The synthesis, spectroscopic and crystal structure of 2-chloro-1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1,3,2-diazaphospholidine 2-oxide are reported.
Keywords: crystal structure; N-heterocyclic phosphine; NHP; 1,3,2-diazaphospholidine 2-oxide
Abstract
The title compound, C26H38ClN2OP, was synthesized by reacting phosphoryl chloride with N,N′-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)ethane-1,2-diamine in the presence of N-methylmorpholine which acted as an auxilliary base to quench the HCl released as a by-product. The resultant N-heterocyclic phosphine five-membered ring adopts a half-chair conformation and features a tetracoordinate P atom ligated by the chelating diamine [P—N = 1.6348 (14) and 1.6192 (14) Å], one double-bonded O atom [P1—O1 = 1.4652 (12) Å] and one Cl atom [P1—Cl1 = 2.0592 (7) Å]. The sterically hindered 2,6-diisopropylphenyl (Dipp) groups twist away from the central heterocycle, with torsion angles of −75.66 (19) and 83.39 (19)° for the P—N—Car—Car links. A number of intramolecular C—H⋯N, C—H⋯O and C—H⋯Cl close contacts occur. In the crystal, molecules are linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to generate [010] chains. C—H⋯π interactions are also observed.
Chemical context
1,3,2-Diazaphospholidines are a class of N-heterocyclic phosphines (NHPs) that feature an N—P—N moiety bridged by a C2H4 fragment, thus forming a five-membered ring. Derivatives are often substituted by alkyl, aryl, or halogen groups at the phosphorus position (denoted as position 2), allowing them to serve as both ligands and/or precursors in organometallic chemistry (Gudat, 2010 ▸). The title compound, 2-chloro-1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1,3,2-diazaphospholidine 2-oxide, is closely related to these compounds and its analogs are commonly used as precursor molecules for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals targeted towards immunosuppressants and chemotherapy medications (Gholivand & Mojahed, 2005 ▸). The crystal structure of the title compound is reported herein and features a saturated five-membered NHP substituted at the phosphorus position by both O and Cl atoms.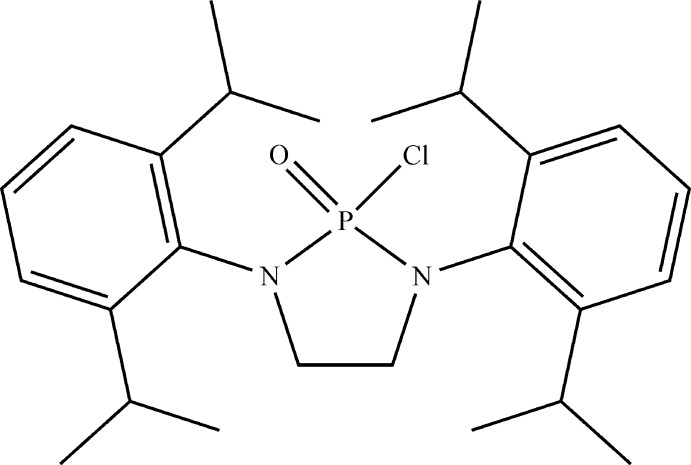
Structural commentary
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1 ▸. The title compound crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/n with one molecule present in the asymmetric unit. Bond lengths between the flanking nitrogen atoms show a statistical difference when compared to each other [P1—N1 = 1.6348 (14) Å and P1—N2 = 1.6192 (14) Å] and is likely caused by the half-chair (or envelope) conformation of the heterocycle at the C2 position. The N—P—N bond angle of 95.60 (7)° deviates significantly from an ideal tetrahedral geometry. Bond lengths between P1—Cl1 and P1—O1 are 2.0592 (7) and 1.4652 (12) Å, respectively, with a bond angle of 105.51 (5)° for the O—P—Cl atoms. The isopropyl groups are oriented away from the central five-membered ring and lead to intramolecular short-contact D—H⋯A interactions between methine atoms H9, H12, H21, and H24, and N1 and N2. Intramolecular short-contact D—H⋯A interactions are also present for Cl1 and O1 atoms and are summarized in Table 1 ▸. The steric demands of the bulky 2,6-diisopropylphenyl groups cause the aromatic rings to twist away from the central five-membered ring with torsion angles of −75.66 (19) and 83.39 (19)° for P1—N1—C3—C4 and P1—N2—C15—C20, respectively. The dihedral angles between the heterocyclic ring (all atoms) and the C3–C8 and C15–C20 aromatic rings are 76.61 (9) and 88.75 (9)°, respectively.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids. H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12—H12⋯Cl1 | 1.00 | 2.91 | 3.543 (2) | 122 |
| C21—H21⋯Cl1 | 1.00 | 2.88 | 3.6006 (19) | 130 |
| C9—H9⋯O1 | 1.00 | 2.63 | 3.273 (2) | 122 |
| C25—H25C⋯O1 | 0.98 | 2.61 | 3.407 (2) | 138 |
| C9—H9⋯N1 | 1.00 | 2.43 | 2.927 (2) | 110 |
| C12—H12⋯N1 | 1.00 | 2.41 | 2.904 (2) | 110 |
| C21—H21⋯N2 | 1.00 | 2.42 | 2.930 (2) | 111 |
| C24—H24⋯N2 | 1.00 | 2.41 | 2.915 (2) | 110 |
| C2—H2A⋯O1i | 0.99 | 2.36 | 3.319 (2) | 164 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Supramolecular features
The crystal of the title compound contains intermolecular short-contact D—H⋯A π-interactions between C6—H6 and the centroid of the C3–C8 ring of a neighboring molecule (transformation =  − x, −1 + y,
− x, −1 + y,  − z), with an H⋯centroid distance of 2.740 (3) Å. The isopropyl groups of the flanking aromatic rings also display short contacts for Cl1 and O1, with H⋯Cl distances measuring 2.950 (5) and 3.086 (6) Å between H14A⋯Cl1 and H23B⋯Cl1, respectively. A significantly short contact of 2.357 (2) Å occurs for H2A⋯O1. A distance this small is likely indicative of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonding (Fig. 2 ▸, Table 1 ▸) accepted by the O atom from a neighbouring ethylene bridge related by symmetry (transformation = x, y − 1, z).
− z), with an H⋯centroid distance of 2.740 (3) Å. The isopropyl groups of the flanking aromatic rings also display short contacts for Cl1 and O1, with H⋯Cl distances measuring 2.950 (5) and 3.086 (6) Å between H14A⋯Cl1 and H23B⋯Cl1, respectively. A significantly short contact of 2.357 (2) Å occurs for H2A⋯O1. A distance this small is likely indicative of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonding (Fig. 2 ▸, Table 1 ▸) accepted by the O atom from a neighbouring ethylene bridge related by symmetry (transformation = x, y − 1, z).
Figure 2.
The packing of the title compound, showing the formation of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (red and cyan lines).
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Groom et al., 2016 ▸) produced two matches for 1,3,2-(diarylamino)phospholidine-2-oxide-2-halide derivatives; 1,3-di(p-tolyl)-2-chloro-1,3,2-diazaphospholidine-2-oxide (p-tolyl = 4-methylphenyl), and the analogous fluorine derivative (CSD identifiers WASFEC and SIVJEN, respectively; Gholivand & Mojahed, 2005 ▸). One other closely related bicyclic structure was found (CSD identifier NUMBAY; Koeller et al., 1995 ▸), which features N-benzyl substituents and a cyclohexyl ring fused to the bridging ethylene C atoms.
Synthesis and crystallization
The synthesis of the title compound was achieved using a similar method as used for 2-chloro-1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1,3,2-diazaphospholidine (Caputo et al., 2008 ▸), except phosphoryl chloride was used instead of phosphorus trichloride. In a 200 ml Schlenk flask, 1.142 g (3.00 mmol, 1 eq.) of N,N′-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)ethane-1,2-diamine were dissolved in 45 ml of THF producing a colourless solution. Separately 0.478 g (3.11 mmol, 1.04 eq.) of phosphoryl chloride and 0.959 g (9.48 mmol, 3.16 eq.) of N-methylmorpholine were dissolved in 75 ml of THF producing a colourless solution, and transferred to a 125 ml pressure-equalizing dropping funnel. The diamine solution was cooled to 195 K using a liquid nitrogen/acetone bath and monitored using a thermocouple, and once cold (ca 10 minutes) the phosphoryl chloride mixture was added dropwise to the diamine solution over 30 minutes. Once the addition was complete, the colourless reaction mixture was left to stir at 195 K for 60 minutes, after which it was allowed to warm to room temperature and left to stir for two days at room temperature. The reaction was monitored by 31P{1H} NMR spectroscopy, and became pale yellow in colour with a slight amount of colourless precipitate as it proceeded. Once the starting material was completely consumed, the reaction mixture was dried in vacuo to give a pale-yellow coloured solid. Extraction of this solid with 50 ml of a 3:2 mixture of pentane:THF produced the desired product as a pale-yellow coloured solution following filtration through Celite, which when dried in vacuo afforded 0.919 g (66%) of the desired product as a faintly yellow coloured powder. Crystals of the product in the form of colourless blocks were obtained by concentrating the filtrate and storing in a 238 K freezer overnight.
1H NMR (CDCl3): δ 7.32 (t, 3 J HH = 7.6 Hz, 2H, p-Dipp), 7.21 (m, 3 J HH = 7.4 Hz, 4H, m-Dipp), 3.86–3.50 (m, 8H, iPr—CH, NHC—CH2), 1.38 (d, 3 J HH = 6.8 Hz, 6H, iPr—CH3), 1.35 (d, 3 J HH = 6.8 Hz, 6H, iPr—CH3), 1.28 (d, 3 J HH = 6.9 Hz, 6H, iPr—CH3), 1.26 ppm (d, 3 J HH = 6.9 Hz, 6H, iPr—CH3). 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3): δ 149.8, 149.6, 131.8, 129.1, 125.0, 124.9, 48.8, 29.0, 25.9, 24.5, 23.9 ppm. 31P{1H} NMR (CDCl3): δ 15.1 ppm. IR (KBr pellet): ν 3068 (w), 2967 (s), 2929 (m), 2869 (m), 1681 (w), 1588 (w), 1464 (s), 1448 (s), 1383 (w), 1368 (w), 1348 (w) 1323 (m), 1268 (s), 1217 (w), 1194 (w), 1106 (m), 1093 (m), 1077 (m), 1056 (m), 1043 (w), 934 (w), 860 (w), 803 (s), 756 (w), 747 (w), 733 (w), 648 (w), 592 (w), 575 (w), 558 (w), 544 (w), 496 (s) 466 (w), 437 (w), 412 cm−1 (w). m.p. 509.7–511.0 K.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. H atoms were included in geometrically idealized positions and refined using a riding model [C—H = 0.95–0.99; U iso(H) = 1.2–1.5U eq(C)]. The methyl H atoms were allowed to rotate, but not to tip, to best fit the electron density.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C26H38ClN2OP |
| M r | 461.00 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 104 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 19.984 (3), 6.6328 (11), 20.140 (3) |
| β (°) | 106.818 (2) |
| V (Å3) | 2555.4 (7) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.23 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.25 × 0.21 × 0.17 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Siemens/Bruker APEXII |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.578, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 30194, 6307, 4640 |
| R int | 0.073 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.669 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.043, 0.109, 1.04 |
| No. of reflections | 6307 |
| No. of parameters | 288 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.43, −0.33 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017005825/hb7671sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017005825/hb7671Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017005825/hb7671Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1544709
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We thank the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (through the Discovery Grants Program to JDM). JDM also acknowledges support from the Canadian Foundation for Innovation, the Nova Scotia Research and Innovation Trust Fund and Saint Mary’s University.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C26H38ClN2OP | F(000) = 992 |
| Mr = 461.00 | Dx = 1.198 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 19.984 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 4093 reflections |
| b = 6.6328 (11) Å | θ = 2.5–24.5° |
| c = 20.140 (3) Å | µ = 0.23 mm−1 |
| β = 106.818 (2)° | T = 104 K |
| V = 2555.4 (7) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.25 × 0.21 × 0.17 mm |
Data collection
| Siemens/Bruker APEXII diffractometer | 4640 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 66 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.073 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 28.4°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | h = −26→26 |
| Tmin = 0.578, Tmax = 0.746 | k = −8→8 |
| 30194 measured reflections | l = −26→26 |
| 6307 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.109 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0435P)2 + 0.5837P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 6307 reflections | Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3 |
| 288 parameters | Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| CL1 | 0.60905 (2) | 0.77730 (7) | 0.42592 (2) | 0.02113 (12) | |
| P1 | 0.70785 (2) | 0.65590 (7) | 0.46135 (2) | 0.01383 (11) | |
| O1 | 0.75532 (6) | 0.81335 (17) | 0.45109 (6) | 0.0181 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.71214 (7) | 0.5695 (2) | 0.53850 (7) | 0.0149 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.70937 (7) | 0.4369 (2) | 0.42630 (7) | 0.0147 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.72101 (10) | 0.3487 (3) | 0.54424 (9) | 0.0196 (4) | |
| H1A | 0.692450 | 0.290717 | 0.572321 | 0.024* | |
| H1B | 0.770625 | 0.312993 | 0.566036 | 0.024* | |
| C2 | 0.69615 (9) | 0.2713 (3) | 0.46958 (9) | 0.0183 (4) | |
| H2A | 0.722531 | 0.149108 | 0.464119 | 0.022* | |
| H2B | 0.645730 | 0.237947 | 0.456523 | 0.022* | |
| C3 | 0.71736 (9) | 0.6963 (2) | 0.59765 (8) | 0.0149 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.78155 (9) | 0.7887 (3) | 0.63099 (9) | 0.0189 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.78352 (10) | 0.9197 (3) | 0.68551 (9) | 0.0245 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.825951 | 0.987103 | 0.708089 | 0.029* | |
| C6 | 0.72518 (11) | 0.9539 (3) | 0.70750 (10) | 0.0273 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.727763 | 1.044273 | 0.744756 | 0.033* | |
| C7 | 0.66305 (10) | 0.8570 (3) | 0.67543 (9) | 0.0256 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.623418 | 0.879569 | 0.691479 | 0.031* | |
| C8 | 0.65767 (9) | 0.7266 (3) | 0.61984 (9) | 0.0192 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.84815 (9) | 0.7422 (3) | 0.61222 (9) | 0.0223 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.834851 | 0.662355 | 0.568225 | 0.027* | |
| C10 | 0.88538 (10) | 0.9329 (3) | 0.59894 (11) | 0.0314 (5) | |
| H10A | 0.926952 | 0.895280 | 0.585271 | 0.047* | |
| H10B | 0.899393 | 1.014211 | 0.641348 | 0.047* | |
| H10C | 0.853666 | 1.011382 | 0.561687 | 0.047* | |
| C11 | 0.89651 (10) | 0.6108 (3) | 0.66826 (11) | 0.0309 (5) | |
| H11A | 0.938829 | 0.578975 | 0.655073 | 0.046* | |
| H11B | 0.872366 | 0.485491 | 0.673151 | 0.046* | |
| H11C | 0.909329 | 0.683572 | 0.712499 | 0.046* | |
| C12 | 0.58966 (9) | 0.6166 (3) | 0.58712 (10) | 0.0247 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.593698 | 0.549291 | 0.544010 | 0.030* | |
| C13 | 0.52710 (11) | 0.7590 (4) | 0.56644 (11) | 0.0407 (6) | |
| H13A | 0.535887 | 0.864893 | 0.536069 | 0.061* | |
| H13B | 0.520044 | 0.820457 | 0.608159 | 0.061* | |
| H13C | 0.485179 | 0.683169 | 0.541819 | 0.061* | |
| C14 | 0.57816 (11) | 0.4518 (4) | 0.63611 (11) | 0.0373 (5) | |
| H14A | 0.535680 | 0.375892 | 0.613176 | 0.056* | |
| H14B | 0.573101 | 0.513955 | 0.678539 | 0.056* | |
| H14C | 0.618349 | 0.360144 | 0.647930 | 0.056* | |
| C15 | 0.72566 (9) | 0.4045 (2) | 0.36189 (9) | 0.0155 (4) | |
| C16 | 0.67152 (9) | 0.3889 (2) | 0.29983 (9) | 0.0172 (4) | |
| C17 | 0.68940 (10) | 0.3713 (3) | 0.23813 (9) | 0.0197 (4) | |
| H17 | 0.653475 | 0.361779 | 0.195399 | 0.024* | |
| C18 | 0.75855 (10) | 0.3673 (3) | 0.23807 (9) | 0.0203 (4) | |
| H18 | 0.769988 | 0.359264 | 0.195532 | 0.024* | |
| C19 | 0.81087 (10) | 0.3752 (3) | 0.30022 (9) | 0.0196 (4) | |
| H19 | 0.858228 | 0.368268 | 0.299803 | 0.023* | |
| C20 | 0.79627 (9) | 0.3931 (3) | 0.36346 (9) | 0.0173 (4) | |
| C21 | 0.59508 (9) | 0.3881 (3) | 0.29800 (9) | 0.0188 (4) | |
| H21 | 0.592775 | 0.410635 | 0.346382 | 0.023* | |
| C22 | 0.55404 (10) | 0.5564 (3) | 0.25268 (10) | 0.0295 (5) | |
| H22A | 0.555477 | 0.537843 | 0.204835 | 0.044* | |
| H22B | 0.574841 | 0.686840 | 0.270126 | 0.044* | |
| H22C | 0.505386 | 0.552822 | 0.253905 | 0.044* | |
| C23 | 0.56189 (11) | 0.1827 (3) | 0.27379 (11) | 0.0306 (5) | |
| H23A | 0.513339 | 0.182330 | 0.275382 | 0.046* | |
| H23B | 0.588161 | 0.076821 | 0.304337 | 0.046* | |
| H23C | 0.562927 | 0.157514 | 0.226146 | 0.046* | |
| C24 | 0.85570 (9) | 0.3942 (3) | 0.43053 (9) | 0.0195 (4) | |
| H24 | 0.834454 | 0.399067 | 0.469768 | 0.023* | |
| C25 | 0.90220 (10) | 0.5797 (3) | 0.43636 (10) | 0.0270 (4) | |
| H25A | 0.925377 | 0.576285 | 0.399635 | 0.041* | |
| H25B | 0.937539 | 0.580306 | 0.481732 | 0.041* | |
| H25C | 0.873536 | 0.701785 | 0.431455 | 0.041* | |
| C26 | 0.89855 (11) | 0.2004 (3) | 0.43818 (10) | 0.0289 (5) | |
| H26A | 0.867806 | 0.083879 | 0.435911 | 0.043* | |
| H26B | 0.934841 | 0.201006 | 0.482942 | 0.043* | |
| H26C | 0.920487 | 0.191919 | 0.400596 | 0.043* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| CL1 | 0.0179 (2) | 0.0199 (2) | 0.0225 (2) | 0.00405 (17) | 0.00101 (17) | 0.00066 (17) |
| P1 | 0.0146 (2) | 0.0125 (2) | 0.0134 (2) | 0.00099 (17) | 0.00254 (17) | 0.00000 (17) |
| O1 | 0.0209 (7) | 0.0144 (6) | 0.0190 (6) | −0.0012 (5) | 0.0058 (5) | 0.0009 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0180 (8) | 0.0122 (7) | 0.0139 (7) | 0.0010 (6) | 0.0035 (6) | −0.0002 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0183 (8) | 0.0135 (7) | 0.0129 (7) | −0.0003 (6) | 0.0054 (6) | −0.0011 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0260 (10) | 0.0132 (9) | 0.0198 (9) | 0.0013 (7) | 0.0068 (8) | 0.0021 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0230 (9) | 0.0135 (9) | 0.0187 (9) | −0.0013 (7) | 0.0066 (7) | 0.0008 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0191 (9) | 0.0131 (8) | 0.0111 (8) | 0.0009 (7) | 0.0024 (7) | −0.0003 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0231 (9) | 0.0170 (9) | 0.0153 (8) | −0.0007 (7) | 0.0034 (7) | 0.0017 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0304 (11) | 0.0233 (10) | 0.0156 (9) | −0.0080 (8) | −0.0001 (8) | −0.0017 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0406 (12) | 0.0220 (10) | 0.0185 (9) | 0.0009 (9) | 0.0074 (9) | −0.0056 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0286 (11) | 0.0297 (11) | 0.0196 (10) | 0.0059 (9) | 0.0088 (8) | −0.0023 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0197 (9) | 0.0214 (9) | 0.0157 (9) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0039 (7) | 0.0006 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0166 (9) | 0.0291 (11) | 0.0185 (9) | −0.0024 (8) | 0.0008 (7) | 0.0016 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0215 (10) | 0.0386 (12) | 0.0308 (11) | −0.0073 (9) | 0.0023 (9) | 0.0077 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0242 (11) | 0.0321 (12) | 0.0318 (11) | −0.0004 (9) | 0.0007 (9) | 0.0051 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0181 (10) | 0.0374 (12) | 0.0192 (9) | −0.0009 (8) | 0.0062 (8) | −0.0030 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0225 (11) | 0.0671 (17) | 0.0309 (12) | 0.0118 (11) | 0.0052 (9) | −0.0062 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0280 (12) | 0.0538 (15) | 0.0309 (12) | −0.0152 (10) | 0.0096 (9) | 0.0020 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0209 (9) | 0.0115 (8) | 0.0155 (8) | 0.0002 (7) | 0.0072 (7) | −0.0014 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0217 (9) | 0.0119 (8) | 0.0191 (9) | −0.0007 (7) | 0.0076 (7) | −0.0019 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0253 (10) | 0.0162 (9) | 0.0160 (9) | −0.0010 (7) | 0.0035 (8) | −0.0017 (7) |
| C18 | 0.0275 (10) | 0.0175 (9) | 0.0190 (9) | −0.0004 (8) | 0.0116 (8) | −0.0024 (7) |
| C19 | 0.0211 (9) | 0.0159 (9) | 0.0237 (9) | 0.0004 (7) | 0.0097 (8) | −0.0007 (7) |
| C20 | 0.0203 (9) | 0.0128 (8) | 0.0196 (9) | −0.0011 (7) | 0.0070 (7) | −0.0004 (7) |
| C21 | 0.0177 (9) | 0.0220 (10) | 0.0151 (9) | −0.0019 (7) | 0.0021 (7) | −0.0018 (7) |
| C22 | 0.0210 (10) | 0.0392 (12) | 0.0280 (11) | 0.0049 (9) | 0.0068 (9) | 0.0092 (9) |
| C23 | 0.0312 (11) | 0.0328 (12) | 0.0304 (11) | −0.0131 (9) | 0.0130 (9) | −0.0099 (9) |
| C24 | 0.0163 (9) | 0.0225 (10) | 0.0199 (9) | 0.0013 (7) | 0.0056 (7) | 0.0004 (7) |
| C25 | 0.0213 (10) | 0.0251 (10) | 0.0305 (11) | −0.0029 (8) | 0.0010 (8) | 0.0019 (8) |
| C26 | 0.0305 (11) | 0.0273 (11) | 0.0270 (11) | 0.0081 (9) | 0.0052 (9) | 0.0032 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| CL1—P1 | 2.0592 (7) | C13—H13A | 0.9800 |
| P1—O1 | 1.4652 (12) | C13—H13B | 0.9800 |
| P1—N2 | 1.6192 (14) | C13—H13C | 0.9800 |
| P1—N1 | 1.6348 (14) | C14—H14A | 0.9800 |
| N1—C3 | 1.437 (2) | C14—H14B | 0.9800 |
| N1—C1 | 1.476 (2) | C14—H14C | 0.9800 |
| N2—C15 | 1.442 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.400 (2) |
| N2—C2 | 1.473 (2) | C15—C20 | 1.404 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.529 (2) | C16—C17 | 1.394 (2) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9900 | C16—C21 | 1.517 (2) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9900 | C17—C18 | 1.382 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C18—C19 | 1.380 (3) |
| C3—C8 | 1.404 (2) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.405 (2) | C19—C20 | 1.392 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.392 (2) | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C9 | 1.517 (2) | C20—C24 | 1.519 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.380 (3) | C21—C22 | 1.523 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C21—C23 | 1.532 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.381 (3) | C21—H21 | 1.0000 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C22—H22A | 0.9800 |
| C7—C8 | 1.394 (2) | C22—H22B | 0.9800 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C22—H22C | 0.9800 |
| C8—C12 | 1.515 (3) | C23—H23A | 0.9800 |
| C9—C11 | 1.529 (3) | C23—H23B | 0.9800 |
| C9—C10 | 1.530 (3) | C23—H23C | 0.9800 |
| C9—H9 | 1.0000 | C24—C25 | 1.526 (3) |
| C10—H10A | 0.9800 | C24—C26 | 1.527 (3) |
| C10—H10B | 0.9800 | C24—H24 | 1.0000 |
| C10—H10C | 0.9800 | C25—H25A | 0.9800 |
| C11—H11A | 0.9800 | C25—H25B | 0.9800 |
| C11—H11B | 0.9800 | C25—H25C | 0.9800 |
| C11—H11C | 0.9800 | C26—H26A | 0.9800 |
| C12—C13 | 1.526 (3) | C26—H26B | 0.9800 |
| C12—C14 | 1.534 (3) | C26—H26C | 0.9800 |
| C12—H12 | 1.0000 | ||
| O1—P1—N2 | 118.91 (7) | C12—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| O1—P1—N1 | 121.71 (7) | C12—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| N2—P1—N1 | 95.60 (7) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| O1—P1—CL1 | 105.51 (5) | C12—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| N2—P1—CL1 | 109.68 (6) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| N1—P1—CL1 | 104.35 (5) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C3—N1—C1 | 122.51 (14) | C12—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C3—N1—P1 | 123.66 (12) | C12—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—P1 | 113.22 (11) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C15—N2—C2 | 123.16 (13) | C12—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C15—N2—P1 | 124.30 (11) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C2—N2—P1 | 112.45 (11) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 105.00 (13) | C16—C15—C20 | 121.87 (15) |
| N1—C1—H1A | 110.7 | C16—C15—N2 | 119.78 (15) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 110.7 | C20—C15—N2 | 118.34 (15) |
| N1—C1—H1B | 110.7 | C17—C16—C15 | 118.09 (16) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 110.7 | C17—C16—C21 | 119.61 (16) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 108.8 | C15—C16—C21 | 122.30 (15) |
| N2—C2—C1 | 105.58 (13) | C18—C17—C16 | 121.10 (17) |
| N2—C2—H2A | 110.6 | C18—C17—H17 | 119.5 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 110.6 | C16—C17—H17 | 119.5 |
| N2—C2—H2B | 110.6 | C19—C18—C17 | 119.58 (16) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 110.6 | C19—C18—H18 | 120.2 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.8 | C17—C18—H18 | 120.2 |
| C8—C3—C4 | 121.87 (15) | C18—C19—C20 | 121.92 (17) |
| C8—C3—N1 | 118.87 (15) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.0 |
| C4—C3—N1 | 119.25 (15) | C20—C19—H19 | 119.0 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 117.57 (16) | C19—C20—C15 | 117.35 (16) |
| C5—C4—C9 | 119.80 (16) | C19—C20—C24 | 119.82 (16) |
| C3—C4—C9 | 122.55 (16) | C15—C20—C24 | 122.81 (15) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.46 (18) | C16—C21—C22 | 112.06 (15) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.3 | C16—C21—C23 | 110.57 (15) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.3 | C22—C21—C23 | 110.65 (16) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.12 (17) | C16—C21—H21 | 107.8 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.9 | C22—C21—H21 | 107.8 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.9 | C23—C21—H21 | 107.8 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 120.96 (18) | C21—C22—H22A | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.5 | C21—C22—H22B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.5 | H22A—C22—H22B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C3 | 117.96 (16) | C21—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C12 | 119.95 (16) | H22A—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| C3—C8—C12 | 122.05 (16) | H22B—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| C4—C9—C11 | 110.16 (15) | C21—C23—H23A | 109.5 |
| C4—C9—C10 | 112.46 (16) | C21—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C11—C9—C10 | 111.41 (16) | H23A—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C4—C9—H9 | 107.5 | C21—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C11—C9—H9 | 107.5 | H23A—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 107.5 | H23B—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10A | 109.5 | C20—C24—C25 | 111.98 (15) |
| C9—C10—H10B | 109.5 | C20—C24—C26 | 110.92 (15) |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 | C25—C24—C26 | 111.09 (15) |
| C9—C10—H10C | 109.5 | C20—C24—H24 | 107.5 |
| H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 | C25—C24—H24 | 107.5 |
| H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 | C26—C24—H24 | 107.5 |
| C9—C11—H11A | 109.5 | C24—C25—H25A | 109.5 |
| C9—C11—H11B | 109.5 | C24—C25—H25B | 109.5 |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 | H25A—C25—H25B | 109.5 |
| C9—C11—H11C | 109.5 | C24—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 | H25A—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 | H25B—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| C8—C12—C13 | 112.45 (17) | C24—C26—H26A | 109.5 |
| C8—C12—C14 | 110.23 (15) | C24—C26—H26B | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—C14 | 110.69 (17) | H26A—C26—H26B | 109.5 |
| C8—C12—H12 | 107.8 | C24—C26—H26C | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 107.8 | H26A—C26—H26C | 109.5 |
| C14—C12—H12 | 107.8 | H26B—C26—H26C | 109.5 |
| O1—P1—N1—C3 | 46.64 (16) | C5—C4—C9—C11 | 71.0 (2) |
| N2—P1—N1—C3 | 175.81 (13) | C3—C4—C9—C11 | −105.6 (2) |
| CL1—P1—N1—C3 | −72.20 (13) | C5—C4—C9—C10 | −53.9 (2) |
| O1—P1—N1—C1 | −124.54 (12) | C3—C4—C9—C10 | 129.42 (18) |
| N2—P1—N1—C1 | 4.63 (13) | C7—C8—C12—C13 | 52.4 (2) |
| CL1—P1—N1—C1 | 116.61 (11) | C3—C8—C12—C13 | −130.01 (18) |
| O1—P1—N2—C15 | −31.45 (16) | C7—C8—C12—C14 | −71.7 (2) |
| N1—P1—N2—C15 | −162.56 (14) | C3—C8—C12—C14 | 106.0 (2) |
| CL1—P1—N2—C15 | 90.01 (14) | C2—N2—C15—C16 | 88.2 (2) |
| O1—P1—N2—C2 | 145.24 (11) | P1—N2—C15—C16 | −95.46 (18) |
| N1—P1—N2—C2 | 14.13 (13) | C2—N2—C15—C20 | −93.0 (2) |
| CL1—P1—N2—C2 | −93.30 (11) | P1—N2—C15—C20 | 83.39 (19) |
| C3—N1—C1—C2 | 168.22 (14) | C20—C15—C16—C17 | −3.1 (3) |
| P1—N1—C1—C2 | −20.48 (17) | N2—C15—C16—C17 | 175.75 (15) |
| C15—N2—C2—C1 | 149.38 (15) | C20—C15—C16—C21 | 176.14 (16) |
| P1—N2—C2—C1 | −27.36 (17) | N2—C15—C16—C21 | −5.0 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2—N2 | 28.46 (18) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.6 (3) |
| C1—N1—C3—C8 | −86.2 (2) | C21—C16—C17—C18 | −178.65 (16) |
| P1—N1—C3—C8 | 103.40 (17) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 1.9 (3) |
| C1—N1—C3—C4 | 94.7 (2) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −1.9 (3) |
| P1—N1—C3—C4 | −75.66 (19) | C18—C19—C20—C15 | −0.5 (3) |
| C8—C3—C4—C5 | −2.7 (3) | C18—C19—C20—C24 | 177.98 (16) |
| N1—C3—C4—C5 | 176.29 (15) | C16—C15—C20—C19 | 3.0 (3) |
| C8—C3—C4—C9 | 173.98 (16) | N2—C15—C20—C19 | −175.83 (15) |
| N1—C3—C4—C9 | −7.0 (2) | C16—C15—C20—C24 | −175.40 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.8 (3) | N2—C15—C20—C24 | 5.8 (2) |
| C9—C4—C5—C6 | −175.06 (17) | C17—C16—C21—C22 | −58.1 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.1 (3) | C15—C16—C21—C22 | 122.71 (18) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −1.2 (3) | C17—C16—C21—C23 | 65.9 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C3 | 0.2 (3) | C15—C16—C21—C23 | −113.34 (19) |
| C6—C7—C8—C12 | 177.92 (17) | C19—C20—C24—C25 | 65.7 (2) |
| C4—C3—C8—C7 | 1.8 (3) | C15—C20—C24—C25 | −115.96 (19) |
| N1—C3—C8—C7 | −177.25 (16) | C19—C20—C24—C26 | −59.0 (2) |
| C4—C3—C8—C12 | −175.87 (16) | C15—C20—C24—C26 | 119.31 (18) |
| N1—C3—C8—C12 | 5.1 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C12—H12···Cl1 | 1.00 | 2.91 | 3.543 (2) | 122 |
| C21—H21···Cl1 | 1.00 | 2.88 | 3.6006 (19) | 130 |
| C9—H9···O1 | 1.00 | 2.63 | 3.273 (2) | 122 |
| C25—H25C···O1 | 0.98 | 2.61 | 3.407 (2) | 138 |
| C9—H9···N1 | 1.00 | 2.43 | 2.927 (2) | 110 |
| C12—H12···N1 | 1.00 | 2.41 | 2.904 (2) | 110 |
| C21—H21···N2 | 1.00 | 2.42 | 2.930 (2) | 111 |
| C24—H24···N2 | 1.00 | 2.41 | 2.915 (2) | 110 |
| C2—H2A···O1i | 0.99 | 2.36 | 3.319 (2) | 164 |
Symmetry code: (i) x, y−1, z.
References
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Caputo, C. A., Price, J. T., Jennings, M. C., McDonald, R. & Jones, N. D. (2008). Dalton Trans. pp. 3461–3469. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Gholivand, K. & Mojahed, F. (2005). Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 631, 1912–1918.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gudat, D. (2010). Recent Developments in the Chemistry of N-Heterocyclic Phosphines, edited by R. K. Bansal, pp. 63–102. Berlin: Springer.
- Koeller, K. J., Rath, N. P. & Spilling, C. D. (1995). Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon, 103, 171–181.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017005825/hb7671sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017005825/hb7671Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017005825/hb7671Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1544709
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




