Abstract
Recently, issues concerning the sustainable and harmless disposal of organic solid waste have generated interest in microbial biotechnologies aimed at converting waste materials into bioenergy and biomaterials, thus contributing to a reduction in economic dependence on fossil fuels. To valorize biomass, waste materials derived from agriculture, food processing factories, and municipal organic waste can be used to produce biopolymers, such as biohydrogen and biogas, through different microbial processes. In fact, different bacterial strains can synthesize biopolymers to convert waste materials into valuable intracellular (e.g., polyhydroxyalkanoates) and extracellular (e.g., exopolysaccharides) bioproducts, which are useful for biochemical production. In particular, large numbers of bacteria, including Alcaligenes eutrophus, Alcaligenes latus, Azotobacter vinelandii, Azotobacter chroococcum, Azotobacter beijerincki, methylotrophs, Pseudomonas spp., Bacillus spp., Rhizobium spp., Nocardia spp., and recombinant Escherichia coli, have been successfully used to produce polyhydroxyalkanoates on an industrial scale from different types of organic by-products. Therefore, the development of high-performance microbial strains and the use of by-products and waste as substrates could reasonably make the production costs of biodegradable polymers comparable to those required by petrochemical-derived plastics and promote their use. Many studies have reported use of the same organic substrates as alternative energy sources to produce biogas and biohydrogen through anaerobic digestion as well as dark and photofermentation processes under anaerobic conditions. Therefore, concurrently obtaining bioenergy and biopolymers at a reasonable cost through an integrated system is becoming feasible using by-products and waste as organic carbon sources. An overview of the suitable substrates and microbial strains used in low-cost polyhydroxyalkanoates for biohydrogen and biogas production is given. The possibility of creating a unique integrated system is discussed because it represents a new approach for simultaneously producing energy and biopolymers for the plastic industry using by-products and waste as organic carbon sources.
Keywords: Biochemicals and bioenergy, Biopolymers, PHAs, Biogas, Biohydrogen
Background
Over the past few decades, the need to reduce pollutant emissions produced by conventional systems of organic waste disposal has promoted the development of technologies that convert organic waste into bioenergy and biomaterials. In the near future, this new approach in waste management, in addition to being eco-friendly, can reasonably replace fossil fuels with biomass (organic waste or energy crops) as a source of both energy and materials (e.g., plastics) and therefore make two contributions toward reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions into the atmosphere [1].
Petrochemical-derived materials can be replaced with biodegradable materials and biochemicals derived from renewable sources. In fact, organic waste materials are interesting renewable resources that can be converted into different value-added products, such as bioethanol or biochemicals obtained by sugar fermentation [2, 3]. Recent technological developments have explored the value of biochemical products as precursors to biopolymers, e.g., succinic acid [4, 5] and 2,3-butanediol [6] derived from lignocellulosic biomass. Some biopolymers can be produced by microorganisms from the accumulation of extracellular materials, such as exopolysaccharides (EPS) [7], and used in the food, chemical, cosmetic, and packaging industries as adhesives, absorbents, lubricants, and cosmetics. Furthermore, several biopolymers, such as polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), polylactides, aliphatic polyesters, and polysaccharides [8], have already been successfully tested as bioplastics [9] because their physical and chemical properties perform just as well as conventional synthetic plastics. Among them, PHAs have gained much attention thanks to their complete biodegradability under various conditions within a period of 1 year [10]. Different bacteria (e.g., Alcaligenes spp., Azotobacter spp., methylotrophs, Pseudomonas spp., Bacillus spp., and recombinant Escherichia coli) have been used in PHA production from different low-cost substrates. In fact, to replace conventional petrochemical-derived plastics, useful substrates for PHA production include organic waste and by-products. In fact, to commercialize PHAs, substantial effort has been devoted to reducing the production cost through the development of bacterial strains and more efficient fermentation/recovery processes because the price of the substrate has the largest influence on the production cost of PHA [11].
To make PHA production more feasible for industrial application, future prospects are mainly focused on promoting less expensive substrates, improved microorganism cultivation strategies, and easier downstream processing methods, which are required for reducing production costs [12]. For this reason, different inexpensive substrates, such as molasses and sucrose, starch-based materials, cellulosic and hemicellulosic materials, sugars, whey, oils, fatty acids and glycerol, and organic matter from waste and wastewater [13], have been tested to produce biopolymers, and the results are promising.
Furthermore, it is important to highlight that the same substrates used to produce biopolymers represent a source of renewable energy (biomethane and biohydrogen) obtainable through an anaerobic digestion process. Therefore, such substrates can be simultaneously used to produce bioenergy and biopolymers, thus achieving a maximum valorization when they are used as organic waste.
The anaerobic digestion process is characterized by biochemical reactions in series carried out by different consortia of bacteria that convert organic compounds into methane, carbon dioxide, water, and ammonia. In the first step, complex and not negligibly sized biomolecules of organic materials are disintegrated and subsequently hydrolyzed into soluble, biodegradable organics by extracellular enzymes [14]. Then, acidogenic microorganisms metabolize products by hydrolysis into volatile fatty acids (VFAs) (acidogenic phase) [15]. Acidogenic products are first converted into acetic acid, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide (acetogenic phase) and, finally, into methane by methane-producing Archaea (methanogenic phase) [16]. The same substrates of methanogenic metabolism are the precursors that form PHAs [17]. Thus, this review gives insights into the current methodology for producing PHAs and biogas, with a focus on the use of organic waste and by-products as raw materials to keep production costs low. Moreover, this review examines the potential of several biological processes that can occur in the development of an innovative unique integrated system able to simultaneously produce bioenergy and biopolymers.
Bio-based and biodegradable polymers: PHAs production and classification
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) represent a group of bio-based and biodegradable polymers, considered similar to petroleum-based polymers [18].
Many bacteria, such as Cupriavidus (C.) necator [10, 19–27], different Pseudomonas (P.) species (P. fluorescens, P. hydrogenovora, P. oleovorans, P. resinovorans, P. aeruginosa, P. mendocina) [25, 28–32], strains belonging to Azotobacter (A.) species (A. vinelandii, A. chroococcum, A. beijerinckii) [33–37], Bacillus (B.) spp. [38–40], recombinant Escherichia (E.) coli [8, 12, 35, 41–44], and Burkholderia (Bk.) spp. [45, 46], synthesize PHAs as intracellular carbon and energy storage, accumulating these polyesters of hydroxyalkanoates as granules in the cytoplasm of cells [47]. Polyhydroxyalkanoic acids produced by bacteria are the building blocks of biodegradable thermoplastics and elastomers currently in use, or candidates to be used, in the medical and pharmaceutical industries as well as in agriculture [48]. The production of PHAs occurs mainly when cells are cultivated in the presence of a carbon source in excess, and their growth is limited by the lack of another nutrient, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, or oxygen [49]. When the supply of the limiting nutrient is restored, PHAs are degraded by an intracellular depolymerase and subsequently metabolized as a carbon and energy source [50], and the number of bacteria rapidly increases.
Polyhydroxyalkanoates can be divided into two groups depending on the number of carbon atoms in the monomer units: short-chain-length (SCL) PHAs, which consist of 3–5 carbon atoms, and medium-chain-length MCL-PHAs, which consist of 6–14 carbon atoms [49]. The length of the side chain and functional group has great importance for the physical properties. The SCL-PHAs are crystalline, brittle, and stiff polymers, with a high melting point and a low glass transition temperature. In contrast, MCL-PHAs show low crystallinity and tensile strength and lower melting points.
Polyhydroxyalkanoates have the general formula shown in Fig. 1 [13], where “n” is equal to 1, and “R” is a methyl group. The most abundant PHA family member is poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (P(3HB)). Using different substrates in a co-feeding system, copolymers of PHB (polyhydroxybutyrate) can be formed, such as polymers containing 3-hydroxyvalerate (3HV) or 4-hydroxybutyrate (4HB) monomers. 3HV can be incorporated into the PHB molecule, forming poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) [P(3HB-3HV)], resulting in a more brittle compound than P(3HB) [47].
Fig. 1.
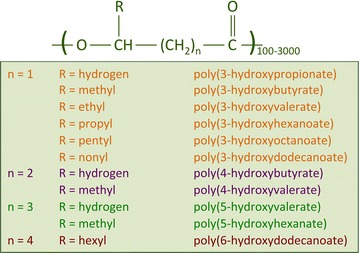
General structure of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs). The most studied PHA type is the homopolymer P(3HB), for which n is equal to 1 and R is a methyl group [13]
Thus, to reduce the environmental footprint by producing and using petrochemical-derived products, they can be replaced partially and even completely by polyesters derived from biological processes (i.e., PHAs) that have the significant advantage of being completely biocompatible [47]. Biocompatibility is the property shown by certain materials that generates non-toxic compounds when they are disposed of after use as well having the same physical property of the artificial material derived from petrol that they would replace [13]. Unlike petroleum-derived plastics that take several decades to degrade, PHAs can be completely bio-degraded within a year by a variety of microorganisms, mainly bacteria and fungi [48]. In particular, several aerobic and anaerobic PHA-degrading bacteria, such as Comamonas sp. [51], Pseudomonas lemoignei [52] from soil, Alcaligenes faecalis [53] and Pseudomonas fluorescens from activated sludge [54] and Pseudomonus stutzeri from lake water [55], and fungi, such as Aspergillus fumigatus [54], have been isolated from various environments. These microorganisms excrete extracellular PHA depolymerases to degrade PHAs into water-soluble monomers and oligomers, using them as a carbon source (or methane under anaerobic conditions) [8].
Thus, life cycle assessment (LCA) conducted on the use of PHAs has been proven as the main advantage to avoid the accumulation of plastics in the environment [56]. Therefore, PHAs are better than petrochemical analogues, such as polyethylene and polypropylene [57–59], in terms of sustainability and environmental protection [60], but the realization and more widespread use of these environmentally friendly processes are related to the cost of the final product. The current PHA price also depends on monomer composition, and it is usually higher for copolymers; overall, it ranges from 2.2 to 5.0 € kg−1 [13, 61, 62], which is less than the typical range of 10–12 € kg−1 reported at the beginning of the past decade [61]. Notwithstanding the burden of costs and the environmental impacts of plastic trash, the current PHA prices are not deemed to be commercially competitive with respect to conventional petroleum-based polymers, which typically cost less than 1.0 € kg−1 [61, 63]. Although the price of PHAs is high, several companies are producing PHA products worldwide to meet the demand of the market, including in the UK, Japan, US, Germany, Brazil, Italy, and China [64, 65].
Suitable substrates and bacterial strains for PHA production
The synthesis of PHAs occurs in many microorganisms under well-defined operating conditions and when they are supplemented with specific substrates, better known as PHA precursors. These compounds are incorporated into PHAs and used as the sole carbon source by microorganisms (or coupled with others as cosubstrates) if the cells are cultivated in the presence of an excess carbon source. Moreover, PHAs are also formed when growth is impaired or restricted by the lack of another nutrient, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, or oxygen [8]. Thus, different PHAs could be synthesized from the combination of different substrates and microorganisms under different growth conditions (aerobic or anaerobic, temperature, and pH).
Relevant substrates for the production of PHAs are as follows: carbon dioxide [66] or fossil resources, such as low-rank coal [67] renewable resources (e.g., starch [19, 20, 26, 38, 68], cellulose [69], sucrose [28, 33, 45]), waste materials (e.g., molasses [33, 39, 41], whey [12, 29, 42–44], glycerol [10]), and chemicals (e.g., propionic acid [70]). To avoid the use of fossil resources due to environmental issues and to limit PHA production costs, renewable resource and waste materials are reasonably considered suitable and promising substrates.
In the following paragraphs, an overview of different works categorized on the basis of the different substrates used is given. The results are presented in terms of the PHA content (%PHAs, %) and concentration ([PHAs], g l−1) calculated by the following Eqs. 1 and 2, respectively, where mPHA is the amount of PHAs (mg), mcells (mg) is the amount of freeze-dried biomass in samples, and CDW is the cell dry weight (g l−1):
| 1 |
| 2 |
Starch-based material as a source of PHAs
Starch is a renewable carbon source available in large amounts. Prior to fermentation, starch is hydrolyzed to glucose by a two-step process, liquefaction and saccharification, because PHA-producing bacteria cannot synthesize amylase enzymes for starch degradation. Commercial hydrolyzing enzymes are often used, but they contribute to an increase in the cost of the glucose production process [35]. Kim [35] used soluble starch to produce P(3HB), obtained after 70 h of incubation with 25 g l−1 of PHB (content of 46% in cell dry weight), in fed-batch cultures of A. chroococcum strain 23 under oxygen-limiting conditions. Halami [38] reported the ability of the isolated strain Bacillus cereus CFR06 to accumulate PHAs in a starch medium composed of soluble starch, yeast extract, and salts. The genus Bacillus was identified as one of the first gram-positive bacteria suitable to produce PHAs and was cultivated under nitrogen limitation in Luria–Bertani (LB) broth for 24 h at 37 °C on a rotary shaker at 100–150 rpm min−1. The results obtained were less promising than those found by Kim [35] because, after 72 h of incubation, a P(3HB) concentration of 0.48 g l−1 with a content of 48% was achieved. Koutinas et al. [19] proved the potential of C. necator (synonym Wautersia eutropha and formerly classified as Alcaligenes eutrophus, formerly classified as Ralstonia (R.) eutropha [68]) in PHB production from a specific substrate derived from wheat. The authors conducted fed-batch tests using a 500-ml shake flask on a 250 rpm rotary shaker at 30 °C and a pH range of 6.5–6.8. The results showed a PHB concentration of 51.1 g l−1 using a culture medium with free amino nitrogen as substrate at a concentration of 1.2 g l−1. Under the same operating conditions (working volume, rpm, temperature, and pH range), Xu et al. [20] compared the batch and fed-batch modes using C. necator NCIMB 11599 grown on wheat-derived media. They demonstrated that more PHB was accumulated in cells operating in fed-batch mode. In fact, the use of fed-batch mode allowed for an increase in PHB concentration to 130.2 g l−1 (PHB cells content ~80%) compared with batch fermentation that showed a production of 41.5 g PHB l−1 (PHB cells content ~66%). Haas et al. [21] used saccharified waste potato starch as a carbon source for PHB production by C. necator NCIMB 11599, obtaining a PHB concentration of 94 g l−1, with a specific yield from starch of 0.22 PHB g starch g−1 under phosphate-limiting conditions. Poomipuk et al. [71] isolated and selected the strain Cupriavidus sp. KKU38, which was able to accumulate PHAs up to 65.27% (PHA concentration of 2.8 g l−1) from cassava starch hydrolysate as a sole carbon source in a 250-ml flask (Table 1).
Table 1.
Overview of studies reporting PHA production from starch-based materials
| Strain | Type of PHA | Operation mode | Time to PHAmax [h] | PHA concentration [g l−1] | PHA content [%] | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Azotobacter chroococcum 23 | P(3HB) | Fed-batch | 70 | 25 | 46 | [35] |
| Bacillus cereus CFR06 | P(3HB) | Batch | 72 | 0.48 | 48 | [38] |
| Cupriavidus necator NCIMB 11599 | P(3HB) | Fed-batch | 168 | 51.1 | 70 | [19] |
| Cupriavidus necator NCIMB 11599 | P(3HB) | Batch | 69 | 41.5 | 66 | [20] |
| Fed-batch | 171 | 130.2 | 80 | |||
| Cupriavidus necator NCIMB 11599 | P(3HB) | Batch | 72 | 94 | 22 | [21] |
| Cupriavidus sp. KKU38 | PHA | Batch | 96 | 2.8 | 65.3 | [71] |
| Recombinant E. coli SKB99 | P(3HB) | Batch | 72 | 1.2 | 40 | [72] |
However, to overcome the high costs of the hydrolysis of starch into glucose by a two-step process (liquefaction and saccharification), making this feedstock less economically viable, Bhatia et al. [72] constructed the recombinant E. coli strain SKB99 harboring plasmids containing genes for starch hydrolysis (from Paenibacillus sp.) and PHB synthesis (from R. eutropha). This engineered strain utilized starch as the sole carbon source, with a maximum PHB production of 1.24 g l−1 (PHB content 40%) for 72 h with 2% (w/v) starch (Table 1). In addition, the accumulation of PHB started with the growth of the strain E. coli SKB99 and remained consistent until it attained the stationary phase, highlighting that PHB production in this engineered strain is not regulated by the stress response, unlike in R. eutropha and other microorganisms.
Therefore, starch-based materials are suitable substrates for PHA accumulation and, in particular, for P(3HB) accumulation. However, PHA accumulation strictly depends on the bacterial species and strains that exhibit different biotechnological performances depending on the carbon source and the culture conditions. The best results were obtained using C. necator NCIMB 11599 cultured on wheat and hydrolyzed waste potatoes under nutrient (nitrogen or phosphorus)-limiting conditions, operating in batch and fed-batch mode, respectively.
Molasses and sucrose as sources for PHAs
Molasses is a common industrial by-product of sugar production, is much cheaper than glucose, and is extensively used as a carbon source for PHA production from biological processes. Liu et al. [41] demonstrated that recombinant E. coli (HMS174/pTZ18u-PHB) can efficiently utilize molasses as the sole carbon source to produce PHB. A fed-batch feeding strategy was developed to improve cell growth and PHB production. The final PHA concentration was 31.6 g l−1, and 80% of PHAs was accumulated (Table 2). Jiang et al. [28] isolated a strain of (PHB)-accumulating bacteria from the soil in Alaska (USA), identified as P. fluorescens A2a5. This microorganism is capable of accumulating a large amount of granules in its cells when grown in sugarcane liquor medium. Batch cultivation was carried out at 25 °C in a 5-l bioreactor inoculated with 1% inoculum (v/v) at pH 7.0. In this way, a maximum cell dry weight (CDW) of 32 g l−1 with a PHB concentration of 22.4 g l−1 was obtained, and the PHB content was approximately 70%. C. necator was aerobically grown in a well-balanced medium consisting of sugarcane and inorganic nutrients to reach a high cell density [45]. Then, cell growth was shifted to PHB synthesis by limiting nutrients other than the carbon source. The fed-batch fermentation process was carried out by continually feeding (45–50 h) a high concentration of sugar syrup to achieve a biomass of nearly 65–70% PHB, with a concentration ranging from 80 to 100 g l−1 (Table 2).
Table 2.
Overview of studies reporting PHA production from molasses and sucrose
| Strain | Type of PHA | Operation mode | Time to PHAmax [h] | PHA concentration [g l−1] | PHA content [%] | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recombinant E. coli (HMS174/pTZ18u-PHB) (C. necator genes) | P(3HB) | Fed-batch | 31.5 | 31.6 | 80 | [41] |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens A2a5 | P(3HB) | Batch | 96 | 22.4 | 70 | [28] |
| Cupriavidus necator | P(3HB) | Fed-batch | 45–50 | 80–100 | 65–70 | [45] |
| Bacillus cereus M5 | P(3HB) | Batch | 72 | 0.13 | 73.8 | [39] |
| Azotobacter vinelandii UWD | P(3HB) | Fed-batch | 35 | 23 | 66 | [33] |
| Bacillus megaterium BA-019 | P(3HB) | Fed-batch | 24 | 72.7 | 42 | [73] |
The effect of different molasses concentrations (1–5 g molasses/100 ml water) on PHB production by B. cereus M5 was investigated by Yilmaz and Beyatli [39]. They observed that PHB productivity by this strain decreased with increasing molasses concentration. In fact, the highest P(3HB) concentration produced by this strain was 0.1 g l−1 (polymer content of 73.8%) with 1% molasses concentration.
Azotobacter vinelandii UWD was investigated by Page et al. [33] using molasses as the sole carbon source. Fed-batch bioreactors were operated with 5% (w/v) molasses at pH 7.2 and inoculated with 4% (v/v) of the pre-grown strain. In the beet molasses medium, NH4 was depleted by 10–12 h to establish NH4-limiting conditions and fix nitrogen during the PHA production phase of growth. After 35 h, a P(3HB) concentration of 23 g l−1 and a polymer content of 66% were achieved.
Kulpreecha et al. [73] tested B. megaterium BA-019 on sugarcane molasses (20 g l−1) as a carbon source and urea or ammonium sulfate at 0.8 g l−1 as the investigated nitrogen sources. In the experiments, a cell dry mass concentration of 72.7 g l−1 in 24 h, with a PHB content of 42% (w/w), was achieved under nitrogen-limiting conditions operating in fed-batch mode (Table 2).
In addition, with sugarcane, C. necator showed the best PHA concentration among the bacterial strains (recombinant E. coli, A. vinelandii UWD, and B. megaterium) operating in fed-batch mode with molasses as a carbon source. In fact, C. necator is able to accumulate approximately 100 g l−1 synthesizing glucose (from starch) and sucrose (from sugarcane).
Lignocellulosic material as a source for PHAs
To produce fuels and other valuable bioproducts, lignocellulosic biomass from dedicated crops and agricultural and forestry waste are promising renewable sources [74–77].
Lignocellulosic materials, consisting of lignin (complex polyphenolic structure), cellulosic (b-d-1,4-glucan), and hemicellulosic (d-arabinose, d-xylose, d-mannose, d-glucose, d-galactose, and sugar alcohols) fibers, constitute the most abundant renewable resources on our planet [13].
The composition of lignocellulosic biomass differs in terms of lignin (10–25%), cellulose (30–60%), and hemicellulose (25–35%) content [78].
Silva et al. [46] studied the potential of two bacterial strains, Bk. cepacia IPT 048 and Bk. sacchari IPT 101A, in producing P(3HB), comparing biosynthesis from xylose and glucose with bagasse hydrolysate. In high-cell-density cultures using a mixture of xylose and glucose under P limitation, both strains reached a maximum P(3HB) concentration of 60 g l−1 dry biomass, containing 60% biopolymer. Higher polymer content and yield were observed under P limitation than under N limitation for Bk. sacchari IPT 101A, whereas Bk. cepacia IPT 048 showed a similar performance in the presence of both growth-limiting nutrient conditions. Using bagasse hydrolysate as the carbon source, polymer contents reached 62 and 53% for B. sacchari IPT 101A and B. cepacia IPT 048, respectively, with a CDW of 4.4 g l−1 for both strains under N limitation (Table 3).
Table 3.
Overview of studies reporting PHA production from lignocellulosic materials
| Strain | Type of PHA | Operation mode | Time to PHAmax [h] | PHA concentration [g l−1] | PHA content [%] | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burkholderia sacchari IPT 101 | P(3HB) | Batch | 25 | 2.73 | 62 | [46] |
| Burkholderia cepacia IPT 048 | P(3HB) | Batch | 25 | 2.33 | 53 | [46] |
| Cupriavidus necator | PHA | Batch | 48 | 3.9 | 65 | [22] |
| Recombinant E. coli (C. necator genes) | P(3HB) | Batch | 60 | 1.7 | 35.8 | [69] |
| 60 | 4.4 | 73.9 | ||||
| R. eutropha ATCC 17699 (C. necator) | P(3HB) | Batch | 48 | 11.4 | 75.5 | [79] |
Yu and Stahl [22] also studied the performance of C. necator with the same substrate. In their experiment, the cultures were shaken in flasks at 200 rpm and 30 °C for 48 h with pH adjusted to approximately 7.5. They demonstrated that P(3HB) was the predominant biopolyester formed from the hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse, with a concentration of 3.9 g l−1, corresponding to a P(3HB) accumulation of 65% of the CDW, achieved with a high carbon-to-nitrogen ratio (C/N = 20 or above). Since a minimum nitrogen level should be maintained during cultivation, this high C/N ratio implies a high concentration of residual organic carbon or a high amount of hydrolysates. A moderate C/N ratio (7–10) may be used to yield a low concentration (less than 1 g l−1) of residual carbons and a moderate level of PHA content in the cells (45–50% w/w).
Lee et al. [69] investigated P(3HB) production from xylose and hydrolyzed cellulose by growing recombinant E. coli strains with C. necator PHA biosynthesis genes, testing the effects of supplementing a complex nitrogen source on cell growth and PHB production. The cells were cultivated for 60 h in a 250-ml flask containing 50 ml of medium in a shaking incubator at 250 rpm. When the strain TG1 (pSYL107) was grown on 20 g l−1 xylose, it was capable of accumulating 1.7 g l−1 of P(3HB) with 35.8% of polymer content. A higher P(3HB) concentration, equal to 4.4 g l−1, and a polymer content of 73.9% were reached when the previous culture medium was supplemented with 10 g l−1 of soybean hydrolysate. To evaluate the effects of the nitrogen source, tryptone and peptone were also tested, achieving 47.7 and 10.3% of PHB content, respectively.
The ability of R. eutropha ATCC 17699 (C. necator) to produce PHB in the presence of different waste biomass hydrolysates (rice paddy straw, soybean husk, sunflower husk, and wood straw) was evaluated by Saratale and Oh [79]. The most suitable substrate for PHB accumulation by this strain was the rice paddy straw hydrolysate, which was selected by the authors for optimization of the process, obtaining the maximal PHA accumulation (75.45%) and PHB production (11.42 g l−1) within 48 h of fermentation.
Moreover, lignin and its derivatives are also used for PHA production. Tomizawa et al. [80] tested PHA-accumulating strains on mineral salt media containing each of the 18 lignin derivatives and hydroxybenzoic acids, including intermediates derived from the metabolism of lignin derivatives in bacteria. Most of the strains grew poorly in media containing lignin derivatives, such as p-coumaric acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, and sinapinic acid.
On the contrary, R. eutropha PHB-4 accumulated P(3HB) from 3-hydroxybenzoic acid and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid as the sole carbon sources, with a PHA content of 65 and 63 wt% and a dry cell weight of 1.6 and 0.69 g l−1, respectively.
Although C. necator species seems to be the best bacterial candidate for PHB production using lignocellulosic hydrolysate, the accumulation is lower than that obtained with sucrose- and starch-based materials as carbon sources. The lowest PHA accumulation could be due to the presence of specific toxic compounds (e.g., furfural, HMF, p-hydroxybenzoic aldehyde, and vaniline) that are usually released during the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass, which are known to have an inhibitory effect on microbial growth and metabolism.
Whey-based culture media as a source for producing PHAs
Whey is the major by-product of cheese factories, representing 80–90% of the volume of transformed milk [42]. It contains approximately 4.5% (w/v) lactose, 0.8% (w/v) protein, 1% (w/v) salts, and 0.1–0.8% (w/v) lactic acid, and its high biological oxygen demand (40 g l−1) makes it difficult to dispose. The discharge of large amounts of cheese whey into the environment can damage the chemical and physical structure of soil and pollute groundwater and can also affect the air [81]. This by-product represents an attractive low-cost substrate for producing PHAs.
As seen in the previous sections, C. necator is one of the best-known bacteria among PHA-producing microorganisms, but it is unable to hydrolyze lactose or metabolize galactose [82]. In fact, C. necator was able to use lactose only after the expression of genes encoding β-galactosidase and galactokinase, although at a very slow rate [83]. Therefore, recombinant E. coli containing the C. necator PHA biosynthesis genes for the production of PHB from glucose is considered a good candidate for PHB production from whey [42]. Lee et al. [42] cultivated recombinant E. coli strains in a defined medium supplemented with varying concentrations of whey solution and obtained 5.2 g l−1 of PHB, corresponding to 81.3% (w/w) of PHB, with a concentration of 30 g l−1 of whey solution (Table 4). Kim [35] also studied recombinant E. coli strains as PHB-accumulating microorganisms under O2 limitation compared with conditions without O2 limitation. The highest PHB accumulation (80%) was observed under O2-limiting conditions, with a PHB concentration of 25 g l−1. Instead, without O2 limitation, 57% of PHB was achieved with a concentration of 32 g l−1. A recombinant E. coli strain containing the PHA biosynthetic genes from Azotobacter spp., specially designed for the production of PHB from milk whey, was studied by Nikel et al. [43]. Fed-batch cultures were carried out at 37 °C in a 5.6-l fermentor with a starting volume of 2.0 l and a controlled pH of 7.20. The feeding solution used for fed-batch cultures was a concentrated and deproteinated whey solution containing 25% (w/v) lactose. They reported that after 24 h, the cells accumulated PHB up to 72.9% of their cell dry weight, reaching a PHA concentration of 51.1 g l−1. Physical analysis of PHB collected from the recombinants showed that its molecular weight was similar to PHB produced by an Azotobacter spp. strain.
Table 4.
Overview of studies reporting PHA production from whey-based culture media
| Strain | Type of PHA | Operation mode | Time to PHAmax [h] | PHA concentration [g l−1] | PHA content [%] | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recombinant E. coli (C. necator genes) | P(3HB) | Batch | 49 | 5.2 | 81.3 | [42] |
| Recombinant E. coli (C. necator genes) GCSC 6576 | P(3HB) | Fed-batch with oxygen limitation | 52 | 25 | 80 | [35] |
| Fed-batch without oxygen limitation | 35 | 32 | 57 | |||
| Pseudomonas hydrogenovora DSM 1749 | P(3HB) | Fed-batch | 41 | 1.27 | 12 | [29] |
| P(3HB-co-3HV) | 31 | 1.44 | 12 | |||
| Recombinant E. coli K24 K (Azotobacter spp. genes) | P(3HB) | Fed-batch | 24 | 51.1 | 72.9 | [43] |
| Recombinant E. coli CGSC 4401 | P(3HB) | Fed-batch | 36.5 | 96.2 | 80.5 | [12] |
| Recombinant E. coli CGSC 4401 (A. latus genes) | P(3HB) | Fed-batch 30-l bioreactor | 26 | 35.5 | 70 | [44] |
| Fed-batch 300-l bioreactor | 20 | 20 | 67 |
A new fermentation strategy using a cell recycle membrane system was developed by Ahn et al. [12] for the efficient production of P(3HB) from whey by a recombinant E. coli strain harboring the Alcaligenes latus PHA biosynthesis genes.
Cell fed-batch cultures of recombinant E. coli CGSC 4401 (pJC4) were carried out to overcome the volumetric limitation of a fermentor (2.7 l) fed with a solution with low lactose solubility to increase PHB productivity. A whey solution containing 210 g lactose l−1 was used as a feeding solution. The final cell concentration, PHB concentration, and PHB content obtained in 39 h were 150, 100 g l−1, and 67%, respectively. In another experiment, a whey solution containing 280 g lactose l−1 was used as a feeding solution. After 36.5 h, a PHB concentration and a PHB content of 96.2 g l−1 and 80.5%, respectively, were obtained using a whey solution concentrated to contain 280 g lactose l−1 as a feeding medium. No inhibitory effects of the by-products or nutrients on cell growth and PHB production were found during fermentation by the authors.
The production of P(3HB) from whey by fed-batch cultures of recombinant E. coli harboring a plasmid containing the Alcaligenes latus PHA biosynthesis genes was examined by Park et al. [44]. Fed-batch cultures of recombinant E. coli SGSC 4401 (pJC4) were carried out at 30 °C in 30 l (working volume of 10 l) and 300 l (working volume of 150 l) fermenters supplying only air. The culture pH was controlled at 6.9. With lactose below 2 g l−1, the cells grew to 12 g l−1 with 9% (w/w) P(3HB) content in a 30 l fermenter. The accumulation of P(3HB) could be triggered by increasing lactose to 20 g l−1. Using this strategy, 35.5 g l−1 was obtained with a 70% (w/w) P(3HB) content after 26 h. The same fermentation strategy was used in a 300 l fermenter, and a 20 g l−1 with 67% (w/w) P(3HB) content was obtained in 20 h by Park et al. [44]. Koller et al. [29] compared the production of PHB under nitrogen-limiting conditions obtained with P. hydrogenovora using the following two substrates: hydrolyzed whey permeate and glucose/galactose medium. Shake flasks (1 l) containing 250 ml of hydrolyzed whey permeate or synthetic medium supplemented with glucose and galactose (each 2.5 g l−1) were both inoculated with 5% (v/v) P. hydrogenovora. The flasks were shaken at 30 °C for 48 h. Furthermore, the study investigated the influence of the 3HV precursor sodium valerate on the bacterial growth of P. hydrogenovora. Thanks to its advanced properties compared with those of highly crystalline pure PHB [29], the ability of the strain to biosynthesize P(3HB-co-3HV) in media supplemented with hydrolyzed whey permeate and sodium valerate was evaluated. In these two different experiments, PHA content was confirmed at 12% for both types of PHAs, but the PHA concentration was higher when sodium valerate was added to P(3HB-co-3HV) production (Table 4).
A recombinant strain of E. coli was generally used to obtain the PHA concentration (more than 90 g l−1) from whey-based culture media because C. necator is unable to hydrolyze lactose. In fact, several studies tested different lactose concentrations to correlate this parameter to PHA accumulation. Fed-batch experiments supplemented with a high amount of lactose (hydrolyzed from chees whey) were performed to obtain a higher PHA concentration. Otherwise, when increasing the lactose concentration to 280 g l−1, a relevant increase in PHA concentration was not observed.
In addition, it is interesting to note that with whey-based culture media, the oxygen-limiting conditions enhance PHB biosynthesis from recombinant E. coli but decrease PHA concentration in the cells.
Fatty acid and glycerol culture media as source for PHAs
Pure glycerol is an important industrial feedstock, with applications in the food, drug, cosmetic, and tobacco industries, while crude glycerol is the main by-product of biodiesel production, with low value due to the presence of impurities (such as methanol, salts, and fatty acids). Thus, crude glycerol represents a waste product with an associated disposal cost [10]. For this reason, it can be used as an attractive substrate for PHA production.
Cupriavidus necator DSM 545 was used by Cavalheiro et al. [10] to accumulate P(3HB) from waste glycerol and from commercial glycerol as a control substrate. For C. necator cultivated on basal medium supplemented with pure glycerol and nitrogen depletion, a maximum of 51.2 g l−1 of P(3HB) at 33.5 h was reached, with a PHB content of 62% (Table 5). On the contrary, using waste glycerol as a carbon source, productivity was lower because only 38.5 g l−1 was achieved with a PHB content of 50% in 34.5 h.
Table 5.
Overview of studies reporting PHA production from oil, fatty acid, and glycerol culture media
| Strain | Type of PHA | Operation mode | Time to PHAmax [h] | PHA concentration [g l−1] | PHA content [%] | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. necator DSM 545 | P(3HB) | Fed-batch | 33.5 | 51.2 | 62 | [10] |
| C. necator H16 (ATCC 17699) | P(3HB) | Batch | 72 | 2.9–3.4 | 79–82 | [23] |
| C. necator H16 (pJRDEE32d13) | P(3HB) | Fed-batch | 96 | 85–95 | 72–76 | [24] |
| C. necator H16 | P(3HB) | Batch | 96 | 1.24 | 19.7 | [25] |
| Pseudomonas resinovorans | PHA | Batch | 48 | 0.14 | 15.2 | [30] |
Production of PHAs from various plant oils or oleic acid by C. necator H16 was studied by Fukui and Doi [23]. The strain was tested on olive oil, corn oil, and palm oil and in all these plant oils. The strain was cultivated in a 100-ml nitrogen-limited mineral salt medium containing 1% plant oil at 30 °C for 72 h. The wild-type strain produced P(3HB) at a high polymer content (79–82%) but at low concentrations (2.9–3.4 g l−1).
Kahar et al. [24] produced a copolymer of 3HB with 5 mol% (R)-3-hydroxyhexanoate, P(3HB-co-3HHx), from soybean oil as a sole carbon source with a recombinant strain of C. necator. The medium for PHA production in the fermentor was a mineral salt medium, and the initial concentration of NH4Cl was set at 4 g l−1. Additional NH4Cl was intermittently fed into the culture broth to avoid nitrogen source depletion. Soybean oil was added to the fermentor for an initial concentration of 20 g l−1. A high content of P(3HB) (85–95 g l−1) and a high PHA content of 71–74% (w/w) were achieved during 96 h.
Füchtenbusch et al. [25] studied R. eutropha and P. oleovorans cultivated in a mineral salt medium with the oil from rhamnose production as the sole carbon source under aerobic conditions at 30 °C in nutrient broth or in mineral salt medium.
The concentration of ammonium was limited to 0.05% (m/v) to promote the accumulation of PHAs. The cultivation of P. oleovorans and R. eutropha was performed in 300 ml at 28 °C. C. necator accumulated only P(3HB) at 6.3 g l−1, with a polyester content of 19.7% during the first 96 h (Table 5). The same authors tested P. oleovorans under the same operating conditions using the same carbon source. After 96 h, this strain accumulated 5 g l−1, with a P(3HB-co-3HHx) content of 17.3%.
Different Pseudomonas species (P. oleovorans, P. resinovorans, P. putida, and P. citronellolis) were tested by Cromwick et al. [30] in 2-l shake flasks. The bacteria were evaluated for their ability to grow and produce PHAs using tallow-free fatty acids and tallow triglyceride as carbon substrates; however, only P. resinovorans was able to grow and produce PHAs. The PHA concentration in this case was 0.12–0.15 g l−1, with a 15.2% polymer content, using unhydrolyzed tallow as the substrate.
The different fatty acids and glycerol waste materials used as substrates for PHA accumulation highlighted that C. necator was the best candidate operating under nitrogen source depletion, although PHA accumulation depended on the strain and operating mode. In fact, performing the experiments in fed-batch mode, more PHB was accumulated in the cells than operating in batch mode.
Solid agro-industrial by-products and waste as a source of PHA production
Law et al. [40] showed that recombinant B. subtilis could utilize malt waste in the medium as a carbon source better than glucose and thus could substantially lower the cost of PHA production. In the paper by Law and co-authors, the pha genes (involved into PHA accumulation) from B. megaterium were cloned into B. subtilis. The recombinant strain was cultivated by acid hydrolyzed malt waste, and a 1% inoculum was used in a fermentation flask incubated at 37 °C at 280 rpm for 16 h. Their results showed PHA accumulation in a malt waste medium of 2.53% with a PHB concentration of 0.06 g l−1 in 12 h (Table 6).
Table 6.
Overview of studies reporting PHA production from solid agro-industrial by-products
| Strain | Type of PHA | Operation mode | Time to PHAmax [h] | PHA concentration [g l−1] | PHA content [%] | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recombinant Bacillus subtilis 1A304 (105 MU331) | P(3HB) | Batch | 12 | 0.06 | 2.5 | [40] |
| Azotobacter vinelandii UWD (ATCC 53799) | P(3HB-co-3HV) | Batch | 48 | 0.43 | 37 | [34] |
| 18 | 5.48 | 58.3 | ||||
| C. necator (R. eutropha) | P(3HB-co-3HV) | Batch | 45 | 1.13 | 40.8 | [84] |
| Batch | 48 | 1.2 | 34.1 | [26] | ||
| Fed-batch | 73 | 16.5 | 72.6 | [85] | ||
| Activated sludge | P(3HB) | Batch | 96 | 2.7 | 67 | [87] |
Aztoobacter vinelandii UWD strains were tested by Cho et al. [34] with most poly-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-valerate (PHBV) production from swine waste liquor. Strain UWD was cultured in a shake flask with 4% inoculum at 200 rpm, incubated at 30 °C for 18–52 h.
Using undiluted swine waste liquor medium without glucose supplementation, cell growth was limited to 1.2 g l−1 with 37% in 48 h. Cell growth and PHBV production increased when swine waste liquor was diluted twofold and supplemented with 30 g glucose l−1 (5.48 g l−1 and PHBV content 58%).
Industrial fruit and vegetable waste were successfully used as sole carbon sources by Ganzeveld et al. [84] to produce PHBV by R. eutrophus under oxygen-limiting conditions. The fermentor was a 1-l standard fermentor with a working volume of 750 ml. The temperature was controlled at 30 °C. The stirrer speed was adjusted manually to maintain the dissolved oxygen pressure above 30% of the saturation concentration. A concentration of 1.1 g PHBV l−1, or 40% (w/w) of the cell dry weight, was obtained.
Starchy wastewater was used by Yu [26]. The waste was first digested in a thermophilic upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor to form acetic, propionic, and butyric acids. PHA formation from individual acids was further investigated under nitrogen-limiting conditions by active biomass of R. eutropha. PHA formation from acid effluent in 48 h was 1.2 g l−1, with a PHA content of 34.1% (Table 6).
Another suitable substrate for PHA production is food scraps, a complex form of organic solid waste that is unusable by PHA-producing microbes, such as R. eutropha. Hydrolysis and acidogenesis are the main processes used to convert biodegradable solids into short-chain volatile fatty acids, such as acetic, propionic, and butyric acids, which are utilized by PHA-producing bacteria. This approach was used by Du et al. [85] by coupling organic acid production with anaerobic acetogenesis to produce PHAs. The PHA-synthesis reactor (2-l air-bubbling bioreactor) was maintained at 30 °C via a water jacket and pH 7.5. The dissolved oxygen concentration was maintained at 20% of air saturation or above. The PHA content and concentration reached their maximal values of 72.6% and 16.5 g l−1, respectively, in 73 h.
Other studies were conducted on the use of excess activated sludge from a wastewater treatment plant fed with industrial waste streams as a substrate for PHB accumulation [86]. Wastewater from food processing (producing mainly potato chips, wafers, and sweets) and starch-rich grain-based alcohol industries (rice grain-based and jowar grain-based distillery spent wash) was used as a substrate for PHB production by Khardenavis et al. [87]. In their work, different types of wastewater were tested in 250-ml conical flasks and incubated on a rotary shaker at 150 rpm at 30 °C: wastewater derived directly from industry, filtered wastewater, and deproteinized wastewater, each in the absence and presence of an external nitrogen source; the highest biomass concentration of 6.6 g l−1 (dry weight) was produced in 96 h in a raw rice grain-based distillery spent wash with the addition of di-ammonium hydrogen phosphate, accumulating 2.7 g l−1 PHB with a content of 67%; a deproteinized jowar grain-based distillery spent wash and filtered food processing wastewater yielded lower PHB and biomass accumulation.
The studies carried out using solid agro-industrial by-products and waste demonstrated that the accumulation of PHAs was lower than that obtained with the other complex starting matrices, which was also observed when lignocellulosic hydrolysates were used as carbon sources. In addition, with this organic biomass, the highest accumulation was achieved using C. necator species, although the operating mode strongly influenced the process. Interestingly, activated sludge from a wastewater treatment plant was used as mixed cultures for PHA production from industrial waste streams. In particular, the PHA concentration was similar to that observed with pure cultures, overcoming the high costs derived from the production of pure cultures and the disposal of waste activated sludge.
Integrated systems to simultaneously produce intracellular (PHAs) and extracellular by-products (biosurfactants)
Bacterial strains actively involved in PHA accumulation can be used at industrial scale to reduce the production costs of biopolymers due to their ability to convert waste materials into valuable intracellular and extracellular bi-products (e.g., PHAs and exopolysaccharides (EPS), respectively) that are useful for biochemical production. PHAs represent intracellular carbon and energy storage, while EPS and biosurfactants are produced as extracellular substances to protect the cells from desiccation and predation or are a carbon source. These substances are of industrial interest for washing powders and fabric softener production [88]. They are used also in the food, chemical, cosmetic, and packaging industries as adhesives, absorbents, lubricants, and cosmetics [89–91].
Biosurfactants are amphipathic molecules with polar and non-polar heads produced by different bacterial genera (e.g., Acinetobacter, Arthrobacter, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Rhodococcus, and Enterobacter) [92]. Biosurfactants present as a wide variety of structures because their synthesis is influenced by the carbon source [93]. In fact, they can be produced on different substrates, such as sugars, lipids, alkanes, and waste materials [92]. The main property of biosurfactants is the ability to reduce surface and interfacial tension, forming microemulsions [94]. Among biosurfactants, rhamnolipids are the most studied thanks to the simultaneous production of PHAs and rhamnolipids by P. aeruginosa IFO3924 [31]. In their work, batch cultivation was conducted at 30 °C in 3-l fermentors equipped with an agitator using 7 g l−1 of decanoate as a carbon source. In this experiment, basal salt medium was used to increase the concentration of the nitrogen source. After a 3-day cultivation, considerable PHA content (23% of CDW corresponding to a concentration of 2.2 g l−1) and rhamnolipid amounts (298 mg l−1) were produced.
Another type of extracellular polymeric substance is EPS, a mixture of high molecular polymers, which supplies carbon units when substrate is limited. Wang and Yu [27] studied the simultaneous biosynthesis of EPS (an extracellular product) and PHB (an intracellular product) by R. eutropha. They observed that EPS production was closely coupled with cell growth, while PHB was synthesized only under nitrogen-limiting conditions and cell growth-limiting conditions. In fact, the experiments were conducted at different concentrations of glucose and NH4-N to evaluate their influence on EPS and PHB production. Furthermore, the previous authors observed that the PHB content in dry cells decreased with increasing nitrogen concentration, while the EPS concentration increased. While keeping the nitrogen concentration constant, further experiments were conducted at varying glucose concentrations, and the results showed that an increase in glucose concentration promoted biomass growth and PHB production. The relevant production (shown in Table 7) of both polymers was observed when glucose and nitrogen were supplied at concentrations of 40 and 3 g l−1, respectively.
Table 7.
Overview of studies reporting PHA production coupled to metabolites used in industry
| Strain | Type of PHA | Operation mode | Time to PHAmax [h] | PHA concentration [g l−1] | PHA content [%] | Produced metabolites [g l−1] | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa IFO3924 | PHA | Batch | 72 | 0.5 | 23 | Rhamnolipids 0.3 | [31] |
| Ralstonia eutropha ATCC 17699 | PHB | Batch | 60 | 12.7 | 62 | EPS 0.18 | [27] |
| Azotobacter beijerinckii WDN-01 | PHB | Batch | 40 | 2.73 | 54.6 | EPS 1.2 | [37] |
| Azotobacter chroococcum 6B | PHB | Batch | 48 | 0.74 | 28 | EPS 2.1 | [36] |
| Pseudomonas mendocina NK-01 | PHAMCL | Batch | 48 | 0.316 | 25.3 | Alginate oligosaccharides 0.57 | [32] |
Among EPS, alginates are of great commercial interest for their use in a wide range of applications in the food industry, such as in frozen custards, restructured foods, cream and cake mixtures, and beer production. They are composed of variable amounts of β-d-mannuronic acid and C5-epimer α-l-guluronic acid linked via β-1,4-glycosidic bonds. When extracting alginates from harvested material, the uronic acids are converted into the salt forms mannuronate and guluronate through a neutralization step. The proportion, distribution, and length of these blocks determine the chemical and physical properties of the alginate molecules. Commercial alginates are currently extracted from marine algae, such as Laminaria and Macrocystis, but can also be obtained from bacterial species, such as A. vinelandii, P. aeruginosa, and P. mendocina [31]. The co-production of alginates and PHAs by P. mendocina using glucose as a carbon source was studied by Guo et al. [32]. The simultaneous production of MCL-PHA and alginate oligosaccharide (AO) cultivation was performed in 200 l fermenters with 120 l mineral salt medium containing 20 g l−1 glucose at 30 °C and 200 rpm of impeller speed for 48 h. The authors reported that 0.316 g l−1 PHAMCL and 0.57 g l−1 AO were obtained at the end of the fermentation process. The MCL-PHA production reached a maximum of 0.360 g l−1 at 36 h when the carbon source was almost exhausted. At 48 h, the utilization of intracellular stored MCL-PHA took place, corresponding to a decrease in PHA content to 0.316 g l−1.
Moreover, the production of PHB and EPS by A. beijerinckii was investigated by Pal et al. [37] under nitrogen-free conditions with an excess of carbon. This strain was maintained by growth on nitrogen-free glucose medium at 30 °C for 48 h and was then stored at 4 °C. Nitrogen-free liquid medium was inoculated with 4% (v/v) inoculum, and the flasks were incubated at 30 °C on a rotary shaker. The highest production of PHB (2.73 g l−1) was reached when glucose was supplemented at 3% (w/v), observing an EPS amount of 1.2 g l−1.
Quagliano and Miyazaki [36] studied the simultaneous production of PHB and EPS by A. chroococcum, evaluating the influence of ammonium addition with glucose, fructose, and sucrose. The organism was grown aerobically in 250- and 500-ml flasks at a one-third volume of the culture medium with the carbon sources alone or supplemented with 0.1 g l−1 of (NH4)2SO4. The flasks were incubated in a rotatory shaker at 220 rpm at 30 °C for 72 h.
The highest PHB content was obtained with sucrose (1.1 g l−1), but EPS production was almost unobservable. Instead, the experiments conducted with glucose showed a maximum EPS concentration (2.1 g l−1), with PHB production of 0.74 g l−1.
Thus, some microorganisms, such as P. aeruginosa, R. eutropha, A. beijerinckii, A. chroococcum, and P. mendocina, are able to concurrently produce PHAs and biosurfactants using the same type of organic substrate. However, the bacterial technological performance during the coupled process of PHA and biosurfactant production leads to a lower accumulation of PHAs. In particular, the optimal operating conditions for PHA and biosurfactant production are different. In fact, Wang and Yu [27] observed that without nitrogen-limiting conditions, the PHB content in dry cells decreased, whereas the EPS concentration increased, demonstrating that nutrient-limiting conditions promote only PHA accumulation.
Bioenergy production from industrial and agricultural waste
Anaerobic digestion and biogas production
Anaerobic digestion is a consolidated biological treatment, mainly used for reducing organic content in the sludge produced from municipal wastewater treatment plants, thus achieving its stabilization [95]. In the past few decades, the need to drastically reduce the use of landfills for the disposal of organic waste and producing energy from renewable resources has promoted the use of anaerobic digestion for treating a wide range of organic solids, e.g., organic waste and energy crops [96, 97]. To calculate bioenergy production potential based on anaerobic digestion for biomethane, official data for food waste generation and management were collected by Dung et al. [98] from 21 countries, evaluating a methane potential equal to 379.769 kWh year−1.
Treatment systems based on the anaerobic digestion process are flexible because they can have different configurations according to the number of stages (one or two stages); can operate at different temperatures, mostly at 35 °C (mesophilic) or 55 °C (thermophilic); can be fed in batch, semi-batch, or continuous; can take place in completely stirred or plug flow reactors; and can work with a content of solids lower than 10% in mass (wet system) or higher than 20% (dry system), preceded by several innovative pretreatments to increase waste solubilization [99].
Treating organic waste through anaerobic digestion results in economic and environmental advantages [97–100]; after treatment, the waste material is reduced in quantity, and it is more stable and less harmful for the environment because it is a source of a renewable energy, e.g., biogas, that does not alter the balance of CO2 in the atmosphere and therefore does not contribute to global warming [101]. Additionally, biogas refined to biomethane is also used to feed gas networks [102] as a surrogate to natural gas, and finally, the by-product of anaerobic digestion, named digestate, can be reused in agriculture as fertilizer [103, 104] thanks to its relevant content of nutrients. The performance and results of anaerobic digestion are strictly dependent on the environmental conditions [105–108], such as temperature, pH, nutrients content, presence of inhibitors [107], substrate composition and particle size, micronutrient availability, and the microbial strains used as the inoculum. Anaerobic digestion is driven by a complex microbiome containing both bacteria and Archaea. Each trophic group in the microbiome contains different microorganisms involved in different metabolic tasks [109]. A strong syntrophic relationship exists between different consortia of microorganisms, since biochemical reactions in series are carried out (Fig. 2). Bacteria are crucial in the hydrolyzation and acidogenic step of the anaerobic digestion process.
Fig. 2.
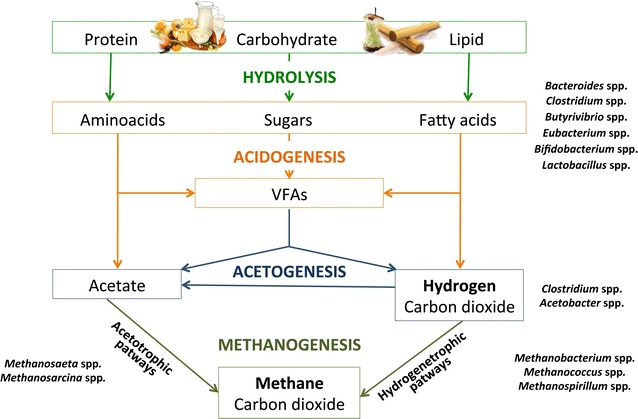
Phases of biological production of methane with the occurrence of VFAs, acetate, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. Anaerobic bacteria involved are positioned according to their probable role in the process
Novaes [110] reported that the anaerobic species belonging to the families Streptococcaceae and Enterobacteriaceae as well as the genera Bacteroides, Clostridium, Butyrivibrio, Eubacterium, Bifidobacterium, and Lactobacillus are most commonly involved in the anaerobic digestion process. Furthermore, during the process, bacteria, such as Clostridia, fermented the hydrolyzed products of proteins to VFAs, CO2, and hydrogen (H2).
In addition, Archaea are important in the methanogenic phase of anaerobic digestion. Methanogenic Archaea are strictly anaerobic and are able to transform fermentation products into CH4 [111]. Some of these bacteria synthesize CH4 using acetic acid, including the Methanosaeta, Methanosarcina, and Methanothrix genera. These are acetoclastic or acetotrophic methanogens. Additionally, other groups of methanogens synthesize CH4 by utilization of H2 and CO2 or methyl compounds, such as Methanobacterium, Methanococcus, Methanospirillum, or Methanomassiliicoccus [111].
These bacteria are potentially able to use all types of biomass suitable for producing biogas: sewage sludge from aerobic wastewater treatment, animal manure, harvest residues, organic waste from agriculture and food processing factories, dairy waste, organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW), fruit and vegetable waste, and energy crops, which are substrates commonly used for feeding anaerobic digesters [112].
The amount of biogas obtainable from a specific substrate depends on the operating conditions and its content of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Lipids require a longer time than carbohydrates and proteins to be converted into biogas but have a more efficient conversion rate in terms of biogas produced per gram of substrate thanks to a high number of C and H atoms in their molecules [113]. Lipids are commonly present in food waste and in several wastewater types from factories, such as those that process meat, produce dairy, or refine fat [114]. Lipids can often be the cause of inconveniences, such as the inhibition of methanogenic microorganisms or their flotation and subsequent washout [115].
Organic waste from agriculture, food waste, and OFMSW is mainly composed of carbohydrates. Such wastes are easily degraded; if their feeding is not accurately controlled, volatile fatty acids (VFAs) produced by the acidification step of the anaerobic digestion tend to accumulate, causing a sharp drop in the pH value, which inhibits the activity of methanogenic Archaea [116] and leads to underperformance of the process.
Wastes rich in proteins are commonly produced by meat and fish processing factories, slaughterhouses, and farms (animal slurry and manure). These wastes are characterized by a low C/N ratio [117–119] that can hamper and even inhibit the activities of microorganisms [120]. Furthermore, proteins undergoing anaerobic digestion are converted into ammonia as an end product, which is rather toxic to microorganisms [121] and should be considered when looking for cost-effective ammonia removal techniques [122].
Wastes rich in cellulose (CWs) are produced by paper and cardboard as well as textile factories. CWs are also found, in large amounts, in unsorted municipal solid wastes (MSWs) and therefore are not useful for recycling. The C/N ratio in CWs is usually high, ranging from 173/1 up to values higher than 1000/1 [123], while the optimum C/N ratio ranges from 20/1 to 30/1 [124].
Microalgae can be an alternative substrate for renewable energy recovery. The co-digestion of microalgae with different types of wastes, such as pig/dairy manure [125], lipid waste (fat, oil, and grease) [126], waste activated sludge [127], and corn straw [128], has been extensively evaluated for biomethane production. Zhen et al. [129] examined the technical potential of methane production from microalgae through co-digesting with food waste. The results showed that supplementing food waste significantly improved microalgae digestion performance compared to the digestion of a single food waste, with the highest methane yield of 639.8 ± 1.3 ml g−1 VSadded.
In fact, an estimation of the amount of methane that can be produced from a specific substrate is commonly obtained through a specific test called the biomethane potential test (BMP). The BMP can be used as an index of the anaerobic biodegradation potential, as it is the experimental value of the ultimate specific biomethane production for the indefinite degradation time [130]. However, in practice, BMP is estimated at a well-defined degradation time that can be a specific day, e.g., the 30th [131, 132] or 50th [133] of incubation or the day when biomethane production is approximately zero [134] or less than 5 mld−1 [131]. BMP can be expressed specifically as a volume of methane per amount of waste (dm3 CH4 kg−1 waste), volume of waste (dm3 CH4 dm−3 waste), per mass volatile solids added (dm3 CH4 kg−1 VS), or COD (chemical oxygen demand) added (dm3 CH4 kg−1 COD). The volume is usually expressed at standard conditions in terms of pressure (1 atm) and temperature (0 °C). Other units for expressing methane potential are also used [135].
For the same substrate, the BMP results can be variable because it is affected by the operating conditions in terms of temperature, mixing intensity, pH adjustment, substrate/inoculum (S/I) ratio, substrate particle size, liquid/volume ratio, nutrient content, inoculum, and if the substrate has been previously pretreated (e.g., mechanically, thermally, chemically) or mixed with one or more other substrates to perform a co-digestion process [136]. In Table 8, the methane yields from different substrates are reported (adapted from Raposo et al. [112]).
Table 8.
Methane yields of solid organic substrates.
Adapted from Raposo et al. [85]
| Solid organic substrate | Methane yield [ml CH4 g−1 VSadded] | References |
|---|---|---|
| Apple fresh wastes | 317 | [179] |
| Banana peeling | 289 | [179] |
| Cabbage leaves 2 mm size | 309 | [180] |
| Carrot peeling | 388 | [179] |
| Cauliflower leaves | 341–352 | [181] |
| Cellulose | 356–375 | [132] |
| Cocksfoot | 325 | [182] |
| Food wastes | 245–510 | [183] |
| Fruit and vegetable wastes | 470 | [184] |
| Glucose | 335 | [185] |
| Kitchen waste | 432 | [115] |
| Leather fleshing | 490 | [186] |
| Lettuce residues | 294 | [179] |
| Maize residues | 317 | [187] |
| Mandarin peels 2 mm size | 486 | [180] |
| OFMSW | 353 | [188] |
| Orange peeling | 297 | [179] |
| Paper and cardboard | 109–128 | [189] |
| Pineapple peel | 400 | [190] |
| Potato waste | 320 referred to gVSremoved | [191] |
| Rape oil seed | 800–900 | [133] |
| Rice straw | 347–367 | [192] |
| Starch | 348 | [133] |
| Sugar beet | 340 | [193] |
| Sunflower | 428–454 | [194] |
| Textiles | 228 | [195] |
| Tomato skins and seeds | 218 | [187] |
| Wheat straw | 267 | [196] |
| Algal biomass | 640 | [129] |
Biohydrogen production
Hydrogen is considered an ideal source of energy because it represents a clean combustible and is also easily convertible to electricity [137]. Biological hydrogen production is related to biogas production for two main reasons: a similar production process, and the same substrates are suitable. These two gaseous products are derived from the same biological process that switches on hydrogen production when hydrogen-using microorganisms are inhibited, such as homoacetogens and methanogens; inhibition is commonly achieved through heat treatment of the inoculum to remove all microorganisms, except for spore-forming fermenting bacteria (i.e., species belonging to the families Clostridiaceae, Streptococcaceae, Sporolactobacillaceae, Lachnospiraceae, and Thermoanaerobacteriacea) [138]. The most common bacteria used in dark fermentation to produce hydrogen are Clostridium [139] and Thermoanaerobacterium [140, 141]. Moreover, several studies have reported successful hydrogen production by mixed cultures in batch or bioreactors [142, 143]. The advantages of using mixed cultures for biohydrogen production are several and are as follows: no need for sterilization, a high adaptive capacity owing to the microbial diversity, the capacity to use a mixture of substrates, and the possibility of obtaining a stable and continuous process [141].
Furthermore, the same organic substrates, such as solid waste, can be used to produce biogas and biohydrogen, thus converting residues into a source of bio-energies [138]. Many processes for hydrogen production have been extensively investigated; among them, hydrogen production by photosynthetic bacteria, algae, and fermentative bacteria is the most interesting because it is environmentally sustainable.
In autotrophic conversions, biohydrogen can be produced by photosynthetic microorganisms, i.e., microalgae and photosynthetic bacteria that convert solar energy to hydrogen [144]. Photosynthetic bacteria (e.g., purple non-sulfur bacteria) utilize the end products of dark fermentation, converting them into H2 via photofermentation with simultaneous VFA reduction [145–150]. The major limitation of photofermentation systems is its poor H2 production rate due primarily to the slow growth of photosynthetic bacteria and the low light conversion efficiency of photobioreactors [149]. A photobioreactor (PBR) was developed by Chen et al. [149] to enhance phototrophic H2 production by Rhodopseudomonas palustris WP3-5 using acetate as the sole carbon source. The photobioreactor was illuminated by combinative light sources, reaching a maximum H2 yield of 62.3%.
Under heterotrophic conditions, two types of fermentation occur: photofermentation carried out by photosynthetic bacteria and dark fermentation [151] carried out by anaerobic bacteria that convert carbohydrates into biohydrogen [144]. Different rumen bacteria, such as Clostridia, methylotrophs, methanogenic archae, or facultative anaerobic bacteria (E. coli, Enterobacter spp., Citrobacter spp.), and aerobic bacteria (Alcaligenes spp., Bacillus spp.) have been studied to perform dark fermentation. In particular, Clostridium butyricum and Clostridium articum produce butyric acid and propionate as major products, respectively, and both products are of interest for hydrogen production [152]. Indeed, photofermentation takes place under anaerobic conditions involving purple non-sulfur photosynthetic bacteria using light as an energy source for synthesizing hydrogen [153]. The ability of purple non-sulfur bacteria to convert organic acids to biohydrogen is coupled with their ability to synthesize PHB under anaerobic conditions.
In fact, Luongo et al. [154] investigated hydrogen and poly-b-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) production during photofermentative treatment of the effluent from a dark fermentation reactor fed with the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. They compared the hydrogen and PHB production of an adapted culture of Rhodobacter sphaeroides AV1b and a mixed consortium of purple non-sulfur bacteria. The mixed cultures resulted in 1.5-fold more H2 produced than the pure culture (559 and 364 N ml H2 l−1, respectively). On the contrary, R. sphaeroides cultures showed higher PHB productivity (155 mg PHB g COD−1) than the mixed cultures (55 mg PHB g COD−1).
As for methane production through anaerobic digestion, biohydrogen can be produced by different bacterial strains using several organic substrates. For example, Cappelletti et al. [155] focused their study on H2 production from molasses and cheese whey with the aim of valorizing food industry wastes by their recycling; mesophilic, thermophilic, and hyperthermophilic bacteria were tested to produce H2. Among them, Thermotoga strains showed the most promising results; in particular, T. neapolitana was the best performing strain (Table 9). This result was confirmed by studies conducted on T. neapolitana using other organic substrates, such as rice straw [156], beet pulp pellet, corn starch, and rice flour [157]. Such substrates are particularly suitable for producing H2 thanks to their easy biodegradability and are also convenient because they are present in different carbohydrate-rich wastewaters and agricultural residues [158]. Other substrates commonly used for biohydrogen production are protein- and fat-rich wastes. A C. butyricum strain was studied by Chen et al. [159] for its ability to produce H2 from a sucrose-based medium. In particular, C. butyricum CGS5 can efficiently produce hydrogen (2.78 mol H2 mol−1 sucrose) on an iron-containing medium [159]. The same microbial strain (C. butyricum CGS5) was isolated from soil with nine cellulolytic bacterial strains belonging to Cellulomonas sp. and Cellulosimicrobium cellulans by Lo et al. [160]. Among these strains, only C. butyricum CGS5 exhibited efficient H2 production from rice husk hydrolysates, with a H2 yield of 17.24 mmol H2 g cellulose−1.
Table 9.
Hydrogen yields of different substrates.
| Substrate | Strain | Hydrogen yield | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sucrose | Clostridium butyricum CGS5 | 2.78 [mol H2 mol−1 substrate] | [159] |
| Glucose | Escherichia coli strains | 2 [mol H2 mol−1 substrate] | [162] |
| Glucose | Thermotoga neapolitana | 1.6 [mol H2 mol−1 substrate] | [155] |
| Molasses | Thermotoga neapolitana | 2.6 [mol H2 mol−1 substrate] | [155] |
| Rice straw | Thermotoga neapolitana | 2.7 [mol H2 mol−1 substrate] | [156] |
| Cheese whey | Thermotoga neapolitana | 2.4 [mol H2 mol−1 substrate] | [155] |
| Cheese whey | Clostridium saccharoperbutylacetonicum ATCC 27021 | 2.7 [mol H2 mol−1 substrate] | [161] |
| Starch | Mesophilic bacterium HN001 | 2 [mol H2 mol−1 substrate] | [163] |
| Starch | Mixed culture from compost | 133 [ml H2 g−1 hexose] | [166] |
| Cellulose | Mixed culture from sludge | 92 [ml H2 g−1 hexose] | [164] |
| Mixed waste | Mixed culture from anaerobic digestion sludge | 201 [ml H2 g−1 hexose] | [168] |
| Food waste | Mixed culture from anaerobic digestion sludge | 210 [ml H2 g−1 hexose] | [167] |
| Acetate | Rhodopseudomonas palustris WP3-5 in Photobioreactor | 62.3 [mol H2 mol−1 substrate] | [120] |
| Rice husk | Clostridium butyricum CGS5 | 17.24 [mmol H2 g−1 cellulose] | [160] |
Ferchichi et al. [161] investigated hydrogen production from cheese whey by Clostridium saccharoperbutylacetonicum, studying the influence of the initial pH; they found that slightly acidic initial conditions favored a higher H2 yield than alkaline conditions. The highest hydrogen yield (2.7 mol H2 mol−1 substrate) was actually obtained at pH 6. Bisaillon et al. [162] examined hydrogen production by different strains of Escherichia coli under different feeding regimes to detect the main limiting factors: strains that showed the highest hydrogen yield (2 mol H2 mol−1 substrate) when cultured at limiting concentrations of either ammonia or glucose (1 mM NH4Cl; 0.04% of glucose). Mesophilic bacterium HN001 was tested by Yasuda and Tanisho [163] as a H2 producer from starch. In the same work, the authors focused their studies on the influence of temperature, pH, and substrate concentration; the optimal temperature was found to be approximately 37 °C, with a hydrogen yield of 2 mol H2 mol−1 substrate. Liu et al. [164] investigated H2 production by mixed cultures in batch experiments using cellulose as a substrate; at the optimal pH of 6.5, the maximum hydrogen yield was 92 ml H2 g−1 hexose, and an analysis of 16S rDNA sequences showed that the cellulose-degrading mixed culture was composed of microbes closely affiliated with genus Thermoanaerobacterium. Carbohydrate-rich holocellulose of lignocellulosic organic matter can be made available to the H2 conversion by pretreatment. Examples of lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment methods for hydrogen fermentation were reported by Kumar et al. [165]. They also reported the maximum hydrogen yield associated with pretreatment methods, ranging from 44.9 to 141.29 ml H2 g−1.
The influence of pH was also evaluated by Khanal et al. [166], who used a mixed microbial culture and starch as a substrate. At the optimal pH of 4.5, the maximum hydrogen yield was 133 ml H2 g−1 hexose. At the same pH value, Fang et al. [167] reached a maximum hydrogen yield of 210 ml H2 g−1 hexose using food waste as a substrate. Instead, Valdez-Vazquez et al. [168] studied the influence of temperature using a mixed culture as the inoculum and mixed waste as a substrate. At 37 °C, the maximum hydrogen yield was 210 ml H2 g−1 hexose.
All biotechnological hydrogen production processes have particular limits, since a considerable part of the used substrate is converted into various soluble metabolic products rather than H2. Thus, the major side product of dark fermentation is a multi-compound mixture of VFAs and other constituents, such as alcohols [169]. Therefore, the volatile fatty acid-rich fermentation effluent is a perfect substrate for biologically synthesizing polyesters, e.g., polyhydroxyalkanoate [170, 171], which could have an industrial market [172].
Integrated systems for bioenergy production from industrial and agricultural wastes
Simultaneous production of PHAs and bioenergy from organic wastes
Degradation of biowaste to methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide is a multiple step process with the possibility of producing H2 and bioplastics (from volatile fatty acids) as intermediates [17]. Based on this process, anaerobic digestion can be performed with a two-stage system, where biomass is degraded in the first stage and hydrolysis–acidification occurs. The organic acids produced are processed under aerobic conditions to produce biopolymers and, as an alternative, under anaerobic conditions to produce biogas.
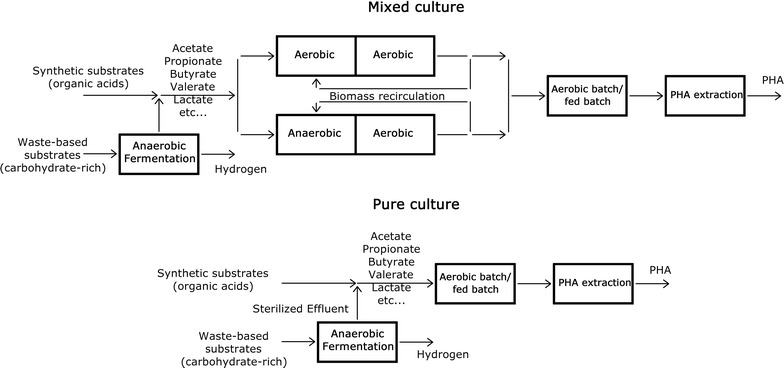
A PHA production system, in its most comprehensive configuration, is composed of four main stages (Fig. 3), as follows:
Feedstock production,
Biomass selection,
PHA production, and
PHA extraction.
Fig. 3.
Cycle of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) production system
(Adapted from Serafim et al. [173])
Simplified configurations can be obtained using synthetic substrates (stage 1 is removed from the cycle), using pure culture (stage 2 is removed from the cycle), or using both synthetic substrates and pure culture (stages 1 and 2 are removed from the cycle).
The aims of each stage are listed below:
To produce organic acids from complex organic solids (e.g., wastes rich in carbohydrates),
To select the microbial strains from the mixed culture that show the highest capacity for PHA accumulation under specific dynamic feeding conditions [173],
To produce PHAs using the selected culture, and
To recover PHAs from microorganisms.
A dark fermentation process can be successfully used to perform the first stage. This process evolves according to the same sequence of biochemical reactions in the anaerobic digestion process, with the exception of the last stage that is repressed using different strategies (e.g., setting a short hydraulic retention time-HRT, keeping the pH low at 5.5, adding chemical compounds toxic to methanogens, and performing thermal shocks).
The dark fermentation process can be optimized to produce VFAs and consequently H2 that is a by-product of the biological process and VFAs, varying (i) the operational conditions (i.e., pH, temperature, HRT, solid retention time—SRT, organic loading rate—OLR); (ii) the configuration of the dark fermentation reactor and feeding system; and (ii) the type of organic waste used to feed the reactor (Fig. 4). The effects of these parameters on VFA production are listed in Table 10 [174].
Fig. 4.
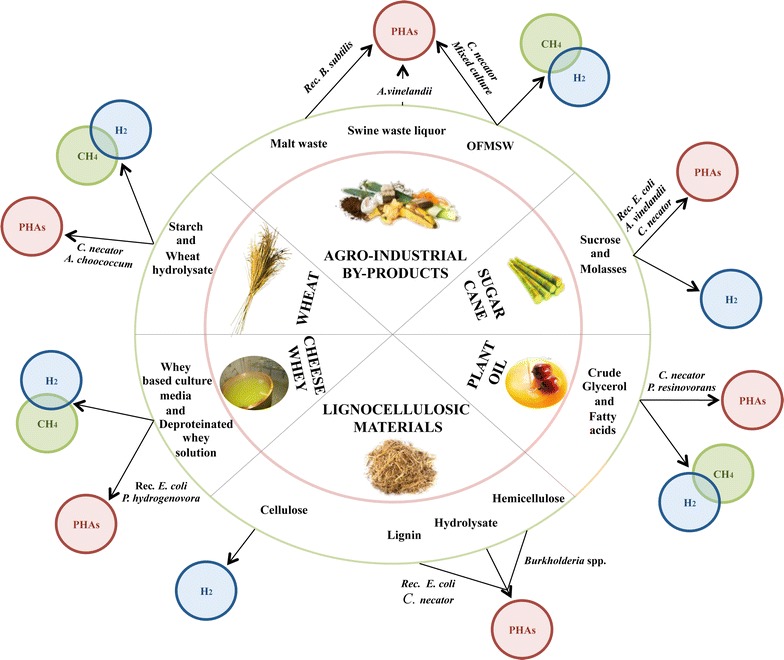
Sustainable PHAs and bioenergy production from organic wastes and by-products converted by different bacterial species: an overview of the principal process considered in this review
Table 10.
Waste, reactor configuration, and operation for the production of VFAs
Adapted from Lee et al. [174]
| Type of waste | Organic content (mg COD l−1) | Reactor type and operating conditions | VFA production | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waste activated sludge | 18.657 | Batch, 55 °C, pH = 8, HRT = 9 days | 368 mg COD gVSS−1 | [197] |
| 14.878 | Batch, 21 °C, HRT = 6 days | 339 mg COD l−1 | [198] | |
| Primary sludge | 22.838 | Batch, 21 °C, HRT = 6 days | 85 mg COD gVSS−1 | [199] |
| 20.631 | Batch, 21 °C, pH = 10, room temp, HRT = 5 days | 60 mg COD gVSS−1 day−1 | [200] | |
| Food waste | 91.900 | Batch, 37 °C, pH = 5.5 | 8950 mg COD l−1 | [201] |
| 146.1 | Batch, 35 °C, HRT = 5 days | 5610 mg COD l−1 | [202] | |
| Kitchen waste | 166.18 | Batch, 35 °C, pH = 7, HRT = 4 days | 36 mg l−1 | [203] |
| OFMSW | 347.0 | Batch, 14–22 °C, pH = 4–5, HRT = 4–4.5 days | 40 mg g−1 VS | [204] |
| 196.7 | Plug flow, 37 °C, pH = 5.7–6.1, HRT = SRT = 6 days, OLR = 38.5 gVS l−1 day−1 | 23.110 mg l−1 | [15] | |
| Palm oil mill | 88.0 | Semi-continuous, 30 °C, pH = 6.5, HRT = 4 days | 15.300 mg l−1 | [205] |
| Olive oil mill | 37.0 | Packed bed biofilm, 25 °C, pH = 5.2–5.5, HRT = 14 days, OLR = 26 g COD l−1 day−1 | 10.700 mg COD l−1 | [206] |
| Cheese whey | 4590 | CSTR, 37 °C, pH = 6, HRT = 2.1 days | 0.84 gVFA-COD g−1 sCOD−1 | [207] |
Various microbes, such as A. eutrophus, B.s megaterium, P. oleovorans, A. beijerincki, Rhizobium, and Nocardia, utilize acetic acid, formic acid, and propionic acid as a substrate for PHA production [70]. A. eutrophus and A. beijerinckii were studied by Kalia et al. [70] and were shown to be capable of accumulating PHAs up to 70% of CDW, under nitrogen and phosphorus-limiting conditions, whereas Pseudomonas spp. and Rhizobium spp. accumulated PHAs at approximately 60% of CDW.
Many other bacterial strains have also been reported to produce PHAs under adverse conditions with different PHA yields. Among them, many purple non-sulfur bacteria, such as R. sphaeroides, Rhodospirillum rubrum, Rhodopseudomonas palustris, Rhodopseudomonas palustris, and Bacillus spp., have been reported to produce H2 and PHA under nutrient-limiting conditions [175].
Patel et al. [17] investigated the metabolic activities of Bacillus strains to transform glucose into H2 and PHB in two stages. Operating in batch mode, Bacillus thuringiensis EGU45 and B. cereus EGU44 reached 1.67–1.92 mol H2 mol−1 glucose, respectively, during the first 3 days. In the next 2 days, Bacillus thuringiensis EGU45 was supplemented with residual medium containing glucose, volatile fatty acids, and residual nutrients (nutrient stress condition) and produced a PHB yield of 11.3% of CDW.
Rhodopseudomonas palustris WP3-5 was studied by Wu et al. [176] to evaluate possible competition between PHB synthesis and H2 production, testing cultures on six different substrates, such as acetate, propionate, malate, lactate, glucose, and lactose. The results highlighted that strain WP3-5 could utilize acetate, propionate, malate, and lactate to produce H2, whereas it was also able to synthesize PHB only on acetate and propionate. PHB synthesis decreased H2; however, under pH-stress conditions, such a decrease was not observed.
Rhodopseudomonas palustris was also studied by Vincenzini et al. [177] to investigate the potential of purple non-sulfur bacteria in the photoproduction of both hydrogen and PHB-containing biomass under limiting amounts of nitrogen. The data demonstrated that under nitrogen-limiting growth conditions, R. palustris synthesized 40 mg l−1 day−1 of PHB and produced 200 ml l−1 day of H2 when the experiments were supplemented with 60 mg l−1 day−1 of nitrogen.
Yu [26] performed a two-step integrated system consisting of microbial acidogenesis and acid polymerization from starchy wastewater. In his work, the starchy organic waste was first digested in a thermophilic upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor to form acetic (60–80%), propionic (10–30%), and butyric (5–40%) acids. The acids in the effluent solution after microfiltration were polymerized into PHAs by A. eutrophus in a second reactor. PHA production from the acid effluent was compared with the production from pure acids in 48 h, and the results were very similar. In batch mode, 1.2 g l−1 of PHAs was accumulated from acid effluent. Instead, 1.0 and 1.3 g l−1 of PHAs were obtained from a mixture of butyric acid and propionic acid in batch and fed-batch mode, respectively.
Albuquerquea et al. [178] designed another integrated system to valorize the use of wastewater for PHA production. They employed a 2-stage continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR) system to effectively select PHA-storing organisms using fermented molasses as feedstock. The acidogenic fermentation (step 1) was carried out in a CSTR operated under anaerobic conditions. The reactor effluent was clarified by microfiltration and used as a feedstock for culture selection (step 2) and PHA batch accumulation (step 3). The culture reached a maximum PHA content of 61%.
The best integrated system developed was based on two-step processes consisting of acidogenic fermentation (operating under anaerobic condition) aimed to produce acid effluent that, after microfiltration, is used in the subsequent aerobic microbial process aimed at PHA polymerization. However, the first step (acidogenic fermentation) is also useful for hydrogen production and could be designed as a dark fermentation process.
Conclusions
Biological processes can be successfully used in innovative and eco-sustainable technology to convert organic waste into bioenergy and biochemicals, separately or simultaneously. Bioprocesses can provide bioenergy or valuable chemicals and, at the same time, perform pollution control, according to technical feasibility, simplicity, economics, and societal needs. Bio-based plastics can completely replace the conventional ones derived from fossil fuels if the production costs can be reduced, and the use of high-performing bacteria fed with organic wastes and by-products as substrates significantly contribute to achieving this objective.
In this context, different organic substrates and by-products can be used to produce bioenergy (hydrogen and methane) and biopolymers (PHAs). Otherwise, the review highlights the possibility of integrating the two production processes to design a unique system for both energy and biopolymer production. The integrated system is a flexible process that aims (i) to produce organic acids from complex organic solid wastes rich in carbohydrates; (ii) to use selected microbial strains or mixed cultures that show the highest capacity for PHA accumulation under specific dynamic feeding conditions; and (iii) to produce bioenergy or accumulate PHAs by microorganisms from acidogenic effluents.
This integrated system represents new perspectives on the use of organic waste and by-products, valorizing organic substrates for the production of both bioenergy and PHAs.
Authors’ contributions
GP developed the whole manuscript preparing and integrating the different parts. VV contributed to write the microbiological aspects of the work and revised the manuscript. AP contributed to write the process system aspects of the work, prepared Table 8, and revised the manuscript. OP conceived the study, participated in its design, and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding
This study was supported by grant from the Ministero dell’Università e della Ricerca Scientifica Industrial Research Project ‘‘Development of green technologies for production of BIOchemicals and their use in preparation and industrial application of POLImeric materials from agricultural biomasses cultivated in a sustainable way in Campania region-BioPoliS” PON03PE_00107_1/1, funded in the frame of Operative National Programme Research and Competitiveness 2007–2013 D. D. Prot. n. 713/Ric. on 29.10.2010.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- OFMSW
organic fraction of municipal solid waste
- PHAs
polyhydroxyalkanoates
- EPS
exopolysaccharides
- GHG
green house gas
- SCL
short-chain length
- MCL
medium-chain length
- P(3HB)
poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)
- PHB
polyhydroxybutyrate
- 3HV
3-hydroxyvalerate
- 4HB
4-hydroxybutyrate
- P(3HB-3HV)
poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)
- LCA
life cycle assessment
- CDW
cell dry weight
- C/N
carbon-to-nitrogen ratio
- PHBV
poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate)
- UASB
upflow anaerobic sludge blanket
- AO
alginate oligosaccharides
- VFAs
volatile fatty acids
- CWs
cellulose wastes
- BMP
biomethane potential test
- COD
chemical oxygen demand
- S/I
substrate/inoculums ratio
- HRT
hydraulic retention time
- SRT
solid retention time
- OLR
organic loading rate
Contributor Information
Giorgia Pagliano, Email: giorgia.pagliano@unina.it.
Valeria Ventorino, Email: valeria.ventorino@unina.it.
Antonio Panico, Email: antonio.panico@unipegaso.it.
Olimpia Pepe, Email: olipepe@unina.it.
References
- 1.Bauen A, Berndes G, Junginger M, Londo M, Vuille F, Ball R, Bole T, Chudziak C, Faaij A, Mozaffarian H. Bioenergy—a sustainable and reliable energy source. Rev Status Prospects. 2009. http://www.ieabioenergy.com/LibItem.aspx?id=6479.
- 2.Mezule WL, Dalecka B, Juhna T. Fermentable sugar production from lignocellulosic. Chem Eng Trans. 2015;43:619–624. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Liguori R, Ventorino V, Pepe O, Faraco V. Bioreactors for lignocellulose conversion into fermentable sugars for production of high added value products. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;100:597–611. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-7125-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ventorino V, Robertiello A, Viscardi S, Ambrosanio A, Faraco V, Pepe O. Bio-based chemical production from Arundo donax feedstock fermentation using Cosenzaea myxofaciens BPM1. BioResources. 2016;11:6566–6581. doi: 10.15376/biores.11.3.6566-6581. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ventorino V, Robertiello A, Cimini D, Argenzio O, Schiraldi C, Montella S, Faraco V, Ambrosanio A, Viscardi S, Pepe O. Bio-Based succinate production from Arundo donax hydrolysate with the new natural succinic acid-producing strain Basfia succiniciproducens BPP7. Bioenergy Res. 2017 [Google Scholar]
- 6.Saratale GD, Jung MY, Oh MK. Reutilization of green liquor chemicals for pretreatment of whole rice waste biomass and its application to 2,3-butanediol production. Bioresour Technol. 2016;205:90–96. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pepe O, Ventorino V, Cavella S, Fagnano M, Brugno R. Prebiotic content of bread prepared with flour from immature wheat grain and selected dextran-producing lactic acid bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013;79:3779–3785. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00502-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lee SY. Bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1996;49:1–14. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19960105)49:1<1::AID-BIT1>3.3.CO;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Steinbüchel A, Füchtenbusch B. Bacterial and other biological systems for polyester production. Trends Biotechnol. 1998;16:419–427. doi: 10.1016/S0167-7799(98)01194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cavalheiro JMBT, De Almeida MCMD, Grandfils C, Da Fonseca MMR. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production by Cupriavidus necator using waste glycerol. Process Biochem. 2009;44:509–515. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2009.01.008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Salehizadeh H, Van Loosdrecht MCM. Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates by mixed culture: recent trends and biotechnological importance. Biotechnol Adv. 2004;22:261–279. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2003.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ahn WS, Park SJ, Lee SY. Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) from whey by cell recycle fed-batch culture of recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett. 2001;23:235–240. doi: 10.1023/A:1005633418161. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Castilho LR, Mitchell DA, Freire DMG. Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) from waste materials and by-products by submerged and solid-state fermentation. Bioresour Technol. 2009;100:5996–6009. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.03.088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Panico A, d’ Antonio G, Esposito G, Frunzo L, Iodice P, Pirozzi F. The effect of substrate-bulk interaction on hydrolysis modeling in anaerobic digestion process. Sustainability. 2014;6:8348–8363. doi: 10.3390/su6128348. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sans C, Mata-Alvarez J, Cecchi F, Pavan P, Bassetti A. Volatile fatty acids production by mesophilic fermentation of mechanically-sorted urban organic wastes in a plug-flow reactor. Bioresour Technol. 1995;51:89–96. doi: 10.1016/0960-8524(95)95866-Z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chynoweth DP, Owens JM, Legrand R. Renewable methane from anaerobic digestion of biomass. Renew Energy. 2001;22:1–8. doi: 10.1016/S0960-1481(00)00019-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Patel SKS, Singh M, Kalia VC. Hydrogen and polyhydroxybutyrate producing abilities of Bacillus spp. from glucose in two stage system. Indian J Microbiol. 2011;51:418–423. doi: 10.1007/s12088-011-0236-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Carvalho Morais C. Production of bacterial biopolymers from industrial fat-containing wastes. 2013. https://run.unl.pt/bitstream/10362/10922/1/Morais_2013.pdf. Accessed Sept 2013.
- 19.Koutinas AA, Xu Y, Wan R, Webb C. Polyhydroxybutyrate production from a novel feedstock derived from a wheat-based biorefinery. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2007;40:1035–1044. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2006.08.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Xu Y, Wanga RH, Koutinas AA, Webba C. Microbial biodegradable plastic production from a wheat-based biorefining strategy. Process Biochem. 2010;45:153–163. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2009.09.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Haas R, Jin B, Zepf FT. Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) from waste potato starch. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2008;72:253–256. doi: 10.1271/bbb.70503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yu J, Stahl H. Microbial utilization and biopolyester synthesis of bagasse hydrolysates. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99:8042–8048. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.03.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fukui T, Doi Y. Efficient production of polyhydroxyalkanoates from plant oils by Alcaligenes eutrophus and its recombinant strain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1998;49:333–336. doi: 10.1007/s002530051178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kahar P, Tsuge T, Taguchi K, Doi Y. High yield production of polyhydroxyalkanoates from soybean oil by Ralstonia eutropha and its recombinant strain. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2004;83:79–86. doi: 10.1016/S0141-3910(03)00227-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Füchtenbusch B, Wullbrandt D, Steinbüchel A. Production of polyhydroxyalkanoic acids by Ralstonia eutropha and Pseudomonas oleovorans from an oil remaining from biotechnological rhamnose production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2000;53:167–172. doi: 10.1007/s002530050004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yu J. Production of PHA from starchy wastewater via organic acids. J Biotechnol. 2001;86:105–112. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1656(00)00405-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang J, Yu H. Biosynthesis of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) and extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) by Ralstonia eutropha ATCC 17699 in batch cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007;75:871–878. doi: 10.1007/s00253-007-0870-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jiang Y, Song X, Gong L, Li P, Dai C, Shao W. High poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) production by Pseudomonas fluorescens A2a5 from inexpensive substrates. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2007;42:167–172. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2007.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Koller M, Bona R, Chiellini E, Fernandes EG, Horvat P, Kutschera C, Braunegg G. Polyhydroxyalkanoate production from whey by Pseudomonas hydrogenovora. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99:4854–4863. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2007.09.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cromwick AM, Foglia T, Lenz RW. The microbial production of poly(hydroxyalkanoates) from tallow. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1996;46:464–469. doi: 10.1007/s002530050845. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hori K, Marsudi S, Unno H. Simultaneous production of polyhydroxyalkanoates and rhamnolipids by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2002;78:699–707. doi: 10.1002/bit.10248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Guo W, Song C, Kong M, Geng W, Wang Y, Wang S. Simultaneous production and characterization of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates and alginate oligosaccharides by Pseudomonas mendocina NK-01. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011;92:791–801. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Page WJ, Manchak J, Rudy B. Formation of poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) by Azotobacter vinelandii UWD. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992;58:2866–2873. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.9.2866-2873.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chou K, Ryu HV, Park C, Goodrich P. Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxy-valerate) from swine waste liquor by Azotobacter vinelandii UWD. Biotechnol Lett. 1997;19:7–10. doi: 10.1023/A:1018342332141. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kim BS. Production of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate from inexpensive substrates. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2000;27:772–777. doi: 10.1016/s0141-0229(00)00299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Quagliano JC, Miyazaki SS. Biosynthesis of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate and exopolysaccharides on Azotobacter chroococcum strain 6B utilizing simple and complex carbon sources. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 1999;82:199–208. doi: 10.1385/ABAB:82:3:199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Pal S, Manna A, Paul AK. Production of poly(β-hydroxybutyric acid) and exopolysaccharide by Azotobacter beijerinckii WDN-01. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 1999;15:11–16. doi: 10.1023/A:1008825009825. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Halami PM. Production of polyhydroxyalkanoate from starch by the native isolate Bacillus cereus CFR06. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008;24:805–812. doi: 10.1007/s11274-007-9543-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yilmaz M, Beyatli Y. Poly-b-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) production by a Bacillus cereus M5 strain in sugarbeet molasses. Zuckerindustrie. 2005;130:109–112. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Law KH, Chenga YC, Leungb YC, Lob WH, Chuac H, Yua HF. Construction of recombinant Bacillus subtilis strains for polyhydroxyalkanoates synthesis. Biochem Eng J. 2003;16:203–208. doi: 10.1016/S1369-703X(03)00039-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Liu F, Li W, Ridgway D, Gu T. Production of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate on molasses by recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett. 1998;20:345–348. doi: 10.1023/A:1005367011378. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lee SY, Middelberg APJ, Lee YK. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production from whey using recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett. 1997;19:1033–1035. doi: 10.1023/A:1018411820580. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Nikel PI, de Almeida A, Melillo EC, Galvagno MA, Pettinari MJ. New recombinant Escherichia coli strain tailored for the production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) from agroindustrial by-products. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72:3949–3954. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00044-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Park SJ, Park JP, Lee SY. Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) from whey by fed-batch culture of recombinant Escherichia coli in a pilot-scale fermenter. Biotechnol Lett. 2002;24:185–189. doi: 10.1023/A:1014196906095. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nonato R, Mantelatto P, Rossell C. Integrated production of biodegradable plastic, sugar and ethanol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001;57:1–5. doi: 10.1007/s002530100732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Silva LF, Taciro MK, Ramos MEM, Carter JM, Pradella JGC, Gomez JGC. Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (P3HB) production by bacteria from xylose, glucose and sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004;31:245–254. doi: 10.1007/s10295-004-0136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Reddy CSK, Ghai R, Kalia VC. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: an overview. Bioresour Technol. 2003;87:137–146. doi: 10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00212-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Suriyamongkol P, Weselake R, Narine S, Moloney M, Shah S. Biotechnological approaches for the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates in microorganisms and plants—a review. Biotechnol Adv. 2007;25:148–175. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Anderson AJ, Dawes EA. Occurrence, metabolism, metabolic role, and industrial uses of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microbiol Rev. 1990;54:450–472. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.450-472.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Taidi B, Anderson JA, Dawes EA, Byrom D. Effect of carbon source and concentration on the molecular mass of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) produced by Methylobacterium extorquens and Alcaligenes eutrophus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1994;40:786–790. doi: 10.1007/BF00173975. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Jendrossek D, Knoke I, Habibian RB, Steinbüchel A, Schlegel HG. Degradation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), PHB, by bacteria and purification of a novel PHB depolymerase from Comamonas sp. J Polym Environ. 1993;1:53–63. doi: 10.1007/BF01457653. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Delafield FP, Doudoroff M, Palleroni NJ, Lusty CJ, Contopoulos R. Decomposition of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate by Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1965;90:1455–1466. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1455-1466.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Tanio T, Fukui T, Shirakura Y, Saito T, Tomita K, Kaiho T, Masamune S. An extracellular poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) depolymerase from Alcaligenes faecalis. Eur J Biochem. 1982;124:71–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Mergaert J, Anderson C, Wouters A, Swings J. Microbial degradation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) in compost. J Polym Environ. 1994;1994(2):177–183. doi: 10.1007/BF02067443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Mukai K, Yamada K, Doi Y. Efficient hydrolysis of polyhydroxyalkanoates by Pseudomonas stutzeri YM1414 isolated from lake water. Polym Degrad Stab. 1994;43:319–327. doi: 10.1016/0141-3910(94)90002-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Patel M, Bastioli C, Marini L, Würdinger E. Life-cycle assessment of bio-based polymers and natural fiber composites. Biopolymers. 2003;10:409–452. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Akiyama M, Tsuge T, Doi Y. Environmental life cycle comparison of polyhydroxyalkanoates produced from renewable carbon resources by bacterial fermentation. Polym Degrad Stab. 2003;80:183–194. doi: 10.1016/S0141-3910(02)00400-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Harding KG, Dennis JS, Von Blottnitz H, Harrison STL. Environmental analysis of plastic production processes: comparing petroleum-based polypropylene and polyethylene with biologically-based poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid using life cycle analysis. J Biotechnol. 2007;130:57–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2007.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Pietrini M, Roes L, Patel MK, Chiellini E. Comparative life cycle studies on poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)-based composites as potential replacement for conventional petrochemical plastics. Biomacromol. 2007;8:2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bm0700892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Atlić A, Koller M, Scherzer D, Kutschera C, Grillo-Fernandes E, Horvat P, Chiellini E, Braunegg G. Continuous production of poly([R]-3-hydroxybutyrate) by Cupriavidus necator in a multistage bioreactor cascade. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011;91:295–304. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3260-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Gholami A, Mohkam M, Rasoul-Amini S, Ghasemi Y. Industrial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates by bacteria: opportunities and challenges. Minerva Biotechnol. 2016;28:59–74. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Chanprateep S. Current trends in biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates. J Biosci Bioeng. 2010;874(110):621–632. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2010.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Valentino F, Morgan-Sagastume F, Campanari S, Villano M, Werker A, Majone M. Carbon recovery from wastewater through bioconversion into biodegradable polymers. N Biotechnol. 2017;37:9–23. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2016.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.DeMarco S. Advances in polyhydroxyalkanoate production in bacteria for biodegradable plastics. Basic Biotechnol eJ. 2005;1:1–4. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Tian PY, Shang L, Ren H, Mi Y, Fan DD, Jiang M. Biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates: current research and development. Afr J Biotechnol. 2009;8:709–714. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Tsuge T. Metabolic improvements and use of inexpensive carbon sources in microbial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates. J Biosci Bioeng. 2002;94:579–584. doi: 10.1016/S1389-1723(02)80198-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Füchtenbusch B, Steinbüchel A. Biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates from low-rank coal liquefaction products by Pseudomonas oleovorans and Rhodococcus ruber. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1999;52:91–95. doi: 10.1007/s002530051492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Vandamme P, Coenye T. Taxonomy of the genus Cupriavidus: a tale of lost and found. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2004;54:2285–2289. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.63247-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Lee SY. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production from xylose by recombinant Escherichia coli. Bioprocess Eng. 1998;18:397–399. doi: 10.1007/s004490050462. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Kalia VC, Raizada N, Sonakya V. Bioplastics. J Sci Ind Res. 2000;59:433–445. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Poomipuk N, Reungsang A, Plangklang P. Poly-β-hydroxyalkanoates production from cassava starch hydrolysate by Cupriavidus sp. KKU38. Int J Biol Macromol. 2014;65:51–64. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Bhatia SK, Shim YH, Jeon JM, Brigham CJ, Kim YH, Kim HJ, Lee YK. Starch based polyhydroxybutyrate production in engineered Escherichia coli. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2015;38:1479–1484. doi: 10.1007/s00449-015-1390-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kulpreecha S, Boonruangthavorn A, Meksiriporn B, Thongchul N. Inexpensive fed-batch cultivation for high poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production by a new isolate of Bacillus megaterium. J Biosci Bioeng. 2009;107:240–245. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2008.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Di Pasqua R, Ventorino V, Aliberti A, Robertiello A, Faraco V, Viscardi S, Pepe O. Influence of different lignocellulose sources on endo-1, 4-β-glucanase gene expression and enzymatic activity of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B31C. BioResources. 2014;9:1303–1310. doi: 10.15376/biores.9.1.1303-1310. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Ventorino V, Parillo R, Testa A, Viscardi S, Espresso F, Pepe O. Chestnut green waste composting for sustainable forest management: microbiota dynamics and impact on plant disease control. J Environ Manag. 2016;166:168–177. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.10.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Ventorino V, Aliberti A, Faraco V, Robertiello A, Giacobbe S, Ercolini D, et al. Exploring the microbiota dynamics related to vegetable biomasses degradation and study of lignocellulose-degrading bacteria for industrial biotechnological application. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8161. doi: 10.1038/srep08161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Ventorino V, Ionata E, Birolo L, Montella S, Marcolongo L, de Chiaro A, Espresso F, Faraco V, Pepe O. Lignocellulose-adapted endo-cellulase producing Streptomyces strains for bioconversion of cellulose-based materials. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:2061. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.02061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Kumar S, Abe H. Practical guide to microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates. 1st ed. Shawbury: iSmithers - A Smithers Group Company; 2010.
- 79.Saratale GD, Oh MK. Characterization of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) produced from Ralstonia eutropha using an alkali-pretreated biomass feedstock. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;80:627–635. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.07.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Tomizawa S, Chuah JA, Matsumoto K, Doi Y, Numata K. Understanding the limitations in the biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) from lignin derivatives. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2014;2:1106–1113. doi: 10.1021/sc500066f. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Zhong J, Stevens DK, Hansen CL. Optimization of anaerobic hydrogen and methane production from dairy processing waste using a two-stage digestion in induced bed reactors (IBR) Int J Hydrog Energy. 2015;40:5470–15476. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.09.085. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Gomez JGC, Méndez BS, Nikel PI, Pettinari MJ, Prieto MA, Silva LF. Making green polymers even greener: towards sustainable production of polyhydroxyalkanoates from agroindustrial by-products. Adv Appl Biotechnol. 2012;2:42–62. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Pries A, Steinbüchel A, Schlegel HG. Lactose-and galactose-utilizing strains of poly(hydroxyalkanoic acid)-accumulating Alcaligenes eutrophus and Pseudomonas saccharophila obtained by recombinant DNA technology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1990;33:410–417. doi: 10.1007/BF00176656. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ganzeveld KJ, Van Hagen A, Van Agteren MH, de Koning W, Schoot Uiterkamp AJM. Upgrading of organic waste: production of the copolymer poly-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-valerate by Ralstonia eutropha with organic waste as sole carbon source. J Clean Prod. 1999;7:413–419. doi: 10.1016/S0959-6526(99)00159-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Du G, Chen LXL, Yu J. High-efficiency production of bioplastics from biodegradable organic solids. J Polym Environ. 2004;12:89–94. doi: 10.1023/B:JOOE.0000010054.58019.21. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Kumar SR, Mudliar SN, Reddy KMK, Chakrabarti T. Production of biodegradable plastics from activated sludge generated from a food processing industrial wastewater treatment plant. Bioresour Technol. 2004;95:327–330. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2004.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Khardenavis AA, Kumar MS, Mudliar SN, Chakrabarti T. Biotechnological conversion of agro-industrial wastewaters into biodegradable plastic, poly β-hydroxybutyrate. Bioresour Technol. 2007;98:3579–3584. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2006.11.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Cameotra SS, Makkar RS. Synthesis of biosurfactants in extreme conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1998;50:520–529. doi: 10.1007/s002530051329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ding Z, Bourven I, Guibaud G, van Hullebusch ED, Panico A, Pirozzi F, Esposito G. Role of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) production in bioaggregation: application to wastewater treatment. App Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;99:9883–9905. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6964-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Palomba S, Cavella S, Torrieri E, Piccolo A, Mazzei P, Blaiotta G, Ventorino V, Pepe O. Polyphasic screening, homopolysaccharide composition, and viscoelastic behavior of wheat sourdough from a Leuconostoc lactis and Lactobacillus curvatus exopolysaccharide-producing starter culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012;78:2–12. doi: 10.1128/AEM.07302-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Torrieri E, Pepe O, Ventorino V, Masi P, Cavella S. Effect of sourdough at different concentrations on quality and shelf life of bread. LWT Food Sci Technol. 2014;56:508–516. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2013.12.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Liang TW, Wu CC, Cheng WT, Chen YC, Wang CL, Wang IL, Wang SL. Exopolysaccharides and antimicrobial biosurfactants produced by Paenibacillus macerans TKU029. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014;172:933–950. doi: 10.1007/s12010-013-0568-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Lin SC. Biosurfactants: recent advances. J Chem Tech Biotechnol. 1996;66:109–120. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4660(199606)66:2<109::AID-JCTB477>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Desai DJ, Banat IM. Microbial production of surfactants and their commercial potential. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1997;61:47–64. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.61.1.47-64.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Appels L, Baeyens J, Degrève J, Dewil R. Principles and potential of the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 2008;34:755–781. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2008.06.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Lema JM, Omil F. Anaerobic treatment: a key technology for a sustainable management of wastes in Europe. Water Sci Technol. 2001;44:33–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Lettinga G. Digestion and degradation, air for life. Water Sci Technol. 2001;44:57–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Dung TNB, Sen B, Chen CC, Kumar G, Lin CY. Food waste to bioenergy via anaerobic processes. Energy Procedia. 2014;61:307–312. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2014.11.1113. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Mancuso G, Langone M, Andreottola G. A swirling jet-induced cavitation to increase activated sludge solubilisation and aerobic sludge biodegradability. Ultrason Sonochem. 2017;35:489–501. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Barton JR, Issaias I, Stentiford EI. Carbon–making the right choice for waste management in developing countries. Waste Manag. 2008;28:69–76. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2007.09.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Abbasi T, Tauseef SM, Abbasi SA. Anaerobic digestion for global warming control and energy generation—an overview. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2012;16:3228–3242. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2012.02.046. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Bekkering J, Broekhuis AA, Van Gemert WJT. Optimisation of a green supply chain—a review. Bioresour Technol. 2010;101:450–456. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.08.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Tambone F, Genevini P, D’Imporzano G, Adani F. Assessing amendment properties of digestate by studying the organic matter composition and the degree of biological stability during the anaerobic digestion of the organic fraction of MSW. Bioresour Technol. 2009;100:3140–3142. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Rehl T, Müller J. Life cycle assessment of biogas digestate processing technologies. Resour Conserv Recycl. 2011;56:92–104. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2011.08.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Mata-Alvarez J, Mace S, Llabres P. Anaerobic digestion of organic solid wastes. An overview of research achievements and perspectives. Bioresour Technol. 2000;74:3–16. doi: 10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00023-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Kerroum D, Mossaab BL, Hassen MA. Production of bio-energy from organic waste: effect of temperature and substrate composition. Int J Energy Res. 2014;38:270–276. doi: 10.1002/er.3044. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Ariunbaatar J, Di Perta ES, Panico A, Frunzo L, Esposito G, Lens PN, Pirozzi F. Effect of ammoniacal nitrogen on one-stage and two-stage anaerobic digestion of food waste. Waste Manag. 2015;38:388–398. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2014.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Kim M, Ahn YH, Speece RE. Comparative process stability and efficiency of anaerobic digestion; mesophilic vs. thermophilic. Water Res. 2002;36:4369–4385. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Kundu K, Sharma S, Sreekrishnan TR. Influence of process parameters on anaerobic digestion microbiome in bioenergy production: towards an improved understanding. BioEnergy Res. 2017;10:288–303. doi: 10.1007/s12155-016-9789-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Novaes RFV. Microbiology of anaerobic digestion. Water Sci Technol. 1986;18:1–14. [Google Scholar]
- 111.Gonzalez-Martinez A, Garcia-Ruiz MJ, Rodriguez-Sanchez A, Osorio F, Gonzalez-Lopez J. Archaeal and bacterial community dynamics and bioprocess performance of a bench-scale two-stage anaerobic digester. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;100:6013–6033. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7393-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Raposo F, De la Rubia MA, Fernández-Cegrí V, Borja R. Anaerobic digestion of solid organic substrates in batch mode: an overview relating to methane yields and experimental procedures. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2012;16:861–877. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2011.09.008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Cirne DG, Paloumet X, Björnsson L, Alves MM, Mattiasson B. Anaerobic digestion of lipid-rich waste-effects of lipid concentration. Renew Energy. 2007;32:965–975. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2006.04.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Li C, Fang HHP. Fermentative hydrogen production from wastewater and solid wastes by mixed cultures. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol. 2007;37:1–39. doi: 10.1080/10643380600729071. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Neves L, Ribeiro R, Oliveira R, Alves MM. Enhancement of methane production from barley waste. Biomass Bioenergy. 2006;30:599–603. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2005.12.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Siegert I, Banks C. The effect of volatile fatty acid additions on the anaerobic digestion of cellulose and glucose in batch reactors. Process Biochem. 2005;40:3412–3418. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2005.01.025. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Callaghan FJ, Wase DAJ, Thayanity K, Forster CF. Continuous co-digestion of cattle slurry with fruit and vegetable wastes and chicken manure. Biomass Bioenergy. 2002;22:71–77. doi: 10.1016/S0961-9534(01)00057-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Cuetos MJ, Gómez X, Otero M, Morán A. Anaerobic digestion and co-digestion of slaughterhouse waste (SHW): influence of heat and pressure pre-treatment in biogas yield. Waste Manag. 2010;30:1780–1789. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2010.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Edström M, Nordberg A, Thyselius L. Anaerobic treatment of animal byproducts from slaughterhouses at laboratory and pilot scale. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2003;109:127–138. doi: 10.1385/ABAB:109:1-3:127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Chen Y, Cheng JJ, Creamer KS. Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: a review. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99:4044–4064. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2007.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Nielsen HB, Angelidaki I. Strategies for optimizing recovery of the biogas process following ammonia inhibition. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99:7995–8001. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.03.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Limoli A, Langone M, Andreottola G. Ammonia removal from raw manure digestate by means of a turbulent mixing stripping process. J Environ Manag. 2016;176:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Zhang P, Zeng G, Zhang G, Li Y, Zhang B, Fan M. Anaerobic co-digestion of biosolids and organic fraction of municipal solid waste by sequencing batch process. Fuel Process Technol. 2008;89:485–489. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2007.11.013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Hawkes DL. Factors affecting net energy production from mesophilic anaerobic digestion. In: Stafford DA, Wheatley BI, Hughes DE, editors. Anaerobic digestion. 1980. http://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US201301314196.
- 125.Astals S, Musenze RS, Bai X, Tannock S, Tait S, Pratt S, Jensen PD. Anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure and algae: impact of intracellular algal products recovery on co-digestion performance. Bioresour Technol. 2015;181:97–104. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Park S, Li YB. Evaluation of methane production and macronutrient degradation in the anaerobic co-digestion of algae biomass residue and lipid waste. Bioresour Technol. 2012;111:42–48. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Wang M, Park C. Investigation of anaerobic digestion of Chlorella sp. and Micractinium sp. grown in high-nitrogen wastewater and their co-digestio with waste activated sludge. Biomass Bioenergy. 2015;80:30–37. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2015.04.028. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Zhong W, Chi L, Luo Y, Zhang Z, Zhang Z, Wu WM. Enhanced methane production from Taihu Lake blue algae by anaerobic co-digestion with corn straw in continuous feed digesters. Bioresour Technol. 2013;134:264–270. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.02.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Zhen G, Lu X, Kobayashi T, Kumar G, Xu K. Anaerobic co-digestion on improving methane production from mixed microalgae (Scenedesmus sp., Chlorella sp.) and food waste: kinetic modeling and synergistic impact evaluation. Chem Eng J. 2016;299:332–341. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.118. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Angelidaki I, Sanders W. Assessment of the anaerobic biodegradability of macropollutants. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol. 2004;3:117–129. doi: 10.1007/s11157-004-2502-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Browne J, Nizami AS, Thamsiriroj T, Murphy JD. Assessing the cost of biofuel production with increasing penetration of the transport fuel market: a case study of gaseous biomethane in Ireland. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2011;15:4537–4547. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2011.07.098. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Owens JM, Chynoweth DP. Biochemical methane potential of municipal solid waste (MSW) components. Water Sci Technol. 1993;27:1–14. doi: 10.1021/es00038a700. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Hansen TL, Schmidt JE, Angelidaki I, Marca E, Jansen JLC, Mosbæk H. Method for determination of methane potentials of solid organic waste. Waste Manag. 2004;24:393–400. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2003.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Xie S, Lawlor PG, Frost JP, Hud Z, Zhan X. Effect of pig manure to grass silage ratio on methane production in batch anaerobic co-digestion of concentrated pig manure and grass silage. Bioresour Technol. 2011;102:5728–5733. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Angelidaki I, Alves M, Bolzonella D, Borzacconi L, Campos JL, Guwy AJ, Kalyuzhnyi S, Jenicek P, van Lier JB. Defining the biomethane potential (BMP) of solid organic wastes and energy crops: a proposed protocol for batch assays. Water Sci Technol. 2009;59:927–934. doi: 10.2166/wst.2009.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Esposito G, Frunzo L, Liotta F, Panico A, Pirozzi F. Bio-methane potential tests to measure the biogas production from the digestion and co-digestion of complex organic substrates. Open Environ Eng J. 2012;5:1–8. doi: 10.2174/1874829501205010001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Yokoi H, Maki R, Hirose J, Hayashi S. Microbial production of hydrogen from starch-manufacturing wastes. Biomass Bioenergy. 2002;22:389–395. doi: 10.1016/S0961-9534(02)00014-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Angenent LT, Khursheed K, Al-dahhan M, Wrenn BA, Dominguez-Espinoza R. Production of bioenergy and biochemicals from industrial and agricultural wastewater. Trends Biotechnol. 2004;22:477–485. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2004.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Shin HS, Youn JH, Kim HS. Hydrogen production from food waste in anaerobic mesophilic and thermophilic acidogenesis. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2004;29:1355–1363. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2003.09.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 140.O-Thong S, Prasertsan P, Birkeland NK. Evaluation of methods for preparing thermophilic hydrogen producing seeds from anaerobic digested sludge with microbial communities aspects. Bioresour Technol. 2009;100:909–918. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.07.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Nitipan S, Mamimin C, Intrasungkha N, Birkeland NK, Sompong O. Microbial community analysis of thermophilic mixed culture sludge for biohydrogen production from palm oil mill effluent. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2014;39:19285–19293. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.05.139. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Lin CY, Lay CH. Carbon/nitrogen-ratio effect on fermentative hydrogen production by mixed microflora. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2004;29:41–45. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3199(03)00083-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Prasertsan P, O-Thong S, Birkeland NK. Optimization and microbial community analysis for production of biohydrogen from palm oil mill effluent by thermophilic fermentative process. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2009;34:7448–7459. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.04.075. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Ghimire A, Frunzo L, Pirozzi F, Trably E, Escudie R, Lens PNL, Esposito G. A review on dark fermentative biohydrogen production from organic biomass: process parameters and use of by-products. Appl Energy. 2015;144:73–95. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.01.045. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Levin DB, Pitt L, Love M. Biohydrogen production: prospect sand limitations to practical application. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2004;29:173–185. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3199(03)00094-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Das D, Veziroglu TN. Hydrogen production by biological processes: a survey of literature. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2001;26:13–28. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3199(00)00058-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Miyake J, Miyake M, Asada Y. Biotechnological hydrogen production: research for efficient light energy conversion. J Biotechnol. 1999;70:89–101. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1656(99)00063-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Lo YC, Chen SD, Chen CY, Huang TI, Lin CY, Chang JS. Combining enzymatic hydrolysis and dark-photofermentation processes for hydrogen production from starch feedstock: a feasibility study. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2008;33:5224–5233. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.05.014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Chen CY, Yang MH, Yeh KL, Liu CH, Chang JS. Biohydrogen production using sequential dark and photo fermentation processes. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2008;33:4755–4762. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.06.055. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Tao Y, Chen Y, Wu Y, He Y, Zhou Z. High hydrogen yield from a two-step process of dark- and photo-fermentation of sucrose. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2006;32:200–206. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2006.06.034. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Pradhan N, Dipasquale L, d’Ippolito G, Panico A, Lens PN, Esposito G, Fontana A. Hydrogen production by the thermophilic bacterium Thermotoga neapolitana. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16:12578–12600. doi: 10.3390/ijms160612578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Hawkes FR, Hussy I, Kyazze G, Dinsdale R, Hawkes DL. Continuous dark fermentative hydrogen production by mesophilic microflora: principles and progress. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2007;32:172–184. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2006.08.014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Eroglu E, Melis A. Photobiological hydrogen production: recent advances and state of the art. Bioresour Technol. 2011;102:8403–8413. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.03.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Luongo V, Ghimire A, Frunzo L, Fabbricino M, D’Antonio G, Pirozzi F, Esposito G. Photofermentative production of hydrogen and poly-β-hydroxybutyrate from dark fermentation products. Bioresour Technol. 2016;228:171–175. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.12.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Cappelletti M, Bucchi G, Mendes JD, Alberini A, Fedi S, Bertin L, Frascari D. Biohydrogen production from glucose, molasses and cheese whey by suspended and attached cells of four hyperthermophilic Thermotoga strains. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2012;87:1291–1307. doi: 10.1002/jctb.3782. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Nguyen TAD, Han SJ, Kim JP, Kim MS, Sim SJ. Thermophilic hydrogen fermentation from Korean rice straw by Thermotoga neapolitana. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2010;35:13392–13398. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.11.112. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Yu X, Drapcho CM. Hydrogen production by the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga neapolitana using agricultural-based carbon and nitrogen sources. Biol Eng Trans. 2011;4:101–111. doi: 10.13031/2013.38506. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Davila-Vazquez G, Arriaga S, Alatriste-Mondrago F, De Leon-Rodrıguez A, Rosales-Colunga LM, Razo Flores E. Fermentative biohydrogen production: trends and perspectives. Environ Sci Biotechnol. 2008;7:27–45. doi: 10.1007/s11157-007-9122-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Chen WM, Tseng ZJ, Lee KS, Chang JS. Fermentative hydrogen production with Clostridium butyricum CGS5 isolated from anaerobic sewage sludge. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2005;30:1063–1070. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2004.09.008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Lo YC, Chen SD, Chen CY, Huang TI, Lin CY, Chang JS. Combining enzymatic hydrolysis and dark-photo fermentation processes for hydrogen production from starch feedstock: a feasibility study. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2008;33(5224):5233. [Google Scholar]
- 161.Ferchichi M, Crabbe E, Gil GHW, Almadidy A. Influence of initial pH on hydrogen production from cheese whey. J Biotechnol. 2005;120:402–409. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.05.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Bisaillon A, Turcot J, Hallenbeck PC. The effect of nutrient limitation on hydrogen production by batch cultures of Escherichia coli. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2006;31:1504–1508. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2006.06.016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Yasuda K, Tanisho S. Fermentative hydrogen production from artificial food wastes. In: Proceedings of the 16th world hydrogen energy conference. Lyon, France; 2006. p. 210.
- 164.Liu H, Zhang T, Fang HHP. Thermophilic H2 production from a cellulose-containing wastewater. Biotechnol Lett. 2003;25:365–369. doi: 10.1023/A:1022341113774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Kumar G, Bakonyi P, Periyasamy S, Kim SH, Nemestóthy N, Bélafi-Bakó K. Lignocellulose biohydrogen: practical challenges and recent progress. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2015;44:728–737. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.01.042. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Khanal SK, Chen WH, Li L, Sung SW. Biological hydrogen production: effects of pH and intermediate products. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2004;29:1123–1131. [Google Scholar]
- 167.Fang HHP, Liu H, Zhang T. Phototrophic hydrogen production from acetate and butyrate in wastewater. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2005;30:785–793. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2004.12.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Valdez-Vazquez I, Ríos-Leal E, Esparza-García F, Cecchi F, Poggi-Varaldo HM. Semi-continuous solid substrate anaerobic reactors for H2 production from organic waste: mesophilic versus thermophilic regime. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2005;30:13–14. [Google Scholar]
- 169.Kumar G, Bakonyi P, Kobayashi T, Xu KQ, Sivagurunathan P, Kim SH, Bélafi-Bakó K. Enhancement of biofuel production via microbial augmentation: the case of dark fermentative hydrogen. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2016;57:879–891. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.107. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Albuquerquea MGE, Martino V, Pollet E, Avérous L, Reis MAM. Mixed culture polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) production from volatile fatty acid (VFA)-rich streams: effect of substrate composition and feeding regime on PHA productivity, composition and properties. J Biotechnol. 2011;151:66–76. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.10.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Morgan-Sagastume F, Karlsson A, Johansson P, Pratt S, Boon N, Lant P, Werker A. Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates in open, mixed cultures from a waste sludge stream containing high levels of soluble organics, nitrogen and phosphorus. Water Res. 2010;44:5196–5211. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.06.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Chen GQ. A microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) based bio-and materials industry. Chem Soc Rev. 2009;38:2434–2446. doi: 10.1039/b812677c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Serafim LS, Lemos PC, Albuquerque MG, Reis MA. Strategies for PHA production by mixed cultures and renewable waste materials. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008;81:615–628. doi: 10.1007/s00253-008-1757-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Lee WS, Chua ASM, Yeoh HK, Ngoh GC. A review of the production and applications of waste-derived volatile fatty acids. Chem Eng J. 2014;235:83–99. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Saharan BS, Grewal A, Kumar P. Biotechnological production of polyhydroxyalkanoates: a review on trends and latest developments. Chin J Biol. 2014;80:29–84. [Google Scholar]
- 176.Wu SC, Liou SZ, Lee CM. Correlation between bio-hydrogen production and polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) synthesis by Rhodopseudomonas palustris WP3-5. Bioresour Technol. 2012;113:44–50. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Vincenzini M, Marchini A, Ena A, De Philippis R. H2 and poly-β-hydroxybutyrate, two alternative chemicals from purple non sulfur bacteria. Biotechnol Lett. 1997;19:759–762. doi: 10.1023/A:1018336209252. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Albuquerque MGE, Concas S, Bengtsson S, Reis MAM. Mixed culture polyhydroxyalkanoates production from sugar molasses: the use of a 2-stage CSTR system for culture selection. Bioresour Technol. 2010;101:7112–7122. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.04.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Buffière P, Loisel D, Bernet N, Delgenes JP. Towards new indicators for the prediction of solid waste anaerobic digestion properties. Water Sci Technol. 2006;53:233–241. doi: 10.2166/wst.2006.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Gunaseelan VN. Biochemical methane potential of fruits and vegetable solid waste feedstocks. Biomass Bioenergy. 2004;26:389–399. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2003.08.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Zubr J. Methanogenic fermentation of fresh and ensiled plant materials. Biomass. 1986;11:159–171. doi: 10.1016/0144-4565(86)90064-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Mähnert P, Heiermann M, Linke B. Batch- and semi-continuous biogas production from different grass species. Agric Eng. 2005;7:1–11. [Google Scholar]
- 183.Liu G, Zhang R, El-Mashad HM, Dong R. Effect of feed to inoculum ratios on biogas yields of food and green wastes. BioResources. 2009;100:5103–5108. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.03.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Scaglione D, Caffaz S, Ficara E, Malpei F, Lubello C. A simple method to evaluate the short-term biogas yield in anaerobic codigestion of was and organic wastes. Water Sci Technol. 2008;58:1615–1622. doi: 10.2166/wst.2008.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Tong X, Smith LH, McCarty PL. Methane fermentation of selected lignocellulosic materials. Biomass. 1990;21:239–255. doi: 10.1016/0144-4565(90)90075-U. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Shanmugam P, Horan NJ. Simple and rapid methods to evaluate methane potential and biomass yield for a range of mixed solid wastes. Bioresour Technol. 2009;100:471–474. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.06.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Dinuccio E, Balsari P, Gioelli F, Menardo S. Evaluation of the biogas productivity potential of some Italian agro-industrial biomasses. Bioresour Technol. 2010;101:3780–3783. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.El-Mashad HM, Zhang R. Biogas production from co-digestion of dairy manure and food waste. Bioresour Technol. 2010;101:4021–4028. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Pommier S, Llamas AM, Lefebvre X. Analysis of the outcome of shredding pretreatment on the anaerobic biodegradability of paper and cardboard materials. Bioresour Technol. 2010;101:463–468. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.07.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Paepatung N, Nopharatana A, Songkasiri W. Bio-methane potential of biological solid materials and agricultural wastes. Asian J Energy Environ. 2009;10:19–27. [Google Scholar]
- 191.Parawira W, Murto M, Zvauya R, Mattiasson B. Anaerobic batch digestion of solid potato waste alone and in combination with sugar beet leaves. Renew Energy. 2004;29:1811–1823. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2004.02.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Sharma SK, Mishra IM, Sharma MP, Saini JS. Effect of particle size on biogas generation from biomass residues. Biomass. 1988;17:251–263. doi: 10.1016/0144-4565(88)90107-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Lehtomäki A, Viinikainen TA, Rintala JA. Screening boreal energy crops and crop residues for methane biofuel production. Biomass Bioenergy. 2008;32:541–550. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2007.11.013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Amon T, Amon B, Kryvoruchko V, Machmüller A, Hopfner-Sixt K, Bodiroza V. Methane production through anaerobic digestion of various energy crops grown in sustainable crop rotations. Bioresour Technol. 2007;98:3204–3212. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2006.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Jokela JPY, Vavilin VA, Rintala JA. Hydrolysis rates, methane production and nitrogen solubilisation of grey waste components during anaerobic degradation. Bioresour Technol. 2005;96:501–508. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2004.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Bauer A, Leonhartsberger C, Bösch P, Amon B, Friedl A, Amon T. Analysis of methane yields from energy crops and agricultural by-products and estimation of energy potential from sustainable crop rotation systems in EU-27. Clean Technol Environ Policy. 2010;12:153–161. doi: 10.1007/s10098-009-0236-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Zhang P, Chen Y, Zhou Q. Waste activated sludge hydrolysis and short-chain fatty acids accumulation under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions: effect of pH. Water Res. 2009;43:3735–3742. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.05.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Jiang S, Chen Y, Zhou Q, Gu G. Biological short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) production from waste-activated sludge affected by surfactant. Water Res. 2007;41:3112–3120. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2007.03.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Ji Z, Chen G, Chen Y. Effects of waste activated sludge and surfactant addition on primary sludge hydrolysis and short-chain fatty acids accumulation. Bioresour Technol. 2010;101:3457. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Wu H, Yang D, Zhou Q, Song Z. The effect of pH on anaerobic fermentation of primary sludge at room temperature. J Hazard Mater. 2009;172:196–201. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Elbeshbishy E, Hafez H, Dhar BR, Nakhla G. Single and combined effect of various pretreatment methods for biohydrogen production from food waste. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2011;36:11379–11387. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.02.067. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Kim HJ, Kim SH, Choi YG, Kim GD, Chung TH. Effect of enzymatic pretreatment on acid fermentation of food waste. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2006;81:974–980. doi: 10.1002/jctb.1484. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Zhang B, Zhang LL, Zhang SC, Shi HZ, Cai WM. The influence of pH on hydrolysis and acidogenesis of kitchen wastes in two-phase anaerobic digestion. Environ Technol. 2005;26:329–340. doi: 10.1080/09593332608618563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Bolzonella D, Fatone F, Pavan P, Cecchi F. Anaerobic fermentation of organic municipal solid wastes for the production of soluble organic compounds. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2005;44:3412–3418. doi: 10.1021/ie048937m. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Hong SK, Shirai Y, Nor Aini AR, Hassan MA. Semi-continuous and continuous anaerobic treatment of palm oil mill effluent for the production of organic acids and polyhydroxyalkanoates. J Environ Sci. 2009;3:552–559. doi: 10.3923/rjes.2009.552.559. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Beccari M, Bertin L, Dionisi D, Fava F, Lampis S, Majone M, Valentino F, Vallini G, Villano M. Exploiting olive oil mill effluents as a renewable resource for production of biodegradable polymers through a combined anaerobic–aerobic process. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2009;84:901–908. doi: 10.1002/jctb.2173. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Bengtsson S, Hallquist J, Werker A, Welander T. Acidogenic fermentation of industrial wastewaters: effects of chemostat retention time and pH on volatile fatty acids production. Biochem Eng J. 2008;40:492–499. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2008.02.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]


