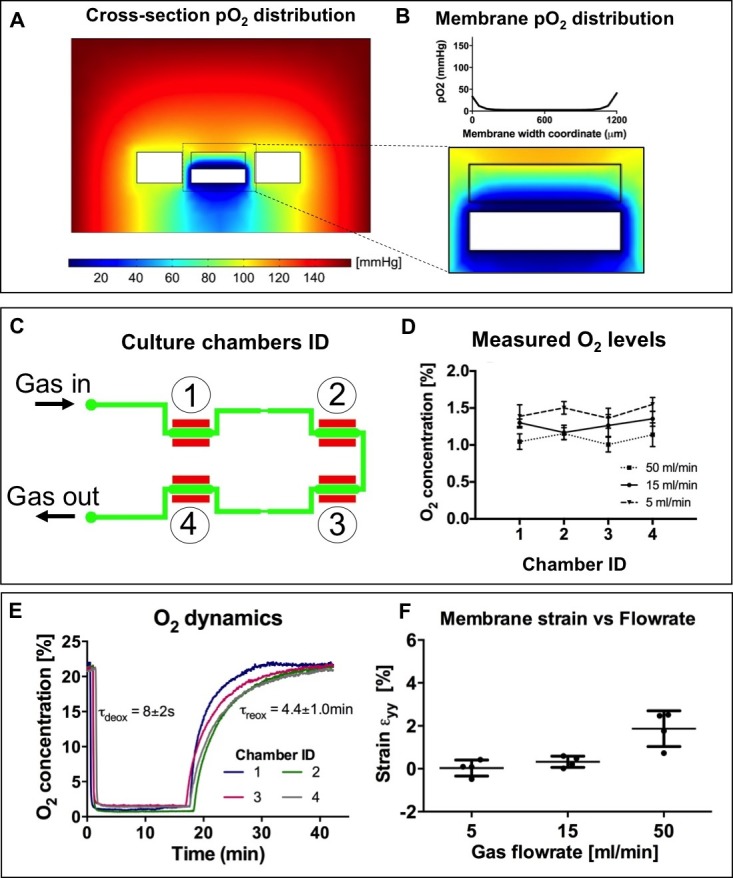
The microdevice was fabricated as previously described (Ugolini et al., 2016). Briefly, four stretching units are arranged in a single device composed of a thin polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) membrane sandwiched between two microstructured PDMS layers. Figure 5—figure supplement 1 shows a picture of the microdevice together with a sketched cross-section of a stretching unit of the device. In each stretching unit, a central culture chamber (blue) is flanked by two actuation chambers (red) connected to a single actuation line, meant for vacuum application and straining of the central membrane. A lower fluidic channel (green), common to all units, is designed for environmental conditioning and flows below each central culture chamber. Figure 5—figure supplement 1 also shows the stimulation system: microdevices were actuated by a vacuum line for generating mechanical strain and a gas line for controlling oxygen concentrations. As for the vacuum line, programmable electromechanical valves modulated the vacuum to switch cyclically from atmospheric pressure to the desired vacuum pressure (namely −200 mmHg for 2% strain and −600 mmHg for 8% strain, applied for half a cycle at a rate of 1 Hz). The pneumatic stretch system was previously described and validated (Ugolini et al., 2016). The flowrate of humidified gas mixture (95% N2; 5% CO2) was regulated with a flowmeter and delivered to the microdevices through low-permeability gas tubing. Numerical modeling and experimental characterization of the oxygen control system is described in Figure 5—figure supplement 2. Numerical models of a 2D cross-section of the microdevice culture chamber show that the spatial distribution of oxygen tension is uniform along the width of the culture membrane, with limited border effect near the side walls (Figure 5—figure supplement 2A,B). We employed a needle-based, fine-tip (spatial resolution ≈ 50 µm) oxygen sensor adjusted with a micromanipulator (PreSens, Germany) to reach the culture membrane. Measured oxygen concentration values confirm that the culture membrane is conditioned to ≈1% O2 at varying flowrates and consistently throughout all four culture chambers (Figure 5—figure supplement 2C,D). The low-oxygen conditioning occurs within seconds, while reoxygenation occurs within minutes (Figure 5—figure supplement 2E). Membrane strains upon application of varying gas flowrates were measured as previously described (Ugolini et al., 2016). Gas flowrates of 5 ml/min and 15 ml/min do not cause significant membrane strain (Figure 5—figure supplement 2F).
Cell culture
Normal human ventricular cardiac fibroblasts from one donor were purchased from Lonza (Lonza Bioscience, Singapore). Cells were cultured in FGM-3 medium (Lonza Bioscience, Singapore) and in a humidified incubator at 90% N2, 5% O2, 5% CO2 at all times unless otherwise indicated. Microdevices were autoclave-sterilized, plasma-treated and coated with human fibronectin (Sigma-Aldrich, Singapore) for 30 min at room temperature. Cells were seeded for experiments at a passage number of four. After pre-loading each culture chamber of the microdevices with 80 µl of medium, 20 µl of cell suspension (106 cells/ml) were manually injected in the wells of the culture chambers. During experiments, microdevices were kept in humidified chambers to avoid culture medium evaporation.
Immunofluorescence
Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 10 min. After 15 min of permeabilization with PBS containing 0.5% Triton-X, cells were blocked for 1 hr at room temperature with 3% bovine serum albumin. Cells were then probed overnight at 4°C with the following primary antibodies: anti-collagen I (mouse, AbCam, UK; RRID:AB_305411), to identify alterations in collagen I in the culture; anti-phospho-Histone-H3 (PHH3, Ser10, rabbit, Santa-Cruz, US; RRID:AB_2233067), for mitotic cells; anti-YAP (rabbit, Santa-Cruz, US; RRID:AB_2273277) to localize nuclear or cytoplasmic localization of the YAP/TAZ complex, a mechano-sensing associated transcription factor and main effector of the Hippo proliferative pathway; anti-αSMA (Smooth Muscle Actin, rabbit, AbCam, UK; RRID:AB_2223021) to identify myofibroblast differentiation from expression and localization of αSMA. CFs cultured under standard culture medium supplemented with 30 ng/ml TGF-β (Sigma-Aldrich, Singapore) were considered positive controls for αSMA stainings. The following secondary antibodies were used for 2 hr at room temperature: goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 488 and goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 564 (AbCam, UK). Nuclear staining was performed by incubating cells with DAPI. Negative controls were present for all immunofluorescence stainings.
Image processing
Images were acquired with a Zeiss 710 Confocal microscope. Imaging parameters were not changed during acquisitions. For quantitative analyses of immunofluorescence markers, three images per culture chamber were taken at 10X magnification, thus sampling roughly half of the total area of the culture membrane and screening about 500 cells per replicate. Images were acquired from the central region of the culture membrane. Collagen I analyses were performed by intracellular fluorescence intensity quantification: the intracellular integrated density parameter was calculated by manually drawing outlines of about 50 cells per replicate from images, correcting for background intensity and normalizing for cell area. Cell proliferation analyses were performed by manually counting nuclei positive for PHH3 and dividing by the total number of nuclei (automatically counted) to estimate the fraction of mitotic cells. YAP localization analyses were performed by manually discriminating cytoplasmic or nuclear staining as previously described (Codelia et al., 2014; Dupont et al., 2011) and dividing by the total number of nuclei (automatically counted) to estimate the level of YAP nuclear translocation.
Supernatant analyses
A volume of culture medium (100 µl) was collected per each culture chamber from the microfluidic devices after 24 hr. Supernatants were stored at −80°C prior to analysis. Residual cells and debris in the supernatant were removed by centrifugation. Concentrations of secreted factors in the supernatants were assessed via multiplex bead-based array according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Luminex, Austin, TX). Each measurement was run in duplicate.
Statistical analyses
All data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical comparisons were performed using GraphPad (Prism) software. All data were initially analyzed for normality using Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests. Two-way ANOVA tests followed by Bonferroni post-hoc tests were applied to determine statistical significance of differences and evaluate synergistic or separate contribution of mechanical strain stimulation and oxygen dynamics stimulation. When data groups did not pass normality tests, non-parametric statistical tests were employed (Kruskal-Wallis test). A p-value lower than 0.05 was considered significant. All data were collected from a pool of six independent experiments with a minimum number of biological replicates of four. We designed the approximate sample size required for the study by performing power analysis based on previously reported data on human cardiac fibroblasts (CF) proliferative responses under mechanical strain (Ugolini et al., 2016). In addition, we considered preliminary data obtained from human CFs cultured at different oxygen levels. An effect size was computed from this data (fraction of mitotic PHH3+ cells under 2% vs. 8% strain: 2.0 ± 0.5 vs. 0.5 ± 0.3; expression of MMPs at physoxia vs. hypoxia: 1.02 ± 0.2 vs. 2.00 ± 0.1 ng/ml). An a priori power analysis performed with GPower (v.3.1) software assured that a sample size of n = 4 is sufficient to achieve α = 0.01 and 1-β (power) = 0.90.
Acknowledgements
GSU was awarded a PhD Scholarship from the Italian Ministry of Education, supported by funds from InterPolytechnic Doctoral School mobility scholarship and by Progetto Rocca MIT-Italy exchange program. The research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF), Prime Minister’s Office, Singapore, under its CREATE programme, Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART) BioSystems and Micromechanics (BioSyM) IRG.
Funding Statement
No external funding was received for this work.
Funding Information
This paper was supported by the following grants:
Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology Centre to Roger Kamm.
National Research Foundation to Roger Kamm.
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Author contributions
GSU, Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing.
AP, Supervision, Investigation, Methodology, Writing—review and editing.
MR, Supervision, Methodology, Writing—review and editing.
GBF, Supervision, Methodology, Writing—review and editing.
RK, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing—review and editing.
MS, Conceptualization, Supervision, Methodology, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing—review and editing.
References
- Agarwal A, Goss JA, Cho A, McCain ML, Parker KK. Microfluidic heart on a chip for higher throughput pharmacological studies. Lab on a Chip. 2013;13:3599–3608. doi: 10.1039/c3lc50350j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ai F, Chen M, Yu B, Yang Y, Xu G, Gui F, Liu Z, Bai X, Chen Z. Berberine regulates proliferation, collagen synthesis and cytokine secretion of cardiac fibroblasts via AMPK-mTOR-p70S6K signaling pathway. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology. 2015;8:12509–12516. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atance J, Yost MJ, Carver W. Influence of the extracellular matrix on the regulation of cardiac fibroblast behavior by mechanical stretch. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 2004;200:377–386. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum J, Duffy HS. Fibroblasts and myofibroblasts: what are we talking about? Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. 2011;57:376–379. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3182116e39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers SL, Borg TK, Baudino TA. The dynamics of fibroblast-myocyte-capillary interactions in the heart. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2010;1188:143–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05094.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown RD, Jones GM, Laird RE, Hudson P, Long CS. Cytokines regulate matrix metalloproteinases and migration in cardiac fibroblasts. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2007;362:200–205. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.08.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt RP, Bishop JE. Mechanical load enhances the stimulatory effect of serum growth factors on cardiac fibroblast procollagen synthesis. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 1997;29:1141–1151. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1996.0347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartledge JE, Kane C, Dias P, Tesfom M, Clarke L, Mckee B, Al Ayoubi S, Chester A, Yacoub MH, Camelliti P, Terracciano CM. Functional crosstalk between cardiac fibroblasts and adult cardiomyocytes by soluble mediators. Cardiovascular Research. 2015;105:260–270. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvu264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver W, Nagpal ML, Nachtigal M, Borg TK, Terracio L. Collagen expression in mechanically stimulated cardiac fibroblasts. Circulation Research. 1991;69:116–122. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.69.1.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy RM, Zheng P, O'Mahony M, Izmirly P, Zavadil J, Gardner L, Buyon JP. Role of hypoxia and cAMP in the transdifferentiation of human fetal cardiac fibroblasts: implications for progression to scarring in autoimmune-associated congenital heart block. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2007;56:4120–4131. doi: 10.1002/art.23061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codelia VA, Sun G, Irvine KD. Regulation of YAP by mechanical strain through jnk and hippo signaling. Current Biology. 2014;24:2012–2017. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.07.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla Costa AP, Clemente CF, Carvalho HF, Carvalheira JB, Nadruz W, Franchini KG. FAK mediates the activation of cardiac fibroblasts induced by mechanical stress through regulation of the mTOR complex. Cardiovascular Research. 2010;86:421–431. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvp416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandel M, Lehmkuhl H, Knosalla C, Suramelashvili N, Hetzer R. Strain and strain rate imaging by echocardiography - basic concepts and clinical applicability. Current Cardiology Reviews. 2009;5:133–148. doi: 10.2174/157340309788166642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobaczewski M, Bujak M, Li N, Gonzalez-Quesada C, Mendoza LH, Wang XF, Frangogiannis NG. Smad3 signaling critically regulates fibroblast phenotype and function in healing myocardial infarction. Circulation Research. 2010;107:418–428. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.216101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont S, Morsut L, Aragona M, Enzo E, Giulitti S, Cordenonsi M, Zanconato F, Le Digabel J, Forcato M, Bicciato S, Elvassore N, Piccolo S. Role of YAP/TAZ in mechanotransduction. Nature. 2011;474:179–183. doi: 10.1038/nature10137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgley AJ, Krum H, Kelly DJ. Targeting fibrosis for the treatment of heart failure: a role for transforming growth factor-β. Cardiovascular Therapeutics. 2012;30:e30–e40. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5922.2010.00228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eek C, Grenne B, Brunvand H, Aakhus S, Endresen K, Smiseth OA, Edvardsen T, Skulstad H. Strain echocardiography predicts acute coronary occlusion in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. European Journal of Echocardiography. 2010;11:501–508. doi: 10.1093/ejechocard/jeq008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D, Takawale A, Lee J, Kassiri Z. Cardiac fibroblasts, fibrosis and extracellular matrix remodeling in heart disease. Fibrogenesis & Tissue Repair. 2012;5:15. doi: 10.1186/1755-1536-5-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flachskampf FA, Schmid M, Rost C, Achenbach S, DeMaria AN, Daniel WG. Cardiac imaging after myocardial infarction. European Heart Journal. 2011;32:272–283. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangogiannis NG. The inflammatory response in myocardial injury, repair, and remodelling. Nature Reviews Cardiology. 2014;11:255–265. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2014.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz S, Hofmann U, Fraccarollo D, Schäfer A, Kranepuhl S, Hagedorn I, Nieswandt B, Nahrendorf M, Wagner H, Bayer B, Pachel C, Schön MP, Kneitz S, Bobinger T, Weidemann F, Ertl G, Bauersachs J. Monocytes/macrophages prevent healing defects and left ventricular thrombus formation after myocardial infarction. The FASEB Journal. 2013;27:871–881. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-214049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao Q, Guo M, Zeng W, Wang Y, Yang L, Pang X, Li H, Suo Y, Jiang X, Yu C. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 secreted by hypoxia cardiac fibroblasts triggers cardiac stem cell migration in vitro. Stem Cells International. 2015;2015:836390. doi: 10.1155/2015/836390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao Y, Chu M, Hong J, Shang J, Xu D. Hypoxia induces cardiac fibroblast proliferation and phenotypic switch: a role for caveolae and caveolin-1/PTEN mediated pathway. Journal of Thoracic Disease. 2014;6:1458–1468. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.08.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonschior P, Gonschior GM, Conzen PF, Hobbhahn J, Goetz AE, Peter K, Brendel W. Myocardial oxygenation and transmural lactate metabolism during experimental acute coronary stenosis in pigs. Basic Research in Cardiology. 1992;87:27–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00795387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu J, Liu X, Wang QX, Tan HW, Guo M, Jiang WF, Zhou L, xing WQ, wei TH, feng JW. Angiotensin II increases CTGF expression via MAPKs/TGF-β1/TRAF6 pathway in atrial fibroblasts. Experimental Cell Research. 2012;318:2105–2115. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.06.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillén I, Blanes M, Gómez-Lechón MJ, Castell JV. Cytokine signaling during myocardial infarction: sequential appearance of IL-1 beta and IL-6. The American Journal of Physiology. 1995;269:R229–235. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1995.269.2.R229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo XG, Uzui H, Mizuguchi T, Ueda T, Chen JZ, Lee JD. Imidaprilat inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity in human cardiac fibroblasts induced by interleukin-1beta via NO-dependent pathway. International Journal of Cardiology. 2008;126:414–420. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.08.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Y, Dong Z, Shi Y, Wang W, Wang L, Sun J, Sun X, Tian Z, Yao J, Li Z, Cheng J, Tian Y. Sonodynamic therapy inhibits fibrogenesis in rat cardiac fibroblasts induced by TGF-β1. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry. 2016;40:579–588. doi: 10.1159/000452571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusch G, Libby P, Gersh B, Yellon D, Böhm M, Lopaschuk G, Opie L. Cardiovascular remodelling in coronary artery disease and heart failure. The Lancet. 2014;383:1933–1943. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60107-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoit BD. Strain and strain rate echocardiography and coronary artery disease. Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging. 2011;4:179–190. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.110.959817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humeres C, Vivar R, Boza P, Muñoz C, Bolivar S, Anfossi R, Osorio JM, Olivares-Silva F, García L, Díaz-Araya G. Cardiac fibroblast cytokine profiles induced by proinflammatory or profibrotic stimuli promote monocyte recruitment and modulate macrophage M1/M2 balance in vitro. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2016;101:69–80. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husse B, Briest W, Homagk L, Isenberg G, Gekle M. Cyclical mechanical stretch modulates expression of collagen I and collagen III by PKC and tyrosine kinase in cardiac fibroblasts. AJP: Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 2007;293:R1898–R1907. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00804.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kania G, Blyszczuk P, Eriksson U. Mechanisms of cardiac fibrosis in inflammatory heart disease. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 2009;19:247–252. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2010.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi M, Takahashi M, Hata T, Kashima Y, Usui F, Morimoto H, Izawa A, Takahashi Y, Masumoto J, Koyama J, Hongo M, Noda T, Nakayama J, Sagara J, Taniguchi S, Ikeda U. Inflammasome activation of cardiac fibroblasts is essential for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation. 2011;123:594–604. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.982777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi T, Komiyama N, Nishimura S. In-Vivo higher plasma levels of Platelet-Derived growth factor and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in coronary artery at the very onset of myocardial infarction with ST-Segment elevation. Annals of Vascular Diseases. 2015;8:297–301. doi: 10.3400/avd.oa.15-00057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenning G, Zeisberg EM, Kalluri R. The origin of fibroblasts and mechanism of cardiac fibrosis. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 2010;225:631–637. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leask A. TGFbeta, cardiac fibroblasts, and the fibrotic response. Cardiovascular Research. 2007;74:207–212. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leask A. Potential therapeutic targets for cardiac fibrosis: tgfbeta, angiotensin, endothelin, CCN2, and PDGF, partners in fibroblast activation. Circulation Research. 2010;106:1675–1680. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.217737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R, Xiao J, Qing X, Xing J, Xia Y, Qi J, Liu X, Zhang S, Sheng X, Zhang X, Ji X. Sp1 mediates a therapeutic role of MiR-7a/b in angiotensin II-Induced cardiac fibrosis via mechanism involving the TGF-β and MAPKs pathways in cardiac fibroblasts. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0125513. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao XD, Wang XH, Jin HJ, Chen LY, Chen Q. Mechanical stretch induces mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes and G2/M accumulation in cardiac fibroblasts. Cell Research. 2004;14:16–26. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen PJ, Petrov VV, Fagard RH. Induction of cardiac fibrosis by transforming growth factor-beta(1) Molecular Genetics and Metabolism. 2000;71:418–435. doi: 10.1006/mgme.2000.3032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner D, Zietsch C, Tank J, Sossalla S, Fluschnik N, Hinrichs S, Maier L, Poller W, Blankenberg S, Schultheiss H-P, Tschöpe C, Westermann D. Cardiac fibroblasts support cardiac inflammation in heart failure. Basic Research in Cardiology. 2014;109:1–16. doi: 10.1007/s00395-014-0428-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C, Zhao W, Meng W, Zhao T, Chen Y, Ahokas RA, Liu H, Sun Y. Platelet-derived growth factor blockade on cardiac remodeling following infarction. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 2014;397:295–304. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsano A, Conficconi C, Lemme M, Occhetta P, Gaudiello E, Votta E, Cerino G, Redaelli A, Rasponi M. Beating heart on a chip: a novel microfluidic platform to generate functional 3D cardiac microtissues. Lab Chip. 2016;16:599–610. doi: 10.1039/C5LC01356A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollema SA, Delgado V, Bertini M, Antoni ML, Boersma E, Holman ER, Stokkel MP, van der Wall EE, Schalij MJ, Bax JJ. Viability assessment with global left ventricular longitudinal strain predicts recovery of left ventricular function after acute myocardial infarction. Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging. 2010;3:15–23. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.108.802785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita T, Uzui H, Mitsuke Y, Arakawa K, Amaya N, Kaseno K, Ishida K, Nakaya R, Lee JD, Tada H. Predictive utility of the changes in matrix metalloproteinase-2 in the early phase for left ventricular reverse remodeling after an acute myocardial infarction. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2015;4:e001359. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosqueira D, Pagliari S, Uto K, Ebara M, Romanazzo S, Escobedo-Lucea C, Nakanishi J, Taniguchi A, Franzese O, Di Nardo P, Goumans MJ, Traversa E, Pinto-do-Ó P, Aoyagi T, Forte G. Hippo pathway effectors control cardiac progenitor cell fate by acting as dynamic sensors of substrate mechanics and nanostructure. ACS Nano. 2014;8:2033–2047. doi: 10.1021/nn4058984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahrendorf M, Pittet MJ, Swirski FK. Monocytes: protagonists of infarct inflammation and repair after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2010;121:2437–2445. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.916346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada H, Takemura G, Kosai K, Li Y, Takahashi T, Esaki M, Yuge K, Miyata S, Maruyama R, Mikami A, Minatoguchi S, Fujiwara T, Fujiwara H. Postinfarction gene therapy against transforming growth factor-beta signal modulates infarct tissue dynamics and attenuates left ventricular remodeling and heart failure. Circulation. 2005;111:2430–2437. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000165066.71481.8E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan X, Chen Z, Huang R, Yao Y, Ma G. Transforming growth factor β1 induces the expression of collagen type I by DNA methylation in cardiac fibroblasts. PLoS One. 2013;8:e60335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papizan JB, Olson EN. Hippo in the path to heart repair. Circulation Research. 2014;115:332–334. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.304389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavesi A, Adriani G, Rasponi M, Zervantonakis IK, Fiore GB, Kamm RD. Controlled electromechanical cell stimulation on-a-chip. Scientific Reports. 2015;5:11800. doi: 10.1038/srep11800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng H, Carretero OA, Peterson EL, Rhaleb NE. Ac-SDKP inhibits transforming growth factor-beta1-induced differentiation of human cardiac fibroblasts into myofibroblasts. AJP: Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 2010;298:H1357–H1364. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00464.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrov VV, Fagard RH, Lijnen PJ. Stimulation of collagen production by transforming growth factor-beta1 during differentiation of cardiac fibroblasts to myofibroblasts. Hypertension. 2002;39:258–263. doi: 10.1161/hy0202.103268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer MA, Braunwald E. Ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. experimental observations and clinical implications. Circulation. 1990;81:1161–1172. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.81.4.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard MH, Wilkins GT, Ray PA, Weyman AE. Natural history of left ventricular size and function after acute myocardial infarction. assessment and prediction by echocardiographic endocardial surface mapping. Circulation. 1990;82:484–494. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.82.2.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter KE, Turner NA, O'Regan DJ, Ball SG. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces human atrial myofibroblast proliferation, invasion and MMP-9 secretion: inhibition by simvastatin. Cardiovascular Research. 2004;64:507–515. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.07.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter KE, Turner NA. Cardiac fibroblasts: at the heart of myocardial remodeling. Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 2009;123:255–278. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhaleb NE, Pokharel S, Sharma UC, Peng H, Peterson E, Harding P, Yang XP, Carretero OA. N-acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro inhibits interleukin-1β-mediated matrix metalloproteinase activation in cardiac fibroblasts. Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology. 2013;465:1487–1495. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1262-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riches K, Morley ME, Turner NA, O'Regan DJ, Ball SG, Peers C, Porter KE. Chronic hypoxia inhibits MMP-2 activation and cellular invasion in human cardiac myofibroblasts. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2009;47:391–399. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.06.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubille F, Busseuil D, Merlet N, Kritikou EA, Rhéaume E, Tardif JC. Investigational drugs targeting cardiac fibrosis. Expert Review of Cardiovascular Therapy. 2014;12:111–125. doi: 10.1586/14779072.2013.839942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S, Khanna S, Bickerstaff AA, Subramanian SV, Atalay M, Bierl M, Pendyala S, Levy D, Sharma N, Venojarvi M, Strauch A, Orosz CG, Sen CK. Oxygen sensing by primary cardiac fibroblasts: a key role of p21(Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1) Circulation Research. 2003;92:264–271. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000056770.30922.E6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago JJ, Dangerfield AL, Rattan SG, Bathe KL, Cunnington RH, Raizman JE, Bedosky KM, Freed DH, Kardami E, Dixon IM. Cardiac fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation in vivo and in vitro: expression of focal adhesion components in neonatal and adult rat ventricular myofibroblasts. Developmental Dynamics. 2010;239:1573–1584. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroer AK, Merryman WD. Mechanobiology of myofibroblast adhesion in fibrotic cardiac disease. Journal of Cell Science. 2015;128:1865–1875. doi: 10.1242/jcs.162891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen CK, Khanna S, Roy S. Perceived hyperoxia: oxygen-induced remodeling of the reoxygenated heart. Cardiovascular Research. 2006;71:280–288. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen CK, Roy S. Oxygenation state as a driver of myofibroblast differentiation and wound contraction: hypoxia impairs wound closure. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2010;130:2701–2703. doi: 10.1038/jid.2010.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinde AV, Frangogiannis NG. Fibroblasts in myocardial infarction: a role in inflammation and repair. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2014;70:74–82. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.11.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siwik DA, Chang DL, Colucci WS. Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha decrease collagen synthesis and increase matrix metalloproteinase activity in cardiac fibroblasts in vitro. Circulation Research. 2000;86:1259–1265. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.86.12.1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stawowy P, Margeta C, Kallisch H, Seidah NG, Chrétien M, Fleck E, Graf K. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase MT1-MMP/MMP-2 in cardiac fibroblasts by TGF-beta1 involves furin-convertase. Cardiovascular Research. 2004;63:87–97. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talman V, Ruskoaho H. Cardiac fibrosis in myocardial infarction-from repair and remodeling to regeneration. Cell and Tissue Research. 2016;365:563–581. doi: 10.1007/s00441-016-2431-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamamori M, Ito H, Hiroe M, Marumo F, Hata RI. Stimulation of collagen synthesis in rat cardiac fibroblasts by exposure to hypoxic culture conditions and suppression of the effect by natriuretic peptides. Cell Biology International. 1997;21:175–180. doi: 10.1006/cbir.1997.0130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennant R, Wiggers CJ. The effect of coronary occlusion on myocardial contraction. Am. J. Physiol. - Hear. Circ. Physiol. 1935;112:351–361. doi: 10.1016/S0002-8703(35)90365-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, Chaponnier C, Brown RA. Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2002;3:349–363. doi: 10.1038/nrm809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoporis JN, Izhar S, Proteau G, Slaughter G, Parker TG. S100B-RAGE dependent VEGF secretion by cardiac myocytes induces myofibroblast proliferation. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2012;52:464–473. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner NA, Das A, Warburton P, O'Regan DJ, Ball SG, Porter KE. Interleukin-1alpha stimulates proinflammatory cytokine expression in human cardiac myofibroblasts. AJP: Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 2009;297:H1117–H1127. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00372.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner NA, Mughal RS, Warburton P, O'Regan DJ, Ball SG, Porter KE. Mechanism of TNFalpha-induced IL-1alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 expression in human cardiac fibroblasts: effects of statins and thiazolidinediones. Cardiovascular Research. 2007;76:81–90. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2007.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner NA. Effects of interleukin-1 on cardiac fibroblast function: relevance to post-myocardial infarction remodelling. Vascular Pharmacology. 2014;60:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2013.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner NA. Inflammatory and fibrotic responses of cardiac fibroblasts to myocardial damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2016;94:189–200. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi SC, Lewis K, Pikes D, Marcello A, Mujumdar VS, Smiley LM, Moore CK. Stretch-induced membrane type matrix metalloproteinase and tissue plasminogen activator in cardiac fibroblast cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 1998;176:374–382. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199808)176:2<374::AID-JCP16>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugolini GS, Rasponi M, Pavesi A, Santoro R, Kamm R, Fiore GB, Pesce M, Soncini M. On-chip assessment of human primary cardiac fibroblasts proliferative responses to uniaxial cyclic mechanical strain. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 2016;113:859–869. doi: 10.1002/bit.25847. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26444553 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzel SG, Pavesi A, Kamm RD. Microfabrication and microfluidics for muscle tissue models. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology. 2014;115:279–293. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2014.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Amerongen MJ, Harmsen MC, van Rooijen N, Petersen AH, van Luyn MJ. Macrophage depletion impairs wound healing and increases left ventricular remodeling after myocardial injury in mice. The American Journal of Pathology. 2007;170:818–829. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Nieuwenhoven FA, Hemmings KE, Porter KE, Turner NA. Combined effects of interleukin-1α and transforming growth factor-β1 on modulation of human cardiac fibroblast function. Matrix Biology. 2013;32:399–406. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartdal T, Brunvand H, Pettersen E, Smith HJ, Lyseggen E, Helle-Valle T, Skulstad H, Ihlen H, Edvardsen T. Early prediction of infarct size by strain doppler echocardiography after coronary reperfusion. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2007;49:1715–1721. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.12.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivar R, Humeres C, Muñoz C, Boza P, Bolivar S, Tapia F, Lavandero S, Chiong M, Diaz-Araya G. FoxO1 mediates TGF-beta1-dependent cardiac myofibroblast differentiation. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research. 2016;1863:128–138. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winegrad S, Henrion D, Rappaport L, Samuel JL. Self-protection by cardiac myocytes against hypoxia and hyperoxia. Circulation Research. 1999;85:690–698. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.85.8.690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J, Sheng X, Zhang X, Guo M, Ji X. Curcumin protects against myocardial infarction-induced cardiac fibrosis via SIRT1 activation in vivo and in vitro. Drug Design, Development and Therapy. 2016;10:1267–1277. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S104925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xin M, Kim Y, Sutherland LB, Murakami M, Qi X, McAnally J, Porrello ER, Mahmoud AI, Tan W, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Sadek HA, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN. Hippo pathway effector yap promotes cardiac regeneration. PNAS. 2013;110:13839–13844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1313192110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama T, Sekiguchi K, Tanaka T, Tomaru K, Arai M, Suzuki T, Nagai R. Angiotensin II and mechanical stretch induce production of tumor necrosis factor in cardiac fibroblasts. Journal of Cardiac Failure. 1999;276:44–H1976. doi: 10.1016/S1071-9164(99)91145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang P, Su J, Mende U. Cross talk between cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts: from multiscale investigative approaches to mechanisms and functional consequences. AJP: Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 2012;303:H1385–H1396. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01167.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao W, Zhao T, Huang V, Chen Y, Ahokas RA, Sun Y. Platelet-derived growth factor involvement in myocardial remodeling following infarction. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2011;51:830–838. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.06.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]