Abstract
Metabolism of [3H]gibberellin A1 ([3H]GA1) was followed in intact seedlings and excised apices and leaf tissue of both dwarf and normal (tall) plants of d-5 maize (Zea mays L.). The three metabolites produced were tentatively identified as [3H]GAs, [3H]GAs-glucoside ([3H]GAs-glu), and [3H]GA1-X, an unknown.
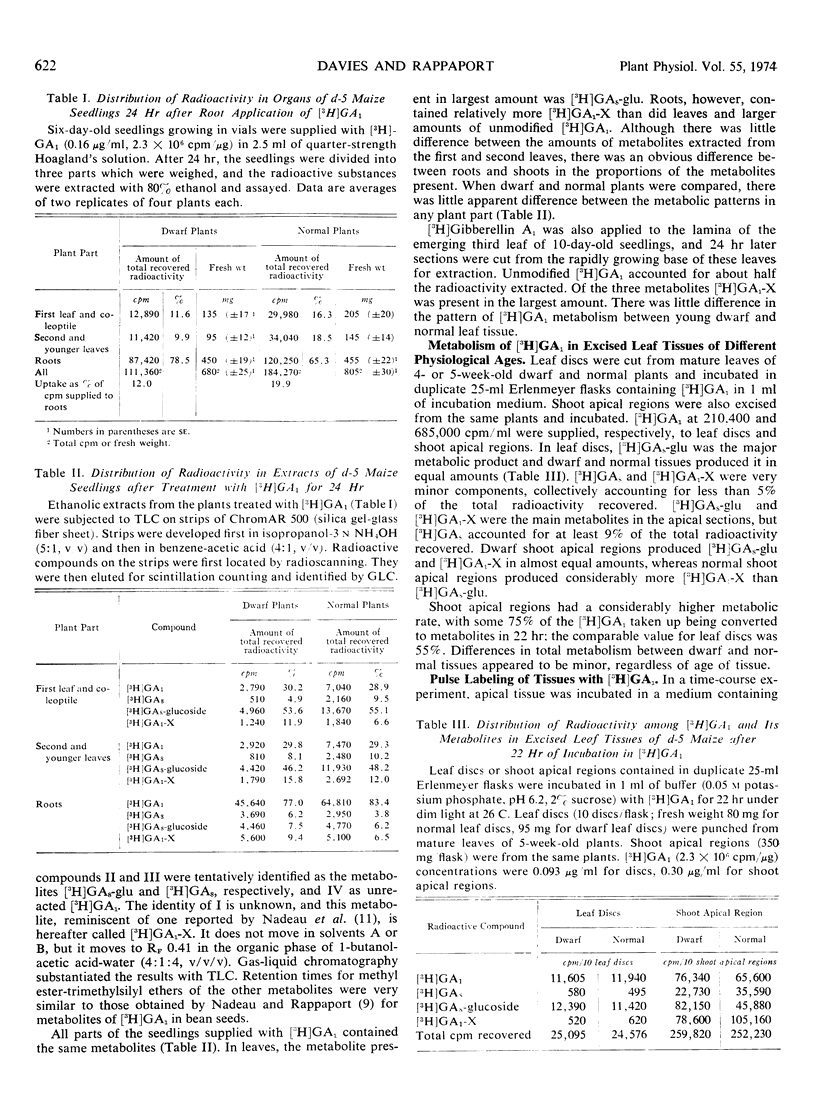
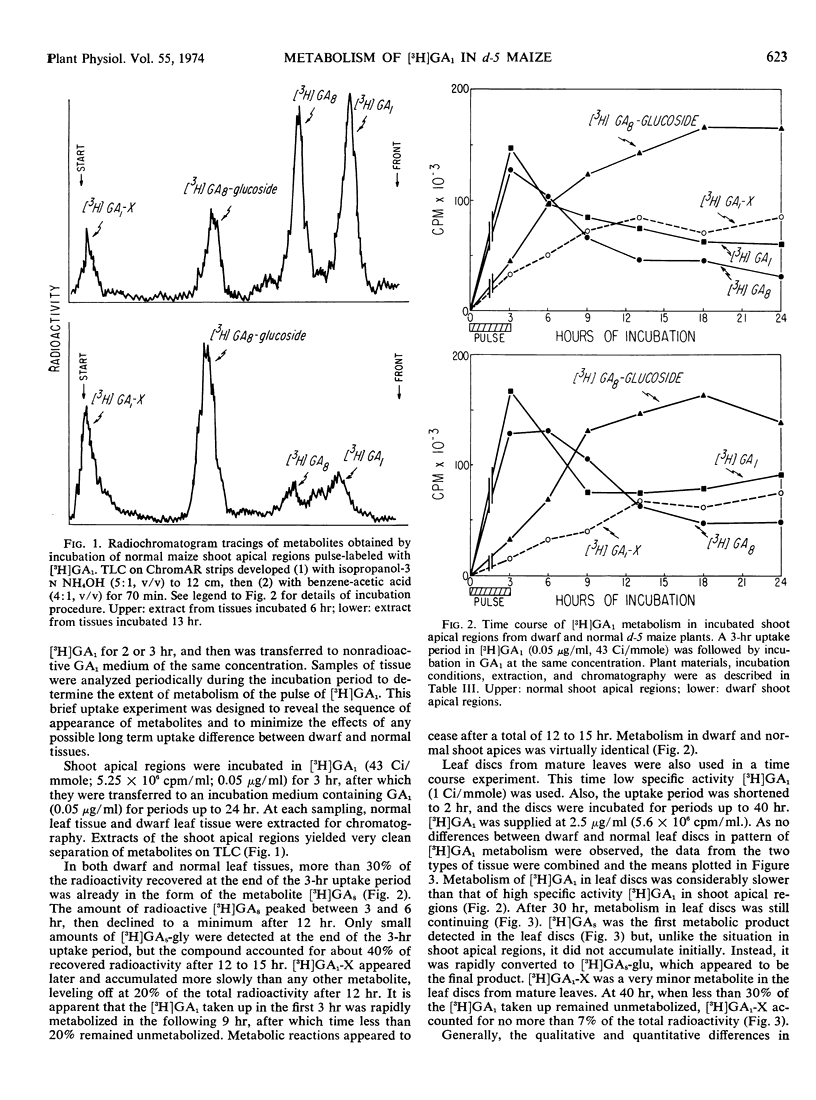
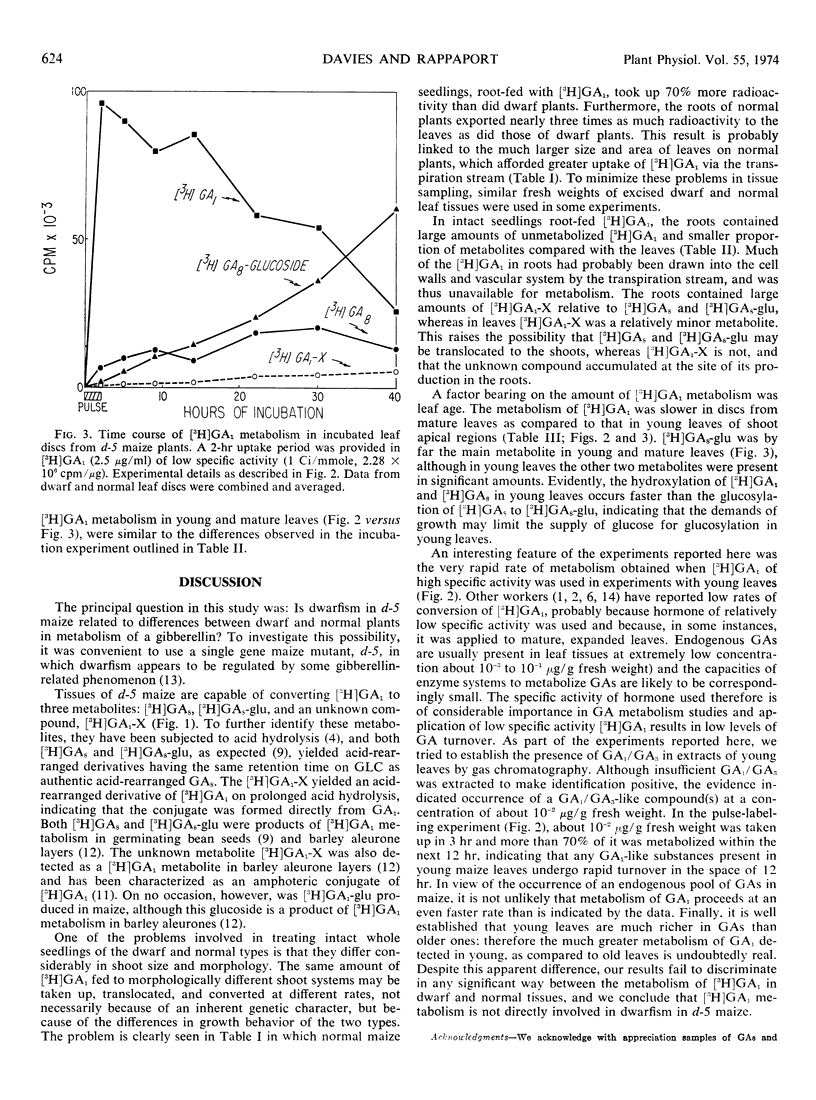
In 3-hour, pulse-labeling experiments with tissues of incubated, expanding leaves, more than 70% of the [3H]GA1 taken up was metabolized to the three products within 12 to 15 hours. [3H]GA1 fed to the roots of 7-day-old seedlings was readily translocated to the leaves, and all three metabolites were found in both roots and leaves. [3H]GA1-X was the major metabolite in roots, whereas in leaves the major metabolite was [3H]GAs-glu. There were no consistent differences in [3H]GA1 metabolism between dwarf and normal plants, indicating that dwarfism in d-5 maize is not associated with modified GA1 metabolism.
In excised, mature leaf tissue, [3H]GA1 metabolism was slower than in excised, young leaf tissue. Mature leaf tissues produced [3H]GAs-glu as by far the major metabolite, with [3H]GAs and [3H]GA1-X as minor metabolites. In contrast, in young leaves the three metabolites appeared sequentially in significant proportions: [3H]GA8 first, followed by [3H]GAs-glu and, finally, [3H]GA1-X.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barendse G. W., Kende H., Lang A. Fate of radioactive gibberellin a(1) in maturing and germinating seeds of peas and Japanese morning glory. Plant Physiol. 1968 May;43(5):815–822. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.5.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES D. F. EXAMINATION OF THE GIBBERELLINS OF ZEA MAYS AND PHASEOLUS MULTIFLORUS USING THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY. Nature. 1964 Jun 27;202:1309–1310. doi: 10.1038/2021309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kende H. Preparation of radioactive gibberellin a(1) and its metabolism in dwarf peas. Plant Physiol. 1967 Nov;42(11):1612–1618. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.11.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau R., Rappaport L. An amphoteric conjugate of [h]gibberellin a(1) from barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1974 Dec;54(6):809–812. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.6.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


