Abstract
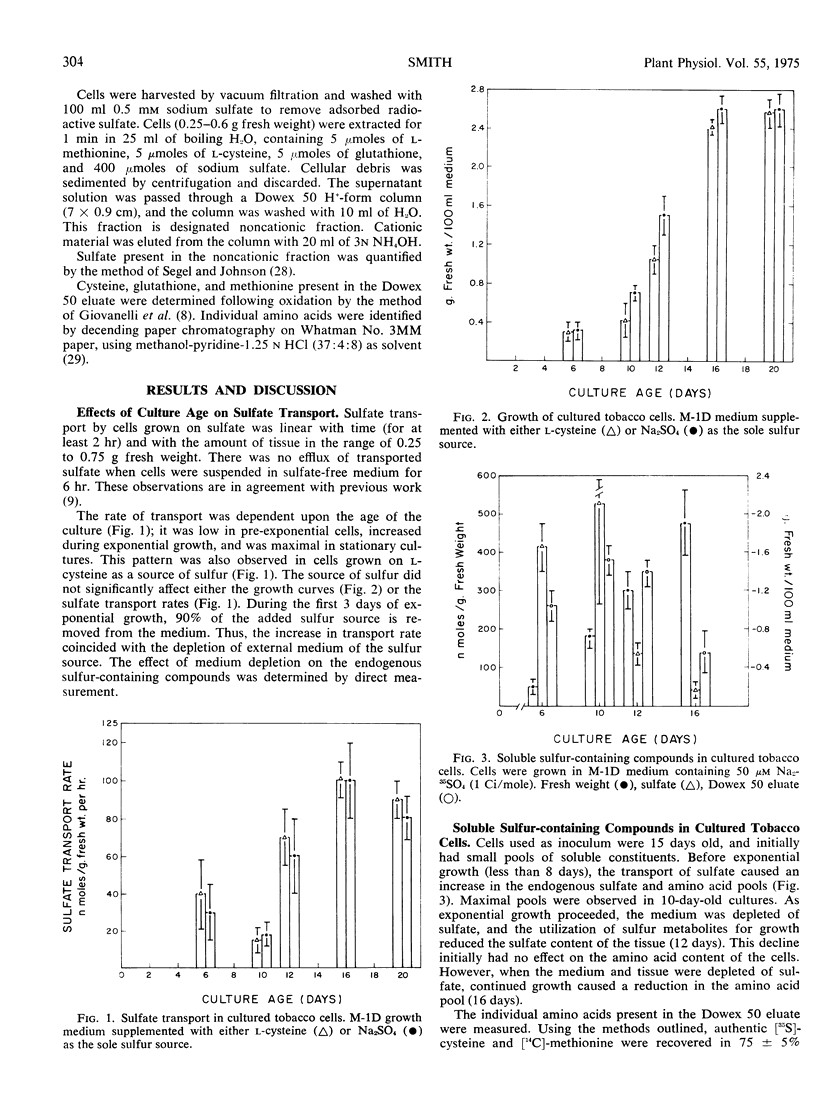
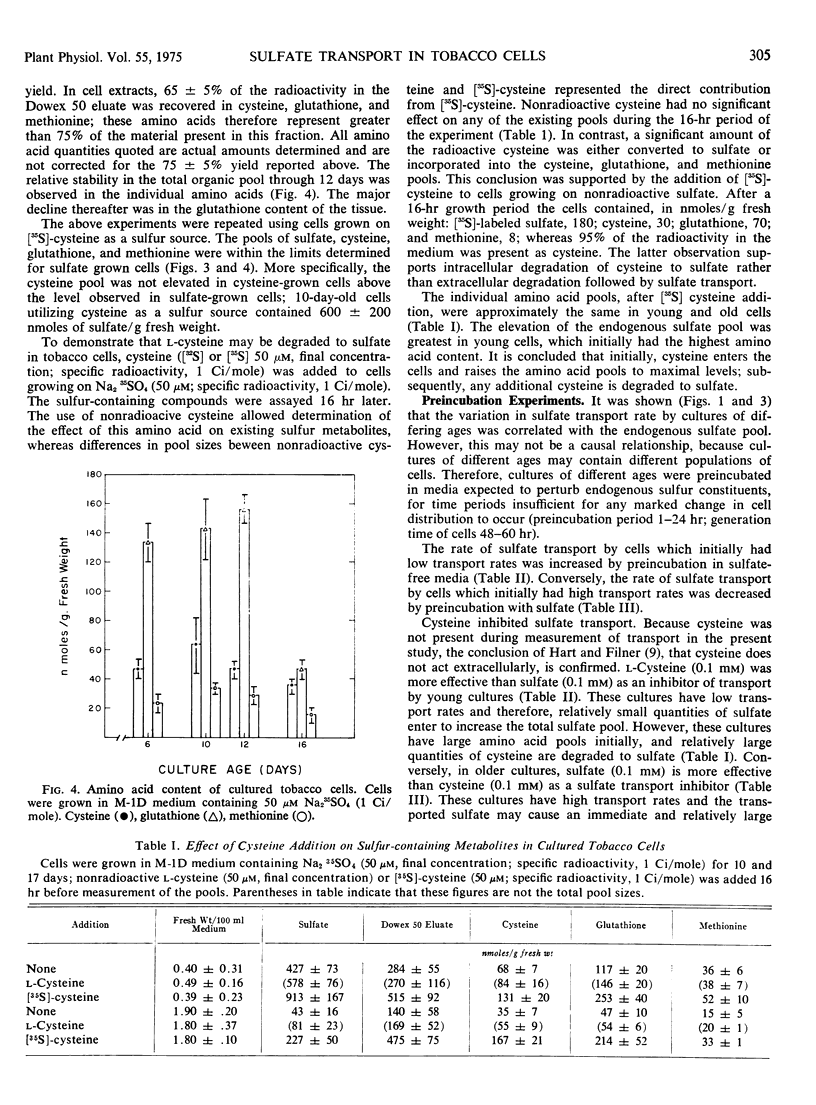
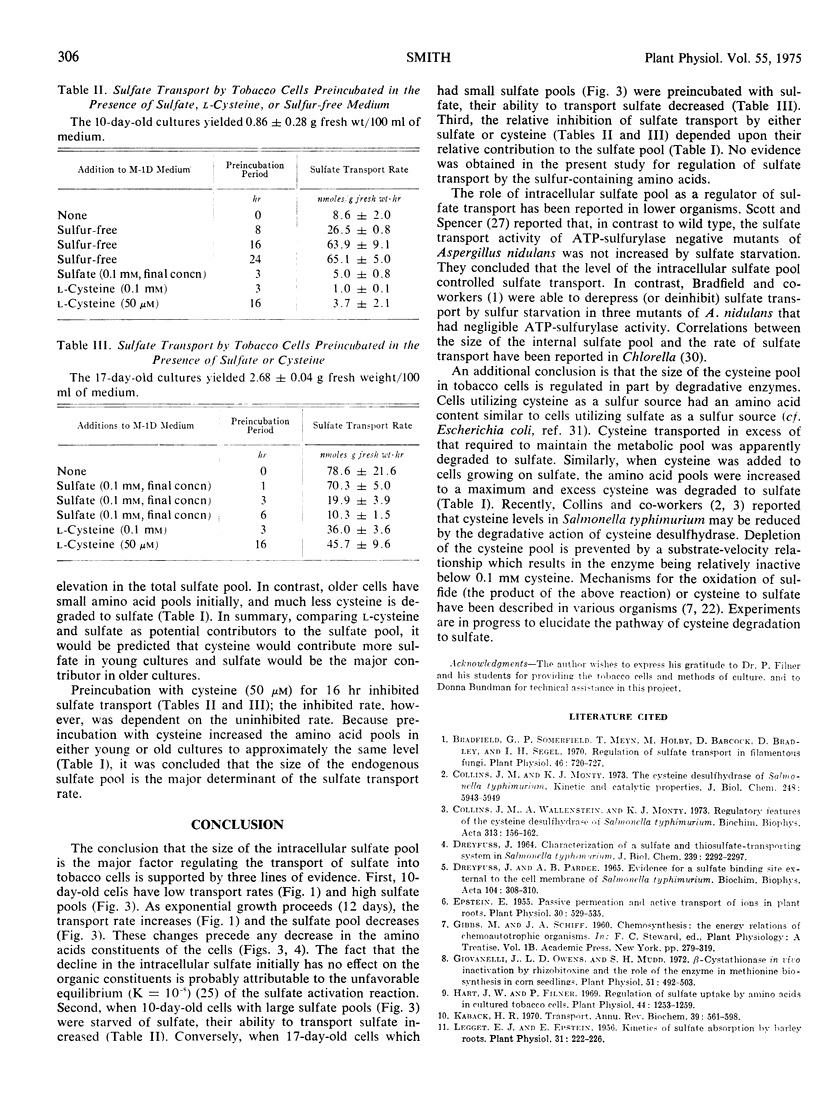
Sulfate transport by tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L. var. Xanthi) cells cultured on either l-cysteine or sulfate as a sole sulfur source was measured. The transport rate on either sulfur source was low during pre-exponential growth, increased during exponential growth, and was maximal in late exponential cells. The initial increase in transport rate was correlated with a decline in the intracellular sulfate, but was not correlated with the amino acid content of the cells which remained relatively constant before the depletion of the endogenous sulfate pool. The previously reported inhibition of sulfate transport by l-cysteine was shown to be caused by an elevation in intracellular sulfate resulting from the degradation of cysteine to sulfate. It is proposed that the intracellular sulfate pool is the major factor regulating the entry of sulfate into tobacco cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradfield G., Somerfield P., Meyn T., Holby M., Babcock D., Bradley D., Segel I. H. Regulation of sulfate transport in filamentous fungi. Plant Physiol. 1970 Nov;46(5):720–727. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.5.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. M., Monty K. J. The cysteine desulfhydrase of Salmonella typhimurium. Kinetic and catalytic properties. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):5943–5949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DREYFUSS J. CHARACTERIZATION OF A SULFATE- AND THIOSULFATE-TRANSPORTING SYSTEM IN SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2292–2297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss J., Pardee A. B. Evidence for a sulfate-binding site external to the cell membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jun 15;104(1):308–310. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90256-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E. Passive Permeation and Active Transport of Ions in Plant Roots. Plant Physiol. 1955 Nov;30(6):529–535. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.6.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart J. W., Filner P. Regulation of sulfate uptake by amino acids in cultured tobacco cells. Plant Physiol. 1969 Sep;44(9):1253–1259. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.9.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:561–598. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.003021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluf G. A. Control of the synthesis, activity, and turnover of enzymes of sulfur metabolism in Neurospora crassa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jun;150(2):714–724. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluf G. A. Genetic and biochemical studies of distinct sulfate permease species in different developmental stages of Neurospora crassa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 May;138(1):254–263. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90306-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluf G. A. Genetic and metabolic controls for sulfate metabolism in Neurospora crassa: isolation and study of chromate-resistant and sulfate transport-negative mutants. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):716–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.716-721.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluf G. A., Metzenberg R. L. Positive control by the cys-3 locus in regulation of sulfur metabolism in Neurospora. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):423–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota N., Galsworthy P. R., Pardee A. B. Genetics of sulfate transport by Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1053-1062.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. Crystallization of a sulfate-binding protein (permease) from Salmonella typhimurium. Science. 1967 Jun 23;156(3782):1627–1628. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3782.1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B., Prestidge L. S., Whipple M. B., Dreyfuss J. A binding site for sulfate and its relation to sulfate transport into Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 10;241(17):3962–3969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. Purification and properties of a sulfate-binding protein from Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5886–5892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B., Watanabe K. Location of sulfate-binding protein in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1049–1054. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1049-1054.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS P. W., LIPMANN F. Enzymatic synthesis of adenosine-5'-phosphosulfate. J Biol Chem. 1958 Sep;233(3):686–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts K. R., Marzluf G. A. The specific interaction of chromate with the dual sulfate permease systems of Neurospora crassa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Feb;142(2):651–659. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90531-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEGEL I. H., JOHNSON M. J. Accumulation of intracellular inorganic sulfate by Penicillium chrysogenum. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jan;81:91–98. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.1.91-98.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloger M., Owens L. D. Control of Free Methionine Production in Wild Type and Ethionine-resistant Mutants of Chlorella sorokiniana. Plant Physiol. 1974 Mar;53(3):469–473. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.3.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallée M., Jeanjean R. Le système de transport de SO42--chez Chlorella pyrenoidosa et sa régulation. II. Recherches sur la régulation de l'entrée. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 11;150(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheldrake J. F. Intracellular concentration of cysteine in Escherichia coli and its relation to repression of the sulphate-activating enzymes. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):697–699. doi: 10.1042/bj1050697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto L. A., Segel I. H. The inorganic sulfate transport system of Penicillium chrysogenum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Jun;114(3):523–538. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90376-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


