Abstract
This Data in Brief contains results from three different survey logistic regression models comparing risks of self-reported diagnoses of cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases among smokers of menthol and non-menthol cigarettes. Analyses employ data from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) cycles administered between 1999 and 2012, combined and in subsets. Raw data may be downloaded from the National Center for Health Statistics. Results were not much affected by which covariates were included in the models, but depended strongly on the NHANES cycles included in the analysis. All three models returned elevated risk estimates for three endpoints when they were run in individual NHANES cycles (congestive heart failure in 2001–02; hypertension in 2003–04; and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in 2005–06), and all three models returned null results for these endpoints when data from 1999–2012 were combined.
Keywords: NHANES, Menthol versus non-menthol, Survey methods, Reanalysis, Cross-model validation
Specifications Table
| Subject area | Epidemiology |
| More specific subject area | Health risks associated with smoking menthol vs. non-menthol cigarettes |
| Type of data | Tables |
| How data was acquired | Downloaded from US National Center for Health Statistics and analyzed using survey logistic regression methods |
| Data format | Analyzed |
| Experimental factors | None |
| Experimental features | Self-reported diagnoses of cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases are compared for smokers of menthol and non-menthol cigarettes |
| Data source location | USA |
| Data accessibility | Data are available from the US National Center for Health Statistics http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/nhanes_questionnaires.htm |
Value of the data
-
•
Results of different models run on the same data set provide insights into how the data (i.e., which cycles of NHANES) and the covariates selected for inclusion in a model influence risk estimates.
-
•
Estimates based on individual (i.e., 2-year) cycles of the NHANES versus estimates from combined cycles of NHANES show inconsistency and illustrate that analyses using individual cycles should not be used to draw causal inferences about the population.
-
•
The data provided here allow comparisons between analyses published in two recent papers that reported contradictory results.
1. Experimental design, materials and methods
Two recent publications reported contradictory findings from analyses of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Vozoris reported a statistically significantly increased adjusted odds of stroke diagnosis among menthol compared with non-menthol cigarette smokers, in particular among non-African Americans, using data from 2007–2008 cycle (incorrectly reported as 2001–2008) of NHANES [5]. Rostron did not detect a difference in stroke risk among smokers of menthol compared with non-menthol cigarettes, based on analyses of NHANES data from the 1999 through 2010 cycles [3]. Our investigation of the reasons for the discordant results reported by Vozoris and Rostron with respect to stroke risk, and the results of new analyses comparing stroke risks among smokers of menthol and non-menthol cigarettes that use all NHANES cycles from 1999 through 2012 is available elsewhere [4]. The differences between the Vozoris [5] and Rostron [3] results were shown to be mainly due to the inadvertent exclusion of all but the 2007–2008 NHANES data from the Vozoris [5] analysis. The data presented here examine risks of other endpoints evaluated by Vozoris (i.e., hypertension (HTN), myocardial infarction (MI), congestive heart failure (CHF), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD)) among smokers of menthol compared with non-menthol cigarettes estimated according to three different logistic regression models: 1) models proposed by Vozoris, using NHANES 2007–2008, 1999–2010, and 1999–2012; 2) models proposed by Rostron, using NHANES 2007–2008, 1999–2010, and 1999–2012; and 3) a new set of models we developed with purposeful selection techniques using NHANES 1999–2012.
NHANES is a nationally representative survey of US, non-institutionalized civilians. It is conducted in two year cycles, with approximately 10,000 individuals in each cycle. Interviews elicit information on demographic characteristics (e.g., age, gender, race/ethnicity), smoking habits, and whether a health professional had ever diagnosed the participant with certain medical conditions. Cycles of the NHANES can be combined, or they can be analyzed individually. Because NHANES employs a complex, multistage, sampling strategy, survey statistics must be used to analyze the data and to generalize findings to the US population. In this case, we used the SURVEYLOGISTIC procedure of SAS/STAT© version 9.4 to perform logistic regression accounting for the complex sampling design, i.e., using both the masked variance pseudo-primary sampling unit (SMDVPSU) and the masked variance pseudo-stratum (SDMVSTRA) variables, using the adjusted 2 year interview weight (WTINT2YR), and using Taylor series linearization to estimate the covariance matrix. Weights were adjusted for the inclusion of multiple surveys [2] by dividing the WTINT2YR variable by the number of cycles used in each analysis. We additionally ran all models within strata defined by age, race/ethnicity, and gender using the SAS DOMAIN statement to specify these subpopulations and to ensure the variance and standard errors were calculated correctly. See associated file SAS CODE.DOCX for the code to combine the cycles of NHANES with common variables and an example of the Proc Logistic code used for analysis.
Following both Vozoris and Rostron, we defined current smokers as those who had smoked ≥1 of the last 30 days and who were ≥20 years old at the time of the interview. Table 1 shows the variables we used in these analyses. We identified cases by their self-reported diagnoses according to the question “has a doctor or other health professional ever told you that you had [high blood pressure, a heart attack, congestive heart failure, a stroke, or COPD (emphysema or chronic bronchitis)]” (yes/no). We considered all other responses to be a non-response and set them as missing. Stroke was the subject of Van Landingham et al. [4], and data are not presented here.
Table 1.
NHANES variables considered in analyses.
| NHANES variable | Description |
|---|---|
| RIDAGEYR | Age |
| RIAGENDR | Gender |
| RIDRETH1 | Race (races were combined as African American (i.e., non-Hispanic Black) or non-African American (i.e., Mexican-American, other Hispanic, non-Hispanic white and Other Races). When non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic White and Mexican Americans were reported, the “other Hispanic” and “other races” were combined into a category (Other). The Other category was not reported separately. |
| SMD070 | Average # of cigarettes smoked per day |
| SMD080, SMD641 | # days smoked in last 30 days. Data were captured in the variable SMD080 in NHANES 1999–2000 and 2001–2002, and in SMD641 starting in 2003. |
| SMD030 | Age started smoking |
| BMXBMI | Body Mass Index |
| INDFMPIR | Poverty to Income Ratio (PIR) |
| DMDEDUC2a | Highest education level |
| INDHHINC, INDHHIN2a | Household Income. Data were captured in the variable INDHHINC in NHANES surveys before 2007, and in INDHHIN2 from 2007 through 2012. |
| BPQ020 | Hypertension |
| MCQ160E | Myocardial Infarction |
| MCD160B | Congestive Heart Failure |
| MCQ160F | Stroke |
| MCQ160G, MCQ160K | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (a yes for either variable indicated a yes for COPD) |
| SMD075 | # of years smoked |
| SMQ140, SMQ170, SMQ200, SMD2130 | Used other tobacco products (a yes for any of these four codes indicated a yes for Used other tobacco products) |
| Calculated variables | |
| Pack yearsb | Eq. 1. Average # of cigarettes smoked per day/20×(Age−Age started smoking+1) |
| Eq. 2. Average # of cigarettes smoked per day/20 × # of years smoked | |
| Eq. 3. Average # of cigarettes smoked per day/20 | |
Values indicating “do not know” and “refused” for these variables were retained in the analyses.
Pack years were calculated using Eq. (1), unless age started smoking was missing. Eq. (2) was used if age started smoking was missing and # of years smoked was available. Eq. (3) was used only as a last resort when only average # of cigarettes per day was available.
We ran three sets of models for each outcome using data from NHANES 2007 to 2008 (as used by Vozoris), from 1999 to 2010 (as used by Rostron) and from 1999 to 2012 (all cycles available when we undertook the project) to determine if the selection of covariates or cycles of the NHANES influenced the results. First, we implemented the model described by Vozoris (Table 2, Table 3, Table 4); second, we implemented the model described by Rostron (Table 5, Table 6, Table 7); last, we developed a new model for each outcome using purposeful selection of covariates (Table 8). Purposeful selection of covariates was conducted as follows: a preliminary model consisted of cigarette type (menthol or non-menthol) and all relevant, potential covariates (Table 1) with cigarette type forced to remain in all models. We identified each covariate, other than cigarette type, with a p-value of greater than 0.05. We refit the model after dropping the covariate with the largest p-value, until only cigarette type and covariates with p-values of 0.05 or less remained. Each covariate that had been dropped was added back individually, and we calculated the relative percent change in the regression coefficient for cigarette type for the larger model compared with the model containing only statistically significant covariates (Eq. (1)). If including a given covariate resulted in a relative percent change in the regression coefficient greater than 15%, that covariate was retained in the model.
| (1) |
Table 2.
Model specified by Vozoris [5]a using data from NHANES 2007–2008; unweighted counts, adjusted odds ratios (AOR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
| Stratum | Diagnosisb | Cigarette preference | Cases | Non-Cases | AOR |
95% CI |
Total N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||||
| All | HTN | Non-Menthol | 225 | 583 | 1158 | |||
| Menthol | 126 | 224 | 1.14 | 0.82 | 1.59 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 40 | 766 | 1156 | ||||
| Menthol | 12 | 338 | 0.99 | 0.47 | 2.10 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 20 | 785 | 1155 | ||||
| Menthol | 11 | 339 | 1.06 | 0.41 | 2.75 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 105 | 704 | 1159 | ||||
| Menthol | 37 | 313 | 1.17 | 0.66 | 2.05 | |||
| Female | HTN | Non-Menthol | 97 | 219 | 506 | |||
| Menthol | 77 | 113 | 1.30 | 0.75 | 2.25 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 14 | 301 | 505 | ||||
| Menthol | 6 | 184 | 0.53 | 0.17 | 1.63 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 7 | 308 | 505 | ||||
| Menthol | 5 | 185 | 0.63 | 0.15 | 2.67 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 59 | 257 | 506 | ||||
| Menthol | 29 | 161 | 1.04 | 0.62 | 1.75 | |||
| Male | HTN | Non-Menthol | 128 | 364 | 652 | |||
| Menthol | 49 | 111 | 1.06 | 0.67 | 1.67 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 26 | 465 | 651 | ||||
| Menthol | 6 | 154 | 1.55 | 0.41 | 5.85 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 13 | 477 | 650 | ||||
| Menthol | 6 | 154 | 0.96 | 0.28 | 3.29 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 46 | 447 | 653 | ||||
| Menthol | 8 | 152 | 1.68 | 0.45 | 6.31 | |||
| African American | HTN | Non-Menthol | 36 | 67 | 278 | |||
| Menthol | 71 | 104 | 1.84 | 0.72 | 4.72 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 4 | 100 | 279 | ||||
| Menthol | 8 | 167 | 1.44 | 0.43 | 4.91 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 3 | 101 | 279 | ||||
| Menthol | 9 | 166 | 1.84 | 0.17 | 20.38 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 11 | 93 | 279 | ||||
| Menthol | 12 | 163 | 0.34 | 0.06 | 1.86 | |||
| Non-African American | HTN | Non-Menthol | 189 | 516 | 880 | |||
| Menthol | 55 | 120 | 1.02 | 0.66 | 1.57 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 36 | 666 | 877 | ||||
| Menthol | 4 | 171 | 0.74 | 0.22 | 2.57 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 17 | 684 | 876 | ||||
| Menthol | 2 | 173 | 0.69 | 0.16 | 3.04 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 94 | 611 | 880 | ||||
| Menthol | 25 | 150 | 1.30 | 0.72 | 2.34 | |||
| Ages ≥70 years | HTN | Non-Menthol | 32 | 24 | 69 | |||
| Menthol | 11 | 2 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 11.20 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 11 | 45 | 69 | ||||
| Menthol | 2 | 11 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 3 | 50 | 66 | ||||
| Menthol | 1 | 12 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 16 | 40 | 69 | ||||
| Menthol | 3 | 10 | 1.88 | 0.14 | 26.05 | |||
| Ages 20 to <70 years | HTN | Non-Menthol | 193 | 559 | 1089 | |||
| Menthol | 115 | 222 | 1.02 | 0.77 | 1.37 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 29 | 721 | 1087 | ||||
| Menthol | 10 | 327 | 0.65 | 0.27 | 1.56 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 17 | 735 | 1089 | ||||
| Menthol | 10 | 327 | 0.68 | 0.25 | 1.83 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 89 | 664 | 1090 | ||||
| Menthol | 34 | 303 | 1.06 | 0.58 | 1.94 | |||
Model controls for age, gender, race/ethnicity, body mass index, total household income, average number of cigarettes smoked per day in the last 30 days, number of days smoked in the last 30 days, and age started smoking. Vozoris [5].
HTN: hypertension; MI: myocardial infarction; CHF: congestive heart failure; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Table 3.
Model specified by Vozoris [5]a using data from NHANES 1999–2010; unweighted counts, adjusted odds ratios (AOR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
| Stratum | Diagnosisb | Cigarette preference | Cases | Non-Cases | AOR |
95% CI |
Total N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||||
| All | HTN | Non-Menthol | 1053 | 2934 | 5771 | |||
| Menthol | 520 | 1264 | 0.90 | 0.75 | 1.08 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 196 | 3810 | 5796 | ||||
| Menthol | 63 | 1727 | 0.97 | 0.64 | 1.47 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 111 | 3888 | 5788 | ||||
| Menthol | 46 | 1743 | 1.08 | 0.66 | 1.75 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 453 | 3562 | 5806 | ||||
| Menthol | 181 | 1610 | 1.25 | 0.92 | 1.69 | |||
| Female | HTN | Non-Menthol | 461 | 1178 | 2552 | |||
| Menthol | 285 | 628 | 0.88 | 0.67 | 1.16 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 72 | 1569 | 2556 | ||||
| Menthol | 21 | 894 | 0.69 | 0.35 | 1.38 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 41 | 1598 | 2553 | ||||
| Menthol | 16 | 898 | 0.93 | 0.42 | 2.07 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 265 | 1379 | 2559 | ||||
| Menthol | 115 | 800 | 1.11 | 0.81 | 1.52 | |||
| Male | HTN | Non-Menthol | 592 | 1756 | 3219 | |||
| Menthol | 235 | 636 | 0.92 | 0.69 | 1.22 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 124 | 2241 | 3240 | ||||
| Menthol | 42 | 833 | 1.28 | 0.77 | 2.13 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 70 | 2290 | 3235 | ||||
| Menthol | 30 | 845 | 1.22 | 0.68 | 2.19 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 188 | 2183 | 3247 | ||||
| Menthol | 66 | 810 | 1.57 | 0.93 | 2.65 | |||
| African American | HTN | Non-Menthol | 183 | 227 | 1355 | |||
| Menthol | 314 | 631 | 0.94 | 0.70 | 1.26 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 28 | 383 | 1360 | ||||
| Menthol | 29 | 920 | 0.65 | 0.32 | 1.32 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 21 | 389 | 1359 | ||||
| Menthol | 26 | 923 | 0.63 | 0.31 | 1.28 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 41 | 371 | 1361 | ||||
| Menthol | 71 | 878 | 0.65 | 0.39 | 1.08 | |||
| Non-African American | HTN | Non-Menthol | 870 | 2707 | 4416 | |||
| Menthol | 206 | 633 | 1.49 | 0.71 | 3.12 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 168 | 3427 | 4436 | ||||
| Menthol | 34 | 807 | 1.05 | 0.67 | 1.65 | |||
| Non-African American | CHF | Non-Menthol | 90 | 3499 | 4429 | |||
| Menthol | 20 | 820 | 1.38 | 0.73 | 2.59 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 412 | 3191 | 4445 | ||||
| Menthol | 110 | 732 | 1.35 | 0.99 | 1.84 | |||
| Ages ≥70 years | HTN | Non-Menthol | 157 | 135 | 367 | |||
| Menthol | 43 | 32 | 0.63 | 0.30 | 1.32 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 43 | 248 | 368 | ||||
| Menthol | 12 | 65 | 1.02 | 0.36 | 2.85 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 26 | 260 | 362 | ||||
| Menthol | 9 | 67 | 1.06 | 0.38 | 2.98 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 65 | 228 | 370 | ||||
| Menthol | 14 | 63 | 0.94 | 0.42 | 2.09 | |||
| Ages 20 to <70 years | HTN | Non-Menthol | 896 | 2799 | 5404 | |||
| Menthol | 477 | 1232 | 0.82 | 0.69 | 0.98 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 153 | 3562 | 5428 | ||||
| Menthol | 51 | 1662 | 0.71 | 0.45 | 1.15 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 85 | 3628 | 5426 | ||||
| Menthol | 37 | 1676 | 0.82 | 0.45 | 1.49 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 388 | 3334 | 5436 | ||||
| Menthol | 167 | 1547 | 1.17 | 0.86 | 1.60 | |||
Model controls for age, gender, race/ethnicity, body mass index, total household income, average number of cigarettes smoked per day in the last 30 days, number of days smoked in the last 30 days, and age started smoking. Vozoris [5].
HTN: hypertension; MI: myocardial infarction; CHF: congestive heart failure; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Table 4.
Model specified by Vozoris [5]a using data from NHANES 1999–2012; unweighted counts, adjusted odds ratios (AOR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
| Stratum | Diagnosisb | Cigarette preference | Cases | Non-Cases | AOR |
95% CI |
Total N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||||
| All | HTN | Non-Menthol | 1236 | 3345 | 6710 | |||
| Menthol | 651 | 1478 | 0.91 | 0.77 | 1.08 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 228 | 4373 | 6736 | ||||
| Menthol | 72 | 2063 | 0.84 | 0.56 | 1.24 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 128 | 4467 | 6727 | ||||
| Menthol | 54 | 2078 | 0.95 | 0.61 | 1.49 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 527 | 4084 | 6747 | ||||
| Menthol | 218 | 1918 | 1.20 | 0.91 | 1.56 | |||
| Female | HTN | Non-Menthol | 522 | 1331 | 2918 | |||
| Menthol | 348 | 717 | 0.91 | 0.70 | 1.19 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 79 | 1776 | 2922 | ||||
| Menthol | 23 | 1044 | 0.63 | 0.32 | 1.25 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 48 | 1805 | 2919 | ||||
| Menthol | 18 | 1048 | 0.76 | 0.36 | 1.61 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 297 | 1561 | 2925 | ||||
| Menthol | 140 | 927 | 1.11 | 0.83 | 1.48 | |||
| Male | HTN | Non-Menthol | 714 | 2014 | 3792 | |||
| Menthol | 303 | 761 | 0.91 | 0.69 | 1.21 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 149 | 2597 | 3814 | ||||
| Menthol | 49 | 1019 | 1.07 | 0.67 | 1.71 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 80 | 2662 | 3808 | ||||
| Menthol | 36 | 1030 | 1.17 | 0.70 | 1.96 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 230 | 2523 | 3822 | ||||
| Menthol | 78 | 991 | 1.35 | 0.85 | 2.13 | |||
| African American | HTN | Non-Menthol | 224 | 276 | 1639 | |||
| Menthol | 407 | 732 | 0.97 | 0.73 | 1.28 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 35 | 466 | 1644 | ||||
| Menthol | 34 | 1109 | 0.60 | 0.33 | 1.11 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 24 | 476 | 1642 | ||||
| Menthol | 31 | 1111 | 0.56 | 0.29 | 1.08 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 47 | 455 | 1645 | ||||
| Menthol | 90 | 1053 | 0.73 | 0.46 | 1.16 | |||
| Non-African American | HTN | Non-Menthol | 1012 | 3069 | 5071 | |||
| Menthol | 244 | 746 | 0.91 | 0.75 | 1.12 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 193 | 3907 | 5092 | ||||
| Menthol | 38 | 954 | 0.88 | 0.56 | 1.38 | |||
| Non-African American | CHF | Non-Menthol | 104 | 3991 | 5085 | |||
| Menthol | 23 | 967 | 1.14 | 0.64 | 2.02 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 480 | 3629 | 5102 | ||||
| Menthol | 128 | 865 | 1.26 | 0.95 | 1.67 | |||
| Ages ≥70 years | HTN | Non-Menthol | 180 | 153 | 421 | |||
| Menthol | 55 | 33 | 0.81 | 0.41 | 1.62 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 49 | 283 | 422 | ||||
| Menthol | 14 | 76 | 1.08 | 0.43 | 2.71 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 30 | 297 | 416 | ||||
| Menthol | 10 | 79 | 1.02 | 0.38 | 2.74 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 73 | 261 | 424 | ||||
| Menthol | 16 | 74 | 0.88 | 0.42 | 1.83 | |||
| Ages 20 to <70 years | HTN | Non-Menthol | 1056 | 3192 | 6289 | |||
| Menthol | 596 | 1445 | 0.82 | 0.69 | 0.96 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 179 | 4090 | 6314 | ||||
| Menthol | 58 | 1987 | 0.60 | 0.39 | 0.93 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 98 | 4170 | 6311 | ||||
| Menthol | 44 | 1999 | 0.71 | 0.41 | 1.23 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 454 | 3823 | 6323 | ||||
| Menthol | 202 | 1844 | 1.11 | 0.84 | 1.46 | |||
Model controls for age, gender, race/ethnicity, body mass index, total household income, average number of cigarettes smoked per day in the last 30 days, number of days smoked in the last 30 days, and age started smoking. Vozoris [5].
HTN: hypertension; MI: myocardial infarction; CHF: congestive heart failure; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Table 5.
Model specified by Rostron [3]a using data from NHANES 2007–2008; unweighted counts, adjusted odds ratios (AOR), and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
| Stratum | Diagnosisb | Cigarette preference | Cases | Non-Cases | AOR |
95% CI |
Total N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||||
| All | HTN | Non-Menthol | 215 | 546 | 1085 | |||
| Menthol | 113 | 211 | 1.03 | 0.74 | 1.42 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 39 | 720 | 1083 | ||||
| Menthol | 10 | 314 | 0.65 | 0.28 | 1.54 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 18 | 740 | 1082 | ||||
| Menthol | 9 | 315 | 0.98 | 0.43 | 2.26 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 99 | 663 | 1086 | ||||
| Menthol | 32 | 292 | 1.02 | 0.55 | 1.88 | |||
| Female | HTN | Non-Menthol | 96 | 208 | 480 | |||
| Menthol | 72 | 104 | 1.20 | 0.68 | 2.12 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 14 | 289 | 479 | ||||
| Menthol | 5 | 171 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 1.15 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 5 | 298 | 479 | ||||
| Menthol | 5 | 171 | 0.91 | 0.27 | 3.10 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 55 | 249 | 480 | ||||
| Menthol | 26 | 150 | 1.01 | 0.56 | 1.82 | |||
| Male | HTN | Non-Menthol | 119 | 338 | 605 | |||
| Menthol | 41 | 107 | 0.83 | 0.50 | 1.37 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 25 | 431 | 604 | ||||
| Menthol | 5 | 143 | 1.19 | 0.22 | 6.34 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 13 | 442 | 603 | ||||
| Menthol | 4 | 144 | 0.79 | 0.22 | 2.90 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 44 | 414 | 606 | ||||
| Menthol | 6 | 142 | 1.07 | 0.30 | 3.79 | |||
| Non-Hispanic Black | HTN | Non-Menthol | 35 | 56 | 257 | |||
| Menthol | 65 | 101 | 1.54 | 0.49 | 4.85 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 4 | 88 | 258 | ||||
| Menthol | 8 | 158 | 1.25 | 0.51 | 3.07 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 3 | 89 | 258 | ||||
| Menthol | 8 | 158 | 2.35 | 0.39 | 14.09 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 10 | 82 | 258 | ||||
| Menthol | 11 | 155 | 0.49 | 0.09 | 2.66 | |||
| Non-Hispanic White | HTN | Non-Menthol | 134 | 327 | 559 | |||
| Menthol | 29 | 69 | 0.91 | 0.56 | 1.48 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 29 | 430 | 557 | ||||
| Menthol | 1 | 97 | 0.32 | 0.02 | 4.26 | |||
| Non-Hispanic White | CHF | Non-Menthol | 11 | 447 | 556 | |||
| Menthol | 0 | 98 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 71 | 390 | 559 | ||||
| Menthol | 12 | 86 | 1.04 | 0.50 | 2.18 | |||
| Mexican American | HTN | Non-Menthol | 28 | 86 | 132 | |||
| Menthol | 7 | 11 | 1.67 | 0.46 | 6.03 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 2 | 111 | 131 | ||||
| Menthol | 0 | 18 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 3 | 110 | 131 | ||||
| Menthol | 0 | 18 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 5 | 109 | 132 | ||||
| Menthol | 2 | 16 | 2.50 | 0.41 | 15.42 | |||
| Ages ≥70 years | HTN | Non-Menthol | 32 | 23 | 65 | |||
| Menthol | 8 | 2 | 1.45 | 0.22 | 9.70 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 12 | 43 | 65 | ||||
| Menthol | 0 | 10 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 3 | 49 | 62 | ||||
| Menthol | 0 | 10 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 16 | 39 | 65 | ||||
| Menthol | 1 | 9 | 1.05 | 0.09 | 12.30 | |||
| Ages 20 to <70 years | HTN | Non-Menthol | 183 | 523 | 1020 | |||
| Menthol | 105 | 209 | 1.04 | 0.76 | 1.43 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 27 | 677 | 1018 | ||||
| Menthol | 10 | 304 | 0.76 | 0.35 | 1.65 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 15 | 691 | 1020 | ||||
| Menthol | 9 | 305 | 0.97 | 0.39 | 2.46 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 83 | 624 | 1021 | ||||
| Menthol | 31 | 283 | 1.08 | 0.57 | 2.04 | |||
Model controls for: age, gender, race/ethnicity, body mass index, PIR, and pack-years of smoking. Rostron [3].
HTN: hypertension; MI: myocardial infarction; CHF: congestive heart failure; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Table 6.
Model specified by Rostron [3]a using data from NHANES 1999–2010; unweighted counts, adjusted odds ratios (AOR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
| Stratum | Diagnosisb | Cigarette preference | Cases | Non-Cases | AOR |
95% CI |
Total N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||||
| All | HTN | Non-Menthol | 1029 | 2935 | 5731 | |||
| Menthol | 510 | 1257 | 0.87 | 0.73 | 1.03 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 191 | 3799 | 5763 | ||||
| Menthol | 59 | 1714 | 0.82 | 0.53 | 1.25 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 105 | 3876 | 5753 | ||||
| Menthol | 43 | 1729 | 1.00 | 0.62 | 1.63 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 441 | 3557 | 5772 | ||||
| Menthol | 169 | 1605 | 1.14 | 0.85 | 1.52 | |||
| Female | HTN | Non-Menthol | 457 | 1173 | 2539 | |||
| Menthol | 285 | 624 | 0.87 | 0.65 | 1.15 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 71 | 1562 | 2544 | ||||
| Menthol | 20 | 891 | 0.62 | 0.30 | 1.31 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 37 | 1593 | 2540 | ||||
| Menthol | 16 | 894 | 0.96 | 0.42 | 2.23 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 262 | 1373 | 2546 | ||||
| Menthol | 108 | 803 | 1.03 | 0.75 | 1.42 | |||
| Male | HTN | Non-Menthol | 572 | 1762 | 3192 | |||
| Menthol | 225 | 633 | 0.87 | 0.65 | 1.17 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 120 | 2237 | 3219 | ||||
| Menthol | 39 | 823 | 1.04 | 0.60 | 1.80 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 68 | 2283 | 3213 | ||||
| Menthol | 27 | 835 | 1.07 | 0.60 | 1.91 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 179 | 2184 | 3226 | ||||
| Menthol | 61 | 802 | 1.42 | 0.84 | 2.39 | |||
| Non-Hispanic Black | HTN | Non-Menthol | 176 | 215 | 1332 | |||
| Menthol | 311 | 630 | 0.93 | 0.68 | 1.27 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 28 | 364 | 1337 | ||||
| Menthol | 27 | 918 | 0.53 | 0.27 | 1.03 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 20 | 371 | 1336 | ||||
| Menthol | 24 | 921 | 0.61 | 0.30 | 1.26 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 37 | 356 | 1338 | ||||
| Menthol | 68 | 877 | 0.70 | 0.41 | 1.20 | |||
| Non-Hispanic White | HTN | Non-Menthol | 609 | 1806 | 2980 | |||
| Menthol | 126 | 439 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 1.06 | |||
| Non-Hispanic White | MI | Non-Menthol | 129 | 2288 | 2983 | |||
| Menthol | 22 | 544 | 0.85 | 0.50 | 1.42 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 63 | 2352 | 2979 | ||||
| Menthol | 14 | 550 | 1.20 | 0.60 | 2.40 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 321 | 2101 | 2988 | ||||
| Menthol | 75 | 491 | 1.18 | 0.84 | 1.66 | |||
| Mexican American | HTN | Non-Menthol | 154 | 607 | 877 | |||
| Menthol | 36 | 80 | 1.34 | 0.68 | 2.63 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 18 | 764 | 899 | ||||
| Menthol | 4 | 113 | 2.82 | 0.36 | 22.11 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 16 | 762 | 895 | ||||
| Menthol | 2 | 115 | 0.46 | 0.11 | 1.95 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 42 | 741 | 900 | ||||
| Menthol | 6 | 111 | 0.69 | 0.27 | 1.76 | |||
| Ages ≥70 years | HTN | Non-Menthol | 150 | 129 | 351 | |||
| Menthol | 41 | 31 | 0.70 | 0.39 | 1.27 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 44 | 234 | 352 | ||||
| Menthol | 10 | 64 | 0.78 | 0.29 | 2.13 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 25 | 247 | 345 | ||||
| Menthol | 8 | 65 | 0.86 | 0.30 | 2.46 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 64 | 216 | 354 | ||||
| Menthol | 11 | 63 | 0.76 | 0.35 | 1.66 | |||
| Ages 20 to <70 years | HTN | Non-Menthol | 879 | 2806 | 5380 | |||
| Menthol | 469 | 1226 | 0.84 | 0.70 | 1.00 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 147 | 3565 | 5411 | ||||
| Menthol | 49 | 1650 | 0.76 | 0.47 | 1.22 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 80 | 3629 | 5408 | ||||
| Menthol | 35 | 1664 | 0.89 | 0.49 | 1.65 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 377 | 3341 | 5418 | ||||
| Menthol | 158 | 1542 | 1.15 | 0.85 | 1.56 | |||
Model controls for: age, gender, race/ethnicity, body mass index, PIR, and pack-years of smoking. Rostron [3].
HTN: Hypertension; MI: myocardial infarction; CHF: congestive heart failure; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Table 7.
Model specified by Rostron [3]a using data from NHANES 1999–2012; unweighted counts, adjusted odds ratios (AOR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
| Stratum | Diagnosisb | Cigarette preference | Cases | Non-Cases | AOR |
95% CI |
Total N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||||
| All | HTN | Non-Menthol | 1202 | 3319 | 6615 | |||
| Menthol | 632 | 1462 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 1.06 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 218 | 4330 | 6648 | ||||
| Menthol | 66 | 2034 | 0.73 | 0.49 | 1.10 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 121 | 4419 | 6637 | ||||
| Menthol | 51 | 2046 | 0.95 | 0.62 | 1.47 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 510 | 4047 | 6658 | ||||
| Menthol | 204 | 1897 | 1.12 | 0.86 | 1.45 | |||
| Female | HTN | Non-Menthol | 515 | 1317 | 2888 | |||
| Menthol | 345 | 711 | 0.89 | 0.68 | 1.18 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 77 | 1758 | 2893 | ||||
| Menthol | 22 | 1036 | 0.60 | 0.29 | 1.22 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 44 | 1788 | 2889 | ||||
| Menthol | 19 | 1038 | 0.92 | 0.44 | 1.89 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 290 | 1547 | 2895 | ||||
| Menthol | 133 | 925 | 1.05 | 0.79 | 1.40 | |||
| Male | HTN | Non-Menthol | 687 | 2002 | 3727 | |||
| Menthol | 287 | 751 | 0.89 | 0.66 | 1.19 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 141 | 2572 | 3755 | ||||
| Menthol | 44 | 998 | 0.88 | 0.53 | 1.47 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 77 | 2631 | 3748 | ||||
| Menthol | 32 | 1008 | 1.01 | 0.59 | 1.73 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 220 | 2500 | 3763 | ||||
| Menthol | 71 | 972 | 1.25 | 0.79 | 1.99 | |||
| Non-Hispanic Black | HTN | Non-Menthol | 213 | 263 | 1597 | |||
| Menthol | 395 | 726 | 0.97 | 0.72 | 1.29 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 35 | 442 | 1602 | ||||
| Menthol | 30 | 1095 | 0.49 | 0.27 | 0.89 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 23 | 453 | 1600 | ||||
| Menthol | 28 | 1096 | 0.57 | 0.30 | 1.10 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 43 | 435 | 1603 | ||||
| Menthol | 85 | 1040 | 0.79 | 0.49 | 1.27 | |||
| Non-Hispanic White | HTN | Non-Menthol | 705 | 2024 | 3377 | |||
| Menthol | 149 | 499 | 0.86 | 0.69 | 1.07 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 146 | 2584 | 3379 | ||||
| Menthol | 24 | 625 | 0.75 | 0.45 | 1.25 | |||
| Non-Hispanic White | CHF | Non-Menthol | 74 | 2655 | 3376 | |||
| Menthol | 18 | 629 | 1.13 | 0.64 | 1.99 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 373 | 2363 | 3385 | ||||
| Menthol | 90 | 559 | 1.17 | 0.86 | 1.60 | |||
| Mexican American | HTN | Non-Menthol | 169 | 645 | 945 | |||
| Menthol | 39 | 92 | 1.33 | 0.74 | 2.37 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 19 | 816 | 967 | ||||
| Menthol | 4 | 128 | 2.41 | 0.33 | 17.75 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 17 | 814 | 963 | ||||
| Menthol | 2 | 130 | 0.39 | 0.07 | 2.11 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 44 | 792 | 968 | ||||
| Menthol | 7 | 125 | 0.61 | 0.27 | 1.36 | |||
| Ages ≥70 years | HTN | Non-Menthol | 172 | 145 | 401 | |||
| Menthol | 52 | 32 | 0.85 | 0.48 | 1.49 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 49 | 267 | 402 | ||||
| Menthol | 12 | 74 | 1.01 | 0.42 | 2.44 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 28 | 282 | 395 | ||||
| Menthol | 9 | 76 | 0.96 | 0.33 | 2.73 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 72 | 246 | 404 | ||||
| Menthol | 13 | 73 | 0.87 | 0.42 | 1.79 | |||
| Ages 20 to <70 years | HTN | Non-Menthol | 1030 | 3174 | 6214 | |||
| Menthol | 580 | 1430 | 0.85 | 0.71 | 1.01 | |||
| MI | Non-Menthol | 169 | 4063 | 6246 | ||||
| Menthol | 54 | 1960 | 0.64 | 0.41 | 1.00 | |||
| CHF | Non-Menthol | 93 | 4137 | 6242 | ||||
| Menthol | 42 | 1970 | 0.81 | 0.48 | 1.37 | |||
| COPD | Non-Menthol | 438 | 3801 | 6254 | ||||
| Menthol | 191 | 1824 | 1.11 | 0.84 | 1.45 | |||
Model controls for: age, gender, race/ethnicity, body mass index, PIR, and pack-years of smoking. Rostron [3].
HTN: hypertension; MI: myocardial infarction; CHF: congestive heart failure; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Table 8.
Analysis of NHANES 1999‐2012a; proportionate distribution of menthol and non-menthol cigarette preference, unweighted counts, adjusted odds ratios (AOR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
| Stratum | Diagnosisb | Cigarette preference | Cases | Non-Cases | AOR |
95% CI |
Total N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||||
| All | HTNc | Non-Menthol | 1316 | 3623 | 7238 | |||
| Menthol | 703 | 1596 | 0.91 | 0.76 | 1.07 | |||
| MId | Non-Menthol | 218 | 4229 | 6509 | ||||
| Menthol | 66 | 1996 | 0.76 | 0.50 | 1.14 | |||
| CHFe | Non-Menthol | 122 | 4443 | 6671 | ||||
| Menthol | 51 | 2055 | 1.00 | 0.66 | 1.54 | |||
| COPDf | Non-Menthol | 507 | 3924 | 6486 | ||||
| Menthol | 202 | 1853 | 1.15 | 0.88 | 1.50 | |||
| Female | HTNc | Non-Menthol | 557 | 1416 | 3137 | |||
| Menthol | 381 | 783 | 0.89 | 0.68 | 1.16 | |||
| MId | Non-Menthol | 77 | 1731 | 2844 | ||||
| Menthol | 22 | 1014 | 0.98 | 0.60 | 1.62 | |||
| CHFe | Non-Menthol | 44 | 1796 | 2902 | ||||
| Menthol | 19 | 1043 | 1.15 | 0.64 | 2.07 | |||
| COPDf | Non-Menthol | 288 | 1513 | 2832 | ||||
| Menthol | 133 | 898 | 1.09 | 0.81 | 1.47 | |||
| Male | HTNc | Non-Menthol | 759 | 2207 | 4101 | |||
| Menthol | 322 | 813 | 0.921 | 0.70 | 1.21 | |||
| MId | Non-Menthol | 141 | 2498 | 3665 | ||||
| Menthol | 44 | 982 | 0.61 | 0.29 | 1.28 | |||
| CHFe | Non-Menthol | 78 | 2647 | 3769 | ||||
| Menthol | 32 | 1012 | 1.00 | 0.62 | 1.63 | |||
| COPDf | Non-Menthol | 219 | 2411 | 3654 | ||||
| Menthol | 69 | 955 | 1.24 | 0.78 | 1.95 | |||
| Non-Hispanic Black | HTNc | Non-Menthol | 745 | 2146 | 3594 | |||
| Menthol | 165 | 538 | 0.88 | 0.70 | 1.09 | |||
| MId | Non-Menthol | 146 | 2549 | 3336 | ||||
| Menthol | 24 | 617 | 0.79 | 0.47 | 1.33 | |||
| CHFe | Non-Menthol | 75 | 2659 | 3383 | ||||
| Menthol | 18 | 631 | 1.14 | 0.62 | 2.13 | |||
| COPDf | Non-Menthol | 373 | 2322 | 3334 | ||||
| Menthol | 90 | 549 | 1.23 | 0.90 | 1.69 | |||
| Non-Hispanic White | HTNc | Non-Menthol | 241 | 296 | 1768 | |||
| Menthol | 441 | 790 | 0.97 | 0.74 | 1.29 | |||
| MId | Non-Menthol | 35 | 434 | 1581 | ||||
| Menthol | 30 | 1082 | 0.50 | 0.28 | 0.91 | |||
| Non-Hispanic White | CHFe | Non-Menthol | 23 | 453 | 1606 | |||
| Menthol | 28 | 1102 | 0.51 | 0.26 | 0.99 | |||
| COPDf | Non-Menthol | 42 | 426 | 1574 | ||||
| Menthol | 83 | 1023 | 0.70 | 0.43 | 1.14 | |||
| Mexican American | HTNc | Non-Menthol | 194 | 747 | 1091 | |||
| Menthol | 44 | 106 | 1.01 | 0.61 | 1.68 | |||
| MId | Non-Menthol | 20 | 772 | 911 | ||||
| Menthol | 4 | 115 | 2.11 | 0.35 | 12.87 | |||
| CHFe | Non-Menthol | 17 | 825 | 975 | ||||
| Menthol | 2 | 131 | 0.51 | 0.11 | 2.27 | |||
| COPDf | Non-Menthol | 44 | 739 | 902 | ||||
| Menthol | 7 | 112 | 0.62 | 0.27 | 1.41 | |||
| Ages ≥70 years | HTNc | Non-Menthol | 191 | 166 | 454 | |||
| Menthol | 61 | 36 | 0.98 | 0.52 | 1.83 | |||
| MId | Non-Menthol | 49 | 268 | 403 | ||||
| Menthol | 12 | 74 | 1.11 | 0.49 | 2.48 | |||
| CHFe | Non-Menthol | 29 | 284 | 399 | ||||
| Menthol | 9 | 77 | 0.76 | 0.27 | 2.14 | |||
| COPDf | Non-Menthol | 71 | 243 | 399 | ||||
| Menthol | 13 | 72 | 0.80 | 0.35 | 1.80 | |||
| Ages 20 to <70 years | HTNc | Non-Menthol | 1125 | 3457 | 6784 | |||
| Menthol | 642 | 1560 | 0.91 | 0.76 | 1.08 | |||
| MId | Non-Menthol | 169 | 3961 | 6106 | ||||
| Menthol | 54 | 1922 | 0.70 | 0.45 | 1.10 | |||
| CHFe | Non-Menthol | 93 | 4159 | 6272 | ||||
| Menthol | 42 | 1978 | 1.02 | 0.65 | 1.59 | |||
| COPDf | Non-Menthol | 436 | 3681 | 6087 | ||||
| Menthol | 189 | 1781 | 1.18 | 0.90 | 1.56 | |||
Models developed using purposeful selection of covariates [1]. The same covariates were included in the models run in the subdomains as were included in the model for the population, overall.
MI: Myocardial infarction; CHF: congestive heart failure; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Odds of hypertension diagnosis controlling for age, gender, BMI, education, ethnicity, gender*ethnicity, BMI*education.
Odds of myocardial infarction (MI) diagnosis controlling for age, age started smoking, PIR, education, race/ethnicity, BMI*PIR, race/ethnicity*education.
Odds of congestive heart failure (CHF) diagnosis controlling for age, BMI, PIR, education, BMI*education.
Odds of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease diagnosis controlling for age, gender, cigarettes smoked per day, days smoked in last 30, age started smoking, BMI, PIR, education, gender*days smoked in last 30, gender*race/ethnicity, education* days smoked in last 30, PIR*education, PIR*race/ethnicity.
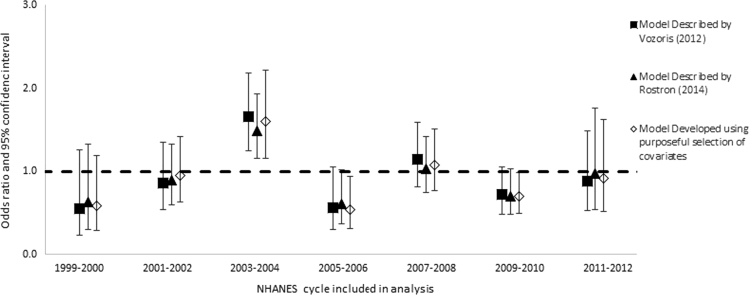
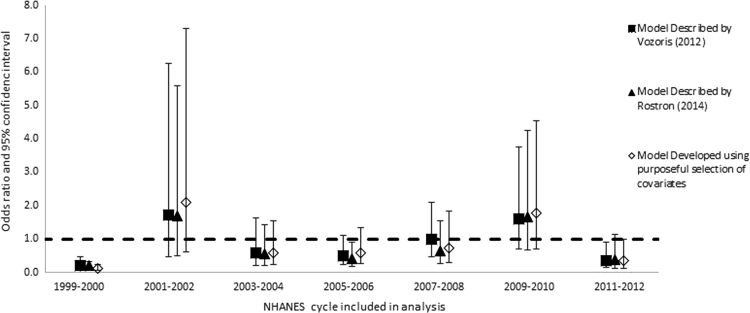
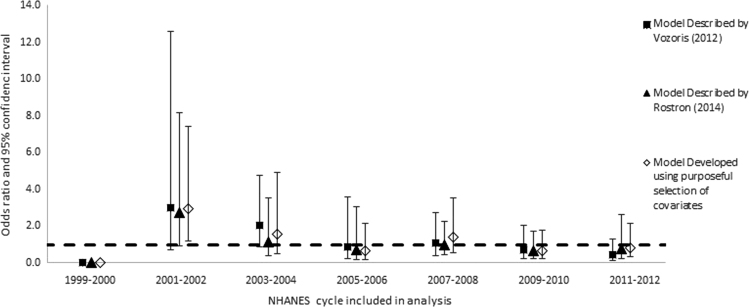
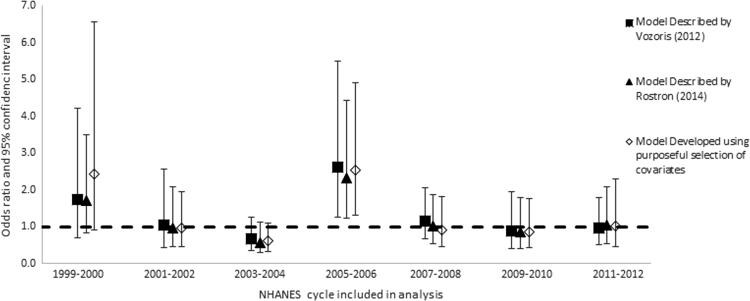
Once we determined the covariates to include in the model (main effects), we explored all the possible interactions between the covariates (excluding cigarette type). We added all interaction terms with p-values less than or equal to 0.1 to the model individually, along with the main effect terms, and retained them if the relevant coefficients in the fully adjusted model were statistically significant, with p-values of 0.05 or less. We retained statistically significant interaction terms in the model only if one or both main effects were also statistically significant. We used domain variables to define strata according to race/ethnicities, genders, and age groups, but did not repeat the model building process. We then re-ran each model for individual cycles of the NHANES in order to determine if there were anomalous or secular patterns in risk of any outcome that might be overlooked in the combined analysis (Fig. 1, Fig. 2, Fig. 3, Fig. 4).
Fig. 1.
Odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals: risk of hypertension among all smokers of menthol vs. non-menthol cigarettes according to three different models, individual cycles of the NHANES from 1999 through 2012.
Fig. 2.
Odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals: risk of myocardial infarction among all smokers of menthol vs. non-menthol cigarettes according to three different models, individual cycles of the NHANES from 1999 through 2012.
Fig. 3.
Odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals: risk of congestive heart failure among all smokers of menthol vs. non-menthol cigarettes according to three different models, individual cycles of the NHANES from 1999 through 2012.
Fig. 4.
Odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals: Risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among all smokers of menthol vs. non-menthol cigarettes according to three different models, individual cycles of the NHANES from 1999 through 2012.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Vozoris for discussing the analytical methods he used, and graciously confirming the reporting error in the previously published paper. In addition, we thank Allison Franzen and Sara Oglesbee for their assistance in formatting the tables and text for submission. The editor of Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, and the reviewers assigned to this paper, provided highly useful recommendations; our paper was greatly improved by following their suggestions.
Footnotes
Transparency data associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.dib.2017.04.021.
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.dib.2017.04.021.
Transparency document. Supplementary material
Supplementary material
.
Appendix A. Supplementary material
Supplementary material
.
References
- 1.Hosmer D., Jr, Lemeshow S., Sturdivant R. Applied Logistic Regression. Third ed. John Wiley & Soncs, Inc.; Hoboken, New Jersey: 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Johnson C., Paulose-Ram R., Ogden C., Carroll M., Kruszon-Moran D., Dohrmann S., Curtin L. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: Analytic Guidelines, 1999–2010. Natl. Cent. Health Stat. Vital Health Stat. 2013;2(161) 〈http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/survey_methods.htm〉 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rostron B. Menthol cigarette use and stroke risk among US smokers: a critical reappraisal. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014;174(5):808–809. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.9600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Van Landingham C., Fuller W., Mariano G., Marano K., Curtin G., Sulsky S. Stroke risk among menthol versus non-menthol cigarette smokers in the United States: analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017;85:65–69. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2017.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Vozoris N. Mentholated cigarettes and cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases: a population-based study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012;172(7):590–591. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2012.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material
Supplementary material