Abstract
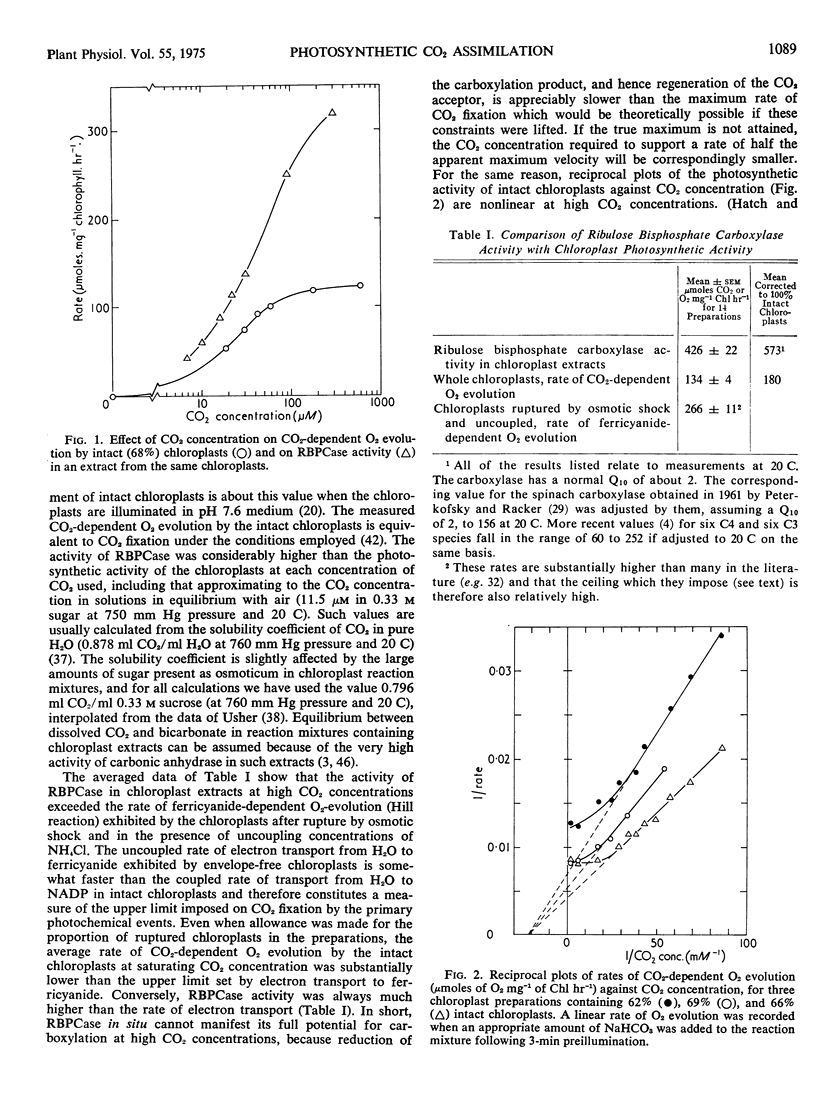
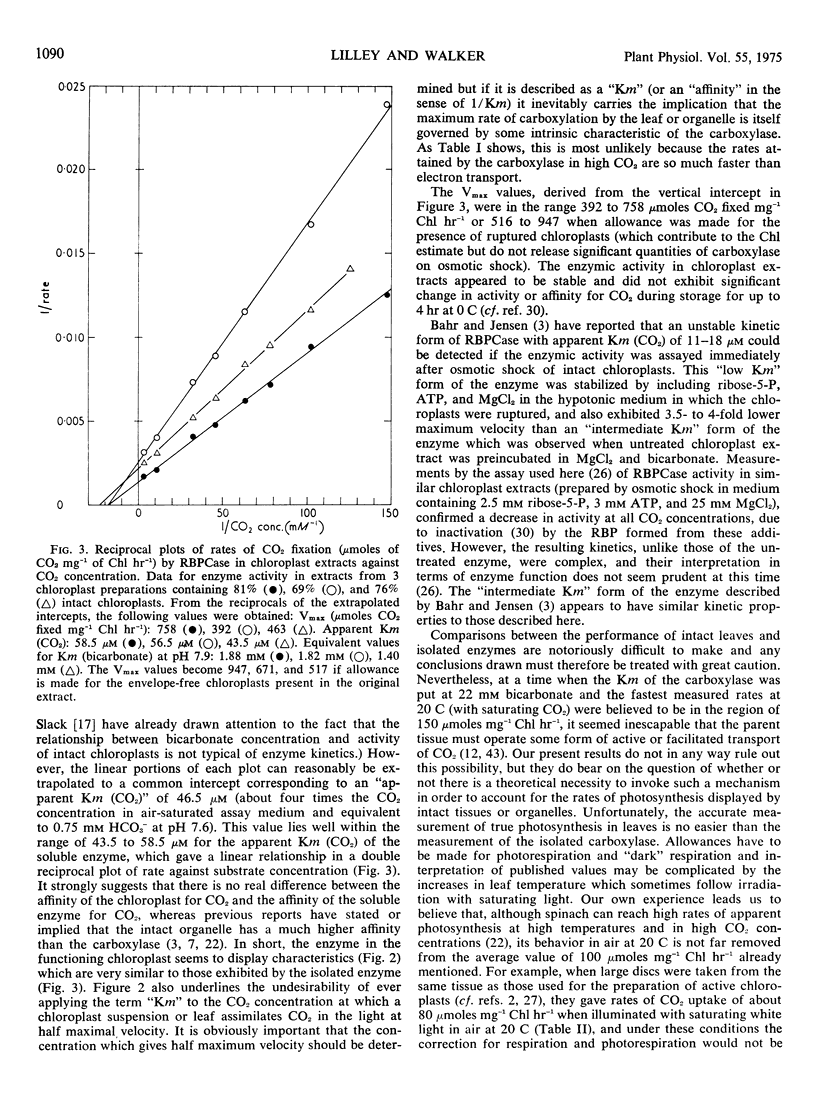
The relationship between rate of photosynthesis and CO2 concentration has been reinvestigated using isolated spinach (Spinacia oleracea) chloroplasts. The apparently low CO2 concentration required for half-maximal photosynthesis is shown to result partly from a ceiling imposed by electron transport. In double reciprocal plots of rate against CO2 concentration, this ceiling results in departures from linearity at high CO2 concentrations. If these rate limitations are disregarded in extrapolation the “true” CO2 concentration required for half maximal carboxylation by intact chloroplasts is approximately 46 μm (CO2).
When assayed under comparable conditions, ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase from these chloroplasts also shows an apparent Km (CO2) of approximately 46 μm, suggesting that its characteristics are not modified by extraction. An improved assay for ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase yielded rates of carboxylation considerably higher than those previously reported, the highest maximal velocities recorded approaching 1000 μmoles CO2 fixed mg−1 chlorophyll hr−1 at 20 C. With such Km and Vmax, values the carboxylase would be able to achieve, at concentrations of CO2 less than atmospheric, rates of CO2 fixation equal to those displayed by the parent tissue or by the average plant under favorable conditions in its natural environment.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahr J. T., Jensen R. G. Ribulose Diphosphate Carboxylase from Freshly Ruptured Spinach Chloroplasts Having an in Vivo Km[CO(2)]. Plant Physiol. 1974 Jan;53(1):39–44. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B., Schürmann P. Regulation of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase in the photosynthetic assimilation of carbon dioxide. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):4956–4964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Activation and inhibition of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phosphogluconate. Plant Physiol. 1973 Oct;52(4):373–379. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.4.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn W., Walker D. A., Baldry C. W. The isolation of spinach chloroplasts in pyrophosphate media. Plant Physiol. 1968 Sep;43(9):1415–1418. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.9.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Filmer D. The active species of "CO2" utilized by ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):1081–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D. The C 4 -pathway of photosynthesis. Evidence for an intermediate pool of carbon dioxide and the identity of the donor C 4 -dicarboxylic acid. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):425–432. doi: 10.1042/bj1250425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heber U., Santarius K. A. Direct and indirect transfer of ATP and ADP across the chloroplast envelope. Z Naturforsch B. 1970 Jul;25(7):718–728. doi: 10.1515/znb-1970-0714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldt W. H., Werdan K., Milovancev M., Geller G. Alkalization of the chloroplast stroma caused by light-dependent proton flux into the thylakoid space. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 31;314(2):224–241. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOSADA M., TREBST A. V., ARNON D. I. Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. XI. Carbon dioxide assimilation in a reconstituted chloroplast system. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:832–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley R. M., Walker D. A. An improved spectrophotometric assay for ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 17;358(1):226–229. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PON N. G., RABIN B. R., CALVIN M. MECHANISM OF THE CARBOXYDISMUTASE REACTION. I. THE EFFECT OF PRELIMINARY INCUBATION OF SUBSTRATES, METAL ION AND ENZYME ON ACTIVITY. Biochem Z. 1963;338:7–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky A., Racker E. The reductive pentose phosphate cycle. III. Enzyme activities in cell-free extracts of photosynthetic organisms. Plant Physiol. 1961 Jul;36(4):409–414. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D. M., Walker D. A. Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Inhibition by DL-glyceraldehyde of carbon dioxide assimilation. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1147–1157. doi: 10.1042/bj1281147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Nakayama N., Akazawa T. Structure and function of chloroplast proteins. V. Homotropic effect of bicarbonate in RuDP carboxylase reaction and the mechanism of activation by magnesium ions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Sep 10;126(3):737–745. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HORECKER B. L., HURWITZ J. The enzymatic formation of phosphoglyceric acid from ribulose diphosphate and carbon dioxide. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):795–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. A., Baldry C. W., Cockburn W. Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts, simultaneous measurement of carbon assimilation and oxygen evolution. Plant Physiol. 1968 Sep;43(9):1419–1422. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.9.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. A. Correlation between Photosynthetic Activity and Membrane Integrity in Isolated Pea Chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1965 Nov;40(6):1157–1161. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.6.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. A., Crofts A. R. Photosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:389–428. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wareing P. F., Khalifa M. M., Treharne K. J. Rate-limiting processes in photosynthesis at saturating light intensities. Nature. 1968 Nov 2;220(5166):453–457. doi: 10.1038/220453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werdan K., Heldt H. W. Accumulation of bicarbonate in intact chloroplasts following a pH gradient. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 14;283(3):430–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90260-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



