Nucl. Acids Res. (2013) 41 (2): 881–899. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1134
In Figure 8A, the Actin control has been duplicated from:
Figure 8A.
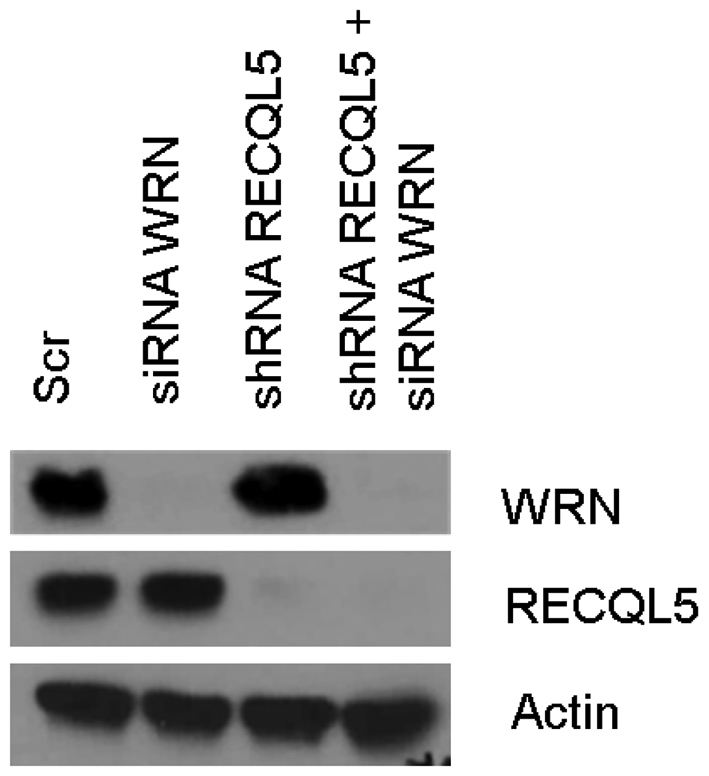
Transient depletion of WRN (using siRNA–WRN) was performed in stable RECQL5 knockdown cells of GM637 fibroblasts. The depletion efficiency was ∼90%.
RECQ1 is required for cellular resistance to replication stress and catalyzes strand exchange on stalled replication fork structures.
Popuri V, Croteau DL, Brosh RM Jr, Bohr VA.
Cell Cycle. 2012 Nov 15;11(22):4252-65. doi: 10.4161/cc.22581.
After review of the original raw data files, the Authors have identified two western blots derived from these experiments. A new Figure 8A is provided below. The original files are also enclosed as Supplementary data for transparency.
The Authors apologise to the Readers for the inconvenience caused.
Supplementary Material
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


