Abstract
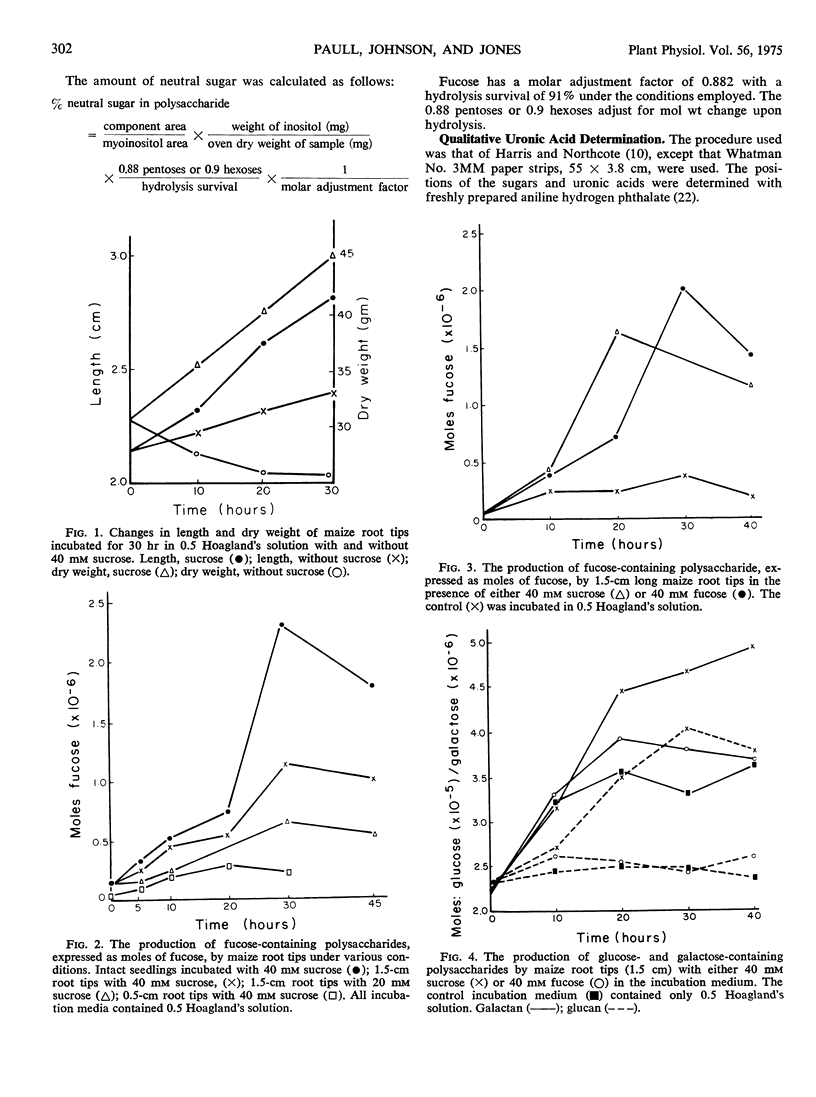
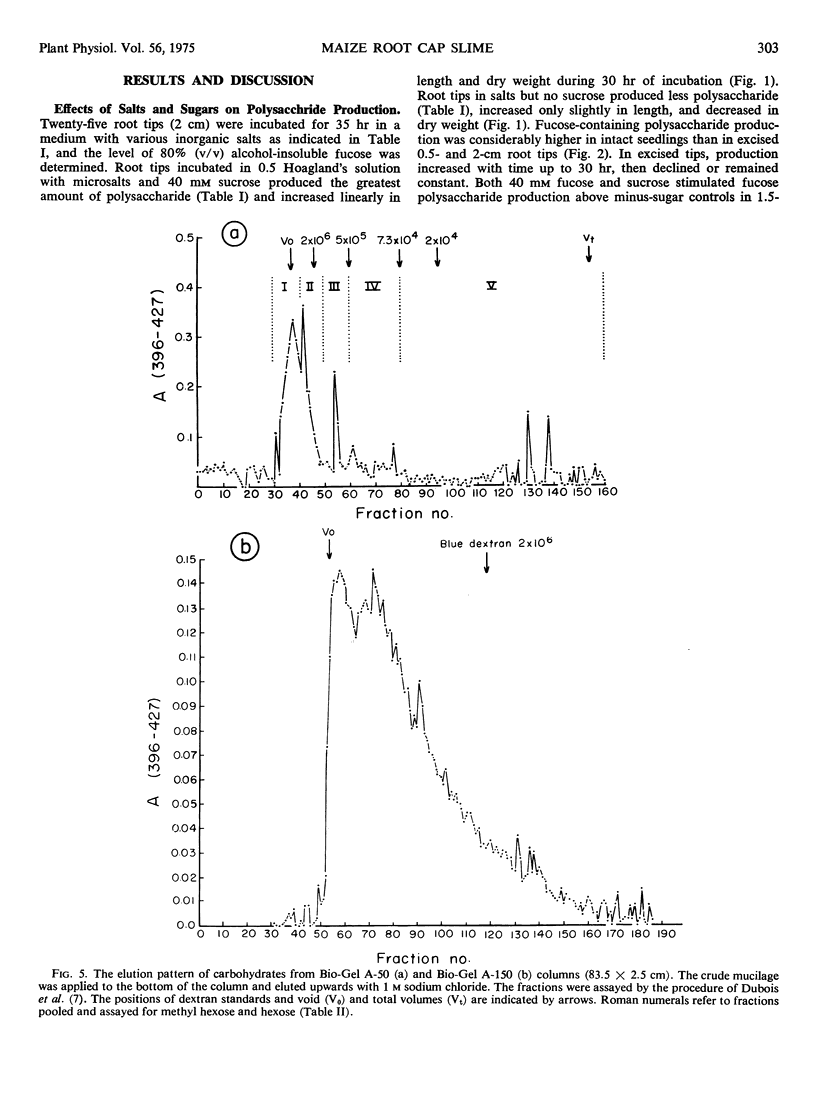
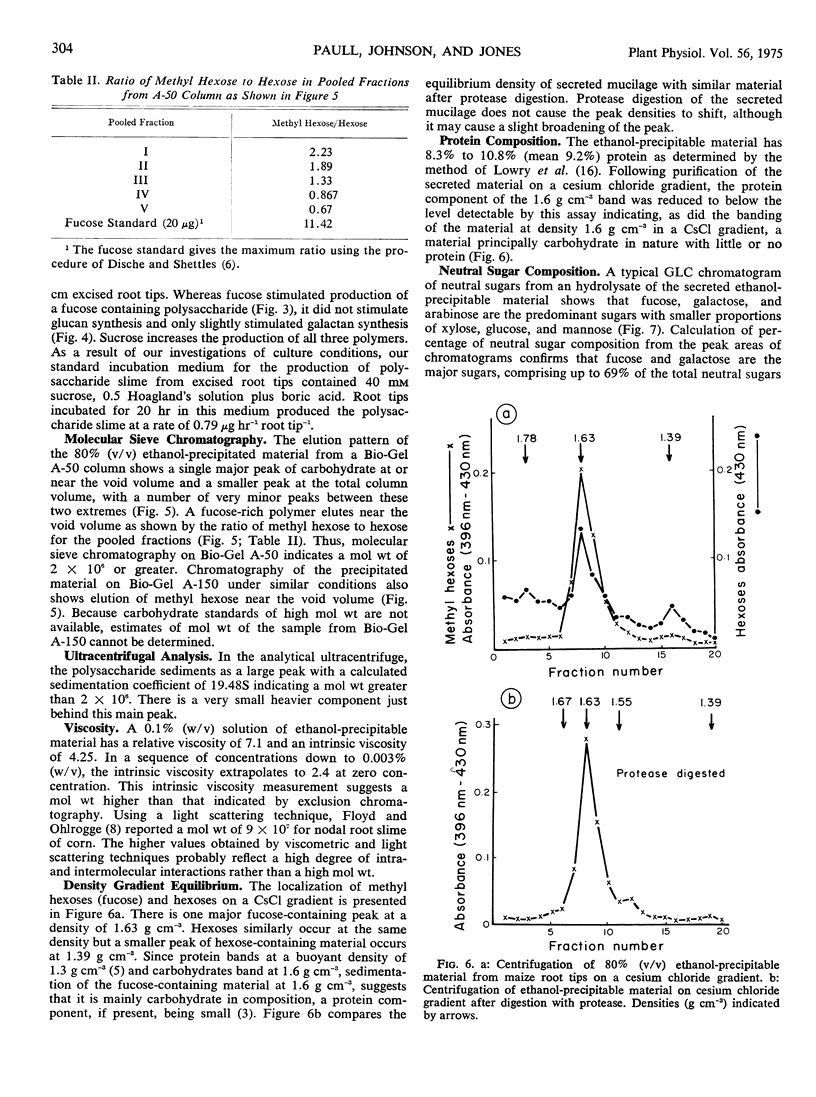
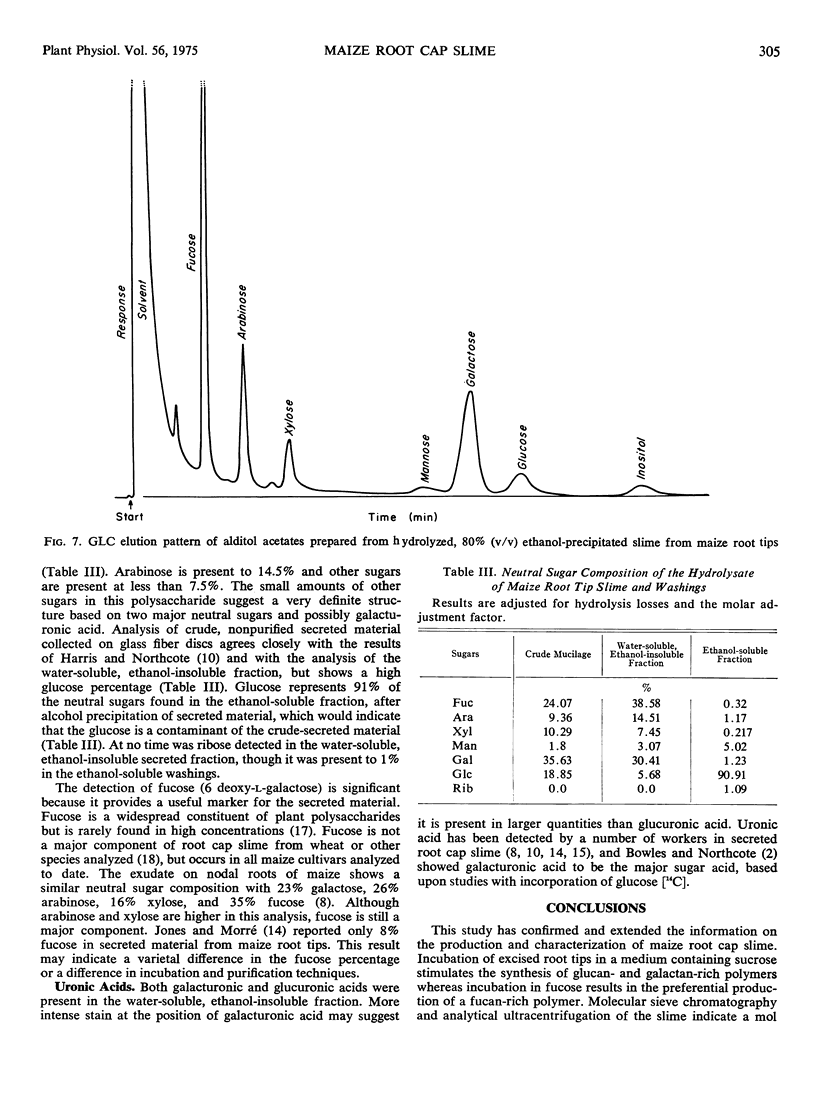
The secreted slime from root cap cells of corn (Zea mays, cv. SX-17) was studied. Production of slime by excised root tips is stimulated by the addition of 40 mM sucrose or fucose and half-strength Hoagland's solution to the incubation medium. Secreted slime was recovered from aqueous solution by precipitation with ethanol. The polymer has a molecular weight greater than 2 × 10−6 daltons and a density of 1.63 g cm−3. Protein is not present in material purified by density gradient centrifugation with cesium chloride. Fucose (39%) and galactose (30%) are the principle neutral sugars found in the purified polymer. Galacturonic and glucuronic acids, arabinose, xylose, mannose, and glucose are also present.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowles D. J., Northcote D. H. The sites of synthesis and transport of extracellular polysaccharides in the root tissues of maize. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(4):1133–1145. doi: 10.1042/bj1301133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeth J. M., Denborough M. A. The use of equilibrium-density-gradient methods for the preparation and characterization of blood-group-specific glycoproteins. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):879–891. doi: 10.1042/bj1170879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. J., Northcote D. H. Patterns of polysaccharide biosynthesis in differentiating cells of maize root-tips. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(3):479–491. doi: 10.1042/bj1200479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins D. J., English P. D., Albersheim P. The specific nature of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Plant Physiol. 1967 Jul;42(7):900–906. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.7.900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northcote D. H., Pickett-Heaps J. D. A function of the Golgi apparatus in polysaccharide synthesis and transport in the root-cap cells of wheat. Biochem J. 1966 Jan;98(1):159–167. doi: 10.1042/bj0980159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson A. C. Proteins and Plant Cell Walls. Proline to Hydroxyproline in Tobacco Suspension Cultures. Plant Physiol. 1964 Jul;39(4):543–550. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.4.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


