Abstract
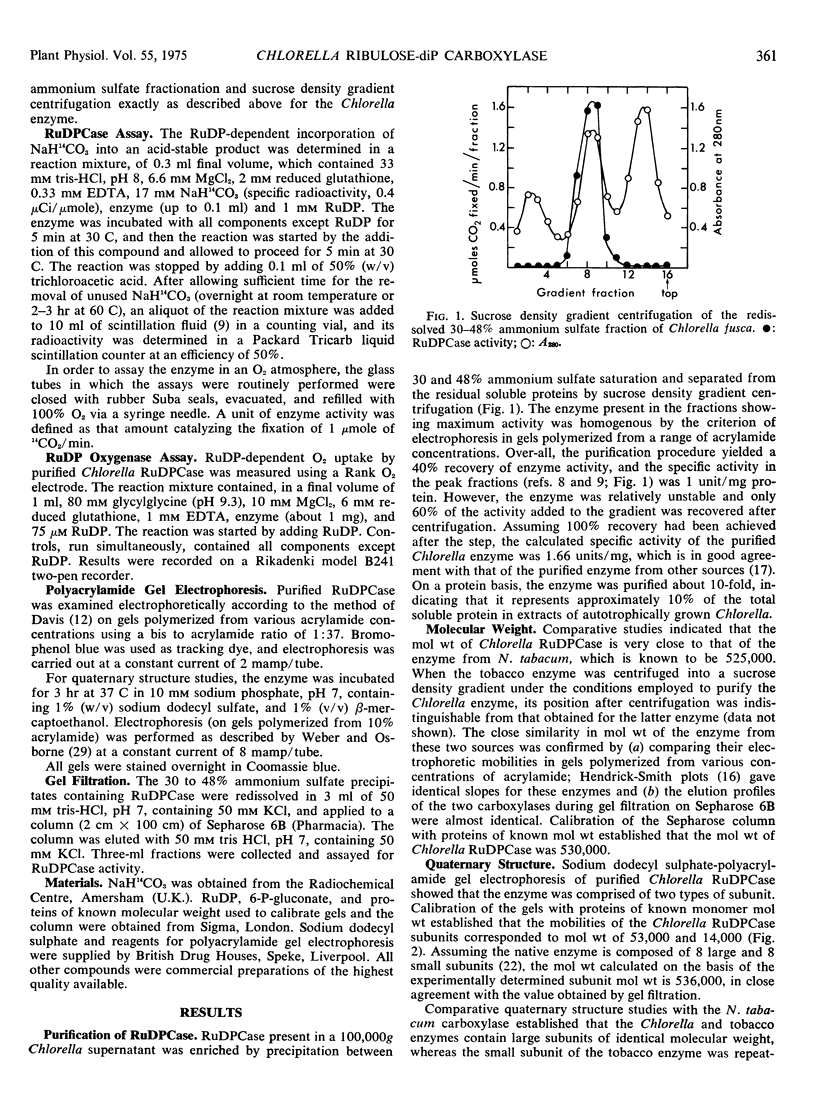
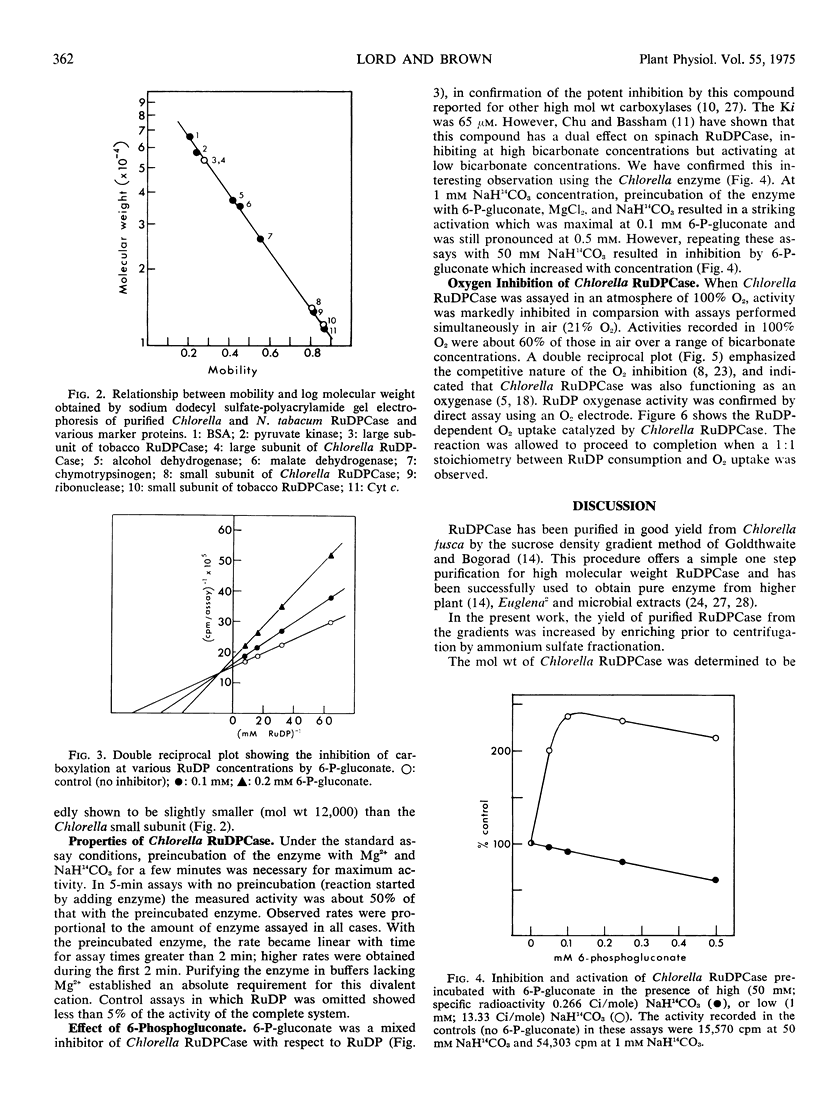
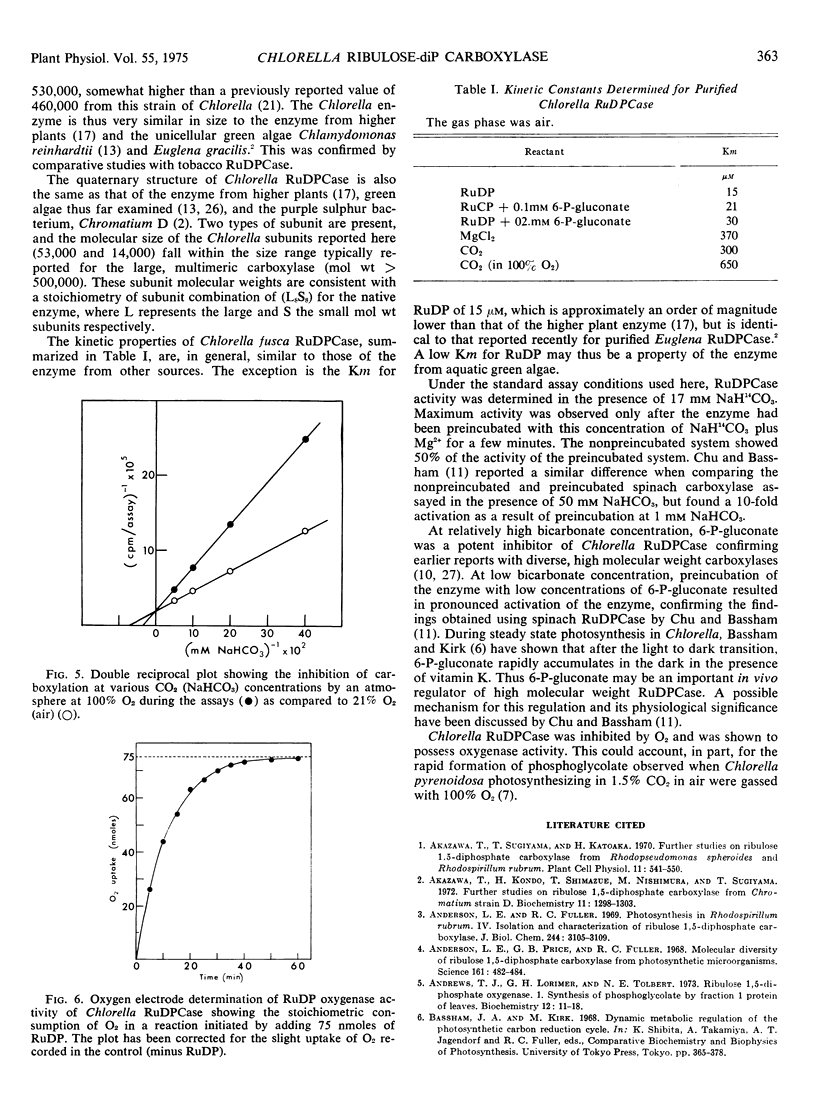
Ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase has been purified from extracts of autotrophically grown Chlorella fusca by ammonium sulfate precipitation and centrifugation on a linear sucrose density gradient. The enzyme was homogeneous by the criterion of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The molecular weight of the enzyme was 530,000, and it was composed of two types of subunit of molecular weight 53,000 and 14,000. Ribulose 1,5-diphosphate, CO2, and Mg2+ had Michaelis constant values of 15 μm, 0.3 mm, and 0.37 mm, respectively. At high bicarbonate concentration (17 mm and 50 mm), 6-phosphogluconate inhibited the enzyme, the inhibition being noncompetitive with respect to ribulose 1,5-diphosphate (Ki 0.065 mm), whereas at low bicarbonate concentration (1 mm), 6-phosphogluconate activated the enzyme. Oxygen was a competitive inhibitor with respect to CO2, suggesting the enzyme also functions as an oxygenase. This was confirmed by direct assay, a 1: 1 stoichiometry between ribulose 1,5-diphosphate consumed and O2 uptake being observed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akazawa T., Kondo H., Shimazue T., Nishimura M., Sugiyama T. Further studies on ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Chromatium strain D. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 28;11(7):1298–1303. doi: 10.1021/bi00757a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. E., Fuller R. C. Photosynthesis in Rhodospirillum rubrum. IV. Isolation and characterization of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3105–3109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews T. J., Lorimer G. H., Tolbert N. E. Ribulose diphosphate oxygenase. I. Synthesis of phosphoglycolate by fraction-1 protein of leaves. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):11–18. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassham J. A., Kirk M. Sequence of Formation of Phosphoglycolate and Glycolate in Photosynthesizing Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Plant Physiol. 1973 Nov;52(5):407–411. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.5.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes G., Ogren W. L. Oxygen inhibition and other properties of soybean ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2171–2176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Activation and inhibition of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phosphogluconate. Plant Physiol. 1973 Oct;52(4):373–379. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.4.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Inhibition of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phosphogluconate. Plant Physiol. 1972 Aug;50(2):224–227. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.2.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Givan A. L., Criddle R. S. Ribulosediphosphate carboxylase from Chlamydomonas reinhardi: purification, properties and its mode of synthesis in the cell. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Mar;149(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90309-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldthwaite J. J., Bogorad L. A one-step method for the isolation and determination of leaf ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Anal Biochem. 1971 May;41(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Andrews T. J., Tolbert N. E. Ribulose diphosphate oxygenase. II. Further proof of reaction products and mechanism of action. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):18–23. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Denend A. R. Ribulose diphosphate carboxylase from autotrophic microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):633–642. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.633-642.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura M., Takabe T., Sugiyama T., Akazawa T. Structure and function of chloroplast proteins. XIX. Dissociation of spinach leaf ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by p-mercuribenzoate. J Biochem. 1973 Nov;74(5):945–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Ito T., Akazawa T. Subunit structure of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Chlorella ellipsoidea. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 31;10(18):3406–3411. doi: 10.1021/bi00794a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Matsumoto C., Akazawa T., Miyachi S. Structure and function of chloroplast proteins. VII. Ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase of Chlorella ellipsoidea. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Feb;129(2):597–602. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. One-step isolation of microbial ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(3):231–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00696237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


