Abstract
AIM
To investigate the regulation of Myopalladin (Mypn) and identify its gene network involved in restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM).
METHODS
Gene expression values were measured in the heart of a large family of BXD recombinant inbred (RI) mice derived from C57BL/6J and DBA/2J. The proteomics data were collected from Mypn knock-in and knock-out mice. Expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) mapping methods and gene enrichment analysis were used to identify Mypn regulation, gene pathway and co-expression networks.
RESULTS
A wide range of variation was found in expression of Mypn among BXD strains. We identified upstream genetic loci at chromosome 1 and 5 that modulate the expression of Mypn. Candidate genes within these loci include Ncoa2, Vcpip1, Sgk3, and Lgi2. We also identified 15 sarcomeric genes interacting with Mypn and constructed the gene network. Two novel members of this network (Syne1 and Myom1) have been confirmed at the protein level. Several members in this network are already known to relate to cardiomyopathy with some novel genes candidates that could be involved in RCM.
CONCLUSION
Using systematic genetics approach, we constructed Mypn co-expression networks that define the biological process categories within which similarly regulated genes function. Through this strategy we have found several novel genes that interact with Mypn that may play an important role in the development of RCM.
Keywords: System genetics, Myopalladin, System proteomics, Cardiomyopathy, Mutation
Core tip: Myopalladin (Mypn) is one of genes associated with many types of familial cardiomyopathies including dilated, hypertrophic and restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM). Using systematic genetics approach, we constructed Mypn co-expression networks of similarly regulated genes that function within defined biological processes. Several novel Mypn-interacting genes with potential important role in the development of RCM were discovered.
INTRODUCTION
Cardiomyopathies are heterogeneous diseases of heart muscle with unknown etiologies in 60%-70% of cases[1]. Outcomes such as heart failure, transplant or death in children and adults due to lack of definite effective treatment make cardiomyopathies one of the most devastating diseases[2]. Familial restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM), a rare form of cardiomyopathy, is characterized by diastolic dysfunction with restrictive physiology due to fibrosis and stiffness of the myocardium. Familial RCM has high incidence of sudden cardiac death, particularly in children with 2-year survival of 50% which drops up to 25% in 5-year survival period[3]. History of familial RCM is documented in 30% of cases with possible presence of dilated or hypertrophic cardiomyopathies (DCM and HCM, respectively)[4]. Only a few genes, troponins (cTnI and cTnT), myosin-binding protein C (MyBP-C) - myosin heavy chain (MYH7), myosin light chain2 and 3 (MYL2, MYL3), desmin (DES) and myopalladin (MYPN), have been reported to be associated with familial RCM.
The MYPN gene, located at chromosome 10q21.3, encodes a 147-kDa protein containing five immunoglobulin (Ig) domains[5]. MYPN localizes to the Z-discs and nucleus in striated muscle and functions in sarcomere assembly and regulation of gene expression. To date, twenty-three monoallelic heterozygous mutations in MYPN associated with DCM, HCM and RCM have been reported[6-8]. Clinical presentation of cardiomyopathy and heart failure typically exhibits in adulthood. Interestingly, different phenotypes were observed in family members and unrelated individuals carrying the same mutation. For instance, teenage siblings carrying the heterozygous c.1585C>T (p.Q529X-MYPN) nonsense mutation exhibited signs of overlapping phenotypes of DCM, HCM and RCM. The c.1585C>T mutation escapes a nonsense-mediated mRNA decay and produces a truncated 65-kDa MYPN protein, acting as a “poison peptide”[7,9]. The phenotype of knock-in mutant mice carrying heterozygous Mypn-Q526X mutation (KI), equivalent to human MYPN-Q529X, resembles RCM[9]. On the other hand, the homozygous mutants with biallelic Mypn-Q526X acted as the Mypn-null model due to ablation/knock-out (KO) of Mypn protein as a result of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay.
Over the last decade, it has become clear that genes do not work in isolation but in a complex combination with other genes and the environment. Thus, it is critical to identify gene networks rather than individual gene for complex traits or many diseases, including cardiomyopathies. We hypothesized that Mypn as a cardiomyopathy causal gene interacts with many other genes in a gene network to cause cardiomyopathy symptoms. The purpose of this investigation is to define novel cardiomyopathy causative genes through Mypn network using combined approaches of systems genetics and proteomics. To explore the Mypn gene network, we used BXD mice, a recombinant inbred (RI) strains derived from C57BL/6J strain (B6) and DBA/2J (D2) mouse cross. The Mypn gene is highly expressed and highly variable in the myocardium of BXD RI muse strains. We identified an upstream modulator of Mypn and defined both pathway and gene network. Proteomics studies in Mypn KI and KO mice defined potential mechanisms through which Q526X-Mypn mutation induced RCM and familial cardiomyopathies in general.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animal care and use statement
BXD and Mypn KI and KO mice described earlier were used[9-11]. Mice were maintained in micro-isolator cages at 25 °C under a 14/10 h light/dark cycle with free access to water and food. PCR analysis of tail genomic DNA was used for genotyping of knock-in and knock-out mice. Genotyping of BXD mice was generated using GigaMUGA genotyping array that typed approximately 150000 SNPs. All animal studies were approved by institutional IACUC of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center (UTHSC).
Tissue harvest, RNA extraction and microarray
The animals were sacrificed under isoflurane anesthesia. Cardiac perfusion were performed after an overnight fast. Hearts were taken immediately after perfusion, and then frozen in liquid nitrogen no more than a minute after sacrifice. The pieces of tissue were taken from frozen heart (most of them from ventricles) randomly. The hearts were harvested from 40 strains of the BXD family (BXD43 - BXD103) and both parental strains (C57BL/6 and DBA/2). Five animals per strain were used for this study.
RNA was extracted using QIAGEN RNA extraction kits (https://www.qiagen.com) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. In order to reduce the inhomogeneous nature of tissues due to the presence of different segments of the heart, the individual RNA sample from 5 mice at same strain were pooled evenly (by microgram of RNA) into a single RNA sample. The pooled RNA samples were then purified using RNEasy kit. The Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer was used to evaluate RNA integrity and quality. The RNA integrity values had to be greater than 1.8 to pass quality control. The RIN of most samples were greater than 2. The Affymetrix Mouse Gene 2.0 ST arrays were used for gene expression measurement and were run in a single batch.
Data processing
Raw microarray data were normalized using the Robust Multichip Array (RMA) method. The expression data were then re-normalized using a modified z-score described previously[12-15]. We calculated the log base 2 of normalized values above, computed Z scores for each array, multiplied the Z scores by 2, and added an offset of 8 units to each value. The reason for this transformation is to produce a set of Z-like scores for each array that have a mean of 8 and standard deviation of 2. The advantage of this modified Z score is that a two-fold difference in expression corresponds approximately to a 1-unit change.
Expression QTL mapping
Expression QTL (eQTL) mapping was performed at gene and exon levels through the WebQTL module on GeneNetwork as published previously[12-14]. This methodology uses regression analysis to determine the association between variability in a trait vs variability in alleles at markers across the genome. Simple interval mapping was performed to identify potential eQTLs that regulate Mypn expression levels and estimate the significance at each location consistent to known genotype data for those sites. Composite interval mapping was also performed to control for genetic variance associated with major eQTLs as well as any potentially masked secondary eQTLs. A quantitative measure of confidence of linkage between the observed phenotype, known genetic markers and expression level of Mypn was provided by creating a likelihood ratio statistic (LRS). Then, we established genome-wide significance for each eQTL using a permutation test that compared the LRS of our novel site with the LRS values for 1000-10000 genetic permutations[16].
Identification of upstream candidate genes
To identify upstream gene of Mypn, we determined the 1.5-LOD location of the significant eQTL of Mypn. All genes in this eQTL region were used for candidate gene analysis. The following criteria were used to identify the most likely candidates: (1) the gene is highly expressed in the heart; (2) the gene is significant (P < 0.05) correlated with Mypn expression in the heart; and (3) the gene has non-synonymous SNP, missense SNP or indel in coding regions of the gene, or the gene has significant cis-eQTL[14].
Genetic correlation and partial correlation analysis
We calculated Pearson product-moment correlations between expression of Mypn and expression of all other probe sets across the genome and produced sets of genetically correlated genes. After that, in order to identify biologically relevant correlates of Mypn, we also performed partial correlation analyses to remove linkage disequilibrium by controlling for cis-regulated genes near Mypn[14]. Both genetic correlation and partial correlation can be computed using the tools on GeneNetwork.
Gene set enrichment analysis
The genes that have both significant genetic correlation and partial correlation with Mypn were selected for gene set enrichment analysis. After removing Riken clones, intergenic sequences, predicted genes, and probes not associated with functional mouse genes, the remaining list of correlates with mean expression levels above baseline in the heart were uploaded to Webgestalt (http://bioinfo.vanderbilt.edu/webgestalt/) for gene enrichment analysis[17]. The P values generated from the hypergeometric test were automatically adjusted to account for multiple comparisons using the Benjamini and Hochberg correction[18]. The categories with an adjusted P value (adjp) of < 0.05 indicated that the set of submitted genes are significantly over-represented in that categories.
Gene network construction
The gene network was constructed and visualized using Cytoscape utility through “Gene-set Cohesion Analysis Tool (GCAT)” (http://binf1.memphis.edu/gcat/index.py). The nodes in the network represent genes and the edge between two nodes represent cosine score of Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) that determines the functional coherence of gene sets is larger than 0.6. The significance of the functional cohesion is evaluated by the observed number of gene relationships above a cosine threshold of 0.6 in the LSI model. The literature P-value (LP) is calculated using Fisher’s exact test by comparing the cohesion of the given gene set to a random one[19].
Protein isolation and 2D-DIGE analysis in Mypn KO and KI mice
To investigate genetic and proteomics correlations and to discover possible posttranslational alterations at the onset of restrictive phenotype, 3-mo-old wild-type (WT), mutant heterozygous MypnWT/Q526X (KI) and homozygous MypnQ526X (KO) male littermate mice were used[9]. The total protein from left ventricular (LV) myocardium was isolated, aliquoted, snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and kept at 80 °C until further analysis. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2D-DIGE) including protein labeling, 2D-electrophoreses, gel analysis and identification of proteins of interests using tandem mass spectrometry (MS) were performed by Applied Biomics (Hayward, CA) using established protocols as described previously[20].
MALDI-TOF (MS) and TOF/TOF (tandem MS/MS)
Tandem MS/MS were performed on a 5800 mass spectrometer (AB Sciex) as described previously[20]. Candidates with either protein score CI% or Ion CI% greater than 95 were considered significant.
RESULTS
Mypn expression levels in heart of BXD mice
Mypn which is highly expressed in the heart shows broad variability in expression among the BXD strains. The average expression of Mypn in all BXD strains was 12.29 ± 0.02 (log2 scale, mean ± SEM). The highest expression levels of 12.52 was found in BXD61 strain and the lowest of 11.89 was found in BXD87 strain (Figure 1), a difference more than 1.5 fold.
Figure 1.
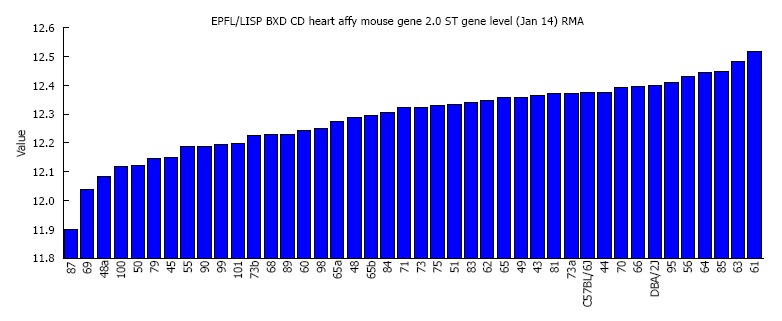
Rank-ordered expression of Mypn in the heart across the 40 BXD strains and their parental strains. The X-axis denotes the strain name while the Y-axis denotes the mean expression given in a LOG2 scale.
eQTL mapping and candidate regulator of Mypn
By performing simple interval mapping for Mypn at the transcript level, we found four suggestive eQTLs that are located on chromosome (Chr) 1, 5, 12 and X, respectively (Figure 2A). Simple interval mapping at exon level showed the expression of exons 6, 12 and 17 map to the same locus on Chr 1; and the expression of exons 7, 14, 18 and 19 map to the same locus at Chr 5. Principal component analyses were then performed to identify the main factor contributing to the variable expression of those exons. The first principal component (PC1) captured 67% of the expression variance for exons 6, 12 and 17. Simple interval mapping for this PC1 identified a significant eQTL with LRS of 19 (genome-wide P < 0.05) at Chr 1 whose location is the same as for gene level (Figure 2B). The first principal component captured 49% of the expression variance for exons 7, 14, 18 and 19. Simple interval mapping for this PC1 identified a suggestive eQTL with LRS of 14.7 at Chr 1 and a significant eQTL with LRS of 17.2 (genome-wide P < 0.05) at Chr 5 whose locations are the same as for gene level (Figure 2C). The first principal component for any other exons did not show any significant eQTLs by performing simple interval mapping. Composite interval mapping at both gene and exon levels revealed no other loci that modulate Mypn expression levels; so, Mypn expression in heart is regulated by two trans-eQTLs. The 1.5 LOD intervals of trans-eQTLs are located from 3 to 13.2 Mb of Chr 1 and 47 to 53 Mb of Chr 5 respectively.
Figure 2.
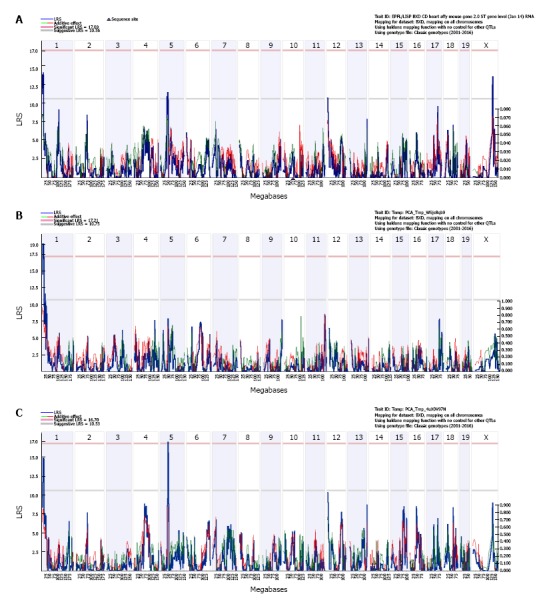
Genetic mapping of Mypn expression in the heart of BXD mice. The interval mapping at the transcript level identified 4 suggestive eQTLs at chromosome 1, 5, 12, and X respectively (A). The interval mapping for the first principal component of exon 6, 12, and 17 showed a significant eQTL (genome-wide P < 0.05) at Chr 1 (B). The interval mapping for the first principal component of exons 7, 14, 18, and 19 showed a suggestive eQTL at Chr 1 and a significant eQTL (genome-wide P < 0.05) at Chr 5 (Figure 2C). The left Y-axis provides LRS score in blue and right Y-axis provides the additive effect in green. The red and green lines show the effect of the D or B allele on trait values, respectively. The upper X-axis shows location by chromosome and the lower X-axis shows location in megabases. The two horizontal lines across the plot make the threshold for genome-wide significant (P < 0.05, red or upper line) and suggestive (P < 0.63, grey or lower line) thresholds. eQTL: Expression quantitative trait locus; LRS: Likelihood ratio statistic.
There are more than 70 genes/probesets in eQTL 1.5 LOD interval at Chr 1 and there are 22 genes/probesets whose expression is significantly correlated with Mypn expression (P < 0.05). After further filtering by expression value, sequence polymorphism, and eQTL type, there are only 3 genes that match the criteria for candidate genes. They are nuclear receptor coactivator 2 (Ncoa2), valosin containing protein (Vcpip1), and serum (Sgk3). Ncoa2 and Vcpip have nonsynonymous SNP between B6 and D2, while Sgk3 is cis-regulated. All three genes are highly expressed in the heart and considered as candidate genes that regulate Mypn expression.
There are more than 30 genes/probesets in eQTL 1.5 LOD interval on Chr 5. The expression of four of them is significantly correlated with Mypn expression (P < 0.05), but only leucine-rich repeat LGI family member 2 (Lgi2) is cis-regulated and is highly expressed in the heart. Accordingly, this gene is considered as the candidate gene at Chr 5 locus that regulates Mypn expression.
Gene function enrichment
The expression of 2843 transcripts/probesets has been found to correlate significantly with that of Mypn (P < 0.05). There are 1704 transcripts/probesets left after partial correction analysis. Among them, 1593 transcripts have unique Entrez gene IDs and were submitted for enrichment analysis. The most significant enrichments in the biological function category are “cellular process” (1026 genes, adjp = 0.000000000001) and “development process” (369 genes, adjp = 0.000000036) including “anatomical structure development” (321 genes, adjp = 0.0000009), “muscle structure development” (64 genes, adjp = 0.00000084) and “muscle cell differentiation” (47 genes, adjp = 0.0000031). The most relevant enrichments in the molecular function category are “cytoskeletal protein binding” (63 genes, adjp < 0.006), “SH3 domain binding” (19 genes, adjp < 0.01), “growth factor binding” (19 genes, adjp < 0.003), and “Protein serine/threonine kinase activity” (47 genes, adjp < 0.01). The most significant enrichments in the cellular component category that is relative to muscle function are “contractile fiber” (24 genes, adjp < 0.009), “myofibril” (21 genes, adjp < 0.03), “sarcomere” (19 genes, adjp < 0.03), “Z disc” (13 genes, adjp < 0.05), “Phosphorylase kinase complex” (3 genes, adjp < 0.02), and “AMP-activated protein kinase complex” (4 genes, adjp < 0.02).
The disease enrichment analysis showed that those genes are significantly involved in 29 diseases (adjp < 0.05, Table 1). Almost all of diseases shown in Table 1 are cardiovascular related diseases, including cardiac arrhythmias, ventricular dysfunction and cardiovascular abnormalities. Diseases such myocardial ischemia, Romano-Ward syndrome, congenital heart defects, congenital long QT syndrome, atrial fibrillation (AF), atrioventricular block, nitrous oxide system (NOS) and coronary disease are the novel diseases that could be an interest.
Table 1.
The disease enrichment analysis
| Disease | Gene No. | Adjusted value |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 59 | 4.38E-05 |
| Heart diseases | 50 | 0.0002 |
| Vascular diseases | 49 | 0.0003 |
| Cardiovascular abnormalities | 27 | 0.0003 |
| Bradycardia | 9 | 0.0067 |
| congenital long QT syndrome | 6 | 0.0094 |
| Metaplasia | 26 | 0.0094 |
| Cerebrovascular disorders | 25 | 0.0094 |
| Arrhythmias, cardiac | 19 | 0.0094 |
| Syncope | 12 | 0.0094 |
| Romano-ward syndrome | 6 | 0.0094 |
| Neovascularization, pathologic | 24 | 0.0094 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 14 | 0.0094 |
| Glycogen storage disease | 8 | 0.0097 |
| Myocardial ischemia | 34 | 0.0097 |
| Glycogen storage disease, type IV | 5 | 0.0181 |
| Heart murmurs | 4 | 0.0207 |
| Congenital abnormalities | 61 | 0.0207 |
| Adhesion | 64 | 0.0207 |
| Heart defects, congenital | 17 | 0.0207 |
| Ventricular dysfunction | 14 | 0.0207 |
| Atrioventricular block nitrous oxide system | 8 | 0.0264 |
| Heart block | 11 | 0.0315 |
| Parkinson disease | 18 | 0.0450 |
| Mesothelioma | 10 | 0.0450 |
| Coronary artery disease | 31 | 0.0450 |
| Stress | 50 | 0.0450 |
| Coronary disease | 31 | 0.0450 |
| Jervell-lange nielsen syndrome | 4 | 0.0450 |
The gene pathway analysis showed that those genes are significantly enriched in 10 pathways. Table 2 demonstrates top seven pathways, including “Insulin signaling pathway”, “Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy”, “Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy”, “ECM-receptor interactions”, and “Focal adhesion” that are known mechanisms involved in the development of cardiomyopathy.
Table 2.
The significantly enriched gene pathways
| Pathway name | No. Gene | Adjusted value |
| Insulin signaling pathway | 28 | 9.47E-06 |
| Endocytosis | 33 | 0.0003 |
| Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | 15 | 0.0171 |
| Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy | 13 | 0.0385 |
| Extracellular matrix-receptor interaction | 14 | 0.0445 |
| Focal adhesion | 24 | 0.0462 |
| Prostate cancer | 14 | 0.0462 |
| Tryptophan metabolism | 9 | 0.0462 |
| Pathways in cancer | 35 | 0.0462 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | 30 | 0.0462 |
MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase.
Genetic network
The strength of correlation among genes with which Mypn is involved can be evaluated by co-expression network. In order to identify known biological relations among co-expressed genes, we selected genes that statistically significantly enriched in sarcomere (19 genes, adjp < 0.03), and uploaded them to GCAT (http://binf1.memphis.edu/gcat/index.py) for the functional coherence analysis and gene network construction. Three genes out of these 19 are not found in the database or have no functional relationship with other genes. The remaining 16 genes showed significant functional cohesion with literature P value of 1.15e-10 (Figure 3). Multiple resources including Chillibot, GeneCard, and PubMed were used to determine whether members of the Mypn co-expression network had been previously associated with cardiomyopathy. In addition to Mypn, another 6 genes in this network (Ldb3, Des, Actn2, Fhod3, Tpm2, Syne1) are already known to relate to cardiomyopathy. Furthermore, 6 genes (Myo18b, Fhod3, Myom1, Bmp10, Myl4, Obscn, Pdlim5) in the network have missense SNP that could change their protein function.
Figure 3.
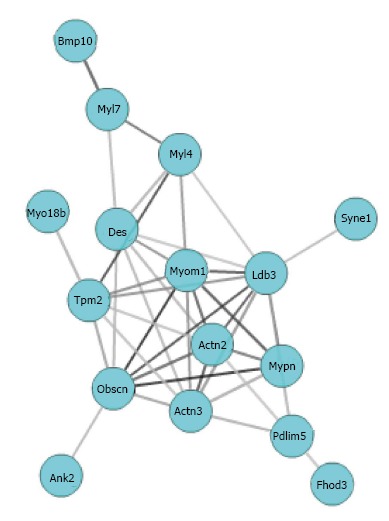
Mypn gene network graph created using Gene-set Cohesion Analysis Tool described in the methods. Gene symbols are located at nodes in circles and lines interconnecting the nodes are based on literature correlation.
Myocardial proteomics in Mypn-KI and Mypn-KO mouse hearts
In order to confirm if the selected transcriptional networks are reproduced on a protein level, the proteomic profile of the myocardium from KI and KO Mypn mice were compared to the myocardial protein profile from WT littermates (n = 3). In 2D-DIGE analysis, about 2100 matched spots on each 2D gel were detected by DeCyder software, among of which a relative abundance of 65 polypeptides were altered between WT vs KI (Figure 4A), WT vs KO (Figure 4B) and KI vs KO (Figure 4C). Out of these 65 peptides, 27 are significantly changed (≥ 1.5 fold and P ≤ 0.05) between WT and both of KO and KI mice. Table 3 demonstrates differential protein profiling in mutant mice vs control WT littermates and strong association of these 27 proteins with RCM phenotype. For example, proteins involved in regulation of focal adhesion, sarcomere, actin-cytoskeleton, microtubule organization and Ca-signaling are upregulated in KI mice compared to control WT mice, while KO hearts display downregulation of these proteins compared to WT.
Figure 4.
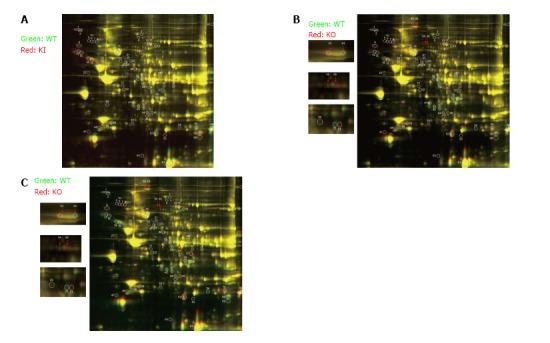
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of heart lysates from 12-wk-old mice. Comparative proteomics analysis revealed 10 non-redundant proteins in KI (heterozygote mutant) vs WT controls (A), 8 non-redundant proteins in KO (homozygote mutant) vs WT mouse hearts (B); 19 non-redundant protein changes in KO vs KI (C). Arrows indicate differential phisphorylation of proteins in WT vs KO and KI vs KO mice hearts (B and C, respectively).
Table 3.
Differentially expressed proteins identified by MALDI MS-MS
| No. | Protein code | Gene ID | KI/WT | KO/WT | KO/KI | Pathways |
| 1 | PKP1 | 18772 | 1.76 | -1.13 | -1.99 | Focal adhesion, apoptosis |
| 2 | HRC | 15464 | 1.62 | 1.06 | -1.53 | Calcium signaling |
| 4 | PYGB | 53313 | 1.61 | 1.16 | -1.39 | Glucagon signaling, insulin signaling |
| 5 | MSN1 | 17698 | -2.68 | 4.71 | 12.57 | Cell shape, actin-cytoskeleton |
| 6 | VINC | 22330 | -4.18 | 4.96 | 20.64 | Cell-cell adhesion, cell shape, actin cytoskeleton |
| 8 | SYNE11 | 64009 | -3.59 | 5.82 | 20.82 | Nucleus-cytoskeleton connection |
| 14 | ADAM10 | 11487 | 1.71 | -1.18 | -2.02 | Inflammation, amiloidosis |
| 17 | TNPO3 | 320938 | -1.11 | 1.51 | 1.67 | Nucleus-cytoskeleton connection |
| 18 | CAPN8 | 170725 | 2.15 | -1.02 | -2.19 | Inflammation |
| 19 | CGNL1 | 68178 | 1.58 | -1.03 | -1.63 | Focal adhesion |
| 20 | VIM | 22352 | 1.43 | 1.40 | -1.02 | Cell division, fibrosis |
| 23 | MYH6 | 17888 | 1.02 | -3.41 | -3.49 | Sarcomere, actin-cytoskeleton |
| 24 | NRAP | 18175 | -1.03 | 1.79 | 1.84 | Focal adhesion, actin cytoskeleton |
| 28 | ANXA3 | 20480 | 1.23 | -1.80 | -2.23 | Prostaglandin synthesis and regulation |
| 29 | LATS2 | 23805 | -1.58 | -1.51 | 1.04 | Hippo signaling pathway, DNA damage |
| 32 | SPTB1 | 20741 | 1.56 | -1.01 | -1.59 | Actin-cytoskeleton |
| 33 | GCC2 | 11426 | 1.04 | -3.78 | -3.92 | Vesicle-mediated transport, retrograde transport at the trans-Golgi-network |
| 37 | ACADS | 12306 | -2.01 | 1.12 | 2.24 | Mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation |
| 39 | FHL2 | 14200 | 1.05 | -2.25 | -2.37 | Focal adhesion, Wnt, calcineurin signaling |
| 39 | MYOZ2 | 59006 | 1.05 | -2.25 | -2.37 | Cytoskeleton, calcineurin signaling, myofibrillogenesis |
| 47 | FGF9 | 14180 | 2.93 | 5.90 | 2.01 | Fibrosis |
| 53 | DST | 13518 | 2.23 | 1.01 | -2.21 | Focal adhesion, actin cytoskeleton |
| 59 | FEZ2 | 56069 | 1.89 | -1.11 | -2.12 | N/A |
| 59 | CSRP3 | 13009 | 1.89 | -1.11 | -2.12 | Stress sensing, myogenesis |
| 62 | MYOM1 | 319565 | -1.37 | 1.58 | 2.15 | Striated muscle contraction |
| 63 | MYOM2 | 17930 | +++ | Sarcomere | ||
| 65 | EZR/MSN | 17698 | +++ | Cell surface organization, adhesion, microtubule |
Genes with statistically significant correlation with that of Mypn in mouse hearts. KI: Knock-in Mypn mouse; KO: Knock-out Mypn mouse; WT: Wild type littermates; -: Proteins downregulated compared to WT; +++: Proteins with differentially phosphorylated proteins in KI vs KO; N/A: Not applicable.
Out of these 27 proteins, 12 were also significantly correlated with Mypn in mouse hearts at the transcriptional level (Table 4). Further, two of them (Syne1 and Myom1, Tables 3 and 4, asterisks) have the closest connection with Mypn representing as potential members of Mypn gene network described above.
Table 4.
Genes whose gene expression has significant correlation with Mypn and gene product have significant change comparing with KI or KO mice
| Protein code | Corr P value | KI/WT | KO/WT | KO/KI |
| CGNL1 | 0.0024 | 1.58 | -1.03 | -1.63 |
| PKP1 | 0.0082 | 1.76 | -1.13 | -1.99 |
| SYNE11 | 0.0114 | -3.59 | 5.82 | 20.82 |
| PYGB | 0.0157 | 1.61 | 1.16 | -1.39 |
| MSN | 0.0194 | -2.68 | 4.71 | 12.57 |
| ANXA3 | 0.0319 | 1.23 | -1.8 | -2.23 |
| MYOM11 | 0.0335 | -1.37 | 1.58 | 2.15 |
| ACADS | 0.035 | -2.01 | 1.12 | 2.24 |
| GCC2 | 0.0375 | 1.04 | -3.78 | -3.92 |
| FEZ2 | 0.0399 | 1.89 | -1.11 | -2.12 |
| LATS2 | 0.0431 | -1.58 | -1.51 | 1.04 |
Genes with statistically significant correlation with that of Mypn in mouse hearts. KI: Knock-in Mypn mouse; KO: Knock-out Mypn mouse; WT: Wild type littermates; -: Proteins downregulated compared to WT.
DISCUSSION
Cardiomyopathies are devastating heart muscle diseases with lack of definite, effective treatment, ultimately resulting in heart failure, transplant or death in children and adults[2]. Clinically, cardiomyopathies are heterogeneous diseases and classified into 5 distinctive groups characterized by changes in chamber size, thickness of myocardial walls, and function[1]. Although many studies have identified disease-causative mutations in all forms of cardiomyopathy, etiology remains unknown in 60%-70% of cases[21,22]. Most of genetic studies consider individual genes and mutations rather than co-regulated genes networks. The systems genetics approach is a powerful tool in identifying candidate genes and constructing genetic networks that regulate complex traits and phenotypes of mono- and poly-genetic diseases[12]. Thus, we used the system biology methodology in BXD RI strains and genetically engineered KI and KO Mypn mice to reveal the gene network that is co-regulated with Mypn, a gene that contributes to the development of cardiomyopathies.
The MYPN protein, a nodal messenger molecule, transmits stretch-signaling from Z-discs to the nucleus in cardiac myocytes[5]. It has been reported that mutations in Mypn cause autosomal dominant cardiomyopathies in humans with variable penetrance[6-8]. Murine models used in this study are well-characterized model of human RCM, which carries a Q526X-Mypn mutation[9]. Characteristic features of RCM phenotype in heterozygous mutant (KI) model include diastolic dysfunction with abnormal relaxation or impaired ventricular filling during diastole without systolic dysfunction due to “poison (mutant) peptide” effect. Homozygous mutants considered as a Mypn-null (KO) models due to ablation of Mypn gene did not manifest RCM phenotypes. Upon this functional knowledge, we sought to expand identifying loci that regulate expressions of Mypn and other genes whose expression levels are co-regulated along with Mypn. We have identified two loci of interest that regulate Mypn expression in the heart. The first locus located at proximal Chr 1 is associated with Mypn exon 6, 12 and 17 (Figure 5). Three genes at this locus, Ncoa2 (nuclear receptor coactivator 2, also know as Grip1), Vcpip1 (valosin containing protein interacting protein 1), and Sgk3 (serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase family member 3), match criteria of candidate genes. Interestingly, Ncoa2 is shown in be required in regulation of muscle-specific gene expression for expression of MYOG (OMIM169980), CDKN1A (OMIM116899) and MEF2C (OMIM600662) in both proliferating and confluent myoblasts[23]. Second locus located at the middle of Chr 5 is associated with Mypn exons 7, 14, 18 and 19. Only one gene, Lgi2 (leucine-rich repeat LGI family, member 2), at this locus matches the criteria of candidate genes.
Figure 5.
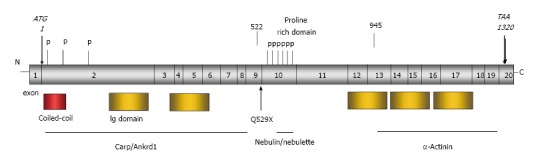
Structure of Mypn gene and functional domain of the protein. The N-terminal domain containing two immunoglobulin (Ig) and coiled-coil domains binds to cardiac ankyrin repeat protein (Carp/Ankrd1), the negative regulator of muscle gene expression. The rod domain contains proline rich domain with phosphorylation residues and binds to the SH3-domain of nebulin/nebulette at the Z-discs. The C-terminal domain containing 3 Ig domains binds to α-actinin at the Z-discs.
To reveal the possible mechanisms by which Mypn variants affect individuals with RCM, we further performed gene enrichment analysis for genes that significantly co-vary with Mypn in the heart. The gene ontology analysis found multiple significant biological processes for Mypn and its correlated genes. It includes “cytoskeletal protein binding”, “SH3 binding domains”, “growth factor binding”, “muscle structure development”, and “muscle cell differentiation”. For example, genes such as Des, Plec, Flnc, Actn2, Actn3, Tpm2, Obscn and Ank2 from “cytoskeletal protein binding” are known cytoskeletal genes associated with cardiomyopathies. Interestingly, many genes from those categories could be candidates for further investigation as possible disease-causative genes for RCM. As shown in Figure 5, Mypn has several phosphorylation sites in the N-terminal Carp/Ankrd1 binding domain. The rod domain of Mypn responsive for the SH3-nebulin/nebulette binding has also several phosphorylation sites at the proline rich domain. Related to this, we found 47 genes involved in the “protein serine/threonine kinase activity”, suggesting possibly novel biological processes in which Mypn may be involved.
The gene ontology analysis also revealed several significant cellular component categories. They are especially enriched at “contractile fiber”, “myofibril”, “sarcomere”, and “Z-disc”. All these cytoskeletal genes encode a protein network team with distinct function of each that play key roles in the orchestrated contractile function of myocytes. We discovered posttranslational changes in Myom2 and Msn/moesin (Table 3) directing our attention to the genes from “phosphorylase kinase complex” and “AMP-activated protein kinase complex”. These findings support the idea that Mypn mutations may alter phosphorylation of other cytoskeletal proteins.
The disease enrichment analysis showed that those genes are considerably involved in 29 diseases. Almost all of those 29 diseases are cardiovascular related, which support the involvement of Mypn and its networked genes in the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases including RCM.
The KEGG database was queried to identify pathways correlated to Mypn expression. We identified 10 significant pathways, most of which are involved in known mechanisms of cardiomyopathy including for instance insulin signaling, HCM, focal adhesion and MARK signaling. We found novel pathways as well, such as ARVC and EMC-receptor interactions that can be of high importance during development of cardiomyopathy.
Further, we used 16 genes that are significantly enriched in the sarcomere to create a gene network. All genes from the “sarcomere” network are highly expressed in the heart and significantly correlated with Mypn expression. We found well-known cardiomyopathy-associated genes such as Ldb3, Des, Actn2, Fhod3, Tpm2, and Syne1 in this network. Other genes in the network including Myo18b, Fhod3, Myom1, Bmp10, Myl4, Obscn, and Pdlim5 are likely to be modifier genes interacting with Mypn to induce cardiomyopathy, especially genes that have missense SNPs. For example, the Z-discs Myo18b (OMIM607295), a potential Mypn-partner gene with nonsynonymous SNPs at exons 7, 18, 22, may alter Mypn protein function and lead to similar phenotypes. A human homozygous p.S2302X nonsense mutation in MYO18B was reported as causative for Klippel-Feil syndrome with nemaline myopathy and facial dysmorphism[24]. We also found that nonsynonymous SNP at exon 2 in Myl4 (a fetal-specific myosin light chain 4 highly expressed in atrial myocardium) to be connected with Mypn. To support our finding, a heterozygous p.G11L mutation in MYL4 (OMIM160770) in a family with early-onset AF was recently reported[25]. Another mutation, p.E17K in MYL4 causes disruption of F-actin–Z-disc complex, consequently disturbing the mechano-electrical integration and calcium signaling in cardiomyocytes leading to atrial myopathy with AF. Given our findings, we highlight possible implication of Mypn gene network in arrhythmia disorders involving primary atrial-specific or overlapping ventricular/atrial inherited myopathies.
Two novel genes (Syne1 and Myom1) in this gene network have been found to interact with Mypn at the protein level in Mypn-KO and KI mice hearts. Both genes are highly expressed the heart and have highly significant correlation with Mypn at the transcriptional level. Human SYNE1 (OMIM608441) encodes the nesprin, a giant 8797-amino acid protein. The N-terminus of nesprin is localized to the sarcomeres of cardiac and skeletal muscle, while the C-terminus is localized to the nuclear envelope participating in a complex that links the nucleoskeleton to the cytoskeleton (LINC)[26]. Mutations in SYNE1 are associated with Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy and DCM[27]. Common features of MYPN and SYNE1 proteins are that both are involved in a force transmission between cytoskeleton and the nucleus. This further highlights importance of Mypn-Syne1 interactions in transducing the mechanical signal into transcriptional response.
Here we report that Myom1, encoding protein Myomesin1/Skelemin, is a novel candidate gene for RCM due to its strong genetic correlations to known RCM networked genes. Myom1 is cis-regulated gene and has non-synonymous SNPs in coding areas with strong downstream effects on cardiomyopathy phenotypes. Myom1 is found to be significantly altered on a protein level in Mypn mouse disease models. Common features of MYOM1 and MYPN proteins are that both contain Ig-domains that play critical structural roles during muscle force-generation[28]. Like MYPN, MYOM1 is also detected in the nucleus and cytoskeleton, suggesting that it may play a role in gene expression and stretch-induced signaling[29]. The only missense mutation, p.V1490I, that affects dimerization and elastic properties of MYOM1 was reported in a family with inherited HCM[30]. Important functions of MYOM1 in regulating titin, a giant molecular spring which is responsible for the passive elasticity of muscle further underscore such a possibilities[31]. We also hypothesize that posttranslational phosphorylation of MYOM1 may contribute to the development of RCM in Mypn mouse models.
In summary, we have discovered two genetic loci that modulate the expression of Mypn. We have found Mypn co-varies with a different sets of genes and enriched in pathways involved in the development of cardiomyopathy. Finally, we constructed a sarcomeric Mypn gene network containing 16 genes. Moreover, expression changes in SYNE1 and MYOM1 were confirmed on a protein level in RCM model in vivo. We emphasize that systems genetic and genomics analysis in patients may define novel candidate genes and mechanisms of cardiomyopathies.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Drs. Evan Williams and Robert Williams for help to edit manuscript and process the gene expression data.
COMMENTS
Background
Genetic differences mediate individual differences in susceptibility to cardiomyopathies and severity of disease symptoms. Mypn gene mutations are associated with familial restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM). Mutant mice carrying human mutations recapitulate the RCM phenotype.
Research frontiers
Most of genetic studies consider individual genes and mutations rather than associated networks of co-regulated genes. Systems genetics and proteomics approaches have proven to be a powerful tool for identifying candidate genes and constructing genetic and protein networks that regulate complex traits and phenotypes of mono- and polygenetic diseases.
Innovations and breakthroughs
This study is the first constructing the Mypn-gene network and discovering novel RCM-causative genes using systems genetics and proteomics approaches.
Applications
The study will provide bases for discovering novel genes that are associated with the development of cardiac muscle diseases.
Terminology
Cardiomyopathies are diseases of heart muscle that ultimately result in heart failure, transplant or death in children and adults.
Peer-review
Very great study, methodology is well.
Footnotes
Supported by National Institutes of Health, Nos. R01 HL128350 (LL), R01 HL53392 and R01 HL087000 (JAT).
Institutional animal care and use committee statement: All animal studies were approved by institutional IACUC of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center (UTHSC).
Conflict-of-interest statement: To the best of our knowledge, no conflict of interest exists.
Data sharing statement: Resources: Principles and Guidelines for Recipients of NIH Grants and Contracts” issued in December, 1999. Dr. Lu Lu is responsible for coordinating data sharing through GeneNetwork (GN) at the: http://www.genenetwork.org/webqtl/main.py. GN is a group of linked data sets and tools used to study complex networks of genes, molecules, and higher order gene function and phenotypes. GN combines more than 25 years of legacy data generated by hundreds of scientists together with sequence data (SNPs) and massive transcriptome data sets (expression genetic or quantitative trait locus data sets). GN connected to numerous links to the UCSC and Ensembl Genome Browsers, PubMed, Entrez Gene, GNF Expression Atlas, ABI Panther, and WebGestalt provide users with rapid interpretive information about genomic regions, published phenotypes and genes.
Manuscript source: Invited manuscript
Specialty type: Cardiac and cardiovascular systems
Country of origin: United States
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): A, A
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
Peer-review started: December 7, 2016
First decision: January 16, 2017
Article in press: March 2, 2017
P- Reviewer: Amiya E, Cosmi E S- Editor: Ji FF L- Editor: A E- Editor: Lu YJ
References
- 1.Maron BJ, Towbin JA, Thiene G, Antzelevitch C, Corrado D, Arnett D, Moss AJ, Seidman CE, Young JB. Contemporary definitions and classification of the cardiomyopathies: an American Heart Association Scientific Statement from the Council on Clinical Cardiology, Heart Failure and Transplantation Committee; Quality of Care and Outcomes Research and Functional Genomics and Translational Biology Interdisciplinary Working Groups; and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation. 2006;113:1807–1816. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.174287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Towbin JA, Bowles NE. The failing heart. Nature. 2002;415:227–233. doi: 10.1038/415227a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Denfield SW, Rosenthal G, Gajarski RJ, Bricker JT, Schowengerdt KO, Price JK, Towbin JA. Restrictive cardiomyopathies in childhood. Etiologies and natural history. Tex Heart Inst J. 1997;24:38–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Webber SA, Lipshultz SE, Sleeper LA, Lu M, Wilkinson JD, Addonizio LJ, Canter CE, Colan SD, Everitt MD, Jefferies JL, et al. Outcomes of restrictive cardiomyopathy in childhood and the influence of phenotype: a report from the Pediatric Cardiomyopathy Registry. Circulation. 2012;126:1237–1244. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.104638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bang ML, Mudry RE, McElhinny AS, Trombitás K, Geach AJ, Yamasaki R, Sorimachi H, Granzier H, Gregorio CC, Labeit S. Myopalladin, a novel 145-kilodalton sarcomeric protein with multiple roles in Z-disc and I-band protein assemblies. J Cell Biol. 2001;153:413–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.153.2.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Duboscq-Bidot L, Xu P, Charron P, Neyroud N, Dilanian G, Millaire A, Bors V, Komajda M, Villard E. Mutations in the Z-band protein myopalladin gene and idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;77:118–125. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvm015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Purevjav E, Arimura T, Augustin S, Huby AC, Takagi K, Nunoda S, Kearney DL, Taylor MD, Terasaki F, Bos JM, et al. Molecular basis for clinical heterogeneity in inherited cardiomyopathies due to myopalladin mutations. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:2039–2053. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Meyer T, Ruppert V, Ackermann S, Richter A, Perrot A, Sperling SR, Posch MG, Maisch B, Pankuweit S. Novel mutations in the sarcomeric protein myopalladin in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013;21:294–300. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2012.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huby AC, Mendsaikhan U, Takagi K, Martherus R, Wansapura J, Gong N, Osinska H, James JF, Kramer K, Saito K, et al. Disturbance in Z-disk mechanosensitive proteins induced by a persistent mutant myopalladin causes familial restrictive cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:2765–2776. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.09.071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Peirce JL, Lu L, Gu J, Silver LM, Williams RW. A new set of BXD recombinant inbred lines from advanced intercross populations in mice. BMC Genet. 2004;5:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-5-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hegmann JP, Possidente B. Estimating genetic correlations from inbred strains. Behav Genet. 1981;11:103–114. doi: 10.1007/BF01065621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chesler EJ, Lu L, Shou S, Qu Y, Gu J, Wang J, Hsu HC, Mountz JD, Baldwin NE, Langston MA, et al. Complex trait analysis of gene expression uncovers polygenic and pleiotropic networks that modulate nervous system function. Nat Genet. 2005;37:233–242. doi: 10.1038/ng1518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.King R, Lu L, Williams RW, Geisert EE. Transcriptome networks in the mouse retina: An exon level BXD RI database. Mol Vis. 2015;21:1235–1251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lu H, Lu L, Williams RW, Jablonski MM. Iris transillumination defect and its gene modulators do not correlate with intraocular pressure in the BXD family of mice. Mol Vis. 2016;22:224–233. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Geisert EE, Lu L, Freeman-Anderson NE, Templeton JP, Nassr M, Wang X, Gu W, Jiao Y, Williams RW. Gene expression in the mouse eye: an online resource for genetics using 103 strains of mice. Mol Vis. 2009;15:1730–1763. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Churchill GA, Doerge RW. Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics. 1994;138:963–971. doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.3.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhang D, Choi DW, Wanamaker S, Fenton RD, Chin A, Malatrasi M, Turuspekov Y, Walia H, Akhunov ED, Kianian P, et al. Construction and evaluation of cDNA libraries for large-scale expressed sequence tag sequencing in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Genetics. 2004;168:595–608. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.034785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Klipper-Aurbach Y, Wasserman M, Braunspiegel-Weintrob N, Borstein D, Peleg S, Assa S, Karp M, Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y, Laron Z. Mathematical formulae for the prediction of the residual beta cell function during the first two years of disease in children and adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Med Hypotheses. 1995;45:486–490. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(95)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Xu L, Furlotte N, Lin Y, Heinrich K, Berry MW, George EO, Homayouni R. Functional cohesion of gene sets determined by latent semantic indexing of PubMed abstracts. PLoS One. 2011;6:e18851. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Huang Y, Powers C, Madala SK, Greis KD, Haffey WD, Towbin JA, Purevjav E, Javadov S, Strauss AW, Khuchua Z. Cardiac metabolic pathways affected in the mouse model of barth syndrome. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0128561. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hershberger RE, Cowan J, Morales A, Siegfried JD. Progress with genetic cardiomyopathies: screening, counseling, and testing in dilated, hypertrophic, and arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy. Circ Heart Fail. 2009;2:253–261. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.108.817346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Towbin JA. Inherited cardiomyopathies. Circ J. 2014;78:2347–2356. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-14-0893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chen SL, Dowhan DH, Hosking BM, Muscat GE. The steroid receptor coactivator, GRIP-1, is necessary for MEF-2C-dependent gene expression and skeletal muscle differentiation. Genes Dev. 2000;14:1209–1228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Alazami AM, Kentab AY, Faqeih E, Mohamed JY, Alkhalidi H, Hijazi H, Alkuraya FS. A novel syndrome of Klippel-Feil anomaly, myopathy, and characteristic facies is linked to a null mutation in MYO18B. J Med Genet. 2015;52:400–404. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Orr N, Arnaout R, Gula LJ, Spears DA, Leong-Sit P, Li Q, Tarhuni W, Reischauer S, Chauhan VS, Borkovich M, et al. A mutation in the atrial-specific myosin light chain gene (MYL4) causes familial atrial fibrillation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11303. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhang Q, Ragnauth C, Greener MJ, Shanahan CM, Roberts RG. The nesprins are giant actin-binding proteins, orthologous to Drosophila melanogaster muscle protein MSP-300. Genomics. 2002;80:473–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Puckelwartz MJ, Kessler EJ, Kim G, Dewitt MM, Zhang Y, Earley JU, Depreux FF, Holaska J, Mewborn SK, Pytel P, et al. Nesprin-1 mutations in human and murine cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010;48:600–608. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.11.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pinotsis N, Chatziefthimiou SD, Berkemeier F, Beuron F, Mavridis IM, Konarev PV, Svergun DI, Morris E, Rief M, Wilmanns M. Superhelical architecture of the myosin filament-linking protein myomesin with unusual elastic properties. PLoS Biol. 2012;10:e1001261. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Reddy KB, Fox JE, Price MG, Kulkarni S, Gupta S, Das B, Smith DM. Nuclear localization of Myomesin-1: possible functions. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2008;29:1–8. doi: 10.1007/s10974-008-9137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Siegert R, Perrot A, Keller S, Behlke J, Michalewska-Włudarczyk A, Wycisk A, Tendera M, Morano I, Ozcelik C. A myomesin mutation associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy deteriorates dimerisation properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;405:473–479. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.01.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Labeit S, Kolmerer B, Linke WA. The giant protein titin. Emerging roles in physiology and pathophysiology. Circ Res. 1997;80:290–294. doi: 10.1161/01.res.80.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


