Abstract
When intact pea (Pisum sativum L.) plants are illuminated, the glycolytic enzyme phosphofructokinase is inactivated. In crude extracts the enzyme is inhibited by dithiothreitol. It would seem that this cytoplasmic enzyme, like glucose-6-P dehydrogenase, is light-inactivated when the enzymes of photosynthetic carbon metabolism are light-activated.
Full text
PDF


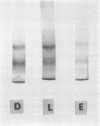
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson L. E. Activation of pea leaf chloroplast sedoheptulose 1,7-diphosphate phosphatase by light and dithiothreitol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 5;59(3):907–913. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. E., Advani V. R. Chloroplast and cytoplasmic enzymes: three distinct isoenzymes associated with the reductive pentose phosphate cycle. Plant Physiol. 1970 May;45(5):583–585. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.5.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. E., Lim T. C. Chloroplast glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase: light-dependent change in the enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 1;27(2):189–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80616-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. E., Ng T. C., Park K. E. Inactivation of pea leaf chloroplastic and cytoplasmic glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenases by light and dithiothreitol. Plant Physiol. 1974 Jun;53(6):835–839. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.6.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. E. Regulation of pea leaf ribulose-5-phosphate kinase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 10;321(2):484–488. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassham J. A., Kirk M., Jensen R. G. Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. I. Diffusion of labeled photosynthetic intermediates between isolated chloroplasts and suspending medium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 15;153(1):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B., Schürmann P., Kalberer P. P. Ferredoxin-activated fructose diphosphatase of spinach chloroplasts. Resolution of the system, properties of the alkaline fructose diphosphatase component, and physiological significance of the ferredoxin-linked activation. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):5952–5959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis D. T., Coultate T. P. The regulatory properties of a plant phosphofructokinase during leaf development. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 12;146(1):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D., Slack C. R. Studies on the mechanism of activation and inactivation of pyruvate, phosphate dikinase. A possible regulatory role for the enzyme in the C4 dicarboxylic acid pathway of photosynthesis. Biochem J. 1969 May;112(5):549–558. doi: 10.1042/bj1120549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. S., Hatch M. D. Properties and regulation of leaf nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-malate dehydrogenase and 'malic' enzyme in plants with the C4-dicarboxylic acid pathway of photosynthesis. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):273–280. doi: 10.1042/bj1190273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly G. J., Turner J. F. Cooperativity in pea-seed phosphofructokinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 22;242(3):559–565. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90149-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly G. J., Turner J. F. The regulation of pea-seed phosphofructokinase by 6-phosphogluconate, 3-phosphoglycerate, 2-phosphoglycerate and phosphoenolpyruvate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun;208(3):360–367. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90207-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latzko E., von Garnier R., Gibbs M. Effect of photosynthesis, photosynthetic inhibitors and oxygen on the activity of ribulose 5-phosphate kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970;39(6):1140–1144. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90678-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K. Methods for starch-gel electrophoresis of sarcoplasmic proteins. An investigation of the relative mobilities of the glycolytic enzymes from the muscles of a variety of species. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(2):139–150. doi: 10.1042/bj1070139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. C., Fall L., Walton G. M., Atkinson D. E. Interaction between energy charge and metabolite modulation in the regulation of enzymes of amphibolic sequences. Phosphofructokinase and pyruvate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):4041–4045. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]