Abstract
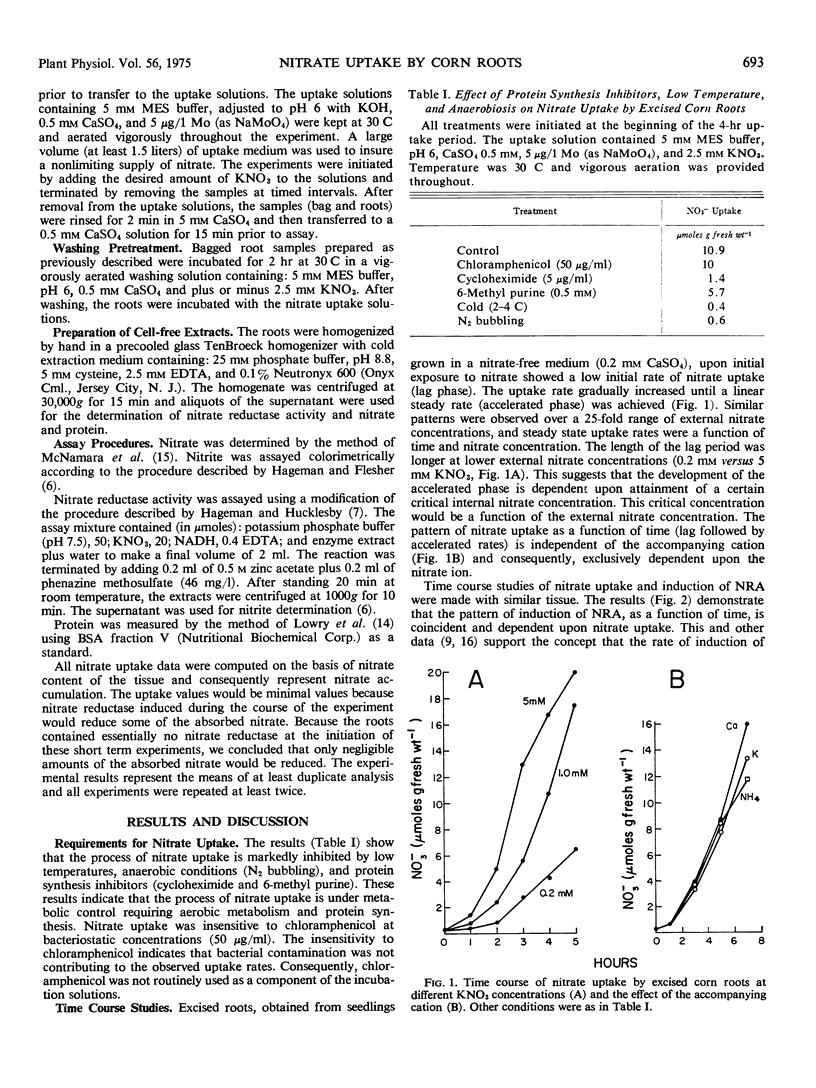
The characteristics of nitrate uptake and induction of nitrate reductase were studied in excised roots of corn (Zea mays L.). Upon initial exposure to nitrate, the low initial rate of nitrate uptake gradually increased until a steady uptake rate was achieved in 1 to 2 hours depending on the NO3− concentration. The pattern was observed over a wide range (0.2-5 mm) of nitrate concentrations and was independent of the accompanying cation.
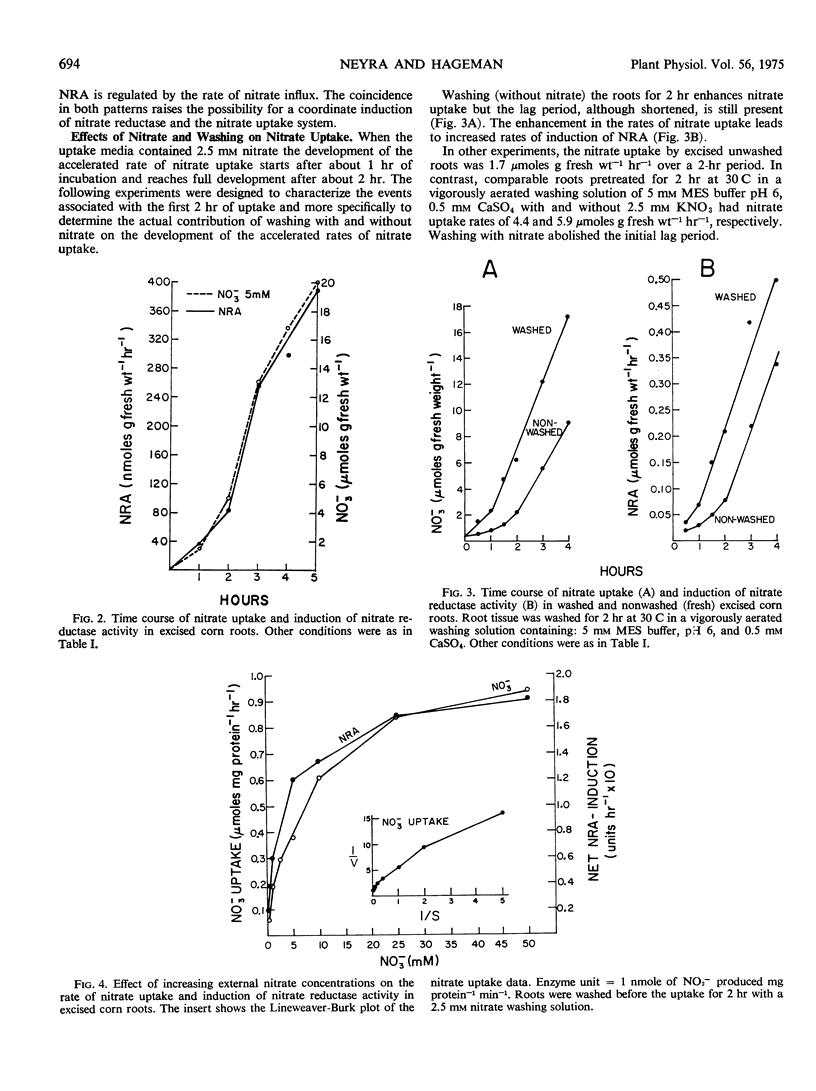
The nitrate uptake pattern as a function of increasing external nitrate concentrations (0.2-50 mm) followed saturation type kinetics. The reciprocal plot of the data was not linear but hyperbolic, indicating that more than one Km for nitrate uptake can be resolved from the data. This suggests the existence of either one carrier system with changing kinetic constants or the existence of dual uptake systems. The pattern of induction of nitrate reductase was coincident with the pattern of nitrate uptake as a function of time and increasing nitrate concentrations. The rate of induction of nitrate reductase was regulated by the rate of nitrate flux.
Washing the roots for 2 hours enhances nitrate uptake by 2.5-fold over the nonwashed tissue. The presence of nitrate in the washing solution leads to further (3.5-fold over control) increases in the rate of nitrate uptake supporting the contention that nitrate plays a specific role in the induction of the inducible nitrate carrier independent of the washing effect.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beevers L., Schrader L. E., Flesher D., Hageman R. H. The Role of Light and Nitrate in the Induction of Nitrate Reductase in Radish Cotyledons and Maize Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1965 Jul;40(4):691–698. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.4.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman E. C., Friedman L. Fatty acids in tissue lipids of rats fed Sterculia foetida oil. J Agric Food Chem. 1971 Mar-Apr;19(2):224–228. doi: 10.1021/jf60174a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith J., Livoni J. P., Norberg C. L., Segel I. H. Regulation of Nitrate Uptake in Penicillium chrysogenum by Ammonium Ion. Plant Physiol. 1973 Oct;52(4):362–367. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.4.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman R. H., Flesher D. Nitrate Reductase Activity in Corn Seedlings as Affected by Light and Nitrate Content of Nutrient Media. Plant Physiol. 1960 Sep;35(5):700–708. doi: 10.1104/pp.35.5.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson W. A., Flesher D., Hageman R. H. Nitrate Uptake by Dark-grown Corn Seedlings: Some Characteristics of Apparent Induction. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):120–127. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hanson J. B. Increased Membrane-bound Adenosine Triphosphatase Activity Accompanying Development of Enhanced Solute Uptake in Washed Corn Root Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1972 Mar;49(3):436–440. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hanson J. B. Induction and development of increased ion absorption in corn root tissue. Plant Physiol. 1972 Mar;49(3):430–435. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.3.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hodges T. K. Characterization of Plasma Membrane-associated Adenosine Triphosphase Activity of Oat Roots. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jul;52(1):6–12. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks A., Wallace W., Stevens D. Synthesis and turnover of nitrate reductase in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1972 Dec;50(6):649–654. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.6.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



