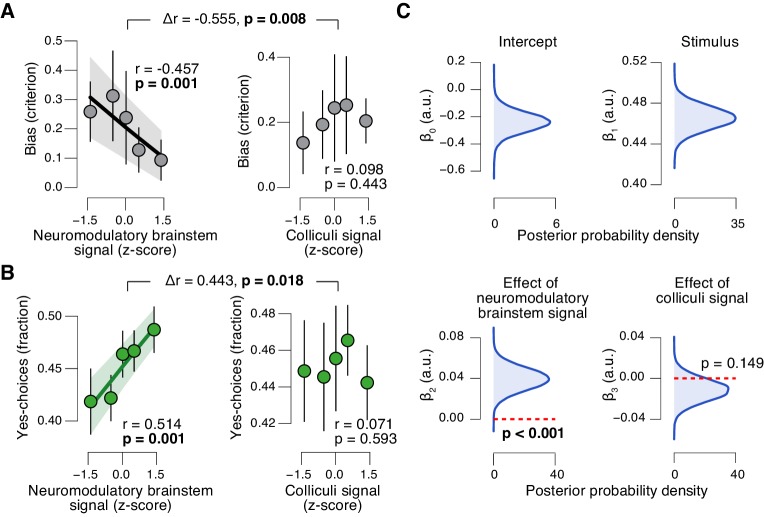
Figure 9. Brainstem neuromodulatory nuclei predict reduction of choice bias.
(A) Correlation between decision bias (criterion) and the combined neuromodulatory brainstem signal (linear combination of responses in LC, SN, VTA, BF-sept, and BF-subl maximizing the correlation to TPR; see Materials and methods; left), and the combined colliculi signal (linear combination of responses in SC and IC maximizing the correlation to TPR; right) (5 bins). Stats, permutation test. (B) As panel A but for the correlation to fraction of ‘yes’-choices. (C) Group-level posterior probability densities for means of parameters in the DDM regression model, through which we assessed the trial-by-trial, linear relationship between single-trial drift and the combined neuromodulatory response or the combined colliculi response (see Materials and methods; see Figure 9—figure supplement 1 for the remaining parameters ‘starting point’, ‘boundary separation’ and ‘non-decision time’). All panels: group average (N = 14); shading or error bars, s.e.m.
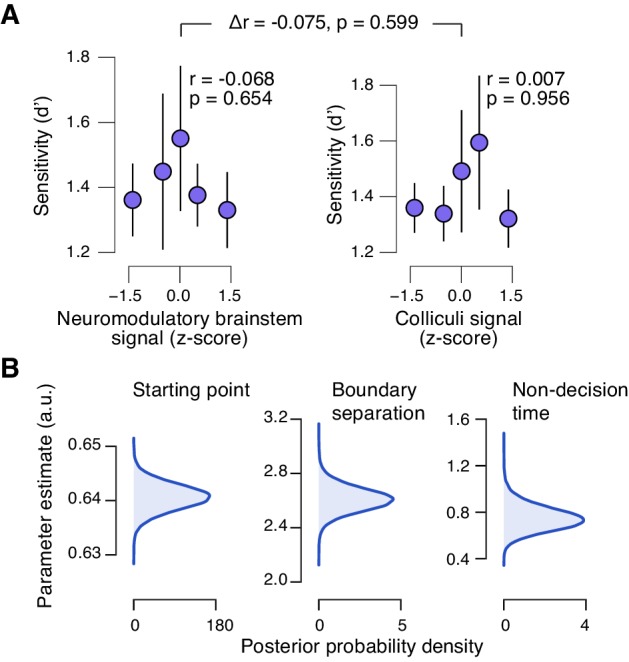
Figure 9—figure supplement 1. Brainstem responses are not associated to sensitivity.