Abstract
Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.49) has been partially purified from Anacystis nidulans and Anabaena flos-aquae by means of ammonium sulfate fractionation and exclusion gel chromatography and the kinetic properties determined.
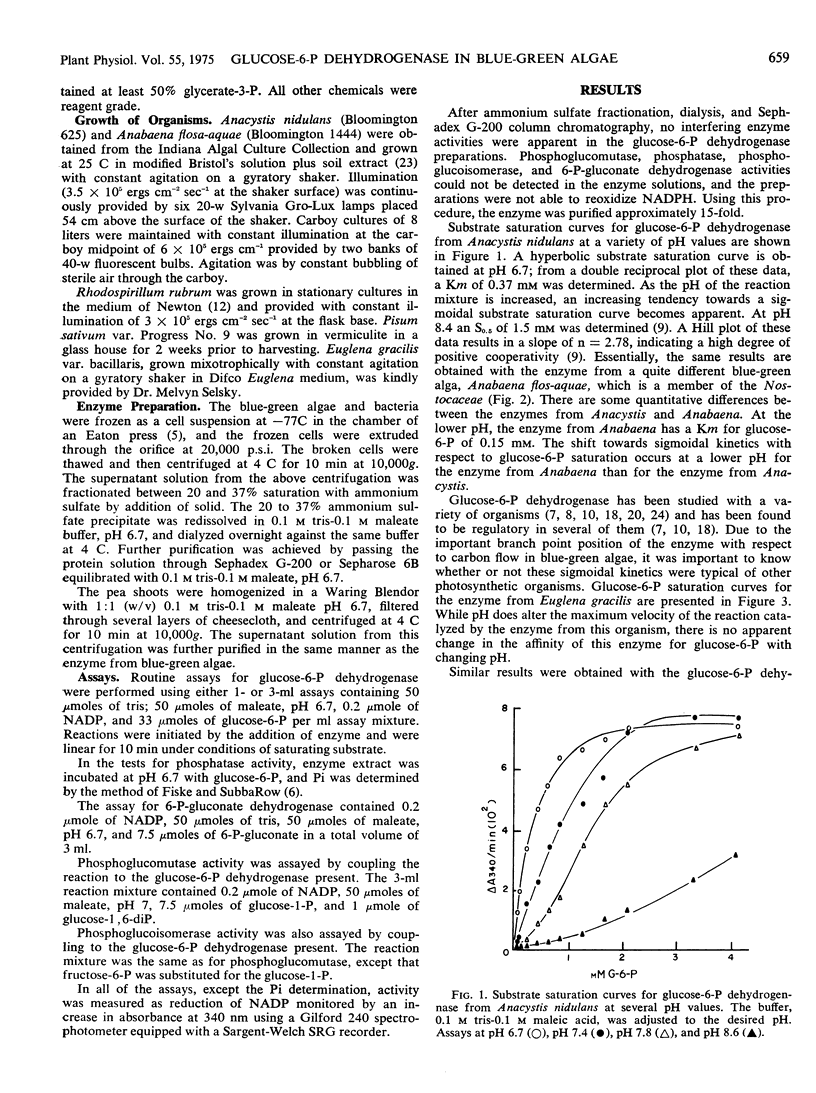
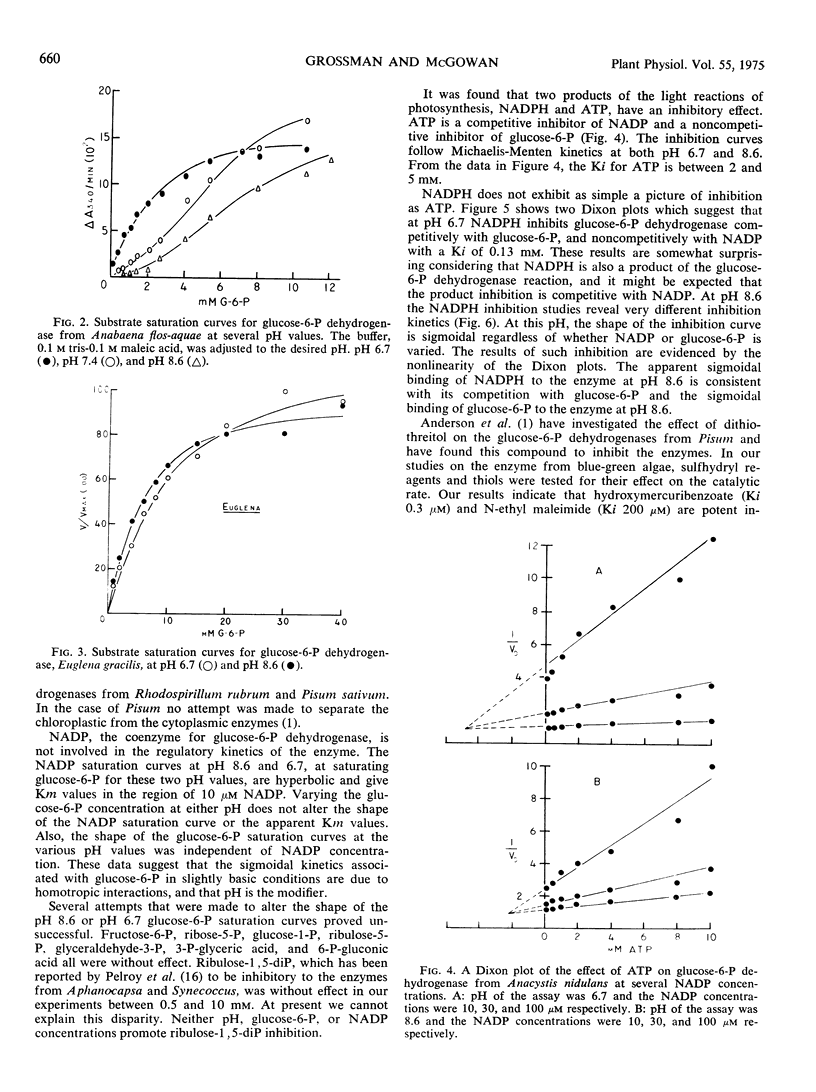
Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase from these blue-green algae exhibits Michaelis-Menten kinetics at pH 6.7. At this pH, Km values of 0.37 mm for glucose 6-phosphate and 10 μm for NADP were determined. At a pH above 7.4, the enzyme exhibits sigmoidal kinetics with respect to glucose 6-phosphate saturation but the saturation curve for NADP remains hyperbolic.
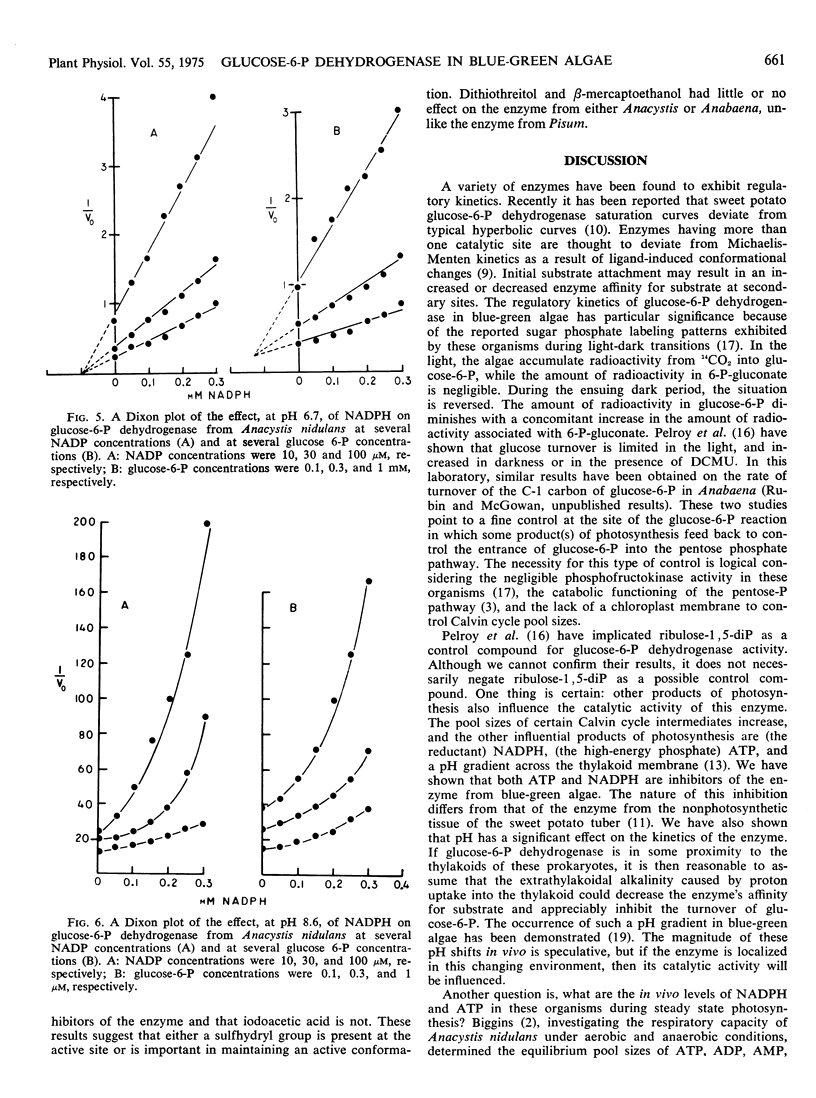
ATP is an inhibitor of the enzyme competitively with NADP with a Ki of 2 to 5 mm. NADPH inhibits the enzyme competitively with glucose 6-phosphate. The inhibition curves for NADPH are hyperbolic at pH 6.7 and sigmoidal at pH 8.6.
The significance of these in vitro kinetics are discussed relative to in vivo data on the control of glucose 6-phosphate turnover in blue-green algae.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson L. E., Ng T. C., Park K. E. Inactivation of pea leaf chloroplastic and cytoplasmic glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenases by light and dithiothreitol. Plant Physiol. 1974 Jun;53(6):835–839. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.6.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggins J. Respiration in blue-green algae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):570–575. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.570-575.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y., Gibbs M. Dark and photometabolism of sugars by a blue green alga: Tolypothrix tenuis. Plant Physiol. 1966 Apr;41(4):731–737. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.4.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EATON N. R. New press for disruption of microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1359–1360. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1359-1360.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosow D. P. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase of human blood platelets. Kinetics and regulatory properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 May;162(1):186–193. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T., Yugari Y. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from rat liver. I. Crystallization and properties. J Biochem. 1967 May;61(5):535–540. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUMANN J., JAGENDORF A. T. LIGHT-INDUCED PH CHANGES RELATED PHOSPHORYLATION BY CHLOROPLASTS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul;107:109–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90276-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce J., Leach C. K., Carr N. G. The incomplete tricarboxylic acid cycle in the blue-green alga Anabaena variabilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Mar;55(3):371–378. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-3-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelroy R. A., Rippka R., Stanier R. Y. Metabolism of glucose by unicellular blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;87(4):303–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00409131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelroy R. A., Rippka R., Stanier R. Y. Metabolism of glucose by unicellular blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;87(4):303–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00409131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanwal B. D. Regulatory mechanisms involving nicotinamide adenine nucleotides as allosteric effectors. 3. Control of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1626–1631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholes P., Mitchell P., Moyle J. The polarity of proton translocation in some photosynthetic microorganisms. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Apr;8(3):450–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A. Physical properties of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6353–6359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., London J., Stanier R. Y. Biochemical basis of obligate autotrophy in blue-green algae and thiobacilli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):972–983. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.972-983.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue R. H., Noltmann E. A., Kuby S. A. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase from brewers' yeast (Zwischenferment). 3. Studies on the subunit structure and on the molecular association phenomenon induced by triphosphopyridine nucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1353–1364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



