Abstract
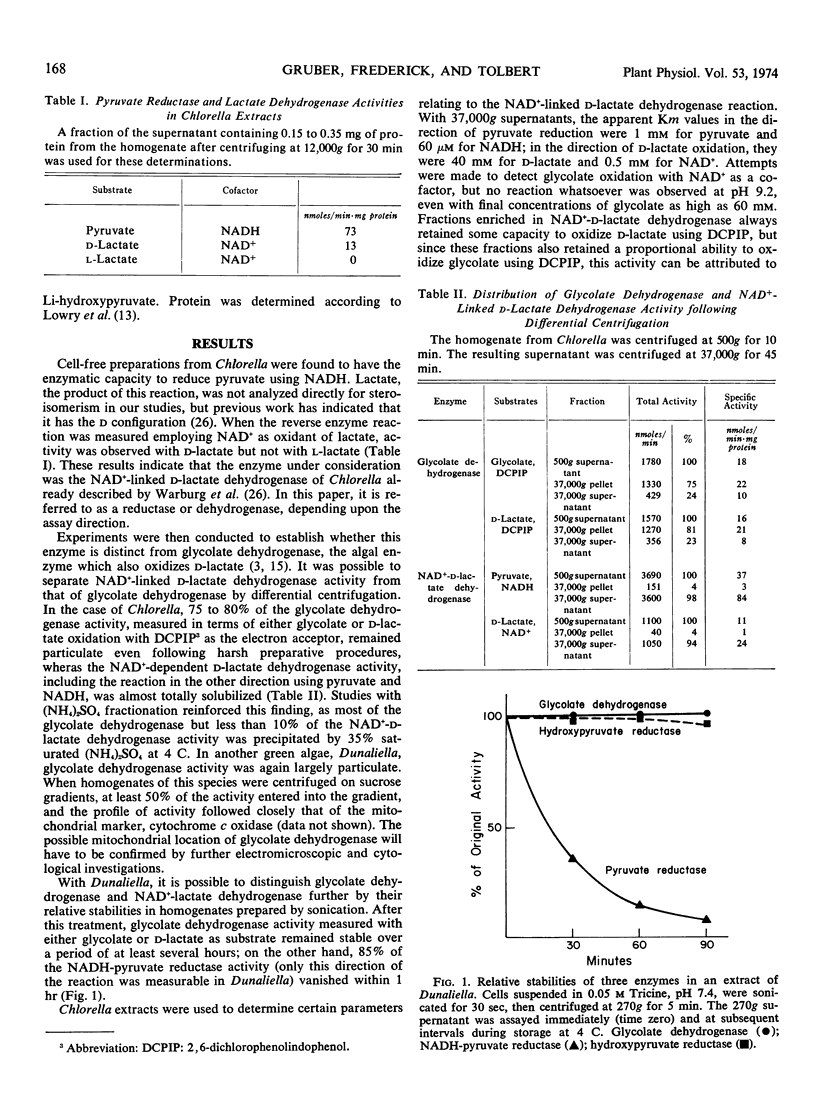
Cell-free extracts of Chlorella pyrenoidosa contained two enzymes capable of oxidizing d-lactate; these were glycolate dehydrogenase and NAD+-dependent d-lactate dehydrogenase. The two enzymes could be distinguished by differential centrifugation, glycolate dehydrogenase being largely particulate and NAD+-d-lactate dehydrogenase being soluble. The reduction of pyruvate by NADH proceeded more rapidly than the reverse reaction, and the apparent Michaelis constants for pyruvate and NADH were lower than for d-lactate and NAD+. These data indicated that under physiological conditions, the NAD+-linked d-lactate dehydrogenase probably functions to produce d-lactate from pyruvate.
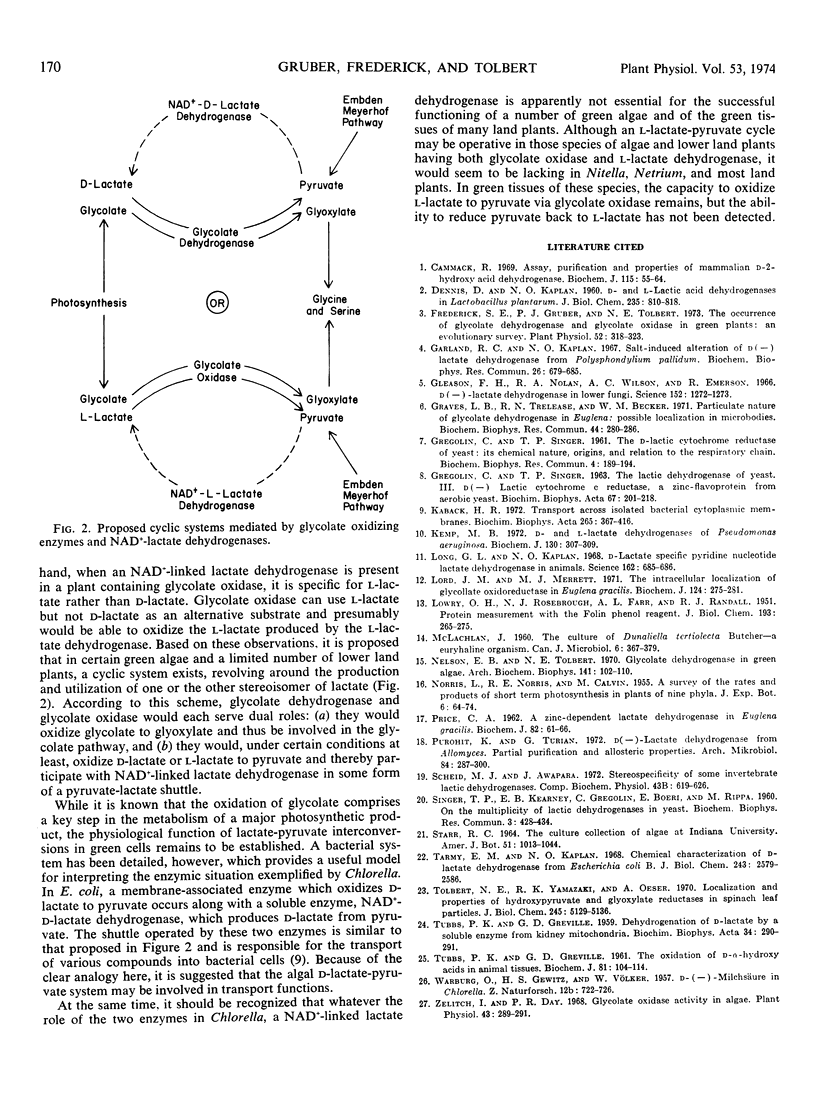
Lactate dehydrogenase activity dependent on NAD+ was found in a number of other green algae and in the green tissues of a few lower land plants. When present in species which contain glycolate oxidase rather than glycolate dehydrogenase, the enzyme was specific for l-lactate rather than d-lactate. A cyclic system revolving around the production and utilization of d-lactate in some species and l-lactate in certain others is proposed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cammack R. Assay, purification and properties of mammalian D-2-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1969 Oct;115(1):55–64. doi: 10.1042/bj1150055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENNIS D., KAPLAN N. O. D- and L-lactic acid dehydrogenases in Lactobacillus plantarum. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:810–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederick S. E., Gruber P. J., Tolbert N. E. The occurrence of glycolate dehydrogenase and glycolate oxidase in green plants: an evolutionary survey. Plant Physiol. 1973 Oct;52(4):318–323. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.4.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGOLIN C., SINGER T. P. The D-lactic cytochrome reductase of yeast: its chemical nature, origins, and relation to the respiratory chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Mar 10;4:189–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGOLIN C., SINGER T. P. The lactic dehydrogenase of yeast. III. D(-)Lactic cytochrome c reductase, a zinc-flavoprotein from aerobic yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 12;67:201–218. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91818-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland R. C., Kaplan N. O. Salt-induced alteration of D(-) lactate dehydrogenase from Polyspondylium pallidum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Mar 21;26(6):679–685. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleason F. H., Nolan R. A. D(-)-lactate dehydrogenase in lower fungi. Science. 1966 May 27;152(3726):1272–1273. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3726.1272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves L. B., Trelease R. N., Becker W. M. Particulate nature of glycolate dehydrogenase in euglena: possible localization in microbodies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):280–286. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90596-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport across isolated bacterial cytoplasmic membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 4;265(3):367–416. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp M. B. D- and L-lactate dehydrogenases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):307–309. doi: 10.1042/bj1300307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long G. L., Kaplan N. O. D-lactate specific pyridine nucleotide lactate dehydrogenase in animals. Science. 1968 Nov 8;162(3854):685–686. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3854.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. M., Merrett M. J. The intracellular localization of glycollate oxidoreductase in Euglena gracilis. Biochem J. 1971 Sep;124(2):275–281. doi: 10.1042/bj1240275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E. B., Tolbert N. E. Glycolate dehydrogenase in green algae. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Nov;141(1):102–110. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICE C. A. A zinc-dependent lactate dehydrogenase in Euglena gracilis. Biochem J. 1962 Jan;82:61–66. doi: 10.1042/bj0820061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit K., Turian G. D(-)-lactate dehydrogenase from Allomyces. Partial purification and allosteric properties. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(4):287–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00409078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid M. J., Awapara J. Stereospecificity of some invertebrate lactic dehydrogenases. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1972 Nov 15;43(3):619–626. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(72)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUBBS P. K., GREVILLE G. D. Dehydrogenation of D-lactate by a soluble enzyme from kidney mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:290–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90276-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUBBS P. K., GREVILLE G. D. The oxidation of D-alpha-hydroxy acids in animal tissues. Biochem J. 1961 Oct;81:104–114. doi: 10.1042/bj0810104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarmy E. M., Kaplan N. O. Chemical characterization of D-lactate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli B. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2579–2586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolbert N. E., Yamazaki R. K., Oeser A. Localization and properties of hydroxypyruvate and glyoxylate reductases in spinach leaf particles. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5129–5136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelitch I., Day P. R. Glycolate oxidase activity in algae. Plant Physiol. 1968 Feb;43(2):289–291. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


