Abstract
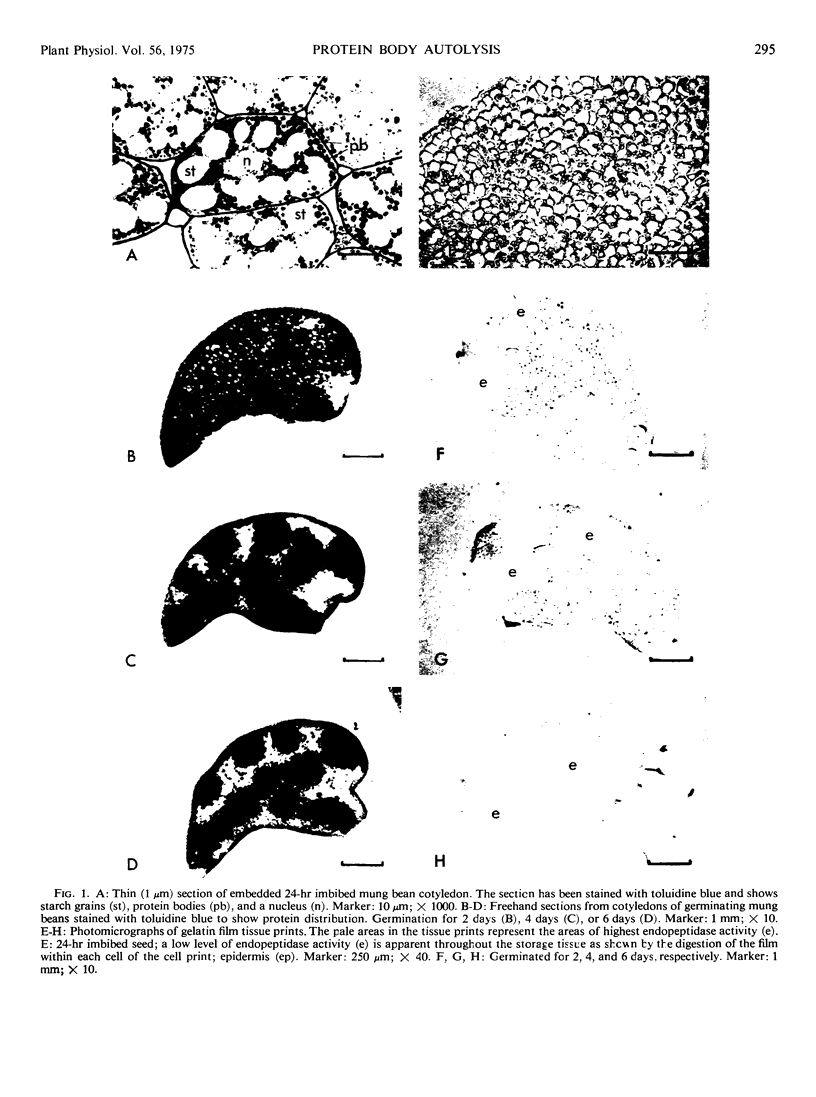
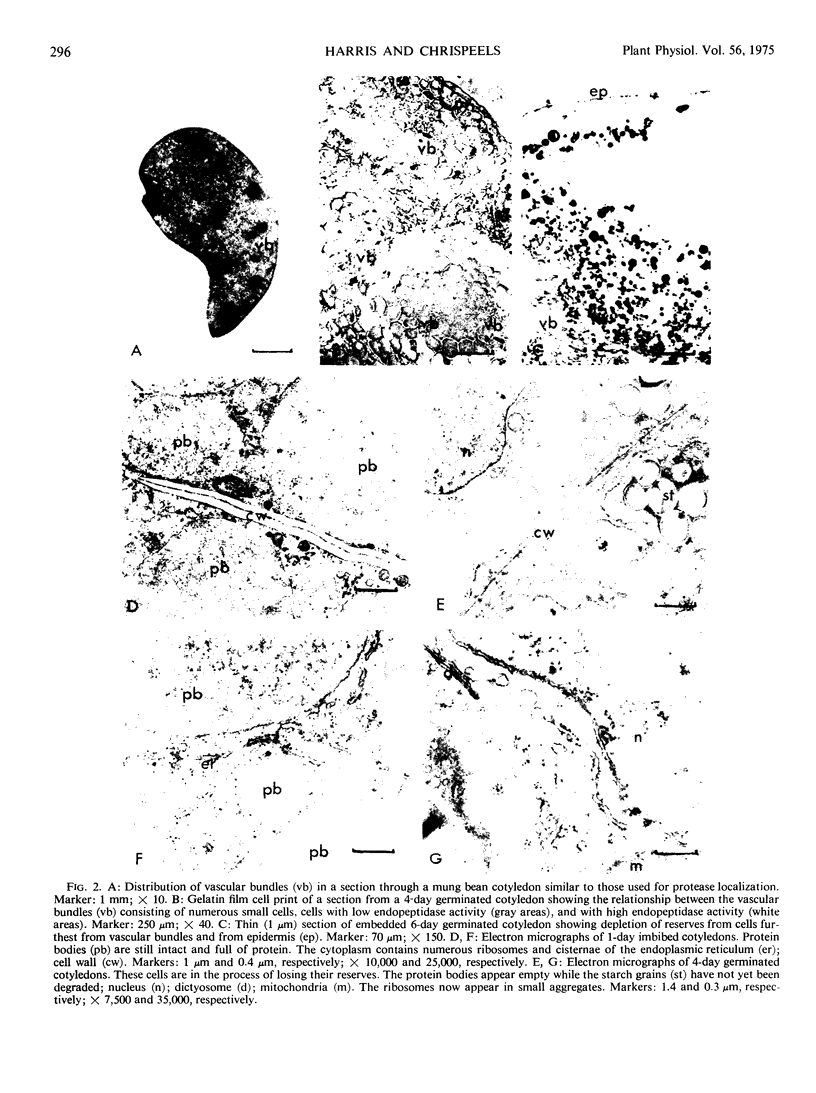
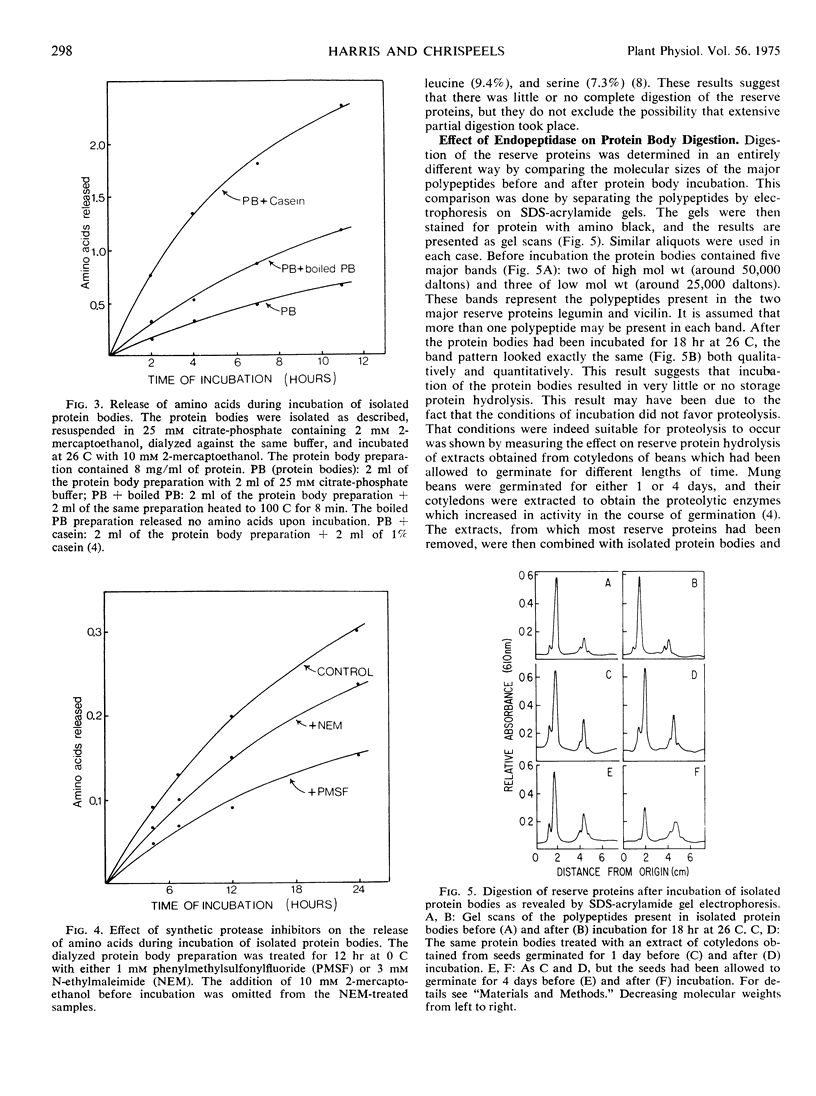
Storage protein hydrolysis in the cotyledons of germinating mung beans (Phaseolus aureus Roxb.) was examined by histochemical techniques, and the autolytic capacity of isolated protein bodies was studied with biochemical methods. The localization of endopeptidase activity within the cotyledons was studied using an India ink-gelatin film technique. After 24 hours of imbibition, a low level of endopeptidase activity was found throughout the storage tissues of the cotyledons. A marked increase in activity was noted in cells farthest from the vascular bundles 48 to 60 hours after the start of imbibition. The decrease in storage protein followed the same spatial distribution starting in the cells farthest from the bundles. The cotyledons contain a population of cells in various stages of endopeptidase activity enhancement and storage protein degradation. A wave of endopeptidase activity moves progressively through the cotyledons towards the vascular bundles leaving behind areas devoid of stored reserves and low in endopeptidase activity. Observations on the morphology of protein bodies during germination indicate that the membrane surrounding them remains intact, while the reserves disappear. This result suggests that the protein bodies may be undergoing autolysis. To determine whether this may indeed be the case, protein bodies were isolated from the meal of mung bean seeds using an aqueous medium containing 80% glycerol. The protein body preparations and the cytoplasm were assayed for the presence of a number of enzymes which may be involved in the breakdown of the storage proteins. The protein bodies contained all, or nearly all, of the carboxypeptidase, α-mannosidase, N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase, and caseolytic activity. The cytoplasm contained all, or most, of the leucine aminopeptidase and the trypsin-like activity (benzoyl arginine-p-nitroanalide as substrate). Incubation of the isolated protein bodies resulted in the release of amino acids. An analysis of the products of hydrolysis indicated that very little, if any, storage protein was being hydrolyzed during the incubation. Hydrolysis of the storage proteins present in the protein bodies was greatly accelerated by the addition of extracts from the cotyledons of 4-day-old seedlings. The results suggest that new enzymic activities not present in the protein bodies isolated from dry seeds must either be activated or synthesized and possibly added to the protein bodies before storage protein breakdown can begin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chrispeels M. J., Boulter D. Control of storage protein metabolism in the cotyledons of germinating mung beans: role of endopeptidase. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jun;55(6):1031–1037. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.6.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey J. W., De Duve C. Digestive activity of lysosomes. I. The digestion of proteins by extracts of rat liver lysosomes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3255–3263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson M. C., Chrispeels M. J. Isolation and Characterization of Glucosamine-containing Storage Glycoproteins from the Cotyledons of Phaseolus aureus. Plant Physiol. 1973 Aug;52(2):98–104. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.2.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham T. A., Gunning B. E. Localization of legumin and vicilin in bean cotyledon cells using fluorescent antibodies. Nature. 1970 Oct 3;228(5266):81–82. doi: 10.1038/228081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ory R. L., Henningsen K. W. Enzymes associated with protein bodies isolated from ungerminated barley seeds. Plant Physiol. 1969 Nov;44(11):1488–1498. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.11.1488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varner J. E., Schidlovsky G. Intracellular Distribution of Proteins in Pea Cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1963 Mar;38(2):139–144. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villiers T. A. Lysosomal activities of the vacuole in damaged and recovering plant cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 8;233(36):57–58. doi: 10.1038/newbio233057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatsu L. Y., Jacks T. J. Association of lysosomal activity with aleurone grains in plant seeds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Mar 20;124(1):466–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90354-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]