Abstract
Background
Waterpipe tobacco smoking (WTS) is increasing in popularity despite evidence of harm and potential for dependence. Intervention development has been hampered by a lack of longitudinal, nationally-representative data on usage patterns and factors independently associated with WTS initiation. Therefore, we aimed to characterize key transitions between WTS states in a nationally-representative group of young adults, with particular attention to factors independently associated with initiation.
Methods
Participants were randomly selected from a national probability-based panel representing 97% of the U.S. A total of 1785 adults ages 18–30 at baseline completed two web-based surveys 18 months apart in 2013 and 2014. Assessments included knowledge of waterpipe tobacco smoke composition, positive and negative attitudes towards WTS, normative beliefs, intention to use waterpipe, and WTS behavior. We used multivariable logistic regression to assess the association between predictive factors and subsequent WTS initiation.
Results
In fully-adjusted models, overall knowledge about toxicants associated with WTS was not associated with subsequent WTS initiation. Similarly, negative attitudes and normative beliefs were not associated WTS uptake. However, baseline positive attitudes were strongly and significantly associated with WTS initiation (Adjusted Odds Ratio [AOR]=1.7, 95% CI=1.2–2.3). Similarly, baseline intention to use WTS was strongly associated with subsequent initiation (AOR=7.0, 95% CI=3.5–13.7).
Conclusions
Prevention efforts may be most successful if they target individuals with clear intentions to use WTS and challenge positive attitudes surrounding WTS.
Impact
Surveillance of WTS trajectories will help inform healthcare and policy surrounding this emerging risk behavior among U.S. young adults.
Keywords: hookah, waterpipe, longitudinal, initiation, Theory of Reasoned Action, Health Belief Model
As traditional cigarette smoking rates decrease in the U.S. (1), rates of new and emerging tobacco and nicotine product use have been steadily increasing (2). This includes waterpipe tobacco smoking (WTS, or “hookah”), which is increasingly popular among adolescent and young adult populations (3, 4). While the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) declared its intention to regulate WTS starting on August 8, 2016 (5), WTS remains exempt from many tobacco control policies (6). Moreover, the popular perception remains that WTS is a fun, relaxing, social activity with few negative associations and repercussions (7, 8). These beliefs and attitudes are concerning given our increasing understanding of the association of WTS with negative health effects—such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and decreased pulmonary function (9)—and potential for dependence (10).
There are three major gaps in the literature that hinder our ability to optimally intervene in this area. First, little is known regarding transitions between various WTS usage states over time. For example, while current cigarette smokers (usually defined as having use at least once in the past 30 days) (11) tend to remain current users, these patterns have not been established regarding WTS. It would be valuable to obtain a more nuanced picture of transitions between various stages of WTS in order to tailor interventions in terms of timing. Related to this, it will be beneficial to conduct longitudinal studies with longer follow-up periods than have been conducted in the past. To our knowledge, the highest-quality longitudinal study was conducted over 6 months (12).
Second, there is a need for better understanding of initiation of WTS, which is generally defined as the transition from never use to ever use. Rates of WTS initiation among U.S. late adolescents and young adults are between 13–23%, and factors associated with WTS initiation are not clearly understood (13–15). One established factor that been clearly associated with WTS initiation is other substance use at baseline; these associations are well-grounded in theory and the empiric evidence base is strong (12, 15). However, what is not established is whether there are associations between baseline theory-based perceptual predictors—such as knowledge, attitudes, normative beliefs, and intentions—and subsequent initiation as would be predicted by relevant conceptual models (16). For example, some prior research suggests that negative attitudes toward WTS protect against WTS initiation (13), while other studies suggest there may be more influence for positive attitudes and normative beliefs (12, 13). Likewise, studies examining knowledge of the harmful components of waterpipe tobacco and effects on WTS are inconclusive (13, 17). It will be important to elucidate associations between these types of predictive factors and initiation because this will directly influence subsequent educational and policy initiatives.
Third, it is now important to conduct high quality studies of WTS with large, nationally-representative samples that include a broad cohort of emerging adults. While research to date has been extremely valuable, the vast majority of it has been localized with limited external generalizability. Additionally, emerging adulthood is increasingly recognized as a crucial time for the development and consolidation of life-long habits and addictions (18). While many studies have involved emerging adults, they have focused on college students (13, 14). Although it is important to understand use among college students, it is also important to address these behaviors in emerging adults not in college, especially considering that other tobacco use is higher than non-college young adults than their collegiate counterparts (19).
Therefore, we conducted a nationally-representative longitudinal study of U.S. young adults over an 18-month period. We attempted to fill the specific gaps in the literature noted above by focusing on two key specific aims. First, we aimed to characterize key transitions between WTS states (e.g., never use; ever use; and current use). Second, we aimed to assess independent associations between key predictors such as knowledge, negative and positive attitudes, normative beliefs, and intentions and subsequent WTS initiation. Based on prior work in this area, we developed 5 a priori hypotheses: (1) positive attitudes toward WTS will be associated with an increased odds of WTS initiation; (2) negative attitudes toward WTS will be associated with a decreased odds of WTS initiation; (3) favorable normative beliefs about WTS will be associated with an increased odds of initiation; (4) intention will be associated with an increased odds of WTS initiation; and (5) WTS knowledge will be associated with WTS initiation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Participants and Procedures
Participants were members of KnowledgePanel®, an online, non-volunteer access panel recruited and maintained by GfK (Growth from Knowledge, formerly Knowledge Networks). This panel was developed through both random digit dialing and address-based recruitment and was designed to be demographically representative of the US population (20). At the time of the study, KnowledgePanel® consisted of approximately 50,000 individuals ages 18 and older (20). Panel members are randomly selected to be invited to participate in online surveys, and are supplied with e-mail addresses, computers, and Internet access if needed. However, considering the ubiquitous nature of electronic communications in today’s world, facilitated access is rarely needed (20).
In March of 2013, 3254 panel members completed a baseline survey about WTS and other health behaviors. Approximately 18 months later, in October of 2014, those individuals were invited to participate in the follow-up survey. Of the 3254 individuals who had completed the baseline survey, 2170 were still on the panel, 878 had left the panel but were still available for contact, and 206 had left the panel and were unable to be contacted. Therefore, the follow-up survey was sent to the 3048 individuals with updated contact information. This study was approved by the University of Pittsburgh Institutional Review Board, and all study participants gave informed consent.
Conceptual Framework
This study was guided by two relevant and complementary health behavior theories typically used to explore young adult substance use—the Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA) and the Health Belief Model (HBM). Consistent with the TRA, prior research demonstrates that those with more positive attitudes towards WTS have greater odds of current WTS, intention for future WTS, and WTS initiation, while those with more negative attitudes have lower odds of current WTS and WTS initiation (13, 21). Also consistent with the TRA, in a relatively small, regional sample, those with more favorable normative beliefs regarding WTS had greater odds of current WTS and WTS intiation (13, 21). These TRA constructs may in turn affect behavioral intention, which is believed to be a strong predictor of behavior (16). Indeed, self-reported intention to use tobacco products, including waterpipe tobacco, has been found to be an independent predictor of cigarette smoking initiation among young adults (22). The HBM has also been useful in understanding youth substance use, because increased perceptions related to severity and susceptibility have been associated with lower substance use (23). However, constructs such as knowledge that are part of the HBM have been inconsistently associated with outcomes related to WTS. For example, while both cross-sectional and longitudinal studies of college students have found no association between knowledge of the harmful components of waterpipe tobacco, a response of “don’t know” has been shown to be protective against current WTS, intention to participate in WTS, and WTS initiation (13, 17).
Measures
At both baseline and follow-up, we surveyed participants regarding socio-demographic factors, waterpipe tobacco smoking behavior, and theory-based predictors such as knowledge, attitudes and normative beliefs. Both the baseline and follow-up questionnaires were extensively pre-tested and median times for completion were 15 and 10 minutes, respectively.
Socio-demographic Factors
GfK maintains a database of key demographic information about panel members, including age, sex, race/ethnicity, household income, and level of education. To supplement this information, we included items to assess living situation and relationship status.
Waterpipe Tobacco Smoking Behavior
In the baseline survey, participants were asked to report on ever, past year, and current (i.e., within the past 30 days) WTS. Instructions immediately preceding the WTS items specifically instructed participants to answer about smoking tobacco from a hookah, to differentiate from smoking other substances, such as marijuana. The term “hookah” was used instead of “waterpipe” for all WTS-related items, because it is the most common term used in the U.S. for this device (24). We used the WTS items to operationalize three key states of WTS. Never use was defined as answering “no” to the item, “Have you ever smoked tobacco from a hookah?” Ever use was defined as answering “yes” to “Have you ever smoked tobacco from a hookah?” but answering “0” to “Within the past 30 days, on how many days did you smoke tobacco from a hookah?” Finally, current use was defined as smoking tobacco from a hookah at least one day in the past month. Participants were presented with the same items in the follow-up questionnaire. This information was used to chart the transitions between the key states of WTS. Participants who transitioned from never use to ever use or current use were defined as initiators, while those who transitioned from ever use to current use were defined as progressors.
Theory-based Predictors
Attitudes towards WTS were assessed with a 6-item scale used in previous research studies (13, 21). These items asked participants whether they believed WTS was attractive; romantic; fun; relaxing; harmful; and addicting, each on a 5-point response scale (Definitely no; Probably no; Don’t Know; Probably Yes; Definitely Yes). The 4 items assessing attitudes towards positive attributes (attractive; romantic; fun; relaxing) were grouped to reflect an overall positive attitude summary scale, while the 2 items assessing attitudes towards negative attributes (harmful; addicting) were grouped to reflect an overall negative attitude summary scale. A higher score on the positive attitude scale indicated a favorable attitude toward WTS, whereas a higher score on the negative attitude scale indicated a less favorable attitude toward WTS. Both summary scales demonstrated strong reliability (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.88 and 0.85, respectively).
Normative beliefs were measured in two complementary ways used in substance use research (13, 21, 25). The first asked participants to estimate the percentage of people their age that have ever smoked tobacco from a hookah, and the second asked participants to indicate how socially acceptable it is for people their age to smoke tobacco from a hookah. This item included a 4-point response scale ranging from “Very socially acceptable” to “Not socially acceptable”.
WTS intention was assessed through the item, “Do you intend to smoke tobacco from a hookah at any time in the rest of your life?” The 4-item response scale for this item asked respondents to select “Definitely Yes,” “Probably Yes,” “Probably No,” or “Definitely No.” Consistent with prior research (26), for analysis, any answer other than “Definitely No” was defined as intention to participate in WTS.
Knowledge about the harmful components of waterpipe tobacco was measured using a set of items asking participants to compare smoking a single cigarette to a single hookah tobacco smoking session and estimate which contained more of the following: tar; nicotine; carcinogens; carbon monoxide; and heavy metals (13, 17). Although a typical hookah session is longer than smoking a single cigarette, this wording was used to be consistent with, and comparable to, other literature on this topic (13, 27, 28). A 4-item response scale allowed respondents to choose “Definitely Hookah”, “Probably Hookah”, “Probably Cigarettes”, or “Definitely Cigarettes”. Based on established research (27, 29), an answer of “Definitely Hookah” or “Probably Hookah” was considered to be correct, while an answer of “Definitely Cigarettes” or “Probably Cigarettes” was considered to be incorrect. Internal consistency was measured using Cronbach’s alpha and demonstrated strong reliability among items (alpha = 0.87).
Analysis
We included all individuals with complete data on the dependent variable at baseline and follow-up. Because less than 1% were excluded for incomplete data, this is unlikely to have affected results. We assessed differences in socio-demographic characteristics between responders and non-responders using Rao-Chi square tests and Cramer’s V. Additionally, we calculated simple frequencies and percentages to characterize use patterns of the dependent variable from baseline to follow-up. We assessed associations between independent variables at baseline and our dependent variable at follow-up using logistic regression, adjusting for a comprehensive set of socio-demographic covariates in multivariable models. We conducted sensitivity analyses with a more parsimonious set of covariates to confirm the robustness of our results. All analyses were conducted using survey weights provided by GfK in order to estimate effects for the general U.S. population, as well as correct for any under- or over-sampling. We defined statistical significance with a two-tailed alpha of 0.05. Data were analyzed using Stata 14 (StataCorp, College Station, TX) (30).
RESULTS
Sample Characteristics
A total of 1796 individuals completed the survey (RR= 59%). The final sample for analysis consisted of 1785 individuals with complete data on WTS items for both baseline and follow-up. Responders and non-responders did not significantly differ on WTS (P = .08), age (P = .15), sex (P = .07), or race/ethnicity (P = .19). Therefore, those with complete data represented the complete population in terms of basic socio-demographics. Additionally, study-specific survey weights were applied to all analyses to adjust for non-responses well as under- or over-sampling.
The weighted age distribution of our sample was approximately equal, with the largest group of 27–30 years (31%). The sample was 50% female and just over half of the sample identified as White, non-Hispanic (57%), followed by Hispanic (22%), Black non-Hispanic (13%), and Other (9%). Additionally, half of the sample reported being single (50%), while a plurality reported living with a parent or guardian (40%), earning an income of $75,000 or greater (47%), and having an education level of high school or less (43%) (data not shown).
Waterpipe Tobacco Smoking Behavior
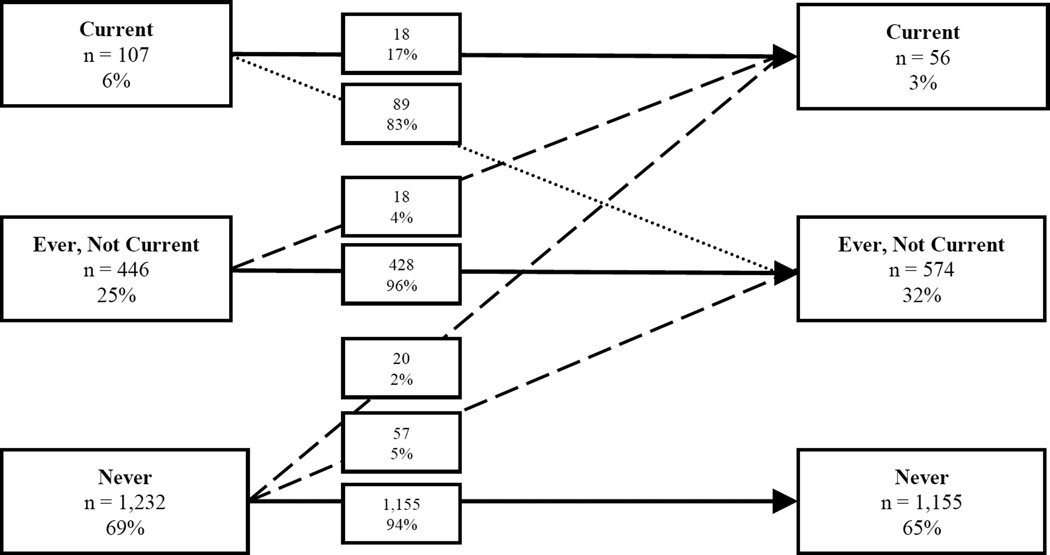
The trajectories of WTS behavior between baseline and follow-up are depicted in Figure 1. Of the baseline never smokers (n = 1232, 69%), 94% remained never smokers at follow-up. Similarly, 96% of ever smokers at baseline (n = 446, 25%) remained ever smokers at follow-up (that is, they did not progress to current smoking). This is in contrast to baseline current smokers (n = 107, 6%), of whom 17% remained current smokers. Of note were the 4% of baseline ever smokers that progressed to current smoking at follow-up and were considered progressors. Additionally, of the 1232 participants reporting never WTS at baseline, 7% reported initiation at follow-up and were considered initiators.
Figure 1.
Longitudinal Waterpipe Tobacco Smoking Trajectories Among U.S. Young Adults. Waterpipe tobacco smoking (WTS) trajectories from baseline to an 18-month follow-up. Solid arrows indicate no change in status or the “sustainers”; dashed arrows indicate an increase from no or any WTS use or the “initiators” and “progressors”; and the dotted arrow indicates a decrease in WTS use.
Waterpipe Tobacco Smoking Initiation
Socio-demographic characteristics of baseline WTS non-smokers (Table 1) are similar and consistent with whole sample characteristics. In bivariable analyses, we found significant associations between WTS initiation and race/ethnicity and yearly household income (Table 1). Those who initiated WTS were more often White, non-Hispanic individuals with an annual household income of $30,000–74,999.
Table 1.
Sample Characteristics by Baseline and Follow-up Waterpipe Tobacco Smoking (WTS) Status
| Characteristic | Baseline WTS Non- Smokers (n = 1,232)a |
WTS Initiation |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (n = 77) |
No (n = 1,155) |
P Valueb |
||
| n (%)c | %c | %c | ||
| Age, y | .41 | |||
| 18–20 | 236 (27) | 38 | 27 | |
| 21–23 | 388 (23) | 20 | 23 | |
| 24–26 | 290 (19) | 21 | 19 | |
| 27–30 | 318 (30) | 21 | 31 | |
| Sex | .54 | |||
| Female | 765 (51) | 47 | 52 | |
| Male | 467 (49) | 53 | 48 | |
| Race/Ethnicity | .02 | |||
| White, non-Hispanic | 787 (55) | 36 | 57 | |
| Black, non-Hispanic | 135 (15) | 29 | 14 | |
| Hispanic | 189 (19) | 29 | 19 | |
| Otherd | 121 (11) | 7 | 11 | |
| Relationship Status | .60 | |||
| Single | 592 (54) | 58 | 53 | |
| In a committed relationship | 636 (46) | 42 | 47 | |
| Living Situation | .07 | |||
| With a parent/guardian | 428 (43) | 30 | 44 | |
| With a significant other | 397 (28) | 25 | 28 | |
| Othere | 405 (29) | 45 | 28 | |
| Yearly Household Income | .04 | |||
| Low (under $30,000) | 358 (20) | 32 | 19 | |
| Medium ($30,000–74,999) | 468 (36) | 43 | 36 | |
| High ($75,000 or more) | 406 (44) | 25 | 45 | |
| Education Level | .25 | |||
| High school or less | 386 (48) | 46 | 49 | |
| Some college | 522 (35) | 45 | 35 | |
| Bachelor’s degree or higher | 324 (16) | 9 | 17 | |
This number includes participants who had WTS data for both baseline and follow-up.
P values were computed using Rao-Chi-square tests.
Individual characteristics summed may not equal the total sample size due to missing data; column percentages may not equal 100 due to rounding.
Includes Multiracial.
Defined as not living with a parent/guardian or significant other.
Theory-based Predictors of Waterpipe Tobacco Smoking Initiation
In multivariable analyses, participants with increased positive attitudes towards WTS had significantly greater odds of WTS initiation (Table 2). No significant associations were found between negative attitudes towards WTS and WTS initiation or WTS normative beliefs and WTS initiation. However, WTS intention, which was reported by 22% of baseline non-smokers, was significantly associated with increased odds of WTS initiation (AOR = 7.0, CI = 3.5–13.7). Of the five knowledge items, only the knowledge that WTS exposes the user to greater amounts of nicotine compared to cigarettes was significantly associated with WTS initiation (AOR = 2.8, CI = 1.1–7.0). Overall knowledge was not significantly associated with WTS initiation. Sensitivity analyses using a more parsimonious set of covariates yielded consistent findings.
Table 2.
Bivariable and Multivariable Associations Between Attitudes, Normative Beliefs, Intention, Knowledge, and Initiation of Waterpipe Tobacco Smoking (WTS)
| Attitude, Subjective Norm, and Knowledge Items | WTS Initiationa |
|
|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | AORb (95% CI) | |
| Positive Attitudesc | ||
| Hookah Seems Attractive | 1.5 (1.1–2.1) | 1.5 (1.1–2.1) |
| Hookah Seems Romantic | 1.6 (1.1–2.3) | 1.6 (1.1–2.1) |
| Hookah Seems Fun | 1.4 (1.1–1.9) | 1.4 (1.1–1.9) |
| Hookah Seems Relaxing | 1.5 (1.1–2.0) | 1.5 (1.2–2.0) |
| Overall Positive Attitude | 1.7 (1.1–2.4) | 1.7 (1.2–2.3) |
| Negative Attitudesc | ||
| Hookah Seems Harmful | 0.8 (0.7–1.0) | 0.8 (0.7–1.0) |
| Hookah Seems Addicting | 0.8 (0.7–1.0) | 0.8 (0.7–1.1) |
| Overall Negative Attitude | 0.8 (0.7–1.0) | 0.8 (0.7–1.0) |
| Normative Beliefs | ||
| Perceived prevalence of WTS among peers.d | 1.0 (0.9–1.1) | 0.9 (0.8–1.1) |
| Perceived acceptability of WTS among peers.e | 1.3 (0.9–1.7) | 1.3 (0.9–1.7) |
| Intention | ||
| No | 1.0 [Reference] | 1.0 [Reference] |
| Yes | 5.5 (2.8–11.0) | 7.0 (3.5–13.7) |
| Knowledge | ||
| Which has more tar? | ||
| Incorrect | 1.0 [Reference] | 1.0 [Reference] |
| Correct | 1.3 (0.4–4.5) | 1.3 (0.4–3.8) |
| Which has more nicotine? | ||
| Incorrect | 1.0 [Reference] | 1.0 [Reference] |
| Correct | 2.6 (0.9–7.3) | 2.8 (1.1–7.0) |
| Which has more carcinogens? | ||
| Incorrect | 1.0 [Reference] | 1.0 [Reference] |
| Correct | 1.9 (0.6–6.7) | 2.0 (0.6–6.2) |
| Which has more carbon monoxide? | ||
| Incorrect | 1.0 [Reference] | 1.0 [Reference] |
| Correct | 1.5 (0.6–4.0) | 1.4 (0.5–3.6) |
| Which has more heavy metals? | ||
| Incorrect | 1.0 [Reference] | 1.0 [Reference] |
| Correct | 1.8 (0.7–4.7) | 1.8 (0.7–4.6) |
| Overall Knowledge Scoref | 1.2 (0.9–1.6) | 1.2 (1.0–1.6) |
Abbreviations: OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; AOR, adjusted odds ratio.
Only baseline waterpipe tobacco non-smokers and those who had complete data on items assessing ever WTS were included in these analyses.
Adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, living situation, relationship status, household income, and education.
Associated odds ratios represent the odds for each unit of increase in the independent variable.
Each point on this scale corresponds with a 10-point increment in percentage.
Responses to this item are based upon a 4-level response scale ranging from “not” to “very.” Associated odds ratios represent the increase in odds for each unit of increase on this scale.
The overall knowledge score was the number of items scored correct summed. Associated odds ratios represent the odds for each 1-point increase in the 6-point scale.
DISCUSSION
In this nationally-representative longitudinal study of U.S. young adults, we found that, over an 18-month period, 4% of baseline ever smokers progressed to current smoking and that approximately 7% of baseline never smokers initiated WTS. A closer examination of WTS initiation found that positive attitudes towards WTS, knowledge of WTS-related nicotine exposure compared to cigarettes, and baseline WTS intention were significantly associated with initiation. In contrast, negative attitudes towards WTS, normative beliefs towards WTS, and knowledge of other WTS components were not significantly associated with WTS initiation.
We also found that the vast majority of baseline never smokers (94%) and ever smokers (96%) maintained their status at the 18-month follow-up. However, it is notable that the prevalence of never smoking decreased by 4 percentage points over the 18-month period, while ever smoking increased by approximately 7 percentage points. This suggests that more individuals are being introduced to WTS in some capacity. In contrast to the sustained never and ever smoking, the majority of baseline current smokers (83%) reverted to ever smoking by follow-up. It is possible that some of these individuals quit WTS over the follow-up period. Indeed, in studies of U.S. waterpipe tobacco users, many have expressed intention to quit at some point in the future (31, 32). However, almost 17% of current smokers sustained their use through the 18-month period, consistent with some international studies (3). Additionally, 4% of baseline ever smokers progressed to current smoking over the follow-up period. These findings suggest a potential for dependence on WTS. Some users of WTS report feeling “hooked” on WTS (33), and a recent study found that half of past-year WTS users endorsed at least one dependence item on a six-item WTS dependence scale (10).
Of the baseline non-smokers, 7% initiated WTS at follow-up. While this initiation rate is lower than in studies focused on college students, it is similar to the only other study of initiation among a more general young adult population (12). A possible reason for the lower initiation rate in this study is that this sample was not limited solely to college students. College entry and progression through the initial years of college have been found to be associated with WTS (13, 15). Thus, by including non-college populations, we may have reduced the number of higher-risk individuals in our sample.
Positive attitudes towards WTS significantly predicted WTS initiation, while negative attitudes did not. The association between positive attitudes and WTS initiation is consistent with studies of college students (13). This is not surprising, as many U.S. waterpipe users view WTS to be a fun activity during which they can socialize, party, or relax (7). However, the lack of association between negative attitudes and WTS initiation is contrary to studies that found negative attitudes to be protective against WTS use or initiation (13, 21). This is akin to cigarette smokers, for whom negative outcome expectations of cigarette smoking may not influence the decision to start smoking (34). It is possible that, like some cigarette smokers, those who participate in WTS may rationalize their behavior by focusing on the positive aspects of WTS and modulating the negative aspects (35).
We also found that knowledge about greater nicotine exposure in WTS compared to cigarettes was associated with higher odds of smoking initiation. It is possible that individuals who had already begun to show interest in WTS were more knowledgeable about this fact than those who had not. Also, it is possible that the novelty and general positive appeal of WTS outweighs the knowledge of the presence of nicotine. This phenomenon has been noted among users of other non-cigarette nicotine and tobacco products, such as e-cigarettes, snus, and nicotine dissolvables (36). In a series of focus groups, about half of the young adult participants reported being willing to try the products, despite knowledge of nicotine content and potential negative health effects, because they were perceived as attractive, modern, and fun (36).
The strongest association with WTS initiation was baseline intention. Those individuals who reported that they intended to smoke tobacco from a hookah at one point in the rest of their lives had approximately 7 times greater odds of initiating WTS compared to those who reported no intention to smoke tobacco from a hookah. This is especially concerning because, consistent with other research (22), approximately one-quarter of baseline non-smokers reported being intention to initiate WTS at one point in the rest of their lives. Extrapolating this to the greater population, almost 9 million baseline non-smokers ages 18–30 may have some intention to participate in WTS (2014 estimated U.S. Census population of 57,702,876 × 69% baseline never smokers × 22% reporting intention) (37). Considering the strong association between baseline intention to participate in WTS and subsequent initiation of WTS, it is clear that this is a ripe opportunity for primary prevention efforts among this particular age group.
While certain theory-based predictors, which may be addressable through intervention, were associated with WTS initiation, the majority of socio-demographic factors were not. This suggests that primary prevention efforts to curb WTS initiation in the general 18–30 year old population may be more effective if they address these theory-based predictors rather than focusing on any one group of individuals. This is consistent with recommendations for the college population, which also found no association between socio-demographic factors and WTS initiation (13). However, this is in contrast to secondary prevention efforts addressing current or ever use, for which efforts may be more beneficial when focused on populations that are younger, white, and male (38). These findings provide important distinctions that can help guide targeting of interventions for future research or for the practice of health professionals.
The two strongest predictors of WTS initiation—positive attitudes and intention—may be addressed through similar prevention and intervention means. Despite the associated negative health effects and potential for addiction, WTS is still viewed as a fun, attractive social activity. This is especially true in online advertisements, where WTS is portrayed as social and pleasurable; however, health warnings or mention of nicotine content are rare (39). Likewise, studies have shown that the waterpipe tobacco industry uses questionable marketing and labeling practices, such as misleading descriptors on packaging and omission of health effects (40, 41).
This study was limited by its self-report survey design. Biochemical validation was not used to confirm WTS status. However, participants were assured of the confidentiality of their answers and had little incentive to be untruthful. This study was also limited by the fact that, despite having a large sample size, there was not enough power to fully examine factors associated with WTS progression (i.e., baseline use followed by increases). The progression from WTS experimentation to more regular use is an area that warrants deeper investigation, and future studies should seek to examine this trajectory specifically by recruiting a greater volume of baseline experimenters. Another limitation is the stem used for the knowledge item, which asked participants to compare their knowledge of toxicant exposure from a WTS session compared to smoking a single cigarette. Because a typical WTS session is longer than smoking a single cigarette, this item could have confused participants, potentially leading them to answer incorrectly. Additionally, this study examined the association between WTS initiation and certain theory-based predictors and did not include information about other substance use. Future studies may seek to examine both sets of factors simultaneously. Finally, although this study had a longitudinal design, data collection at more time points over a longer time period would have yielded data that may have been amenable to more complete longitudinal analysis techniques such as growth mixture modeling.
In conclusion, we found that almost 20% of current WTS users maintained their use through an 18-month follow-up period. We also found initiation and progression rates of 7% and 4%, respectively. Initiation was associated with certain theory-based predictors—such as positive attitudes towards WTS and intention to participate in WTS—but not most socio-demographic factors, suggesting specific targets for prevention efforts. These efforts may be most effective if they counteract positive attitudes towards WTS and intention to participate in WTS in the future.
Acknowledgments
Source of Funding:
This work was supported by the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health (R01-CA140150), awarded to B.A. Primack. The funding agency had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis and interpretation of the data; and preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript.
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest:
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
REFERENCES
- 1.Jamal A, Agaku IT, O’Connor E, King BA, Keremer J, Neff L. Current cigarette smoking among adults — United States, 2005 – 2012. MMWR. 2014;63:1108–1112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lauterstein D, Hoshino R, Gordon T, Watkins B, Weitzman M, Zelikoff J. The changing face of tobacco use among United States youth. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2014;7:29–43. doi: 10.2174/1874473707666141015220110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dugas EN, O’Loughlin EK, Low NC, Wellman RJ, O’Loughlin JL. Sustained waterpipe use among young adults. Nicotine Tob Res. 2014;16:709–716. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntt215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Primack BA, Freedman-Doan P, Sidani JE, Rosen D, Shensa A, James AE, et al. Sustained waterpipe tobacco smoking and trends over time. Am J Prev Med. 2015;49:859–867. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2015.06.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.U.S. Food and Drug Administration [Internet] Washington, D.C: Federal Register; 2016 [updated 2016 May 10; cited 2016 Nov 15]. Deeming tobacco products to be subject to the federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, as amended by the Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act; Restrictions on the sale and distribution of tobacco products and required warning statements for tobacco products. Available from: https://federalregister.gov/a/2016-10685. [PubMed]
- 6.Colditz JB, Ton JN, James AE, Primack BA. Toward effective water pipe tobacco control policy in the United States: Synthesis of federal, state, and local policy texts. Am J Heal Promot. 2016 Jun 17; doi: 10.4278/ajhp.150218-QUAL-736. Epub 2016 Jan 5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Griffiths MA, Ford EW. Hookah smoking: Behaviors and beliefs among young consumers in the United States. Soc Work Public Health. 2014;29:17–26. doi: 10.1080/19371918.2011.619443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Carroll MV, Shensa A, Primack BA. A comparison of cigarette- and hookah-related videos on YouTube. Tob Control. 2013;22:319–323. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2011-050253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.El-Zaatari ZM, Chami HA, Zaatari GS. Health effects associated with waterpipe smoking. Tob Control. 2015;24(1):i31–i43. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2014-051908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sidani JE, Shensa A, Shiffman S, Switzer GE, Primack BA. Behavioral associations with waterpipe tobacco smoking dependence among US young adults. Addiction. 2016;111:351–359. doi: 10.1111/add.13163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Maziak W. The global epidemic of waterpipe smoking. Addict Behav. 2011;36:1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2010.08.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Villanti AC, Cobb CO, Cohn AM, Williams VF, Rath JM. Correlates of hookah use and predictors of hookah trial in U.S. young adults. Am J Prev Med. 2015;48:742–746. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2015.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sidani JE, Shensa A, Barnett TE, Cook RL, Primack BA. Knowledge, attitudes, and normative beliefs as predictors of hookah smoking initiation: a longitudinal study of university students. Nicotine Tob Res. 2014;16:647–654. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntt201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shepardson RL, Hustad JTP. Hookah tobacco smoking during the transition to college: prevalence of other substance use and predictors of initiation. Nicotine Tob Res. 2015:1–7. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntv170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fielder RL, Carey KB, Carey MP. Prevalence, frequency, and initiation of hookah tobacco smoking among first-year female college students: a one-year longitudinal study. Addict Behav. 2012;26:221–224. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2011.10.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Glanz K, Rimer BK, Viswanath K. Health behavior and health education: theory, research and practice. 4th. San Francisco, CA: Wiley & Sons; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nuzzo E, Shensa A, Kim KH, Fine MJ, Barnett TE, Cook RL, et al. Associations between hookah tobacco smoking knowledge and hookah smoking behavior among US college students. Health Educ Res. 2013;28:92–100. doi: 10.1093/her/cys095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stone AL, Becker LG, Huber AM, Catalano RF. Review of risk and protective factors of substance use and problem use in emerging adulthood. Addict Behav. 2012;37:747–775. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2012.02.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Green MP, McCausland KL, Xiao H, Duke JC, Vallone DM, Healton CG. A closer look at smoking among young adults: where tobacco control should focus its attention. Am J Public Health. 2007;97:1427–1433. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2006.103945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Knowledge Networks [Internet] Washington, D.C.: Knowledge Panel Design Summary. GfK KnowledgePanel® 2012 [updated 2012; cited 2015 Nov 6] Available from: http://www.knowledgenetworks.com/ganp/docs/KnowledgePanel(R)-Design-Summary.pdf.
- 21.Barnett TE, Shensa A, Kim KH, Cook RL, Nuzzo E, Primack BA. The predictive utility of attitudes toward hookah tobacco smoking on current use and use among a sample of college students. Am J Health Behav. 2013;37:433–439. doi: 10.5993/AJHB.37.4.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lipkus IM, Reboussin BA, Wolfson M, Sutfin EL. Assessing and predicting susceptibility to waterpipe tobacco use among college students. Nicotine Tob Res. 2015;17:1120–1125. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntu336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Song AV, Morrell HER, Cornell JL, Ramos ME, Biehl M, Kropp RY, et al. Perceptions of smoking-related risks and benefits as predictors of adolescent smoking initiation. Am J Public Health. 2009;99:487–492. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2008.137679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Salloum RG, Osman A, Maziak W, Thrasher JF. How popular is waterpipe tobacco smoking? Findings from internet search queries. Tob Control. 2015;24:509–513. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2014-051675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Primack BA, Switzer GE, Dalton MA. Improving measurement of normative beliefs involving smoking among adolescents. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2007;161:434. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.161.5.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pierce JP, Choi WS, Gilpin EA, Farkas AJ, Merritt RK. Validation of susceptibility as a predictor of which adolescents take up smoking in the United States. Heal Psychol. 1996;15:355–361. doi: 10.1037//0278-6133.15.5.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Cobb CO, Shihadeh A, Weaver MF, Eissenberg TE. Waterpipe tobacco smoking and cigarette smoking: a direct comparison of toxicant exposure and subjective effects. Nicotine Tob Res. 2011;13:78–87. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntq212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Primack BA, Carroll MV, Weiss PM, Shihadeh AL, Shensa A, Farley ST, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of inhaled toxicants from waterpipe and cigarette smoking. Public Health. 2016;131:76–85. doi: 10.1177/003335491613100114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Eissenberg T, Shihadeh A. Waterpipe tobacco and cigarette smoking: direct comparison of toxicant exposure. Am J Prev Med. 2009;37:518–523. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2009.07.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Version 14. 14th. College Station, TX: StataCorp; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ahmed B, Jacob P, Allen F, Benowitz N. Attitudes and practices of hookah smokers in the San Francisco Bay Area. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2011;43:146–152. doi: 10.1080/02791072.2011.587707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Smith-Simone S, Maziak W, Ward KD, Eissenberg TE. Waterpipe tobacco smoking: knowledge, attitudes, beliefs, and behavior in two U.S. samples. Nicotine Tob Res. 2008;42:393–398. doi: 10.1080/14622200701825023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Aboaziza E, Eissenberg T. Waterpipe tobacco smoking: What is the evidence that it supports nicotine/tobacco dependence? Tob Control. 2015;24:i44–i53. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2014-051910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dalton MA, Sargent JD, Beach ML, Bernhardt JM, Stevens M. Positive and negative outcome expectations of smoking: implications for prevention. Prev Med. 1999;29:460–465. doi: 10.1006/pmed.1999.0582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Glock S, Unz D, Kovacs C. Beyond fear appeals: Contradicting positive smoking outcome expectancies to influence smokers’implicit attitudes, perception, and behavior. Addict Behav. 2012;37:548–551. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2011.11.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Choi K, Fabian L, Mottey N, Corbett A, Forster J. Young adults’ favorable perceptions of snus, dissolvable tobacco products, and electronic cigarettes: findings from a focus group study. Am J Public Health. 2012;102:2088–2093. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2011.300525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.United States Census Bureau [Internet] Washington, D.C.: Annual estimates of resident population by single year of age and sex for the United States: 2014 population estimates. [upated 2015 June; cited 2016 May 2] Available from: http://factfinder.census.gov/faces/tableservices/jsf/pages/productview.xhtml?src=bkmk.
- 38.Grekin ER, Ayna D. Waterpipe smoking among college students in the United States: A review of the literature. J Am Coll Heal. 2012;60:244–249. doi: 10.1080/07448481.2011.589419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Primack BA, Rice KR, Shensa A, Carroll MV, DePenna EJ, Nakkash R, et al. hookah tobacco smoking establishments advertised on the Internet. Am J Prev Med. 2012;42:150–156. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2011.10.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nakkash R, Khalil J. Health warning labelling practices on narghile and related accessories (shisha, hookah) waterpipe tobacco products. Tob Control. 2010;19:235–239. doi: 10.1136/tc.2009.031773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jawad M, McEwen A, McNeill A, Shahab L. To what extent should waterpipe tobacco smoking become a public health priority? Addiction. 2013;108:1873–1884. doi: 10.1111/add.12265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]