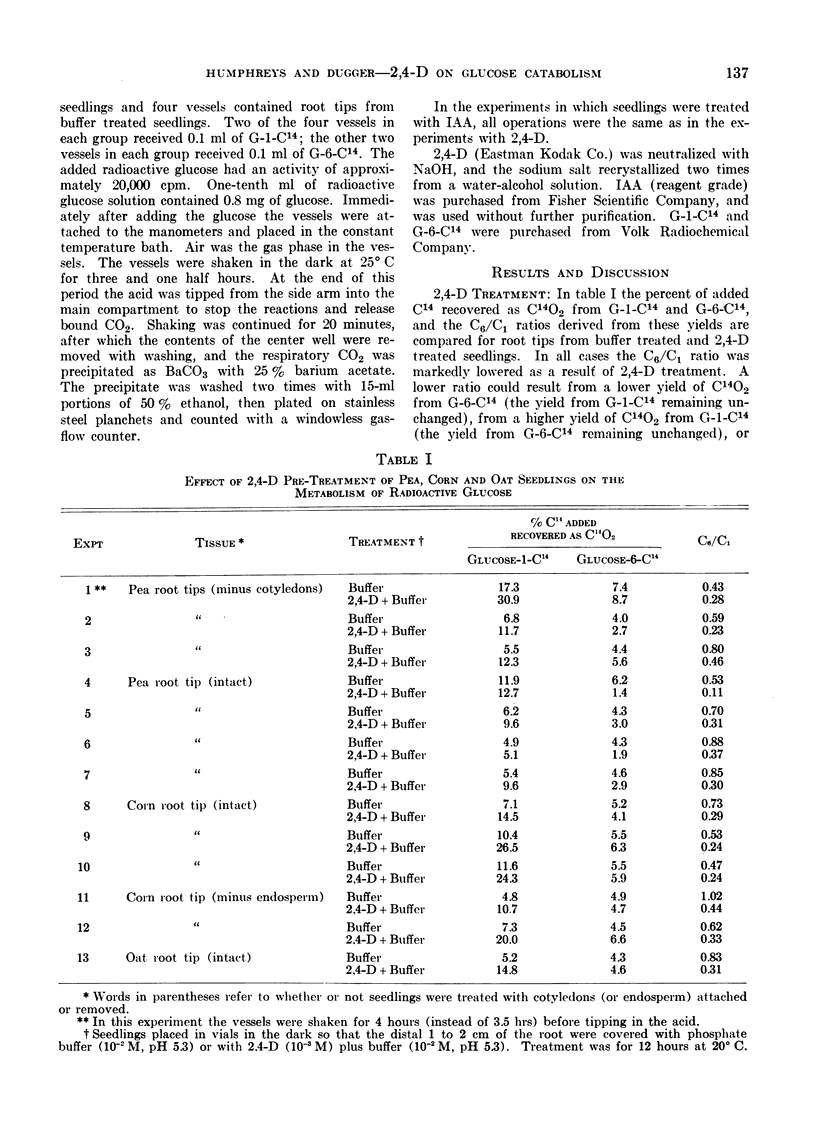
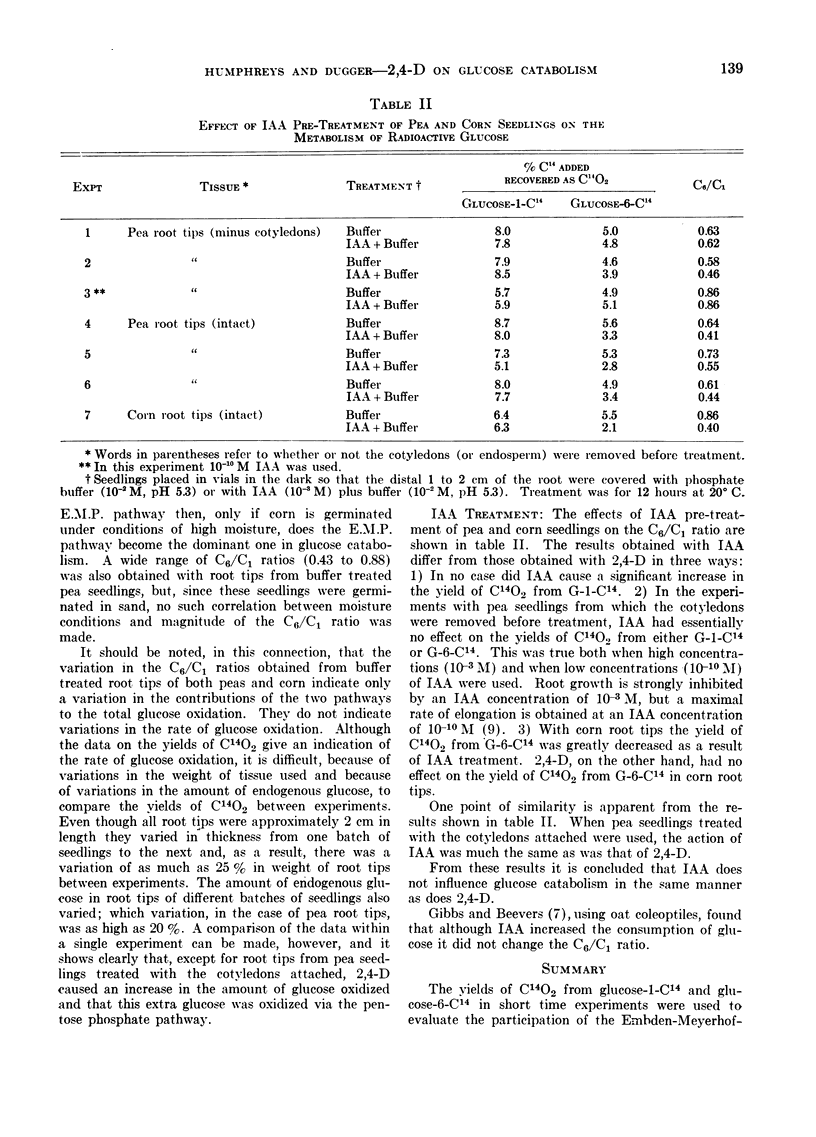
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOOM B., STETTEN D., Jr The fraction of glucose catabolized via the glycolytic pathway. J Biol Chem. 1955 Feb;212(2):555–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOOM B., STETTEN M. R., STETTEN D., Jr Evaluation of catabolic pathways of glucose in mammalian systems. J Biol Chem. 1953 Oct;204(2):681–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beevers H., Gibbs M. Position of C in Alcohol and Carbon Dioxide Formed from Labeled Glucose by Corn Root Tips. Plant Physiol. 1954 Jul;29(4):318–321. doi: 10.1104/pp.29.4.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beevers H., Gibbs M. The Direct Oxidation Pathway in Plant Respiration. Plant Physiol. 1954 Jul;29(4):322–324. doi: 10.1104/pp.29.4.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs M., Beevers H. Glucose Dissimilation in the Higher Plant. Effect of Age of Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1955 Jul;30(4):343–347. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.4.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



