Abstract
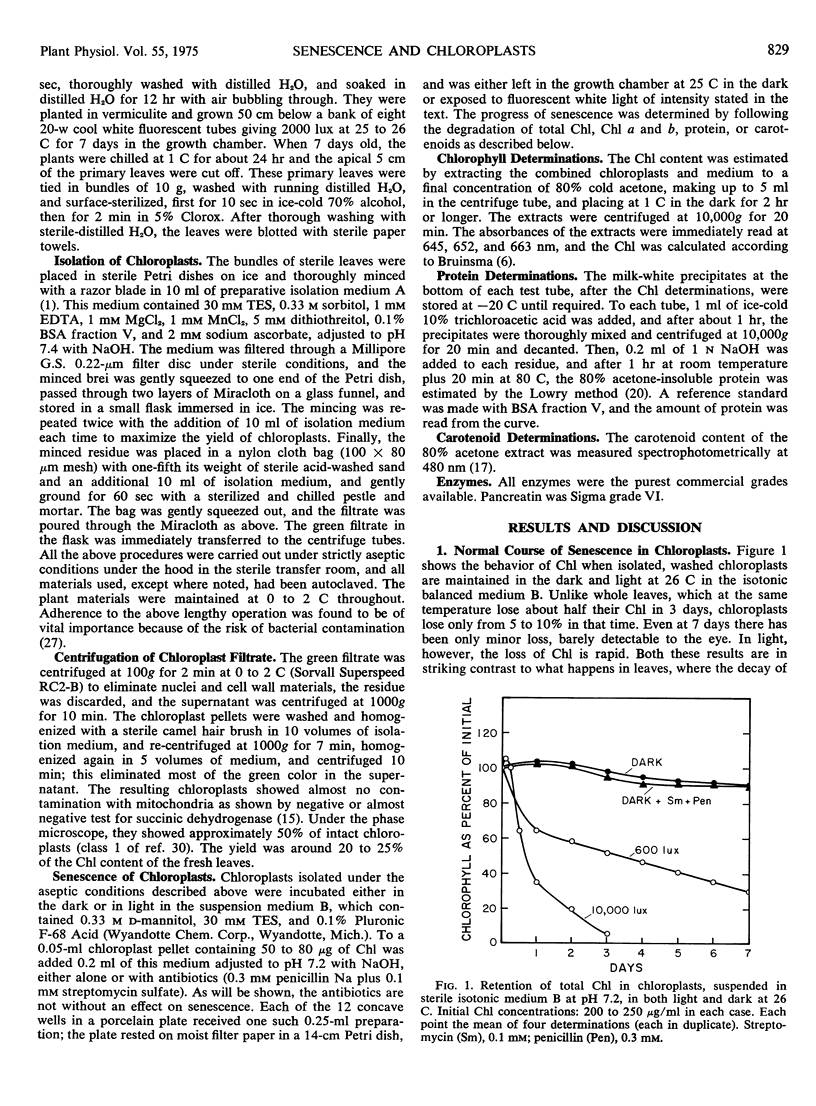
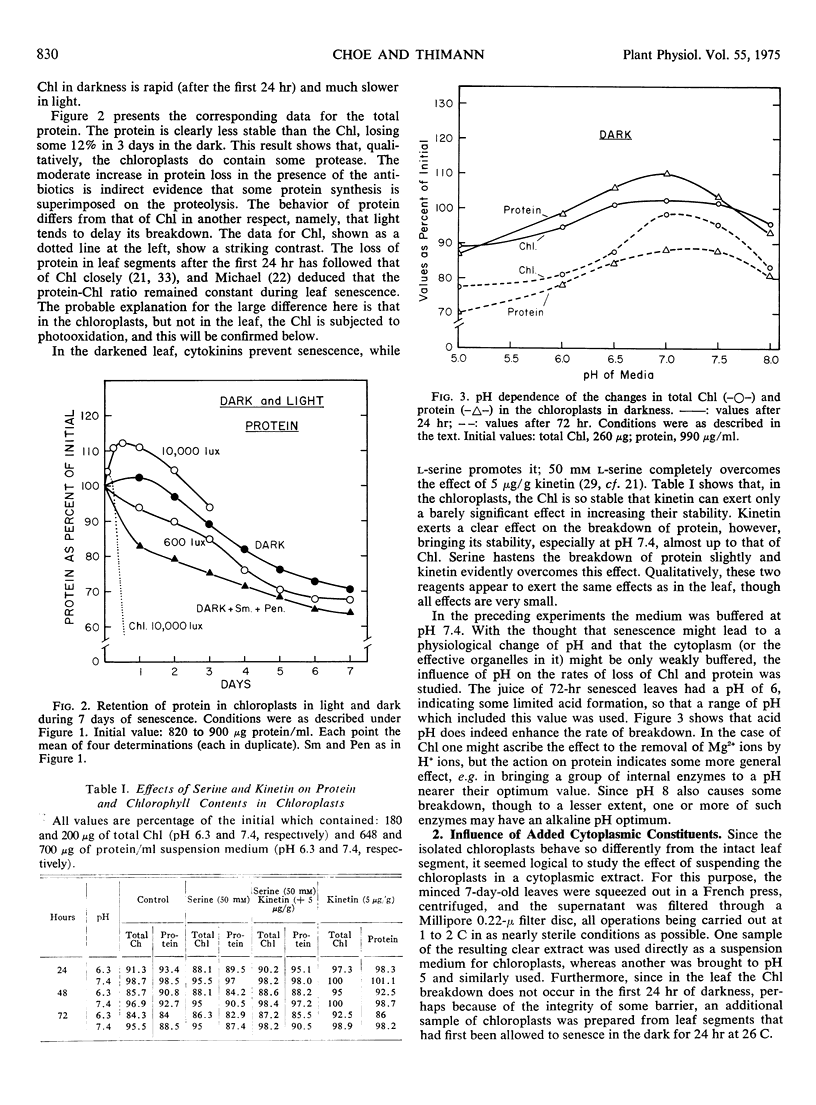
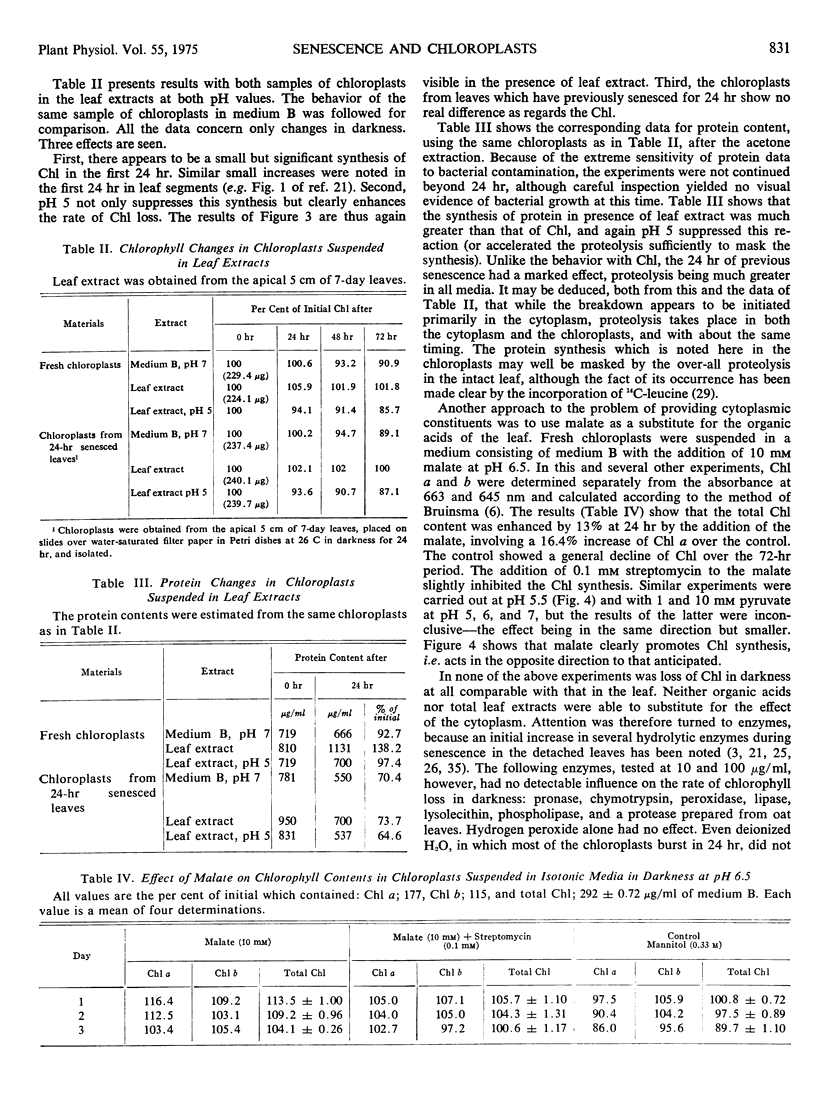
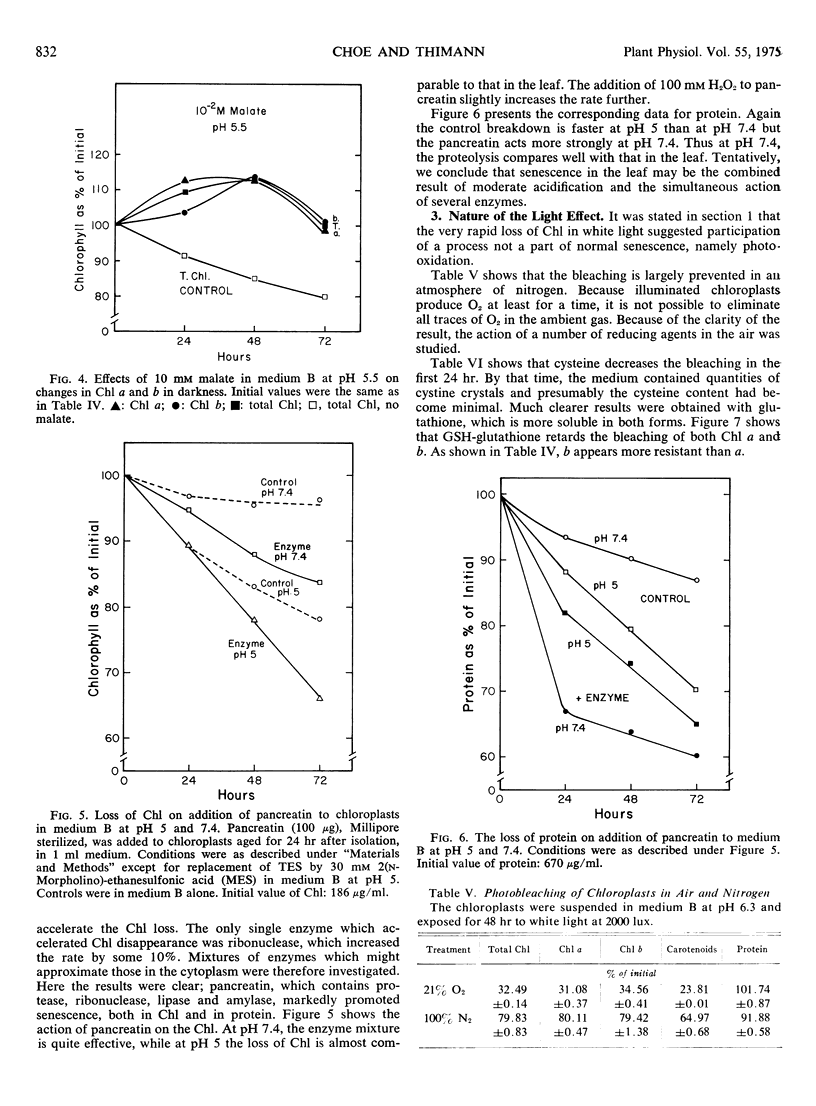
The changes in chlorophyll and protein in senescing chloroplasts isolated from the first leaves of 7-day-old oat (Avena sativa) seedlings have been investigated. In darkness the chlorophyll in these plastids is highly stable, losing only 5 to 10% of its content after 7 days at 26 C. This result contrasts with the behavior of chlorophyll in intact leaves, in which about 80% of the pigment would have disappeared in that time. The protein is less stable than the chlorophyll, though more stable than in the leaf; probably a small amount of protease is present in the plastids. Some protein is also being synthesized in the chloroplasts along with its breakdown; gains of up to 38% in protein and 13% in chlorophyll were observed under different conditions. l-Serine, which actively promotes senescence in the leaf, has only a very slight effect on the chloroplasts, and kinetin antagonizes it. Kinetin also has a small but significant effect in preserving the protein from breakdown. Acid pH somewhat promotes the breakdown, both of chlorophyll and protein. A loss of chlorophyll and protein comparable to that occurring in the senescence of the leaf could not be induced in the chloroplasts by suspending them in malate, in cytoplasmic extract, or in any of a number of enzymes tested alone. Incubation with a mixture of four enzymes was the only treatment which approximated the senescent process in the leaf, causing 34% loss of chlorophyll at pH 5 and 40% loss of protein at pH 7.4, both in 72 hours.
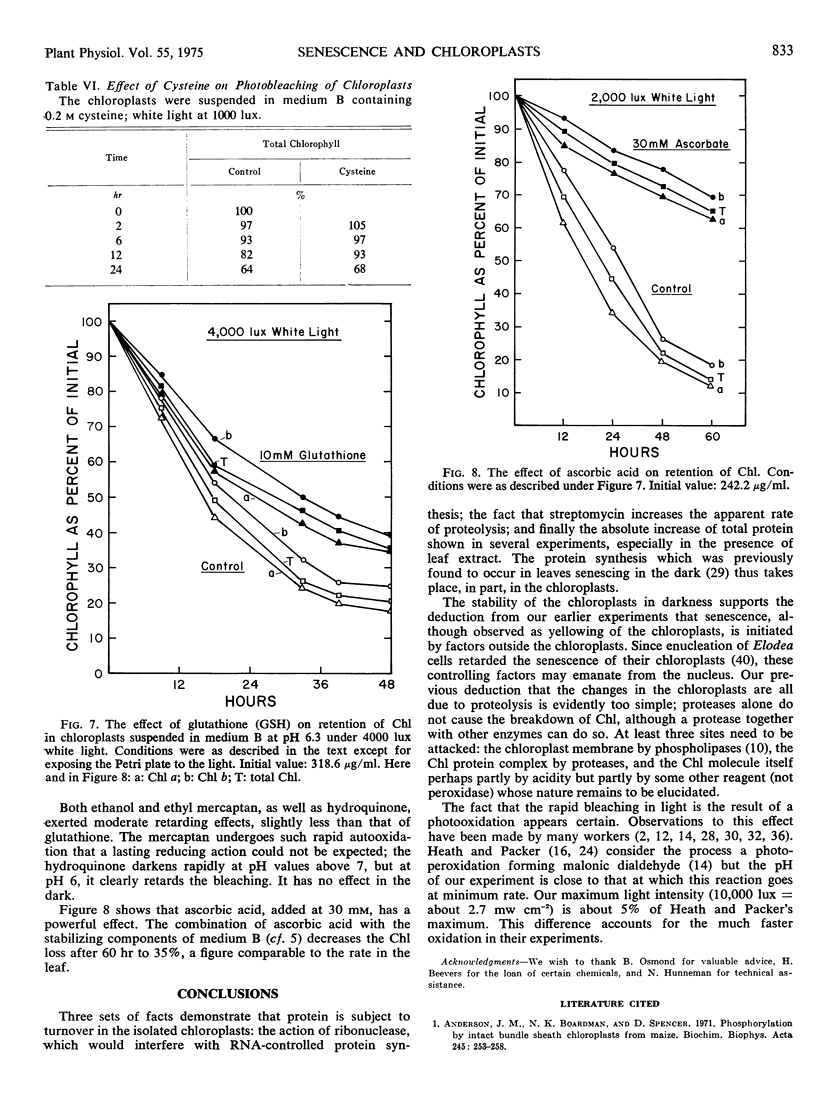
In white light, the chlorophyll and the carotenoids, but not the protein, disappear rapidly. This disappearance was shown to be prevented in an atmosphere of nitrogen or in air by a number of reducing agents, of which ascorbic acid was the most effective. It is, therefore, ascribed to photooxidation rather than to normal senescence.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVRON M. Light inactivation of photophosphorylation by swiss-chard chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Oct 21;44:41–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91520-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. M., Boardman N. K., Spencer D. Phosphorylation by intact bundle sheath chloroplasts from maize. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 6;245(1):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldthwaite J. Energy Metabolism of Rumex Leaf Tissue in the Presence of Senescence-regulating Hormones and Sucrose. Plant Physiol. 1974 Sep;54(3):399–403. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath R. L., Packer L. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Apr;125(1):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiatt A. J. Preparation & some properties of soluble succinic dehydrogenase from higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1961 Sep;36(5):552–557. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.5.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk J. T., Allen R. L. Dependence of chloroplast pigment synthesis on protein synthesis: effect of actidione. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Dec 21;21(6):523–530. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90516-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krotkov G. CARBOHYDRATE AND RESPIRATORY METABOLISM IN THE ISOLATED STARVING LEAF OF WHEAT. Plant Physiol. 1939 Apr;14(2):203–226. doi: 10.1104/pp.14.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C., Thimann K. V. The role of protein synthesis in the senescence of leaves: I. The formation of protease. Plant Physiol. 1972 Jan;49(1):64–71. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer L., Deamer D. W., Heath R. L. Regulation and deterioration of structure in membranes. Adv Gerontol Res. 1967;2:77–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAUER K., CALVIN M. Absorption spectra of spinach quantasomes and bleaching of the pigments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 22;64:324–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90741-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibaoka H., Thimann K. V. Antagonisms between Kinetin and Amino Acids: Experiments on the Mode of Action of Cytokinins. Plant Physiol. 1970 Aug;46(2):212–220. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.2.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetley R. M., Thimann K. V. The Metabolism of Oat Leaves during Senescence: I. Respiration, Carbohydrate Metabolism, and the Action of Cytokinins. Plant Physiol. 1974 Sep;54(3):294–303. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.3.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimann K. V., Tetley R. R., Van Thanh T. The Metabolism of Oat Leaves during Senescence: II. Senescence in Leaves Attached to the Plant. Plant Physiol. 1974 Dec;54(6):859–862. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.6.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


