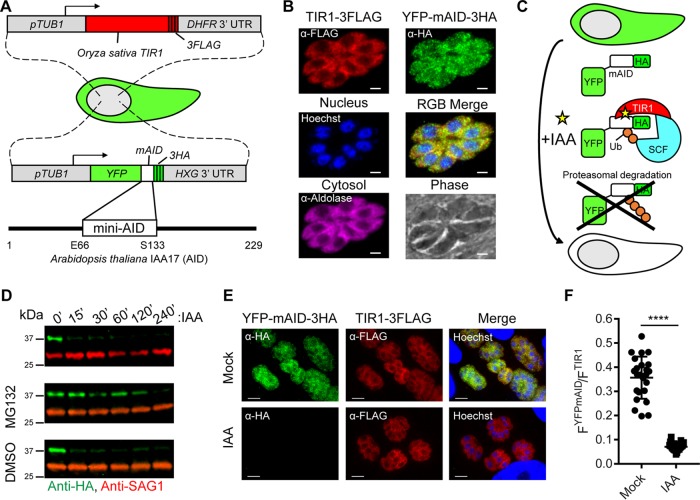
FIG 1 .
Generation of an AID system in T. gondii. (A) Schematic representation of T. gondii engineered to coexpress the auxin receptor TIR1 from Oryza sativa and YFP fused to mAID from Arabidopsis thaliana. (B) Coexpression of TIR1-3FLAG (red) and YFP-mAID-3HA (green) in T. gondii determined by IF microscopy. Aldolase (magenta) and Hoechst dye (blue) highlight the cytosol and nuclei, respectively. Scale bars, 2 µm. (C) Schematic representation of conditional YFP-mAID-3HA depletion. Ub, ubiquitin; SCF, Skp-1, Cullin, F-box (TIR1)-containing complex. (D) Western blot assay of lysed YFP-mAID-3HA parasites, probed with antibodies recognizing HA and SAG1. Parasites were treated with 500 µM IAA or the vehicle (EtOH) for up to 240 min in the presence of 50 µM MG132 or the vehicle (DMSO). Data are from a single experiment of two or more experiments with the same outcome. (E) Coexpression of YFP-mAID-3HA (green) and TIR1-3FLAG (red) following treatment with 500 µM IAA or the vehicle (EtOH) for 4 h determined by IF microscopy with the antibodies indicated. Scale bars, 5 µm. (F) Ratiometric quantification of YFP-mAID-3HA to TIR1-3FLAG IF microscopy per vacuole. Mean values of individual vacuoles (EtOH, n = 24; IAA, n = 23) from two experiments ± the standard deviation, ****, P < 0.0001 (unpaired two-tailed Student t test).